Maximum Penalized-Likelihood Structured Covariance Estimation for Imaging Extended Objects, with Application to Radio Astronomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
3. An Algorithm for Maximum-Likelihood Imaging
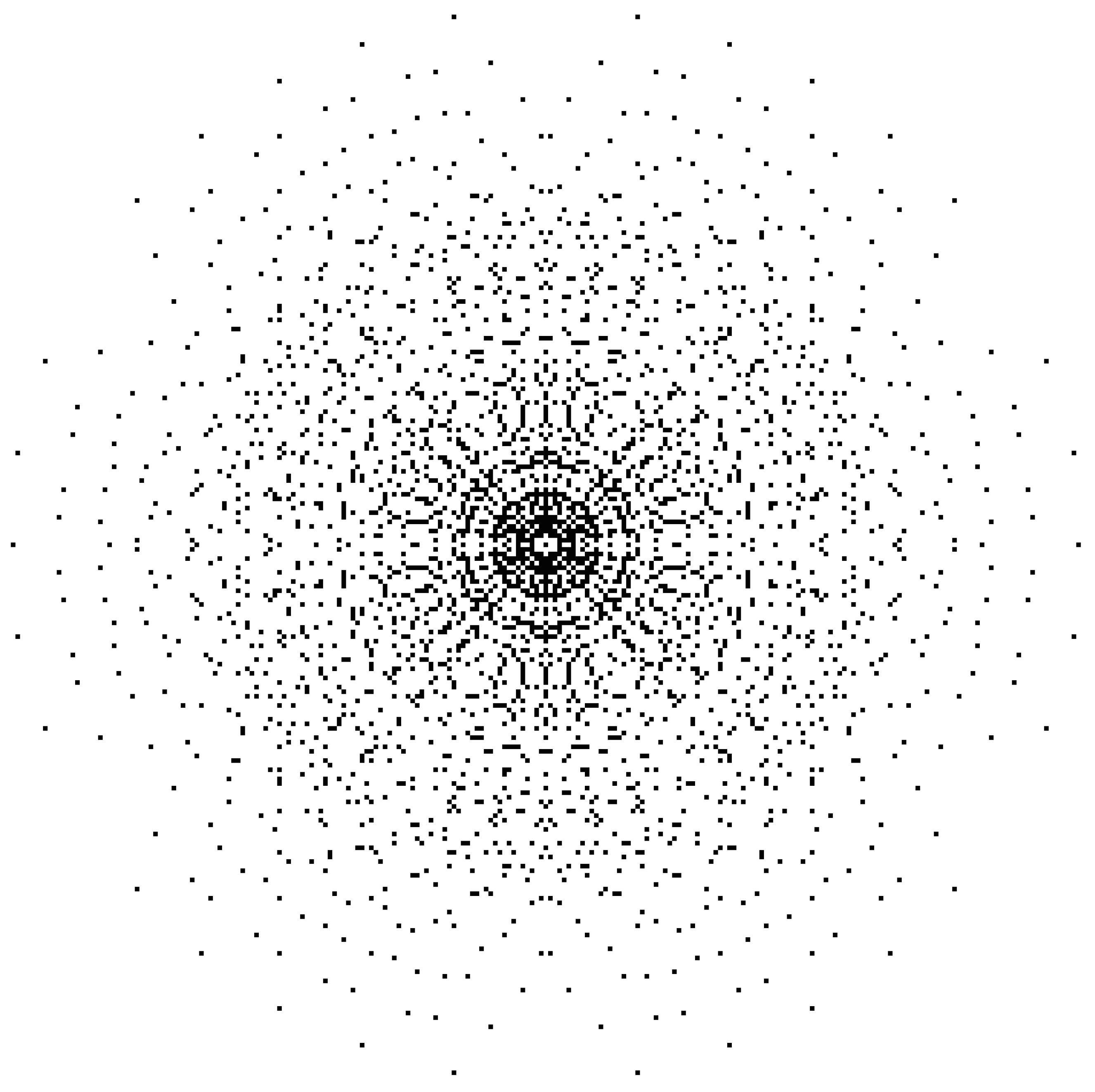
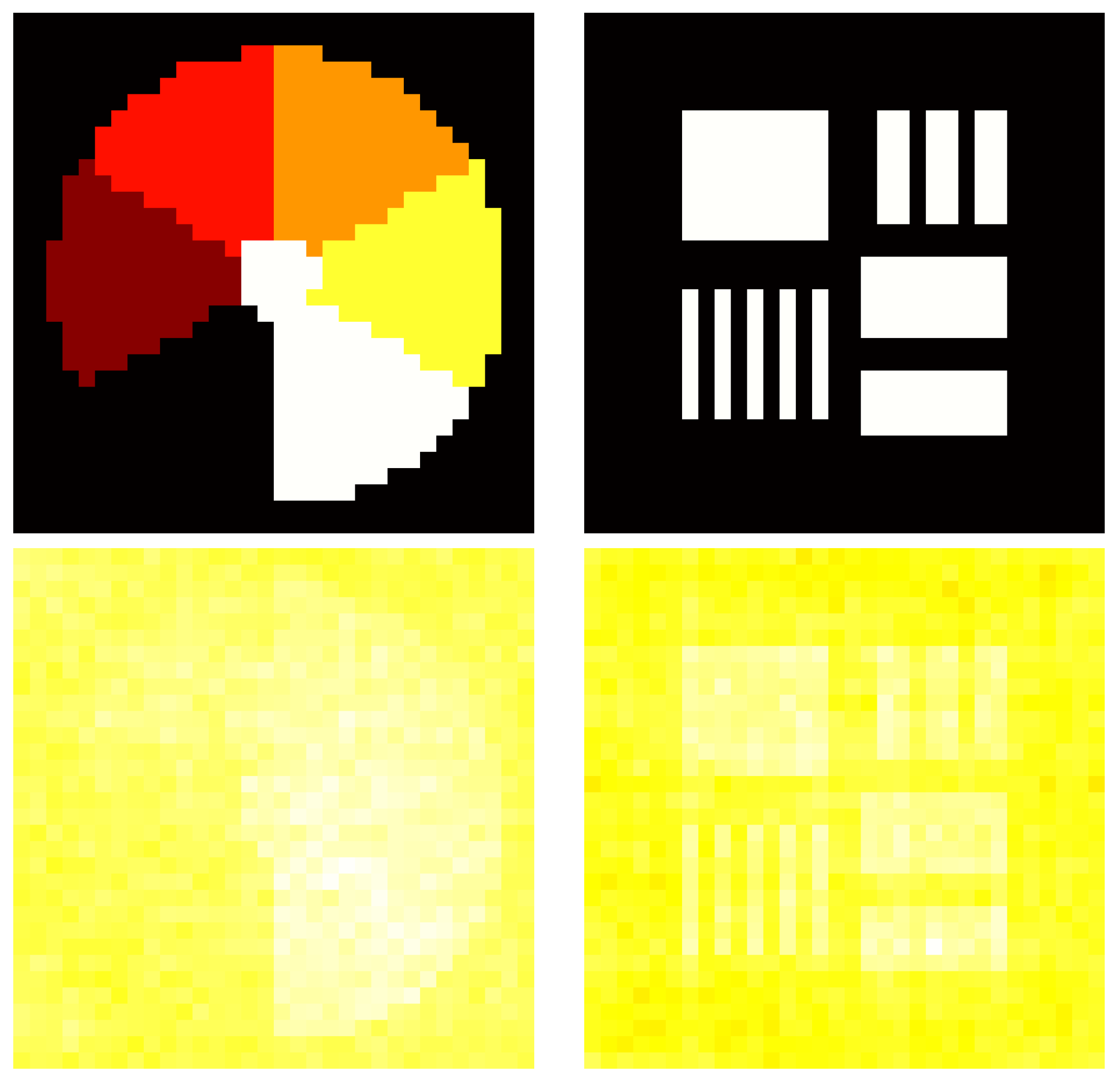
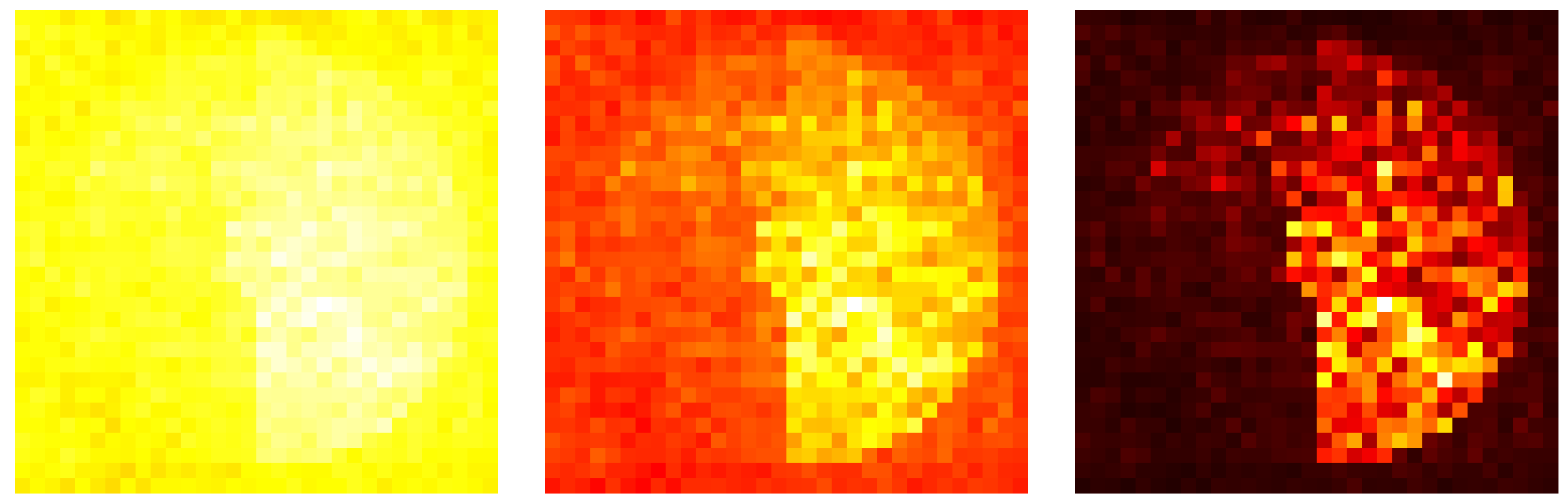
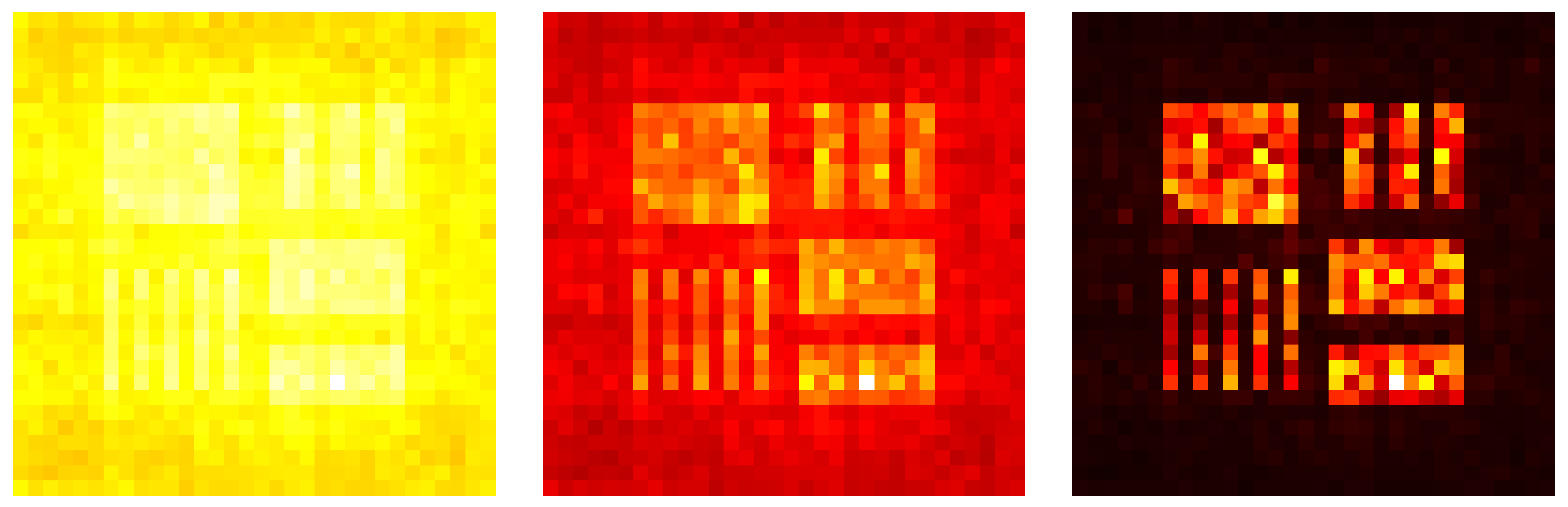
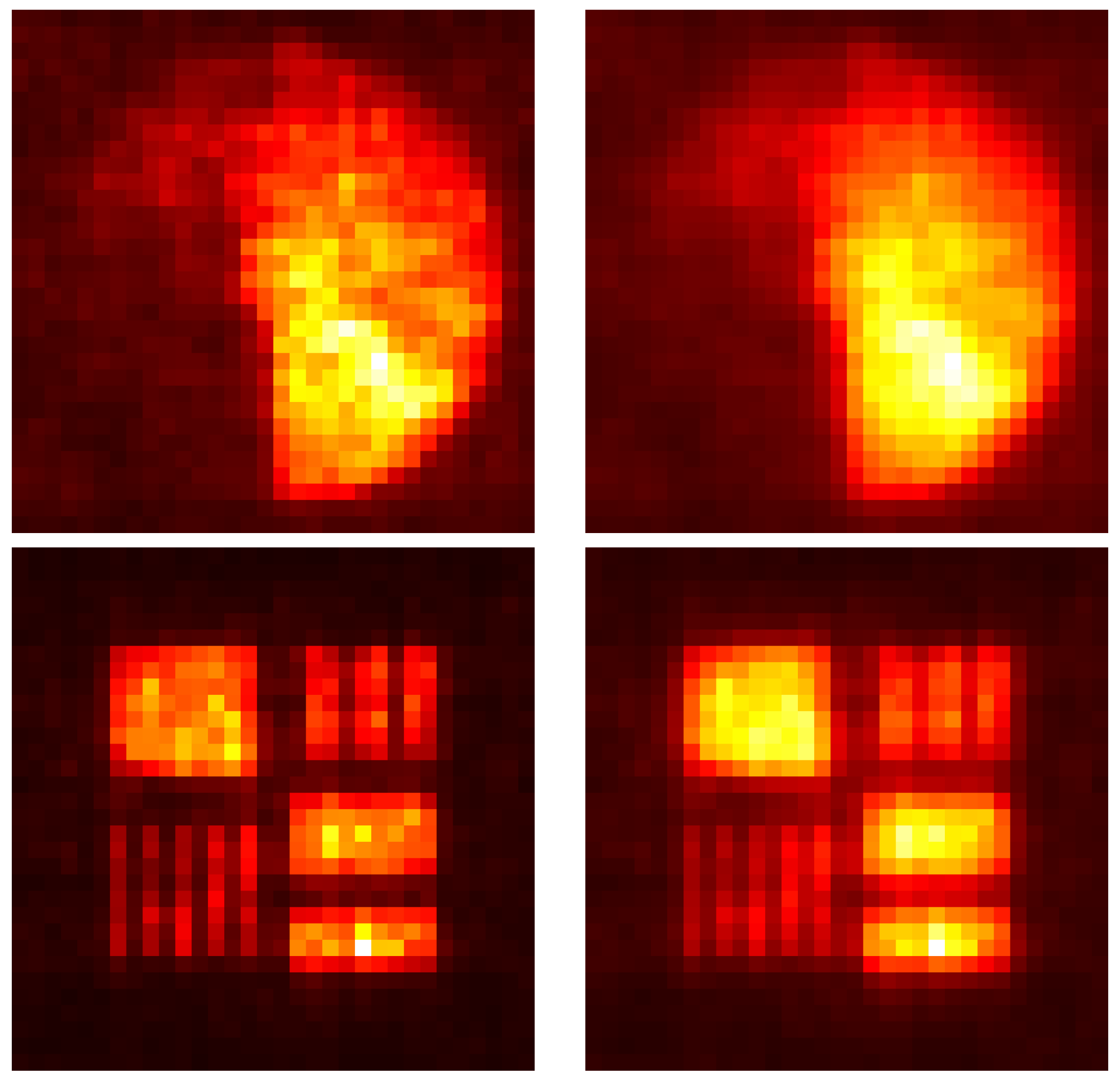
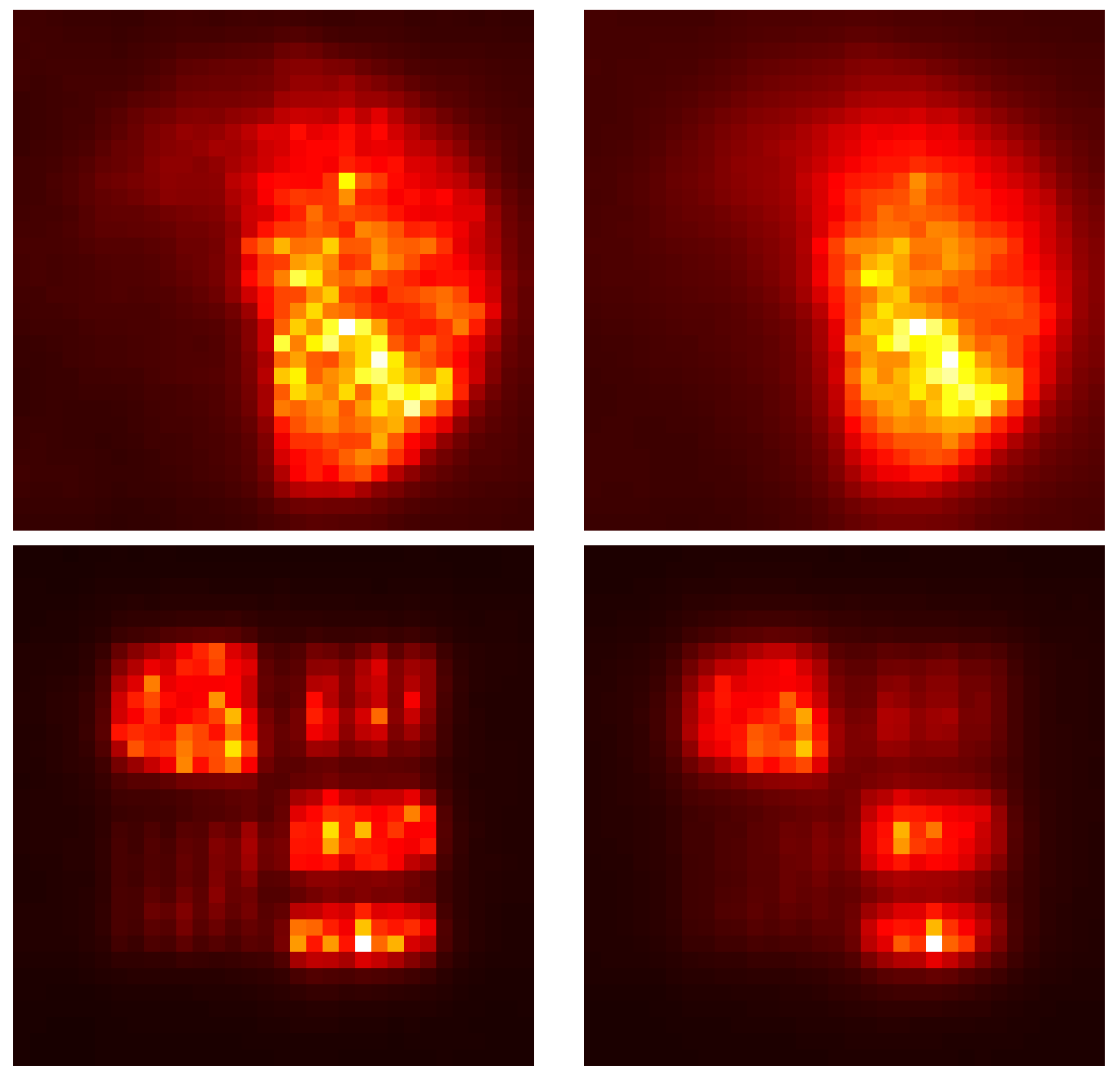
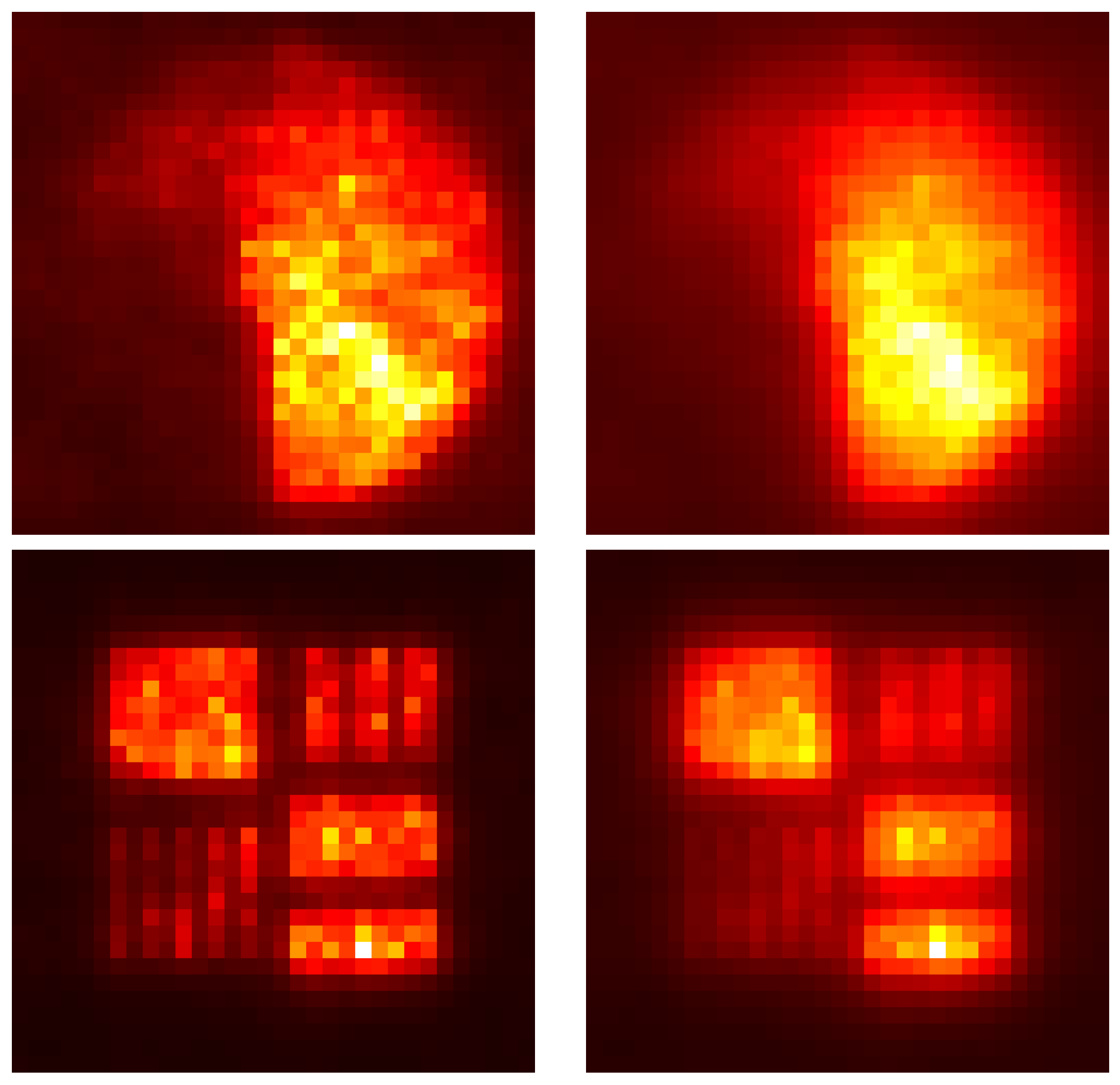
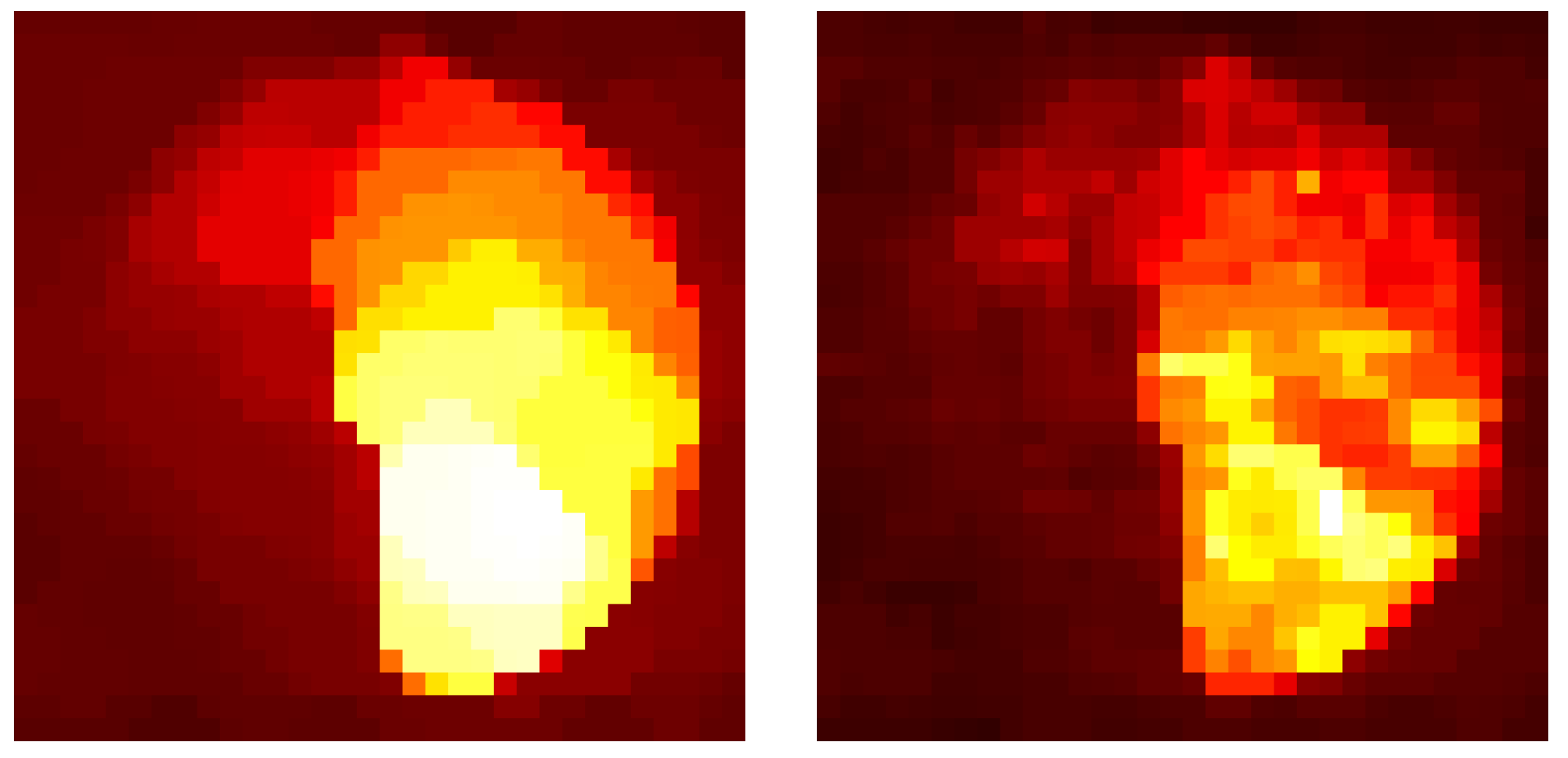
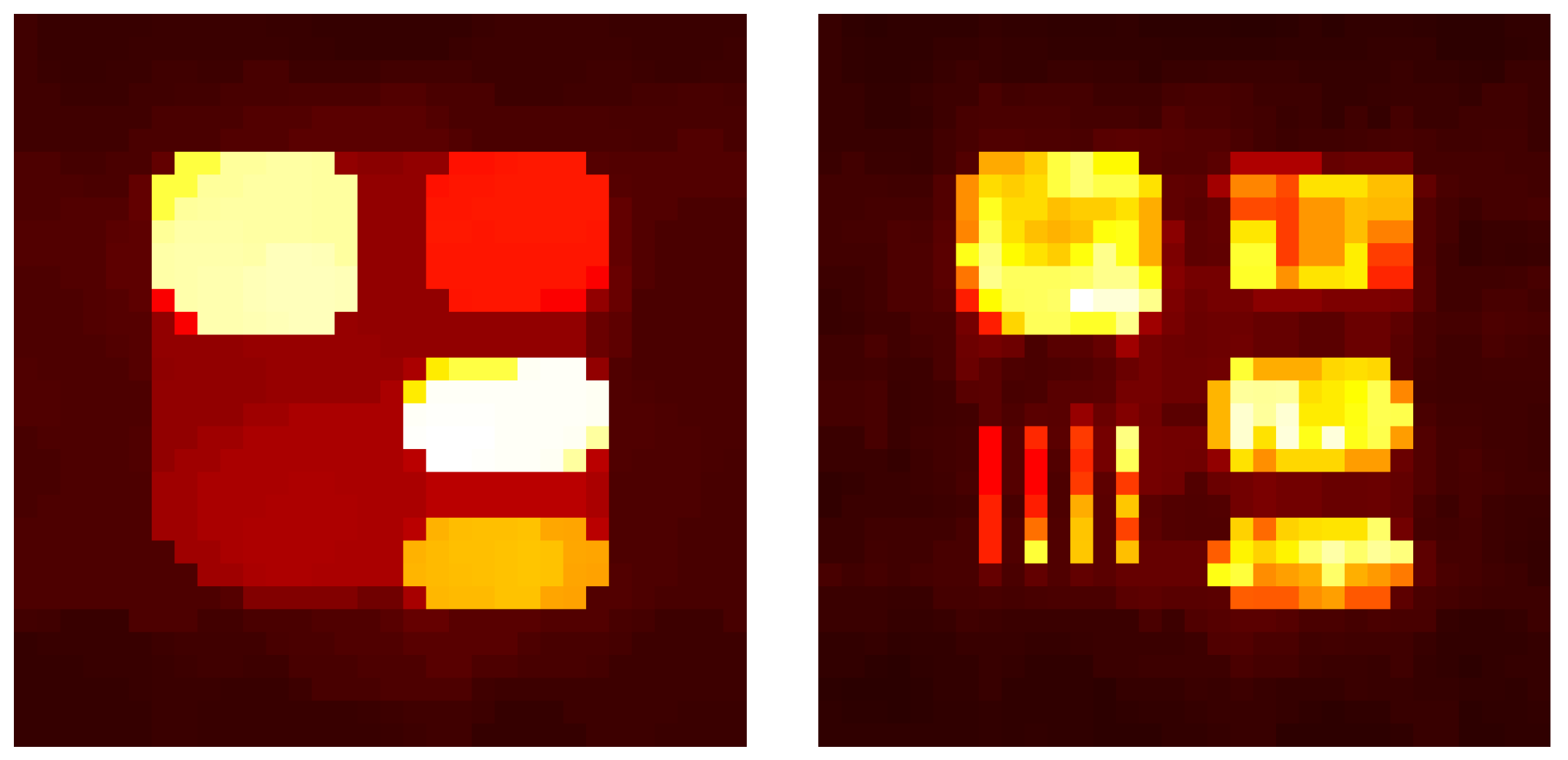
Simulations
4. Regularization Techniques
4.1. The Method of Sieves
4.2. Regularization via Penalties
4.2.1. Entropy Functionals
4.2.2. Good’s Roughness
4.2.3. Silverman’s Roughness
4.2.4. General Markov Random Fields
4.3. Regularization via General Smoothing Steps
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EM | expectation–maximization; |
| SAGE | space-alternating generalized EM; |
| TLA | three-letter acronym; |
| LD | linear dichroism. |
References
- Ryle, M.; Hewish, A. The Synthesis of Large Radio Telescopes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1960, 120, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomalont, E. Earth-Rotation Aperture Synthesis. Proc. IEEE 1973, 61, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, P. (Ed.) Instrumentation and Techniques of Radio Astronomy; IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Felli, M.; Spencer, R. (Eds.) Very Long Baseline Interferometry: Techniques and Applications; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.; Moran, J.; Swenson, G.W., Jr. (Eds.) Inteferometry and Synthesis in Radio Astronomy, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Högbom, J. Aperture Synthesis with a Non-Regular Distribution of Interferometer Baselines. Astron. Astrophys. Suppliment Ser. 1974, 15, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, U. Mathematical-Statistical Description of the Iterative Beam Removing Technique (Method CLEAN). Astron. Astrophys. 1978, 65, 345–356. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, R.; Freedman, A.; Steinberg, R. Sequence CLEAN: A Modified Deconvolution Technique for Microwave Images of Contiguous Targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2002, 38, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ables, J. Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis. Astron. Astrophys. Suppliment Ser. 1974, 15, 383–393. [Google Scholar]
