Characterizing the Effects of Compaction on Agricultural Tilled Soil Macropore Characteristics Using X-Ray Computed Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
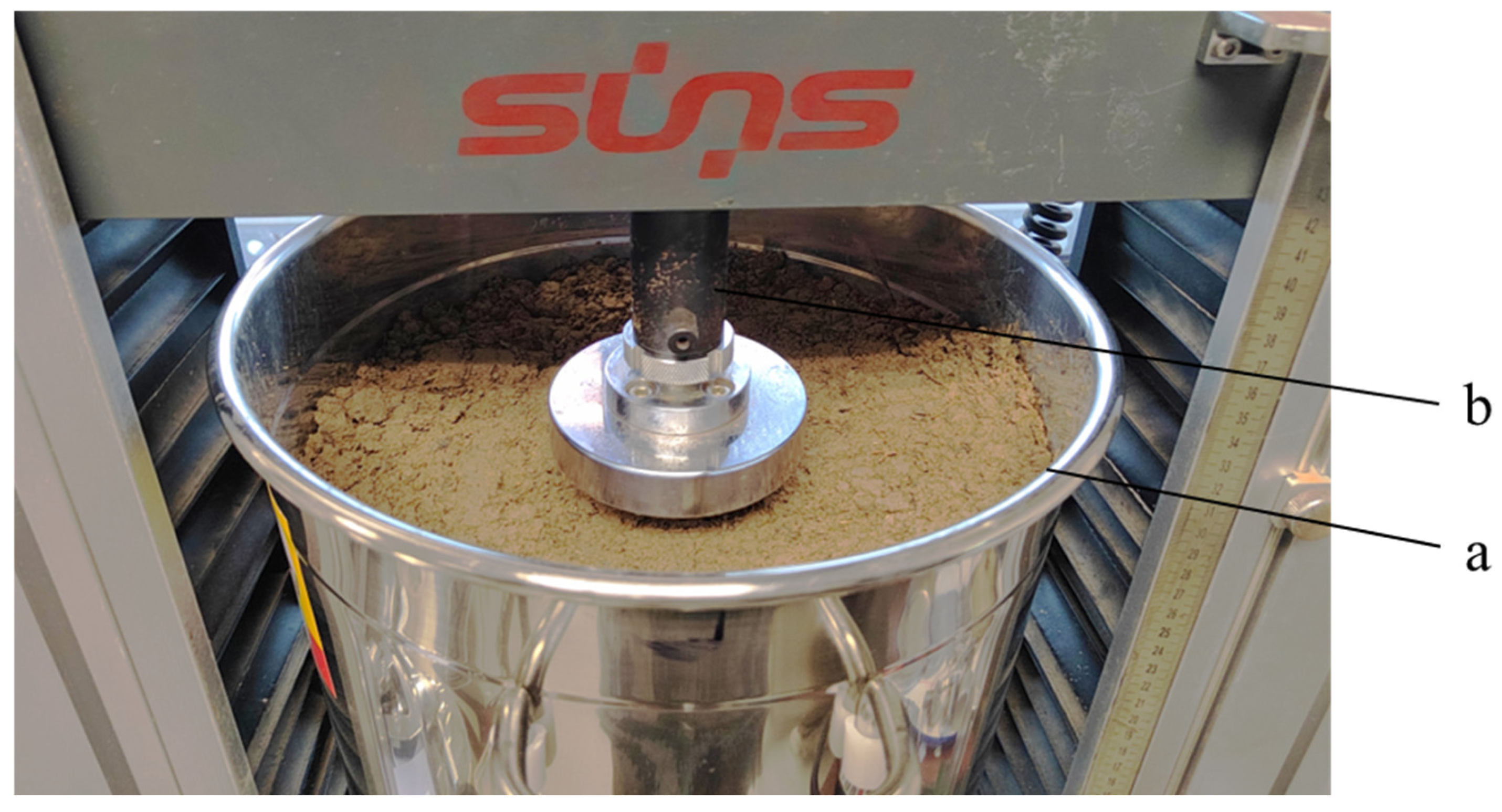
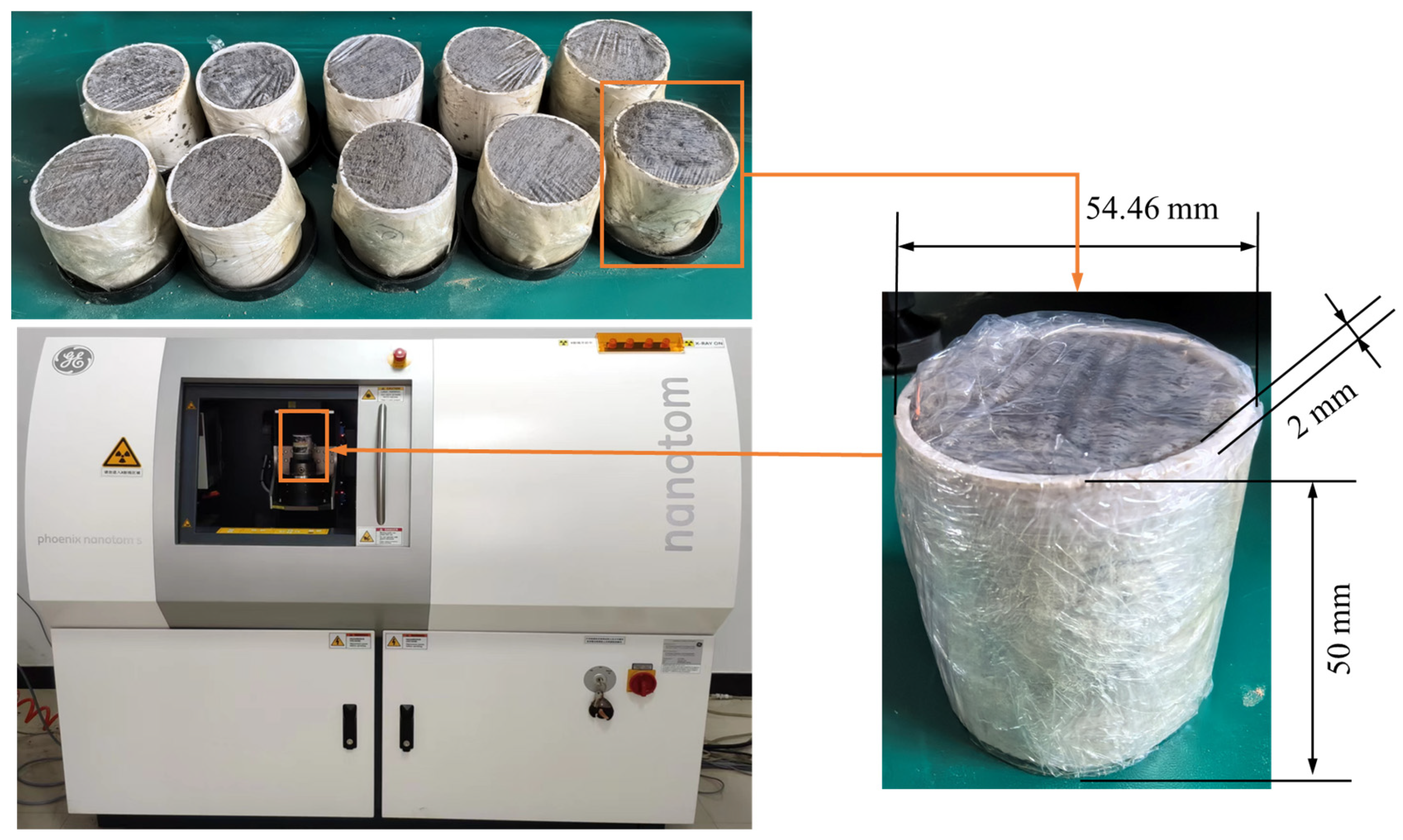
2.1. Soil Site Description and Sampling
2.2. Scanning and Image Analysis
2.3. Macropore Data Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
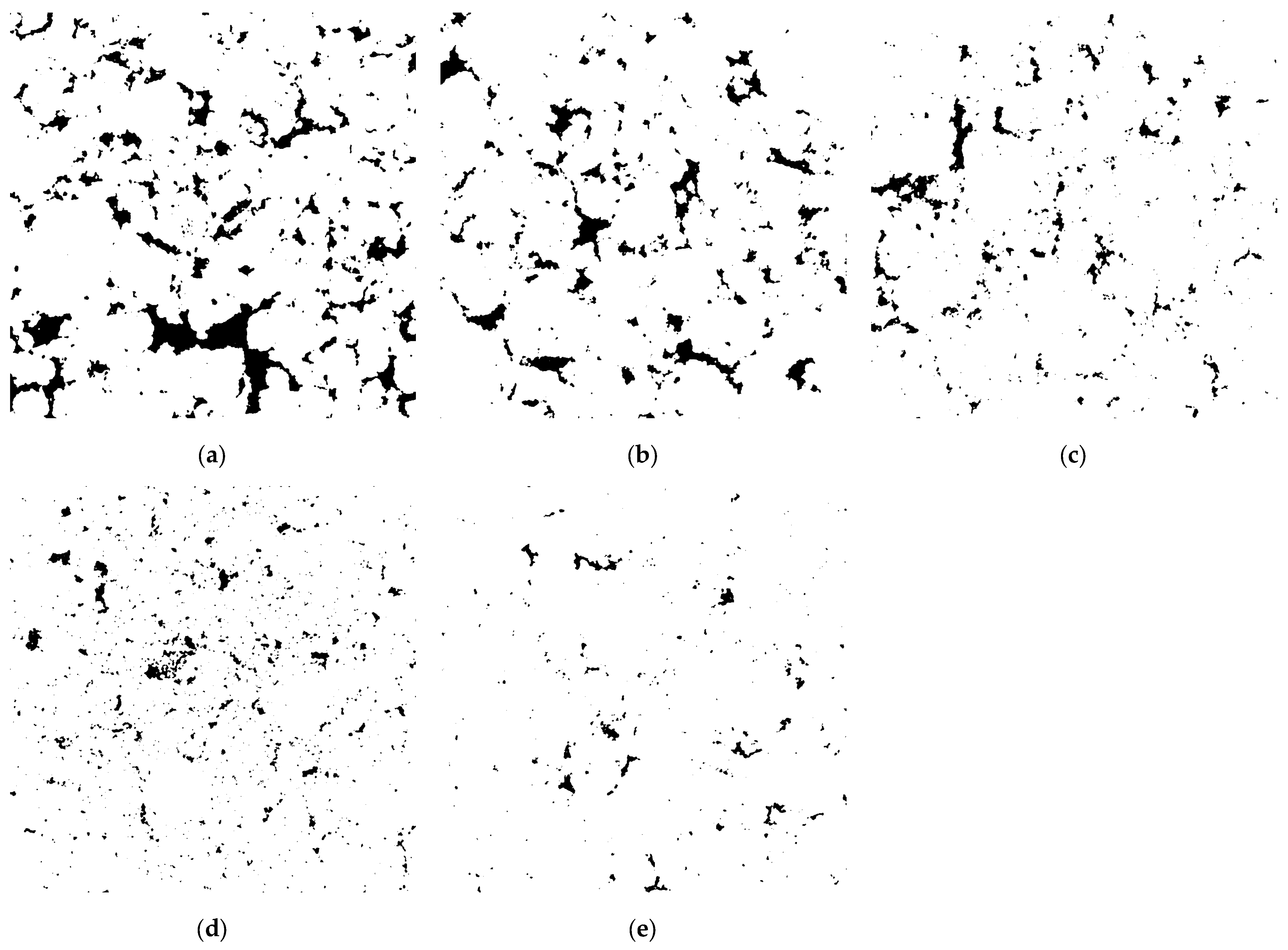
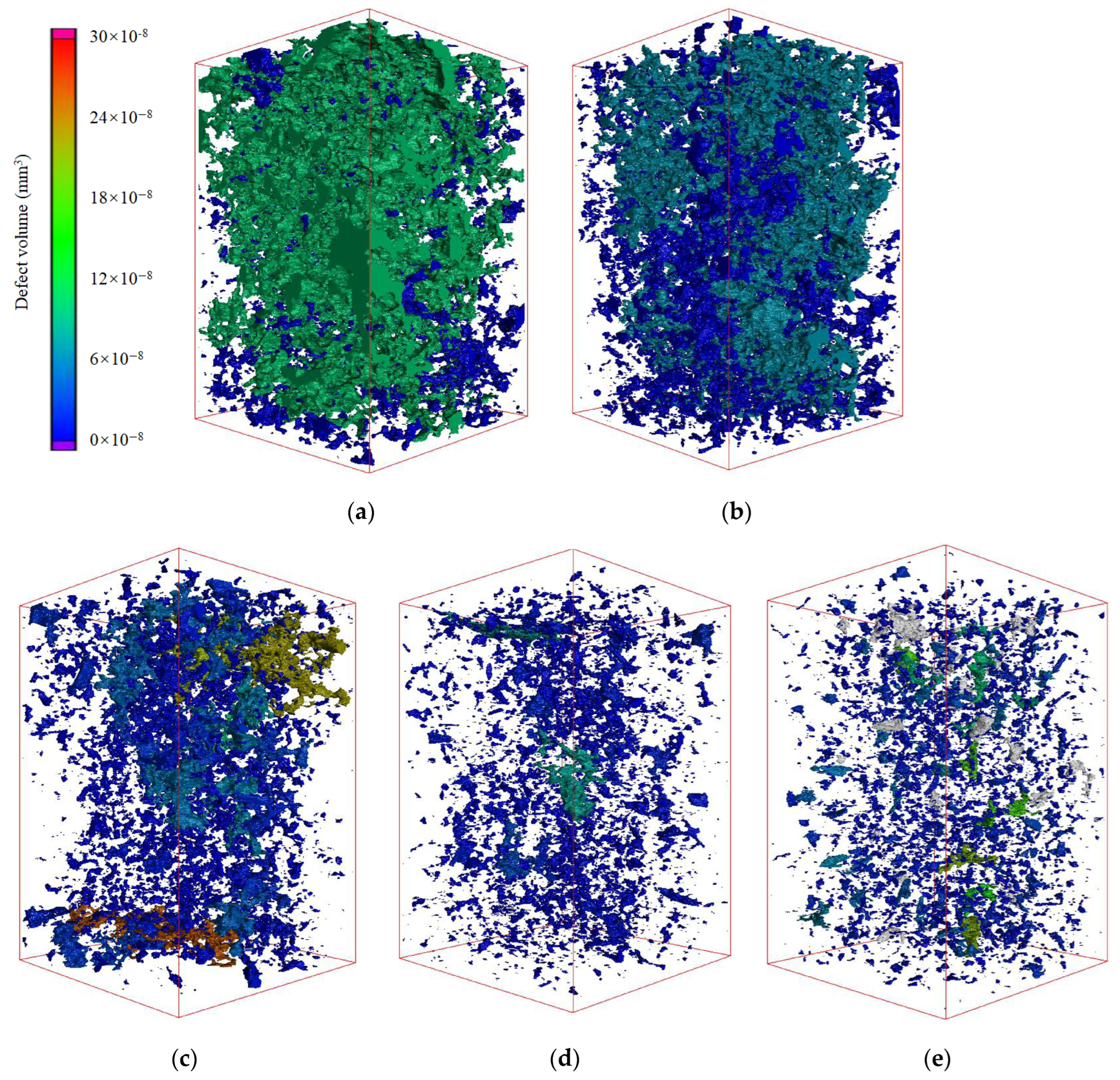
3.1. Pore Structure Visualization
