Abstract
Estimating parameters for multiple datasets can be time consuming, especially when the number of datasets is large. One solution is to sample from multiple datasets simultaneously using Bayesian methods such as adaptive multiple importance sampling (AMIS). Here, we use the AMIS approach to fit a von Mises distribution to multiple datasets for wind trajectories derived from a Lagrangian Particle Dispersion Model driven from 3D meteorological data. A posterior distribution of parameters can help to characterise the uncertainties in wind trajectories in a form that can be used as inputs for predictive models of wind-dispersed insect pests and the pathogens of agricultural crops for use in evaluating risk and in planning mitigation actions. The novelty of our study is in testing the performance of the method on a very large number of datasets (>11,000). Our results show that AMIS can significantly improve the efficiency of parameter inference for multiple datasets.
1. Introduction
A fundamental problem in modelling is the estimation of unknown parameters from empirical data. Frequently however, practical situations require the estimation of individual parameters for a large number of datasets. Fitting the same model to multiple datasets and extracting parameters specific for each dataset is becoming common when dealing with biological and epidemiological data. Examples range from the estimation of specific parameters across different genotypes [1], cell lines [2], patients [3,4], and health district or country-specific parameters [5,6]. The number of individual datasets can increase up to hundreds of thousands when linking geostatistical maps and pathogen transmission models [7,8,9] or combining remote sensing data with crop growth models [10,11]. Inference would be prohibitively slow when using methods such as Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling [12] or importance sampling (IS) [13]. Here, we demonstrate the use of adaptive multiple importance sampling (AMIS) to infer parameters simultaneously from a large number of datasets (>11K) for a model that characterises the distribution of wind trajectories. The wind trajectories are derived from an atmospheric dispersion model derived by meteorological data.
The adaptive multiple importance sampling algorithm is an iterative technique that recycles samples from all previous iterations in order to improve the efficiency of the proposal distribution [14]. Veach and Guibas [15] proposed the use of a deterministic multiple mixture to pool importance samples from different proposal distributions. This idea was extended by Cornuet and co-authors [16], who used the deterministic multiple mixture formula to construct proposal distributions sequentially and adaptively. Adaptive multiple importance sampling has been used in a variety of research fields, including population genetics [17], environment illumination computations [18] and signal communications [19]. Recently, AMIS has shown promising results when dealing with sampling from multiple targets [8,20,21].
The migration pathways achieved by flying insects are highly dependent on the seasonal variation in wind patterns [22,23,24]. For example, swarms follow the seasonal shifts of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), which favours the search for rain-fed areas for feeding [25,26,27,28,29]. In this study, we used the AMIS approach to fit the von Mises distribution to wind trajectories. The von Mises distribution is commonly used for modelling circular data [30], as well as for the statistical modelling of wind direction [31]. The von Mises distribution has two parameters: the directional mean and concentration. Temporal changes in the directional mean can show seasonal variation in global wind patterns, while the concentration can be used as a measure of stochasticity associated with natural variation in turbulent wind flow. Values of concentration close to zero indicate a uniform angular distribution, and high values imply low variance that is consistent with a stronger directional flow. Knowing wind direction and the uncertainties related to it is important when evaluating risk or planning mitigation actions associated with the movements of pest and disease. For example, the visualisation of long-range atmospheric transport have been used to improve risk estimates and early warnings in operational crop disease and insect pest management systems [32,33].
The Lagrangian atmospheric dispersion model, NAME, can forecast or reconstruct wind trajectories at high spatial and temporal resolutions [34]. Originally developed by the UK Met Office to model the release, transport, dispersion and removal of hazardous material in the atmosphere [34], NAME has subsequently been adapted to model the long-distance wind-borne transport of insect vectors of viral diseases [35] and fungal spores [32]. Furthermore, the Lagrangian atmospheric dispersion model, NAME, can simulate wind trajectories that are stochastic so that an ensemble of trajectories provides a probabilistic distribution of the dispersal of particulates such as spores or insects [34]. For our analysis, we considered a domain extending across five sub-Saharan countries (Kenya, Ethiopia, Somalia, Eritrea and Djibouti). This area was selected because it was affected by the 2019–2021 desert locust upsurge [36]. First, to gauge the computational effort required, we used IS to recover parameter values from synthetic data for a single dataset. Then, using synthetic data and three datasets, we showed that AMIS can significantly reduce computational effort while maintaining the quality of inference. Finally, we tested the performance of the method on a very large number of datasets (>11,000) using wind trajectories derived from a Lagrangian Particle Dispersion Model derived from 3D meteorological data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Von Mises Distribution
A random variable has a von Mises distribution if its probability density function is defined as follows [37]:
Here, is the modified Bessel function of the first kind and order zero, is the directional mean, and is the directional concentration.