- Ponsonby, J. An Entropy Measure for Partially Polarized Radiation and its Application to Estimating Radio Sky Polarization Distributions from Incomplete “Aperture Synthesis” Data by the Maximum Entropy Method. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1973, 163, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Snyder, D.; O’Sullivan, J.; Miller, M. The Use of Maximum-Likelihood Estimation for Forming Images of Diffuse Radar-Targets from Delay-Doppler Data. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1989, 35, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Knapp, M.; Robey, F.; Volz, R.; Lind, F.; Fenn, A.; Morris, A.; Silver, M.; Klein, S.; Seager, S. Vector Antenna and Maximum Likelihood Imaging for Radio Astronomy. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2016; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Leshem, A.; van der Veen, A.J. Radio Astronomical Imaging in the Presence of Strong Radio Interference. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2000, 46, 1730–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshem, A.; van der Veen, A.J.; Boonstra, A.J. Multichannel interference mitigation techniques in radio astronomy. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2000, 131, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.; Dudgeon, D. Array Signal Processing; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Grainger, W.; Das, R.; Grainge, K.; Jones, M.; Kneissl, R.; Pooley, G.; Saunders, R. A Maximum-Likelihood Approach to Removing Radio Sources from Observations of the Sunyaev–Zel’dovich effect, with Application to Abell 611. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 337, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mhiri, Y.; Korso, M.; Breloy, A.; Larzabal, P. Regularized maximum likelihood estimation for radio interferometric imaging in the presence of radiofrequency interferences. Signal Process. 