Patent Keyword Analysis Using Bayesian Zero-Inflated Model and Text Mining
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Background
2.1. Text Mining for Patent Data
2.2. Zero-Inflated Count Model
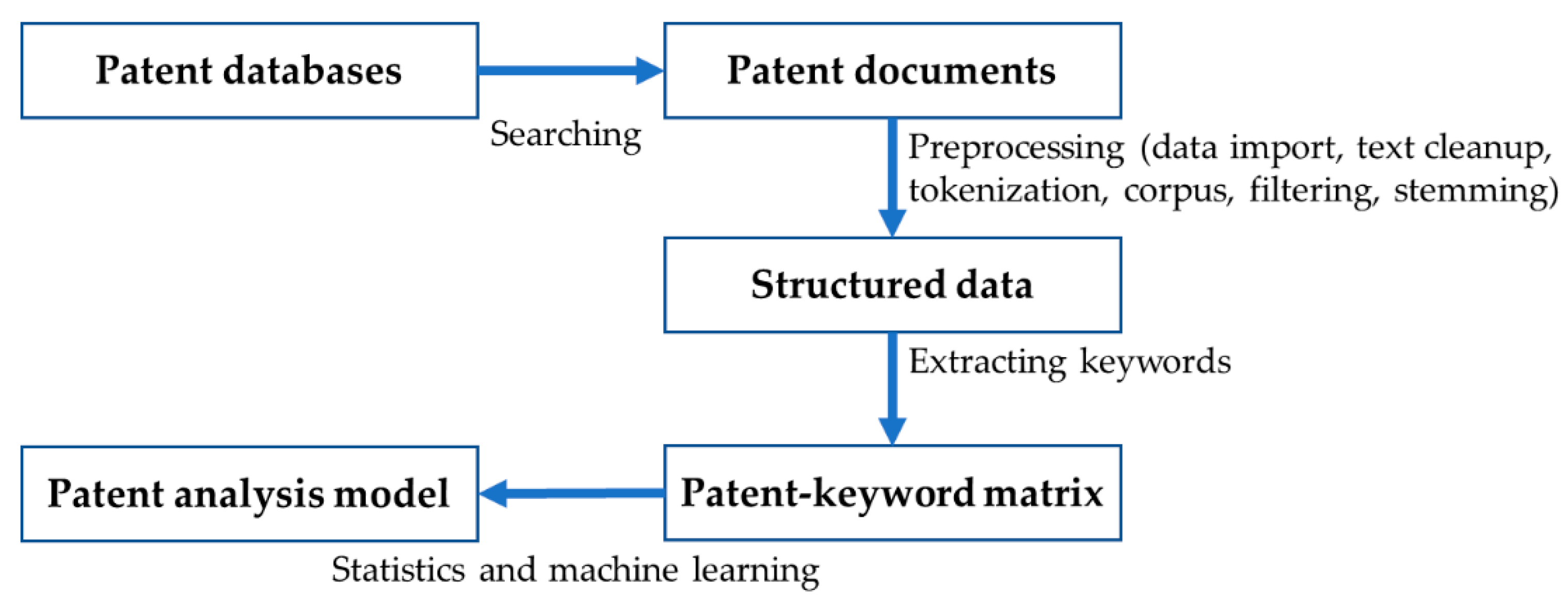
3. Proposed Method for Patent Keyword Analysis
- (Step 1) Data import: cleaning up and structuring the input text for further works
- (Step 2) Stemming: removing word suffixes to the root form
- (Step 3) Whitespace elimination: erasing white space
- (Step 4) Lowe case conversion: converting the words to lower case
- (Step 5) Stopwords removal: removing common words used in most patents
- (Class 1) Corpus: patent document collection, a database for patent documents
- (Class 2) Patent text document: each patent managed by patent document collection
- (Class 3) Patent text repository: a repository used for tracking patent collections
- (Class 4) Patent-keyword matrix: a bag of words for further patent keyword analysis
- (Step 1) Sampling from
- (Step 2) Computing acceptance probability
- (Step 3) Selecting
4. Experiments and Results
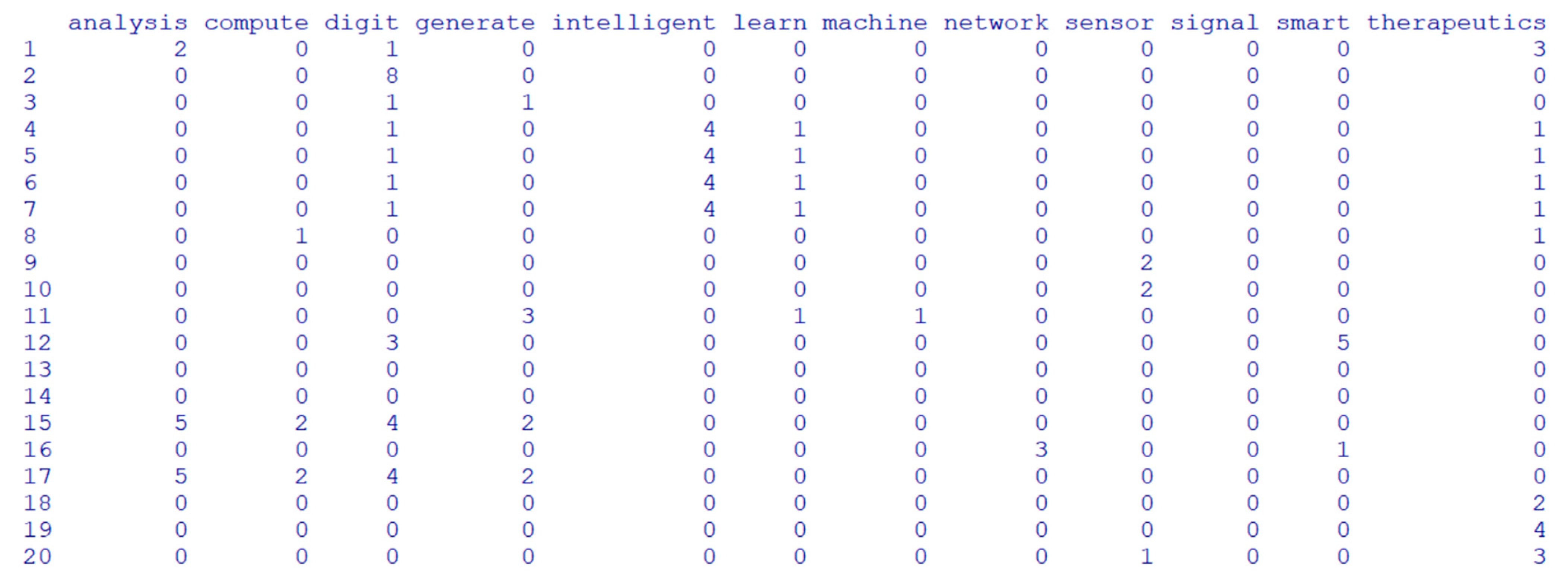
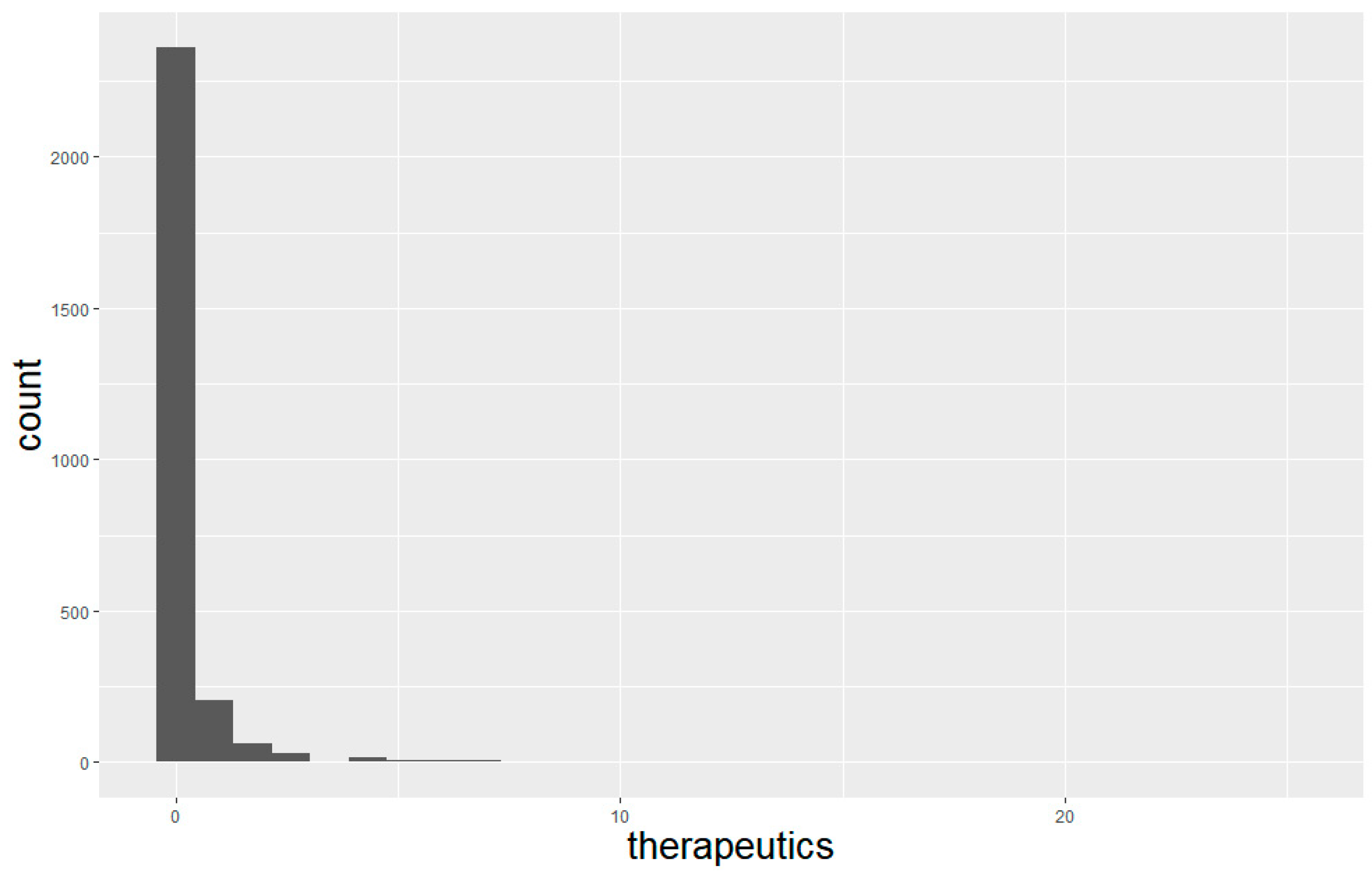
4.1. Text Mining for Constructing Patent-Keyword Matrix
4.2. Patent Keyword Data Analysis Using Bayesian ZIP Regression Model
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, D.; Shao, Z. Patent text mining based hydrogen energy technology evolution path identification. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 49, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reher, L.; Runst, P.; Thomä, J. Personality and regional innovativeness: An empirical analysis of German patent data. Res. Policy 2024, 53, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, M.; Roshani, S. Path-Breaking Directions in Quantum Computing Technology: A Patent Analysis with Multiple Techniques. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jun, S. Zero-Inflated Patent Data Analysis Using Compound Poisson Models. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jun, S. Patent Analysis Using Bayesian Data Analysis and Network Modeling. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Fu, Y.; Chu, P.; Zhang, X. A Bayesian Analysis of Zero-Inflated Count Data: An Application to Youth Fitness Survey. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Kunming, China, 15–16 November 2014; pp. 699–703. [Google Scholar]