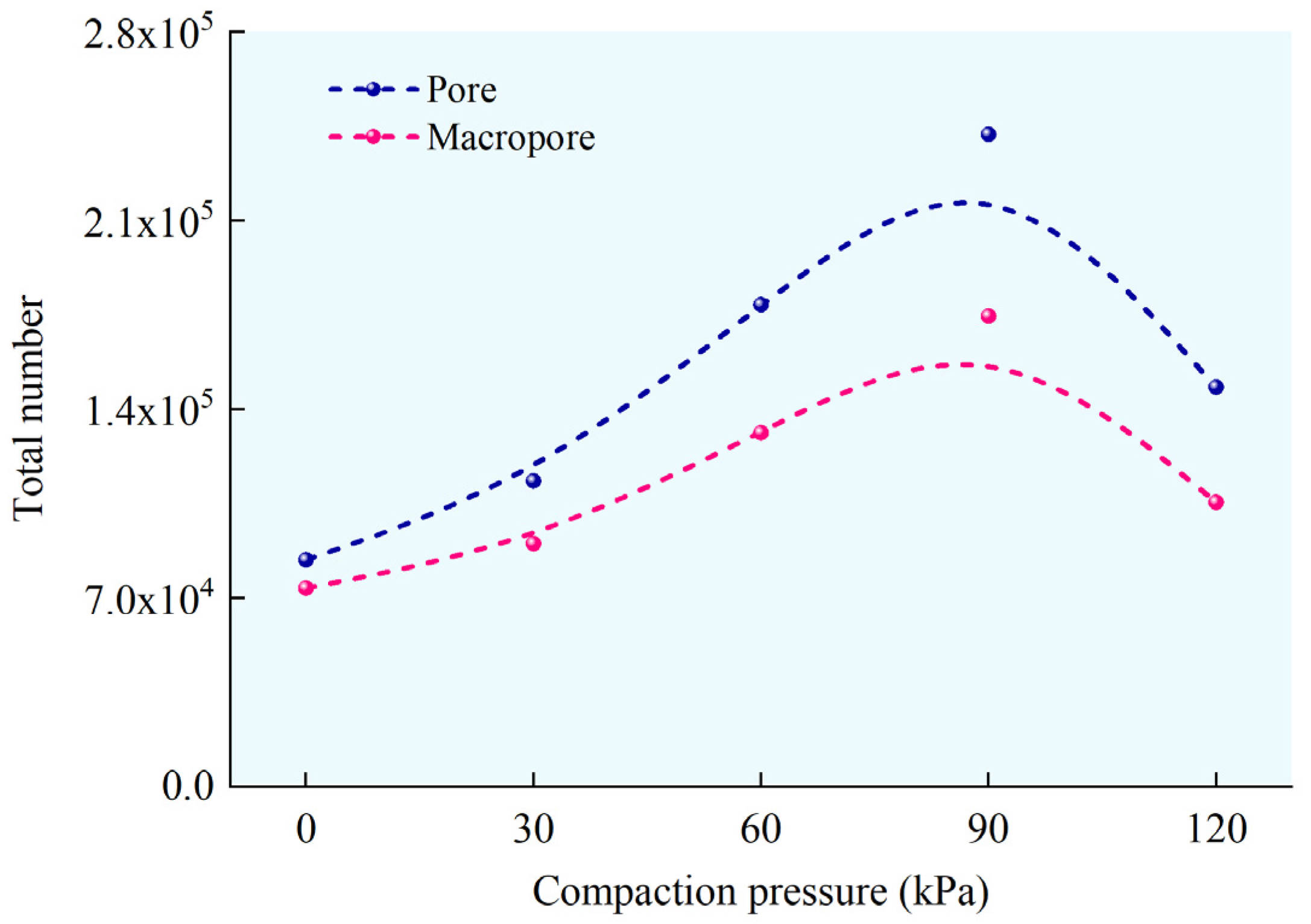
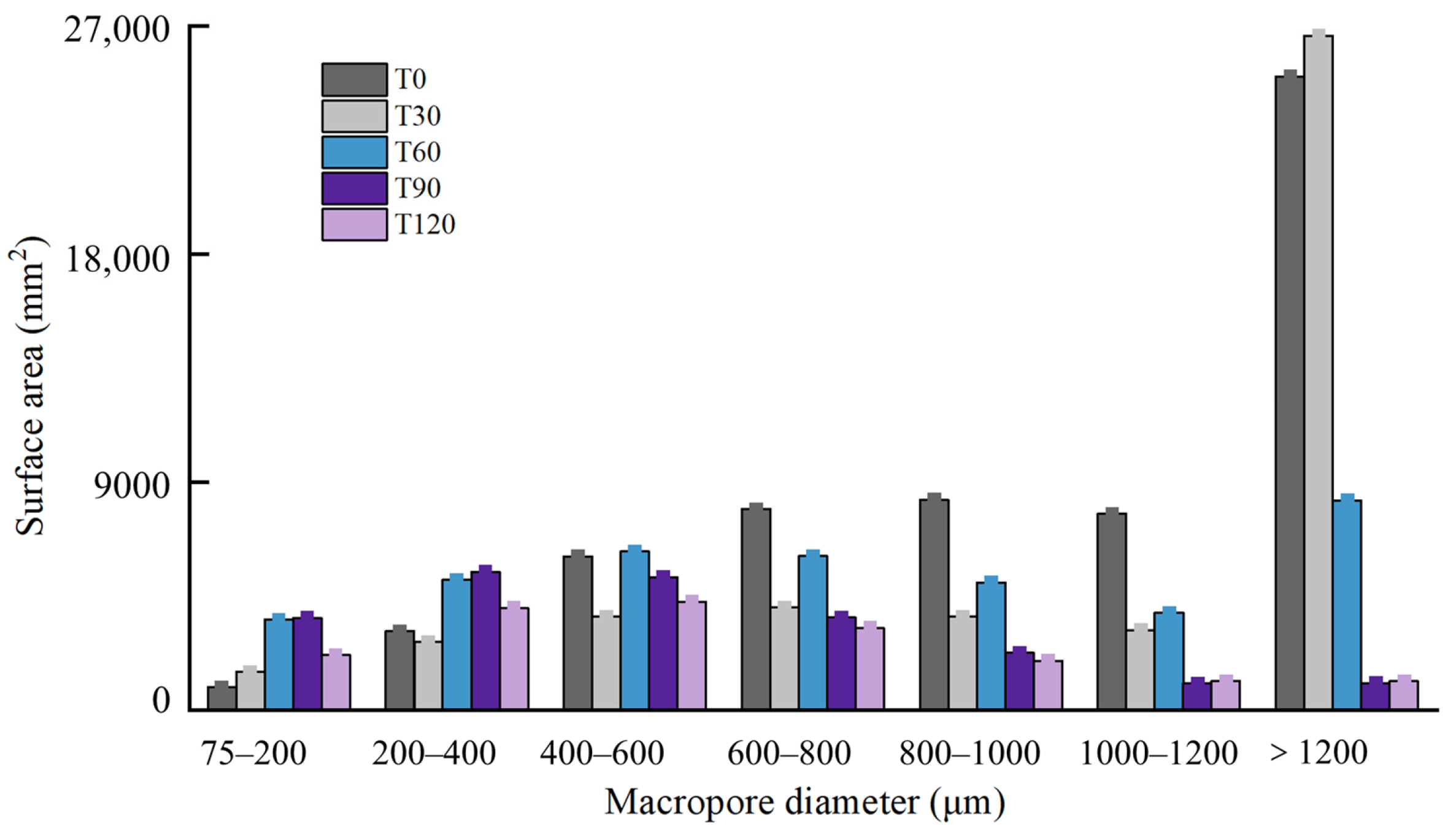
3.2. Macropore Number and Size Distribution
3.3. Macropore Number and Size Distribution Macropore Volume and Size Distribution
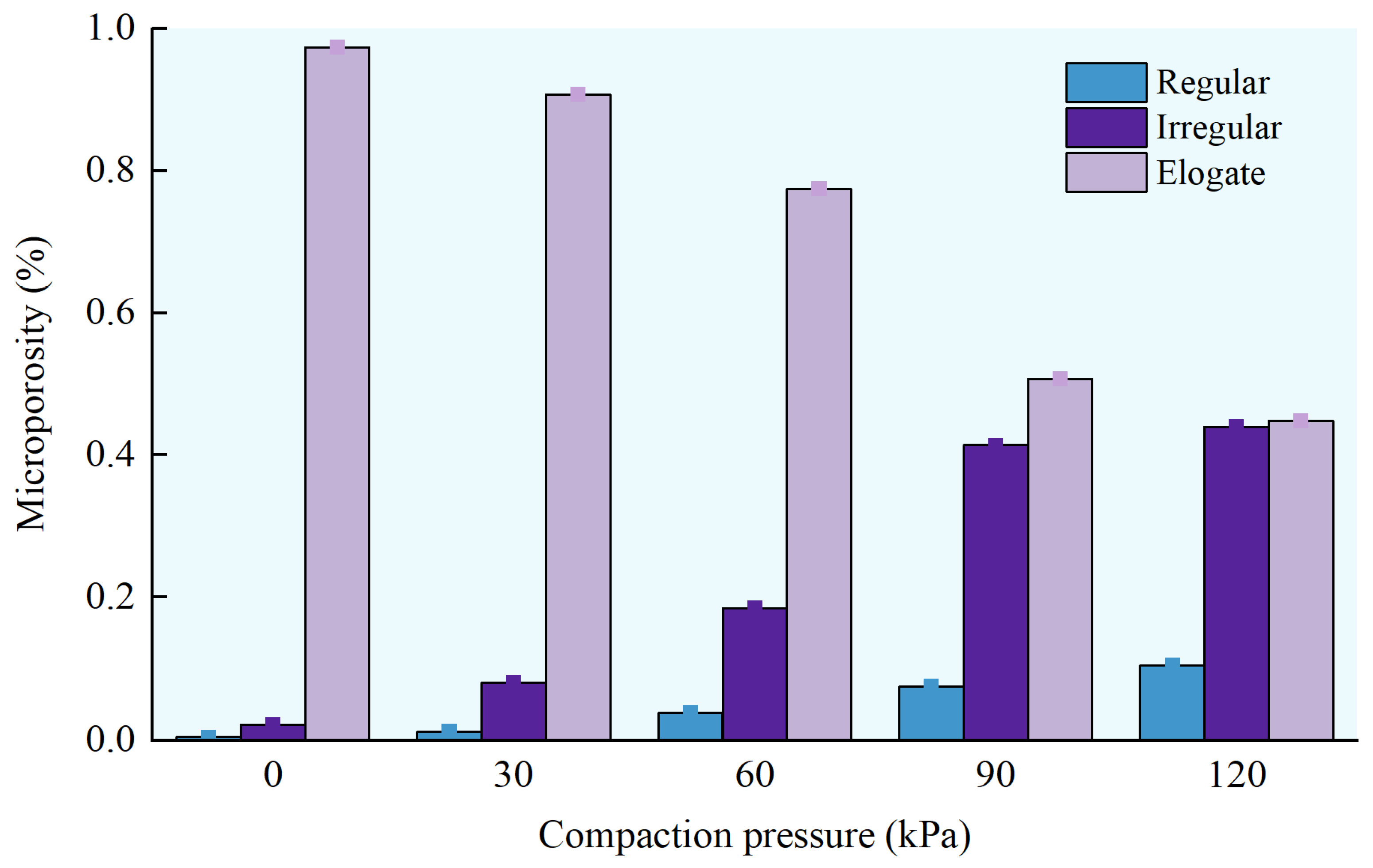
3.4. Shape Characteristics
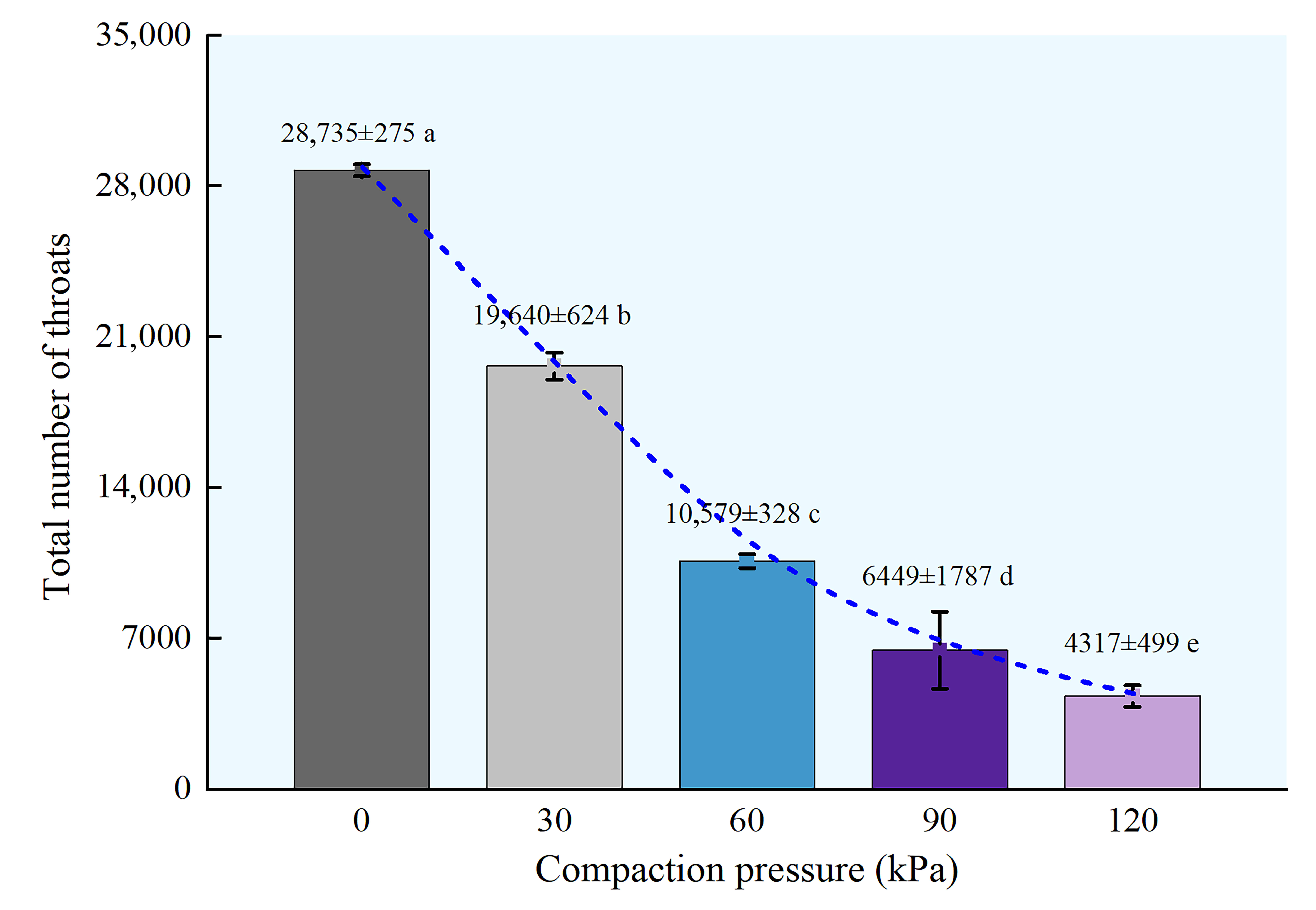
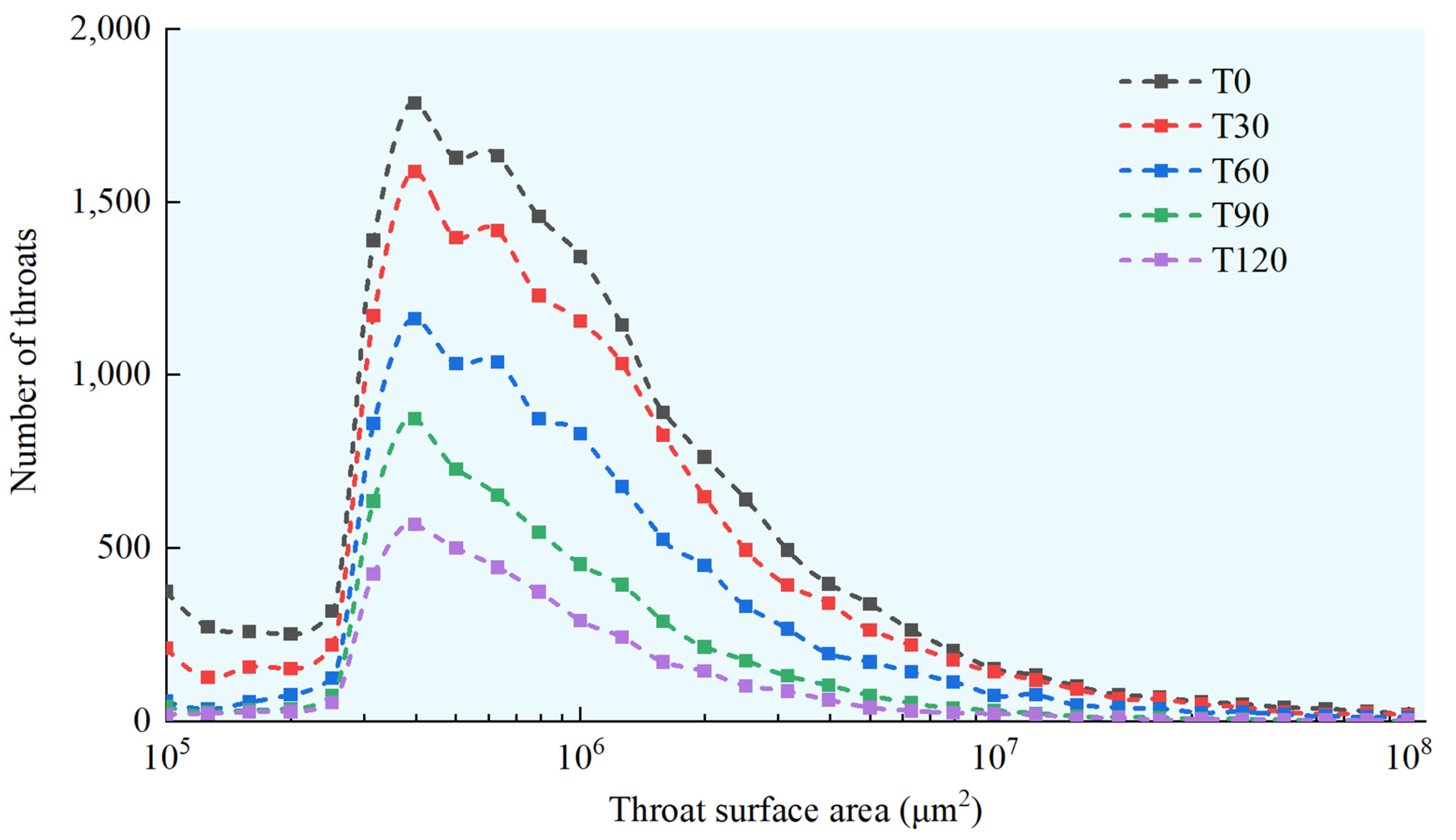
3.5. Pore Throats
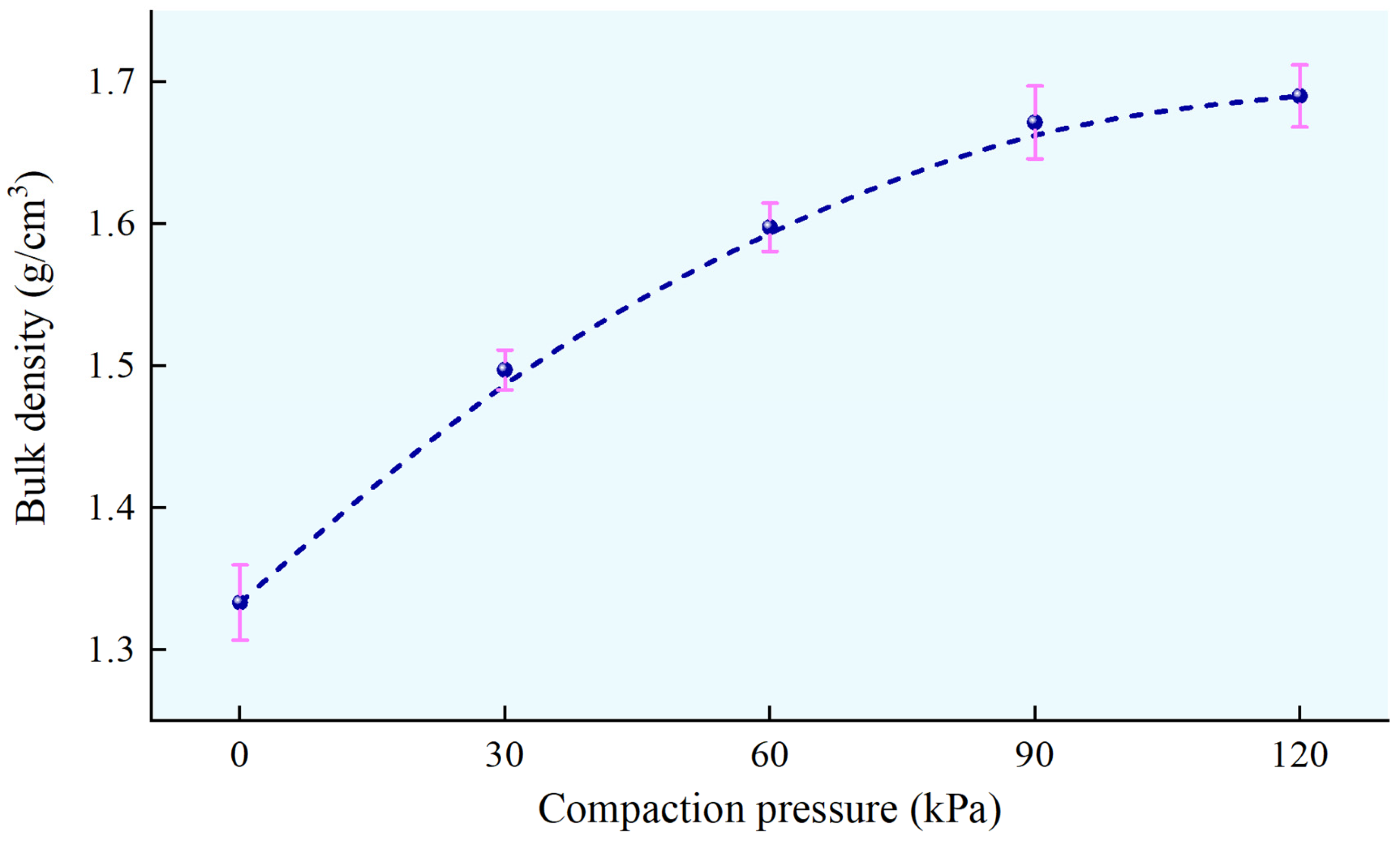
3.6. Bulk Density
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- ∙