2024, 220, 109430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzski, B.; Czekala, I.; Loomis, R.; Quinn, T.; Grzybowski, H.; Frazier, R.; Jennings, J.; Nizam, K.; Jian, Y. Regularized Maximum Likelihood Image Synthesis and Validation for ALMA Continuum Observations of Protoplanetary Disks. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific 2023, 135, 064503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Fuhrmann, D.R. Maximum likelihood narrow-band direction finding and the EM algorithm. IEEE Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1990, 38, 560–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J. Radio Astronomy, 2nd ed.; Cygnus-Quasar Books: Powell, OH, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Burg, J.; Luenberger, D.; Wenger, D. Estimation of Structured Covariance Matrices. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieken, D.; Fuhrmann, D.; Lanterman, A. Spatial Spectrum Estimation for Time-Varying Arrays using the EM Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Allerton Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing, Monticello, IL, USA, 4–6 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann, D. Structured Covariance Estimation: Theory, Application, and Recent Results. In Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE Workshop on Sensor Array and Multichannel Processing, Waltham, MA, USA, 12–14 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann, D. Numerically Stable Implementations of the Structured Covariance Expectation-Maximization Algorithm. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2007, 29, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, D. Structured covariance estimation and radar imaging with sparse linear models. In Proceedings of the 1st IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 13–15 December 2005; pp. 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Neyt, X.; Druyts, P.; Acheroy, M.; Verly, J. Structured covariance matrix estimation for the range-dependent problem in STAP. In Proceedings of the Fourth IASTED International Conference on Antennas, Radar and Wave Propagation, Montreal, QC, Canada, 30 May–1 June 2007; pp. 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Hickman, G.; Krolik, J. MIMO field directionality estimation using orientation-diverse linear arrays. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 43rd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1–4 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Robey, F. A Covariance Modeling Approach to Adaptive Beamforming and Detection. Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Electrical Engineering, School of Engineering and Applied Science, Washington University, St. Louis, MO, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, A.D.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum Likelihood from Incomplete Data via the EM Algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1977, 39, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, L. Statistical Signal Processing: Detection, Estimation and Time Series Analysis; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Poor, V. An Introduction to Signal Detection and Estimation, 2nd ed.; Spinger: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Napier, P.; Thompson, A.; Ekers, R. The Very Large Array: Design and Performance of a Modern Synthesis Radio Telescope. Proc. IEEE 1983, 71, 1295–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, R.A.; Thompson, J.R. Nonparametric Probability Density Estimation; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.; Miller, M. The Use of Sieves to Stabilize Images Produced with the EM Algorithm for Emission Tomography. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1985, 32, 3864–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.; Miller, M.; Thomas, L.J.; Politte, D. Noise and Edge Artifacts in Maximum-Likelihood Reconstruction for Emission Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1987, 6, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, D.L.; Miller, M.I. Random Point Processes in Time and Space, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Grenander, U. Abstract Inference; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Politte, D.; Snyder, D. The Use of Constraints to Eliminate Artifacts in Maximum-Likelihood Image Estimation for Emission Tomography. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1988, 35, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politte, D.G.; Snyder, D.L. Corrections for Accidental Coincidences and Attenuation in Maximum-Likelihood Image Reconstruction for Positron-Emission Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1991, 10, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, P.; O’Sullivan, J.; Snyder, D. A Method of Sieves for Multiresolution Spectrum Estimation and Radar Imaging. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1992, 38, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Snyder, D.; Porter, D.; Moulin, P. An Application of Splines to Maximum Likelihood Radar Imaging. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 1992, 4, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, P. A Wavelet Regularization Method for Diffuse Radar-Target and Speckle-Noise Reduction. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 1993, 3, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieden, B.R. Restoring with maximum likelihood and maximum entropy. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1972, 62, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, G.; Smith, C. (Eds.) Maximum-Entropy and Bayesian Methods in Science and Engineering; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Amato, U.; Hughes, W. Maximum entropy regularization of Fredholm integral equations of the first kind. Inverse Probl. 1991, 7, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, L. Approximate solution of Fredholm integral equations by the maximum entropy method. J. Math. Phys. 1986, 27, 2903–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skilling, J.; Strong, A.W.; Bennett, K. Maximum-entropy image processing in gamma-ray astronomy. Mon. Not. R. Astr. Soc. 1979, 187, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skilling, J.; Bryan, R. Maximum entropy image reconstruction: General algorithm. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1984, 211, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieden, B.; Wells, D.C. Restoring with maximum entropy. III. Poisson sources and backgrounds. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1978, 68, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, S.; Daniell, G. The maximum entropy algorithm applied to image enhancement. Proc. IEEE 1980, 5, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Wernecke, S.; D’Addario, L. Maximum entropy image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1977, 26, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nityananda, R. Maximum Entropy Image Restoration in Astronomy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 24, 127–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioya, H.; Gohara, K. Maximum Entropy Method for Diffractive Imaging. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2008, 25, 2846–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, P. Observations on Maximum Entropy Processing of MR Images. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1991, 9, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, R.; Ripley, B. Using Spatial Models as Priors in Astronomical Image Analysis. J. Appl. Stat. 1989, 16, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.; Johnstone, I.; Hoch, J.; Stern, A. Maximum Entropy and the Nearly Black Object. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1992, 54, 41–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nityananda, R. Maximum Entropy—Flexibility Versus Fundamentalism. In Indirect Imaging; Roberts, J., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984; pp. 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Nagar, D. Matrix Variate Distributions; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Good, I.J.; Gaskins, R.A. Nonparametric roughness penalties for probability densities. Biometrika 1971, 58, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Roysam, B. Bayesian Image Reconstruction for Emission Tomography Incorporating Good’s Roughness Prior on Massively Parallel Processors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 3223–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.; Miller, M. Maximum Likelihood SPECT in Clinical Computation Times Using Mesh-Connected Parallel Computers. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1991, 10, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.; Miller, M. Maximum A Posteriori Estimation for SPECT Using Regularization Techniques on Massively-Parallel Computers. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1993, 12, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.; Butler, C. 3-D Maximum A Posteriori Estimation for SPECT on Massively-Parallel Computers. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1993, 12, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, C.S.; Miller, M.; Miller, T.R.; Wallis, J.W. Massivel parallel computers for 3D single-photon-emission computed tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 1994, 39, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Miller, M. Maximum a posteriori Estimation with Good’s Roughness for Optical Sectioning Microscopy. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1993, 10, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanterman, A. Statistical Radar Imaging of Diffuse and Specular Targets Using an Expectation-Maximization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VII, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–28 April 2000; Volume SPIE Proc. 4053, pp. 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, J. Roughness Penalties on Finite Domains. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1995, 4, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieden, B. Some Analytical and Statistical Properties of Fisher Information. In Proceedings of the Stochastic and Neural Methods in Signal Processing, Image Processing, and Computer Vision, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–26 July 1991; Volume SPIE Proc. 1569. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, B.W. On the Estimation of a Probability Density Function by the Maximum Penalized Likelihood Method. Ann. Stat. 1982, 10, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geman, D.; Reynolds, G. Constrained Restoration and the Recovery of Discontinuities. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, C.; Sauer, K. A Generalized Gaussian Image Model for Edge-Preserving MAP Estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1993, 2, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Nunez-Yanez, J.; Achim, A. Video Super-resolution Using Generalized Gaussian Markov Random Fields. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2012, 19, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.; Jones, M.; Wilson, J.; Nychka, D. A Smoothed EM Approach to Indirect Estimation Problems, with Particular Reference to Stereology and Emission Tomography (with discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1990, 52, 271–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nychka, D. Some Properties of Adding a Smoothing Step to the EM Algorithm. Stat. Probab. Lett. 1990, 9, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, P.; LaRiccia, V. Maximum Smoothed Likelihood Density Estimation for Inverse Problems. Ann. Stat. 1995, 23, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, G.; Anderssen, R. On the Stabilization Inherent in the EMS Algorithm. Inverse Probl. 