- Neelon, B.; Chung, D. The LZIP: A Bayesian Latent Factor Model for Correlated Zero-Inflated Counts. Biometrics 2017, 73, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, O.B.; Bello, T.; Gureje, O. Zero Inflated Poisson and Zero Inflated Negative Binomial Models with Application to Number of Falls in the Elderly. Biostat. Biom. Open Access J. 2017, 1, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Workie, M.S.; Azene, A.G. Bayesian zero-inflated regression model with application to under-five child mortality. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oganisian, A.; Mitra, N.; Roy, J.A. A Bayesian nonparametric model for zero-inflated outcomes: Prediction, clustering, and causal estimation. Biometrics 2021, 77, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Coull, B.A.; Moscicki, A.-B.; Paster, B.J.; Starr, J.R. Bayesian variable selection for multivariate zero-inflated models: Application to microbiome count data. Biostatistics 2020, 21, 499–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.S. A Bayesian joint model for continuous and zero-inflated count data in developmental toxicity studies. Commun. Stat. Appl. Methods 2022, 29, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajihosseini, M.; Amini, P.; Saidi-Mehrabad, A.; Dinu, I. Infants’ gut microbiome data: A Bayesian Marginal Zero-inflated Negative Binomial regression model for multivariate analyses of count data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 15, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, H.C.C.; Louzada, F.; Ramos, P.L.; de Oliveira Júnior, M.R.; Perdoná, G.D.S.C. A Bayesian approach for the zero-inflated cure model: An application in a Brazilian invasive cervical cancer database. J. Appl. Stat. 2022, 49, 3178–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanitjirattikal, P.; Shi, C. A