2.2. Synthetic Wind Data Used for Initial Test
We used the function rvonmises from the R package Rfast [38,39] to sample random variables from the parameterised von Mises distribution.
2.3. NAME Wind Trajectories Based on Historic Meteorology Data
The Lagrangian atmospheric dispersion model, NAME, was used to reconstruct wind trajectories at a high spatial (∼20 km) and temporal (0.5 h) resolution [34], relative to the domain of interest extending across multiple countries. These NAME simulations were derived using historic analysis meteorology data from the global configuration of the Unified Model (UM), the Met Office’s operational Numerical Weather Prediction model [40]. NAME wind trajectories were calculated starting from 3860 source locations spaced on a regular 20 km × 20 km grid across Ethiopia, Somalia, Eritrea and Kenya (Figure 1A). For a given date and location source, 1000 individual trajectories were calculated, each commencing 2 h after local sunrise and terminating 1 h before local sunset (Figure 1B). There is stochastic variation in the direction of individual realisations starting from the same location, due to the turbulent nature of the atmosphere as represented in NAME. We calculated the angle for each trajectory between a vector corresponding to the east direction and a vector connecting the start and end location of a trajectory for a specified time.
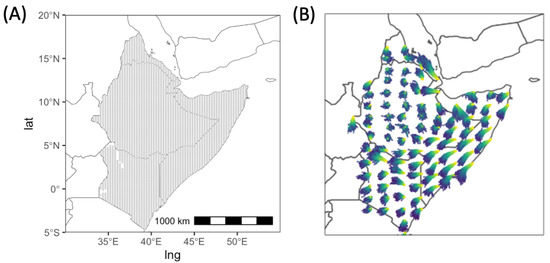
Figure 1.
(A) Source locations for wind trajectories. (B) An example of NAME wind trajectories on the 15th of January 2021 for a subset of source locations. The colours show the difference in hours between points on a trajectory and the initial point.
2.4. Bayesian Inference
Usually, Bayesian inference is performed by deriving a likelihood function and estimating it numerically using Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods [41]. Alternatively, Bayesian inference can be conducted using methods based on the importance sampling approach. Importance sampling methods draw from the proposal distributions, which are standard probability distributions. Figure 2 shows the differences between importance sampling (IS), adaptive importance sampling (AIS) and adaptive multiple importance sampling (AMIS). In the case of IS, we can reconstruct the target from a proposal distribution by re-weighting sampled parameters according to the importance weights, but this may require many samples to have a reasonably good reconstruction [42]. A more efficient scheme is AIS, where samples from previous iterations are used to construct the proposal distribution [43]. In contrast, AMIS recycles all samples from previous iterations to both construct the proposal for the current iteration as well as to reconstruct the target distribution [14].
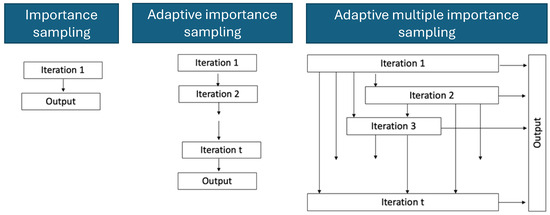
Figure 2.
Diagrammatic illustration of differences between importance sampling (left column), adaptive importance sampling (middle column) and adaptive multiple importance sampling (right column).
2.4.1. Importance Sampling (IS)
Importance sampling is based on using weighted samples from a proposal distribution [42]. The corresponding importance weights for a sampled set of parameters can be calculated as follows:
where is the target density function (i.e., the von Mises distribution function), and is the proposal density function.
2.4.2. Adaptive Importance Sampling (AIS)
Adaptive importance sampling adapts the proposal distribution based on the outcome of the previous iteration [43]. The corresponding importance weights for a sampled set of parameters can be calculated as follows:
where is the proposal density function at iteration l.
At iterations , a suitable proposal is found by fitting a mixture of Student’s t-distributions to the weighted samples. The algorithm continues until all datasets meet the ESS requirement or the maximum number of iterations, L, has been achieved.