1994, 10, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessler, J.; Hero, A. Space-Alternating Generalized Expectation-Maximization Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 2664–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, T. Penalized Maximum-Likelihood Estimation of Covariance Matrices with Linear Structure. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 3027–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Y. On Designing a Supersynthesis Antenna Array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1972, 20, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, N. A Pseudodynamic Programming Technique for the Design of a Correlator Supersynthesis Array. Radio Sci. 1969, 4, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hero, A.; Fessler, J. A Recursive Algorithm for Computing Cramer-Rao-Type Bounds on Estimator Covariance. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1994, 40, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lanterman, A. Maximum Penalized-Likelihood Structured Covariance Estimation for Imaging Extended Objects, with Application to Radio Astronomy. Stats 2024, 7, 1496-1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7040088
Lanterman A. Maximum Penalized-Likelihood Structured Covariance Estimation for Imaging Extended Objects, with Application to Radio Astronomy. Stats. 2024; 7(4):1496-1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7040088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLanterman, Aaron. 2024. "Maximum Penalized-Likelihood Structured Covariance Estimation for Imaging Extended Objects, with Application to Radio Astronomy" Stats 7, no. 4: 1496-1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7040088
APA StyleLanterman, A. (2024). Maximum Penalized-Likelihood Structured Covariance Estimation for Imaging Extended Objects, with Application to Radio Astronomy. Stats, 7(4), 1496-1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7040088