Bayesian zero-inflated binomial regression and its application in dose-finding study. J. Biopharm. Stat. 2020, 30, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Rolka, D.B.; Barker, L.E. Modeling County-Level Rare Disease Prevalence Using Bayesian Hierarchical Sampling Weighted Zero-Inflated Regression. J. Data Sci. 2023, 21, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, M.; Mahmoudi, M.; Mohammad, K.; Mikaeli, J.; Zeraati, H. Bayesian modelling of zero-inflated recurrent events and dependent termination with compound Poisson frailty model. Stat 2020, 9, e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Lu, J.-C. Bayesian analysis of zero-inflated regression models. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2006, 136, 1360–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinerer, I.; Hornik, K. Package ‘tm’ Version 0.7-13, Text Mining Package; CRAN of R Project; R Foundation for Statistical Com-puting: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sidumo, B.; Sonono, E.; Takaidza, I. Count Regression and Machine Learning Techniques for Zero-Inflated Overdispersed Count Data: Application to Ecological Data. Ann. Data Sci. 2023, 11, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S. Zero-Inflated Text Data Analysis using Generative Adversarial Networks and Statistical Modeling. Computers 2023, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Theodoridis, S. Machine Learning a Bayesian and Optimization Perspective; Elsevier: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Roback, P.; Legler, J. Beyond Multiple Linear Regression: Applied Generalized Linear Models and Multilevel Models in R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbe, J.M. Negative Binomial Regression, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbe, J.M. Modeling Count Data; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, A.C.; Trivedi, P.K. Regression Analysis of Count Data, Second Edition; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, D. Zero-Inflated Poisson Regression, with an Application to Defects in Manufacturing. Technometrics 