2.4.3. Adaptive Multiple Importance Sampling (AMIS)
The adaptive multiple importance sampling algorithm (AMIS) is a technique that recycles samples from all previous iterations when constructing a proposal distribution or calculating weights [14]. For each iteration , we sample parameter sets. The corresponding importance weights for a sampled set of parameters can be calculated as follows:
where is a proposal distribution at iteration i.
2.4.4. Effective Sample Size (ESS)
We used Kish’s effective sample size [44,45] as a measure of the quality of the posterior distribution. For IS, ESS is calculated using all sampled parameters:
Here, is a normalised weight, so that .
For AIS, only samples from the last iteration are used to calculate the ESS:
For AMIS, all sampled parameters are used to calculate the ESS after each iteration. The ESS for dataset l after iteration i is
2.4.5. Implementation of AMIS
For the AMIS algorithm, we set a required ESS for all of the datasets, denoted by . We call datasets ‘active’ if they have an ESS below the target, and we used the weights for the active datasets to design the proposal for the next iteration of the AMIS algorithm. This targets the sampling toward areas of the parameter space that favour datasets that have not yet reached the required ESS. At iterations , we use the mean weight over the active dataset to determine the next proposal distribution. A suitable proposal can be constructed by fitting a mixture of distributions to the weighted samples , for . We used student’s t-distributions, but tested the performance of the algorithm also using Normal and Cauchy distributions. The algorithm continues until all datasets meet the ESS requirement or the maximum number of iterations, I, has been achieved. Pseudo code for the algorithm is shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 AMIS for multiple datasets. |
|
3. Results
3.1. Illustrative Simulations
3.1.1. Parameter Estimation Using IS and AIS for a Single Dataset
First, we sampled 1000 angles using parameter values and (Figure 3A). For both IS and AIS, we chose a uniform distribution function as our proposal: . For IS, we varied the number of parameter sets sampled from the proposal from to and calculated the effective sample size (ESS) as a function of the number of parameter sets sampled. Important sampling produced a posterior distribution that recovered the original parameter values (Figure 3B,C) and provided a corresponding fit of the von Mises distribution function to the original (Figure 3D). Although the ESS increased with sample size, the ESS was >25 for samples for this single dataset (Figure 3E). For the AIS, we set and sampled 1000 parameters each iteration. The algorithm required 19 iterations, i.e., 19,000 parameter sets, to reach the required ESS (Figure 3F). The adaptive approach used to construct the proposal distribution considerably decreased the number of iterations and computational time.
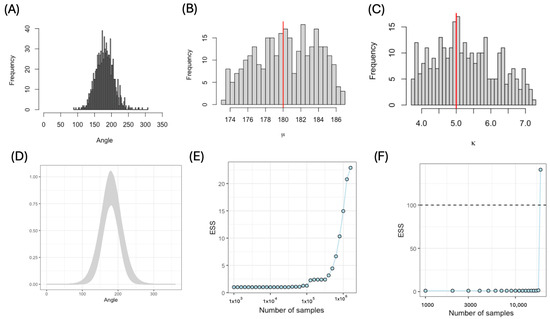
Figure 3.
Parameter estimation using IS and AIS. (A) Distribution of 1000 simulated angles from a von Mises distribution (); (B,C) posterior distributions of parameters (the red lines show the true values of the parameters; here, the proposal distribution was ); (D) fitted von Mises distribution function calculated using parameters from the posterior distribution; (E) effective sample size (ESS) as a function of the number of IS samples; (F) effective sample size (ESS) as a function of the number of AIS samples.