1992, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, R.V.; McKean, J.M.; Craig, A.T. Introduction to Mathematical Statistics, 8th ed.; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moriña, D.; Puig, P.; Navarro, A. Analysis of zero inflated dichotomous variables from a Bayesian perspective: Application to occupational health. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USPTO, The United States Patent and Trademark Office. Available online: http://www.uspto.gov (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- KIPRIS, Korea Intellectual Property Rights Information Service. Available online: www.kipris.or.kr (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Gelman, A.; Carlin, J.B.; Stern, H.S.; Dunson, D.B.; Vehtari, A.; Rubin, D.B. Bayesian Data Analysis, 3rd ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Peck, E.A.; Vining, G.G. Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Zhang, Q.; Yi, G.Y. Package ‘ZIPBayes’ Version 1.0.2, Bayesian Methods in the Analysis of Zero-Inflated Poisson Model; CRAN of R Project; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]


| Keyword | Poisson | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Coefficient | 2.5% | 97.5% | |
| analysis | 0.0710 | −0.2277 | −0.4995 | −0.0023 |
| compute | 0.3612 | 0.0396 | −0.0525 | 0.1231 |
| digit | 0.6107 | −0.0850 | −0.4690 | 0.1871 |
| generate | 0.4939 | −0.0469 | −0.1852 | 0.0831 |
| intelligent | 0.0001 | 0.4070 | 0.1872 | 0.5993 |
| learn | 0.3789 | −0.2505 | −0.8578 | 0.2559 |
| machine | 0.0178 | −1.6314 | −3.4030 | −0.5637 |
| network | 0.0976 | −0.2186 | −0.5096 | −0.0135 |
| sensor | 0.0002 | 0.0994 | 0.0435 | 0.1468 |
| signal | 0.0051 | 0.1355 | 0.0412 | 0.2300 |
| smart | 0.2141 | 0.1821 | −0.1684 | 0.4208 |
| Keyword | Binomial | Poisson | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Coefficient | 2.5% | 97.5% | p-Value | Coefficient | 2.5% | 97.5% | |
| analysis | 0.0468 | −0.8504 | −1.6886 | −0.0121 | 0.0024 | −0.7012 | −1.1547 | −0.2478 |
| compute | 0.0600 | 0.2429 | −0.0100 | 0.4958 | 0.0001 | 0.3124 | 0.1615 | 0.4633 |
| digit | 0.6771 | −0.2036 | −1.1612 | 0.7541 | 0.4680 | −0.2825 | −1.0449 | 0.4800 |
| generate | 0.0461 | −0.3884 | −0.7701 | −0.0067 | 0.0013 | −0.3642 | −0.5859 | −0.1426 |
| intelligent | 0.1638 | 0.4683 | −0.1905 | 1.1271 | 0.0001 | 0.7152 | 0.3635 | 1.0670 |
| learn | 0.9453 | −19.9282 | −4447.3093 | 4407.4530 | 0.0001 | −2.3781 | −3.4261 | −1.3301 |
| machine | 0.9932 | −12.5562 | −833.8303 | 808.7180 | 0.0040 | −1.9705 | −3.3110 | −0.6300 |
| network | 0.2798 | −0.1420 | −0.3993 | 0.1153 | 0.0136 | −0.2302 | −0.4130 | −0.0473 |
| sensor | 0.6688 | 0.0279 | −0.0999 | 0.1557 | 0.0001 | 0.2452 | 0.1191 | 0.3713 |
| signal | 0.3326 | 0.1328 | −0.1357 | 0.4013 | 0.2739 | 0.1288 | −0.1018 | 0.3595 |
| smart | 0.9804 | 0.0117 | −0.9451 | 0.9686 | 0.5902 | −0.1420 | −0.6584 | 0.3744 |
| Keyword | Binomial | Poisson | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Median | 2.5% | 97.5% | Mean | Median | 2.5% | 97.5% | |
| analysis | 0.2479 | 0.0000 | 0.2479 | 0.2479 | −0.9965 | 0.1624 | −1.2947 | −0.7232 |
| compute | 0.3704 | 0.0000 | 0.3704 | 0.3704 | −0.3730 | 0.1038 | −0.5235 | −0.2348 |
| digit | 0.6838 | 0.0000 | 0.6838 | 0.6838 | −0.2641 | 0.1468 | −0.5677 | 0.0140 |
| generate | 0.2783 | 0.0000 | 0.2783 | 0.2783 | −0.2629 | 0.0575 | −0.3688 | −0.1047 |
| intelligent | −0.1029 | 0.1939 | −0.4831 | 0.2830 | 0.1684 | 0.1324 | −0.1180 | 0.4122 |
| learn | 0.0638 | 0.0000 | 0.0637 | 0.0638 | −0.6540 | 0.3595 | −1.4477 | −0.0427 |
| machine | −0.3008 | 0.2998 | −0.8881 | 0.1367 | −2.2396 | 0.7230 | −3.3298 | −0.5564 |
| network | 0.8103 | 0.0000 | 0.8103 | 0.8103 | −0.9770 | 0.1705 | −1.2864 | −0.6796 |
| sensor | 0.1947 | 0.0000 | 0.1947 | 0.1947 | 0.0345 | 0.0295 | −0.0200 | 0.0799 |
| signal | 0.1127 | 0.0000 | 0.1127 | 0.1127 | 0.2777 | 0.0559 | 0.1596 | 0.3512 |
| smart | 0.4618 | 0.0000 | 0.4618 | 0.4618 | −0.5229 | 0.2187 | −0.9659 | −0.1316 |
| Keyword | Poisson | ZIP | Bayesian ZIP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binomial | Poisson | Binomial | Poisson | ||
| analysis | 0.4972 | 1.6765 | 0.9069 | 0.0000 | 0.5715 |
| compute | 0.1756 | 0.5058 | 0.3018 | 0.0000 | 0.2887 |