3.1.2. Parameter Estimation Using AMIS for Multiple Datasets
Next, we considered three datasets with differing means and variances. We sampled 1000 angles with the following values of parameters: set 1 ; set 2 ; and set 3 (Figure 4A). We chose these parameters to produce angle distributions that do not overlap, as well as having different dispersion around their mean. For this case study, we fitted parameters for the three sets simultaneously using the AMIS algorithm. As in the previous example, we chose a uniform distribution function as our proposal: . We set the required effective sample size , and we sampled 1000 parameter sets each iteration. The algorithm stopped when all datasets had . The first dataset reached the required ESS after 5000 sampled parameter sets (Figure 4B). The other two datasets reached the required ESS after 8000 parameter sets to achieve the required . The posterior distributions recovered the original parameters (Figure 4C). To illustrate the adaptive nature of AMIS, we plotted the parameters sampled at each iteration (Figure 4D). The first iteration sampled 1000 parameters from the prior, which we chose as uniform with a wide range. For iteration 2, the algorithm significantly reduced the area where parameters were sampled. At iteration 5, the proposal concentrated in two areas, simultaneously covering parameters lying close to the true values of the three parameters. This is the iteration where the first dataset achieves the required ESS (red diamond). In iterations 6 and 7, the algorithm targets areas close to the true values of datasets two and three. Finally, the algorithm achieves the required ESS for the second dataset at iteration 7 (blue diamond), and for the last dataset, at iteration 8 (green diamond). We also tested AMIS using an alternative prior given by a scaled distribution, which concentrated sampling on the upper right quarter of the parameter space, i.e., opposite the region to where true parameter values were. It required 90,000 parameter sets to reach the required ESS (Supplementary Figure S1), which indicates that AMIS was not sensitive to the prior distribution. We also found that both the student-t and Cauchy distributions had similar performances, but outperformed proposals constructed using mixtures of Normal distributions (Supplementary Figure S2).
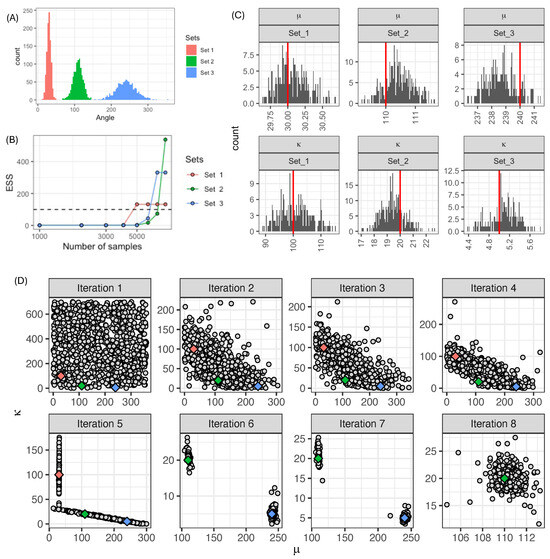
Figure 4.
(A) Three synthetic datasets. (B) Change in effective sample size as a function of the iteration using AMIS (each iteration = 1000 samples). (C) Posterior distribution (grey) and true values (red lines) of parameters. (D) Parameters sampled at each iteration (grey dots) and true values of parameters (diamonds, colour-coded as in (A)).
The performance of the algorithm depends on the choice of several algorithm parameters, such as the number of samples per iteration, the maximum number of iterations and the required effective sample size. These parameters were tuned by performing pilot studies. Our analyses showed that the number of sampled parameters did not increase significantly when we increased the value from 100 to 1000 (Supplementary Figure S3). Setting = 10,000 produced a number of samples close to 50,000, meaning that the algorithm stopped after 50 iterations. We set to ensure that there was enough time for the algorithm to converge.
3.2. Application to NAME Wind Trajectories
Finally, we simultaneously fitted the von Mises distributions to the NAME wind trajectories. We chose three dates: 15 January 2020, 15 August 2020 and 15 January 2021. Our choice was motivated by the following: (i) testing the influence of the ITCZ on local wind, i.e., a southward orientation in January and northward orientation in August; and (ii) comparing annual differences in wind behaviour, i.e., the same day but different year. This resulted in the estimation of parameters for 11,580 datasets, corresponding to 3 × 3860 datasets on a 20 km × 20 km grid. We chose a uniform distribution function as our proposal: . We set the required effective sample size , and we sampled 1000 parameter sets each iteration. It took about sampled parameters for all datasets to reach the required ESS (Figure 5A). For each grid cell and the three days, we provide 100 parameter sets sampled from the posterior distributions in the Supplementary Materials.
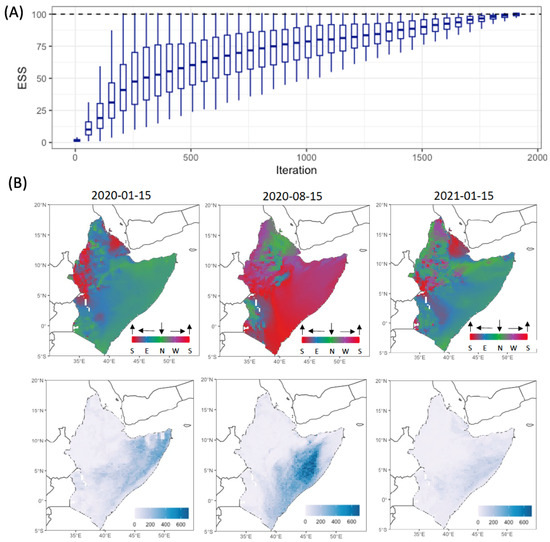
Figure 5.