| digit | 0.6561 | 1.9153 | 1.5249 | 0.0000 | 0.5817 |
| generate | 0.2683 | 0.7634 | 0.4433 | 0.0000 | 0.2641 |
| intelligent | 0.4121 | 1.3176 | 0.7035 | 0.7661 | 0.5302 |
| learn | 1.1137 | 8854.7623 | 2.0960 | 0.0001 | 1.4050 |
| machine | 2.8393 | 1642.5483 | 2.6810 | 1.0248 | 2.7734 |
| network | 0.4961 | 0.5146 | 0.3657 | 0.0000 | 0.6068 |
| sensor | 0.1033 | 0.2556 | 0.2522 | 0.0000 | 0.0999 |
| signal | 0.1888 | 0.5370 | 0.4613 | 0.0000 | 0.1916 |
| smart | 0.5892 | 1.9137 | 1.0328 | 0.0000 | 0.8343 |
| Keyword | Frequency | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | >5 | |
| analysis | 2524 | 106 | 31 | 13 | 9 | 2 | 0 |
| compute | 2436 | 128 | 84 | 16 | 5 | 2 | 14 |
| digit | 2632 | 33 | 11 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| generate | 2347 | 195 | 91 | 28 | 16 | 5 | 3 |
| intelligent | 2620 | 42 | 12 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| learn | 2584 | 77 | 11 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| machine | 2596 | 51 | 19 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 6 |
| network | 2547 | 89 | 28 | 14 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| sensor | 2459 | 97 | 76 | 26 | 13 | 3 | 11 |
| signal | 2534 | 82 | 33 | 19 | 6 | 3 | 8 |
| smart | 2640 | 38 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| therapeutics | 2359 | 204 | 63 | 28 | 17 | 4 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jun, S. Patent Keyword Analysis Using Bayesian Zero-Inflated Model and Text Mining. Stats 2024, 7, 827-841. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7030050
Jun S. Patent Keyword Analysis Using Bayesian Zero-Inflated Model and Text Mining. Stats. 2024; 7(3):827-841. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7030050
Chicago/Turabian StyleJun, Sunghae. 2024. "Patent Keyword Analysis Using Bayesian Zero-Inflated Model and Text Mining" Stats 7, no. 3: 827-841. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7030050
APA StyleJun, S. (2024). Patent Keyword Analysis Using Bayesian Zero-Inflated Model and Text Mining. Stats, 7(3), 827-841. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7030050