(A) Change in the distribution of the effective sample size for individual datasets as a function of the iteration (each iteration is equal to 1000 parameter samples); (B) spatial distribution of sampled parameters: directional mean (top row) and concentration (lower row).
To illustrate global wind trends, we sampled the directional mean and concentration from the posterior distribution for each of the 3860 sites and plotted the spatial distribution of these parameters (Figure 5B) for each of the three selected dates. The directional mean for January had similar trends for both 2020 and 2021, i.e., most of the wind trajectories had southward orientations, but some differences in direction could be seen for small areas. The concentration values showed more variation, with northerly winds concentrated less in 2021 than in 2020. Meanwhile, wind trajectories were directed toward the north on 15 August 2020, with a larger range of concentrations in comparison with wind trajectories in January for both 2020 and 2021.
4. Discussion
In situations when the number of datasets is large, performing Bayesian inference can be time consuming. Here, we investigated how AMIS can be used to effectively estimate parameters for multiple datasets. The novelty of our study was to apply AMIS to multiple targets simultaneously, while changing the target distribution with each iteration based only on those datasets that had not reached the required ESS. As an illustration of this methodology, we fitted the von Mises distribution to wind direction data. For a comparison, we used IS to fit parameters to a single wind angle distribution using synthetic data. Inference using IS recovered the parameter values and captured the original distribution for wind trajectories, but it was prohibitively slow and computationally inefficient ( parameter sets to achieve ESS = 25). We showed that AMIS significantly reduced computational effort while maintaining the quality of the inference (8000 parameter sets to achieve ESS = 100) for three independent datasets. Finally, our results show that AMIS was able to achieve ESS = 100 for >11,000 location and date-specific parameters for the NAME wind trajectories with similar computational requirements as a single dataset fitted using IS ( parameter sets).
The direction of the surface winds is generally influenced by the displacement of the ITCZ [46]. The ITCZ reaches its furthest southward position over Africa at 15° S in winter and its furthest northernmost position at around 15° N in the summer [47]. We fitted the von Mises distribution to NAME wind trajectories at two different seasons (January and August). Our analysis demonstrated a correlation between the ITCZ and local wind trajectories, i.e., a southward orientation in winter and northward orientation in the summer. Certain areas tended to have a smaller concentration in the direction of wind trajectories and, hence, greater variability, which is important to account for when predicting long-distance wind-borne dispersal. Another application of fitting the von Mises distribution to NAME wind data is to compare annual differences in wind behaviour at high resolutions, as illustrated in Figure 5B.
As the amount of data continues to increase at an exponential rate [48] and more multi-set data become available, it will be crucial to have computationally efficient methods for parameter estimation. Our proposed methodology can be easily applied to any type of a problem where the target distribution can be formulated due to the universal way the proposal density function is constructed at each iteration. Further research is required to guide the optimal choice of ESS and number of sampled parameters at each iteration for particular types and sizes of datasets.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/stats7020026/s1, Figure S1: Analysis for prior based on Beta(2,1) distribution. (A) Change in effective sample size as a function of iteration using AMIS (each iteration = 1000 samples). (B) Parameters sampled at each iteration (gray dots) and true values of parameters; Figure S2: Comparison of three proposal distributions. Numbers of samples was were obtained by running parameter estimation 100 times. Boxplots show median, the first and third quartile, and range; Figure S3: Number of sampled parameters as a function of required effective sample size.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R., W.T. and C.A.G.; methodology, R.R. and W.T.; software, R.R.; validation, R.R.; formal analysis, R.R.; investigation, R.R.; resources, C.A.G.; data curation, R.R.; writing—original draft preparation, R.R., W.T. and C.A.G.; writing—review and editing, R.R., W.T. and C.A.G.; visualization, R.R.; project administration, C.A.G.; funding acquisition, C.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The UK Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office. C.A.G. also acknowledges support from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Analysis code and data used in this study can be accessed at the following URL: https://github.com/rretkute/BayesianMultipleDatasets (accessed on 8 March 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, N.; Berman, S.R.; Joubert, D.; Vialet-Chabrand, S.; Marcelis, L.F.M.; Kaiser, E. Variation of photosynthetic induction in major horticultural crops is mostly driven by differences in stomatal traits. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 860229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognetti, M.; Gabor, A.; Yang, M.; Cappelletti, V.; Windhager, J.; Rueda, O.M.; Charmpi, K.; Esmaeilishirazifard, E.; Bruna, A.; de Souza, N.; et al. Deciphering the signaling network of breast cancer improves drug sensitivity prediction. Cell Syst. 2021, 12, 401–418.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, D.B.; Rolland, M.; Dearlove, B.L.; Li, Y.; Robb, M.L.; Schiffer, J.T.; Gilbert, P.; Cardozo-Ojeda, E.F.; Mayer, B.T. Timing HIV infection with a simple and accurate population viral dynamics model. J. R. Soc. Interface 2021, 18, 20210314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanbi, O.D.; Bhuvanagiri, D.C.; Barcelos, E.I.; Nihar, A.; Gonzalez Hernandez, B.; Yarus, J.M.; French, R.H. Integrating multiscale geospatial analysis for monitoring crop growth, nutrient distribution, and hydrological dynamics in large-scale agricultural systems. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 2024, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, R.E.; Huang, C.I.; Knock, E.S.; Spencer, S.E.F.; Brown, P.E.; Mwamba Miaka, E.; Shampa, C.; Keeling, M.J.; Rock, K.S. Quantifying epidemiological drivers of gambiense human African Trypanosomiasis across the Democratic Republic of Congo. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, P.; Desikan, R.; Dixit, N.M. Modeling how antibody responses may determine the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2022, 2, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, S.; Weiss, D.J.; Cameron, E.; Bisanzio, D.; Mappin, B.; Dalrymple, U.; Battle, K.E.; Moyes, C.L.; Henry, A.; Eckhoff, P.A.; et al. The effect of malaria control on Plasmodium falciparum in Africa between 2000 and 2015. Nature 2015, 526, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retkute, R.; Touloupou, P.; Basáñez, M.G.; Hollingsworth, T.D.; Spencer, S.E.F. Integrating geostatistical maps and infectious disease transmission models using adaptive multiple importance sampling. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2021, 15, 1980–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touloupou, P.; Retkute, R.; Hollingsworth, T.D.; Spencer, S.E. Statistical methods for linking geostatistical maps and transmission models: Application to lymphatic filariasis in East Africa. Spat. Spatio-Temporal Epidemiol. 2022, 41, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Severson, E.O.; Hengartner, N.; Meadors, G.; Ke, R. Change in global transmission rates of COVID-19 through May 6 2020. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gómez-Dans, J.L.; Huang, H.; Ma, H.; Wu, Q.; Lewis, P.E.; Liang, S.; Chen, Z.; Xue, J.H.; Wu, Y.; et al. Assimilation of remote sensing into crop growth models: Current status and perspectives. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 276–277, 107609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metropolis, N.; Ulam, S. The Monte Carlo method. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1949, 44, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, H.; Harris, T.E. Estimation of particle transmission by random sampling. Natl. Bur. Stand. Appl. Math. Ser. 1951, 12, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cappé, O.; Douc, R.; Guillin, A.; Marin, J.M.; Robert, C.P. Adaptive importance sampling in general mixture classes. Stat. Comput. 2008, 18, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veach, E.; Guibas, L.J. Optimally combining sampling techniques for Monte Carlo rendering. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques—SIGGRAPH ’95, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–11 August 1995; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornuet, J.; Marin, J.; Mira, A.; Robert, C.P. Adaptive Multiple Importance Sampling. Scand. J. Stat. 2012, 39, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siren, J.; Marttinen, P.; Corander, J. Reconstructing Population Histories from Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 28, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbert, M.; Havran, V. Adaptive multiple importance sampling for general functions. Vis. Comput. 2017, 33, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvira, V.; Santamaria, I. Multiple Importance Sampling for Symbol Error Rate Estimation of Maximum-Likelihood Detectors in MIMO Channels. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.J.; Retkute, R.; Murchie, E.H. Photoacclimation and entrainment of photosynthesis by fluctuating light varies according to genotype in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1116367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusokiene, A.; Prusokas, A.; Retkute, R. Machine learning based lineage tree reconstruction improved with knowledge of higher level relationships between cells and genomic barcodes. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2023, 5, lqad077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheke, R.A.; Tratalos, J.A. Migration, patchiness, and population processes illustrated by two migrant pests. BioScience 2007, 57, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.W.; Nesbit, R.L.; Burgin, L.E.; Reynolds, D.R.; Smith, A.D.; Middleton, D.R.; Hill, J.K. Flight orientation behaviors promote optimal migration trajectories in high-flying insects. Science 2010, 327, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, H. Migration to special habitats. In Migration; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Rainey, R.C. Weather and the movements of locust swarms: A new hypothesis. Nature 1951, 168, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, J. The direction of desert locust migration. J. Anim. Ecol. 1980, 49, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedgley, D.E. (Ed.) Desert Locust Forecasting Manual; Natural Resources Institute: Chatham, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Homberg, U. Sky compass orientation in desert locusts—Evidence from field and laboratory studies. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homberg, U.; Hensgen, R.; Jahn, S.; Pegel, U.; Takahashi, N.; Zittrell, F.; Pfeiffer, K. The sky compass network in the brain of the desert locust. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2022, 209, 641–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardia, K.V. Statistics of directional data. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1975, 37, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, J.A.; Bueno, C.; Ramírez, P. Statistical modelling of directional wind speeds using mixtures of von Mises distributions: Case study. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Cox, J.A.; Hitchings, M.D.T.; Burgin, L.; Hort, M.C.; Hodson, D.P.; Gilligan, C.A. Quantifying airborne dispersal routes of pathogens over continents to safeguard global wheat supply. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Thurston, W.; Smith, J.W.; Schumacher, A.; Millington, S.C.; Hodson, D.P.; Cressman, K.; Gilligan, C.A. Three-Dimensional Visualization of long-range atmospheric transport of crop pathogens and insect pests. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Thomson, D.; Hort, M.; Devenish, B. The U.K. Met Office’s next-generation atmospheric dispersion model, NAME III. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XVII; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgin, L.E.; Gloster, J.; Sanders, C.; Mellor, P.S.; Gubbins, S.; Carpenter, S. Investigating incursions of bluetongue virus using a model of long-distance culicoides biting midge dispersal. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 60, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retkute, R.; Hinton, R.G.K.; Cressman, K.; Gilligan, C.A. Regional differences in control operations during the 2019–2021 desert locust upsurge. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardia, K.V.; Jupp, P.E. Directional Statistics; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Papadakis, M.; Tsagris, M.; Dimitriadis, M.; Fafalios, S.; Tsamardinos, I.; Fasiolo, M.; Borboudakis, G.; Burkardt, J.; Zou, C.; Lakiotaki, K.; et al. Rfast: A Collection of Efficient and Extremely Fast R Functions, R package version 2.0.6; The Comprehensive R Archive Network, 2023; Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- Tsagris, M.; Papadakis, M. Taking R to its limits: 70+ tips. Peerj Prepr. 2018, 6, e26605v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, D.; Baran, A.J.; Boutle, I.; Brooks, M.; Earnshaw, P.; Edwards, J.; Furtado, K.; Hill, P.; Lock, A.; Manners, J.; et al. The Met Office unified model global atmosphere 7.0/7.1 and JULES global land 7.0 configurations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 1909–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Casella, G. Monte Carlo Statistical Methods, 2nd ed.; Springer Texts in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ripley, B.D. Stochastic Simulation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paananen, T.; Piironen, J.; Bürkner, P.C.; Vehtari, A. Implicitly adaptive importance sampling. Stat. Comput. 2021, 31, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, L. Survey Sampling; John Wiley & Sons: Nashville, TN, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Elvira, V.; Martino, L.; Robert, C.P. Rethinking the Effective Sample Size. Int. Stat. Rev. 2022, 90, 525–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Bischoff, T.; Haug, G.H. Migrations and dynamics of the intertropical convergence zone. Nature 2014, 513, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, C.I.; Gohm, A.; Rotach, M.W.; Minda, T.T. Dynamics of gap winds in the Great Rift Valley, Ethiopia: Emphasis on strong winds at Lake Abaya. Weather Clim. Dyn. 2022, 3, 1003–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, I.A.T.; Yaqoob, I.; Anuar, N.B.; Mokhtar, S.; Gani, A.; Ullah Khan, S. The rise of “big data” on cloud computing: Review and open research issues. Inf. Syst. 2015, 47, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).