- Soil macropore structure undergoes its most significant and detrimental changes when compaction pressure increases from 60 kPa to 90 kPa. Within this range, macroporosity plummeted by 64.8%, and the number of beneficial elongated macropores decreased by 46.6%. This identifies 90 kPa as a critical ground pressure threshold beyond which soil structural degradation becomes severe.
- ∙
- Compaction does not merely reduce total porosity but fundamentally alters the pore network. It crushes large well-connected pores into a greater number of smaller isolated pores, leading to a significant loss of connectivity. Furthermore, it promotes the formation of irregularly shaped pores over elongated ones, which are more beneficial for water transport and root growth.
- ∙
- Macroporosity, pore volume, and surface area were the most sensitive to compaction in the large-diameter macropores (>1000 μm), which are the most critical for root development and rapid water infiltration.
- ∙
- While bulk density is a useful field indicator, X-ray CT reveals the specific, often detrimental, changes in pore structure that bulk density alone cannot describe. Adopting pressure-based guidelines directly addresses the cause of the damage.
- ∙
- To preserve soil structure after tillage, the ground pressure exerted by agricultural machinery (e.g., planters, sprayers, and harvesters) should be maintained below 90 kPa. This is particularly crucial for operations conducted on moist soils.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schlüter, S.; Vogel, H.J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, G.F.; Tolon-Becerra, A.; Lastra-Bravo, X.; Tourn, M. Tillage and traffic effects (planters and tractors) on soil compaction and soybean (Glycine max L.) yields in Argentinean pampas. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 110, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Fan, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; McLaughlin, N.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Liang, A. Tillage-induced effects on SOC through changes in aggregate stability and soil pore structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiselmeier, J.; Chandrasekhar, P.; Weninger, T.; Schwen, A.; Julich, S.; Feger, K.; Schwärzel, K. Quantification of soil pore dynamics during a winter wheat cropping cycle under different tillage regimes. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 192, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Nest, T.; Ruysschaert, G.; D’Hose, T.; Cornelis, W. Short-term effects of cover crops and tillage methods on soil physical properties and maize growth in a sandy loam soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 192, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Moncada, M.; Katuwal, S.; Kristensen, J.; Munkholm, L. Effects of bio-subsoilers on subsoil pore-system functionality: Case study with intact soil columns. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzilli, F.; Cilona, A.; Mancini, L.; Tondi, E. Using synchrotron x-ray microtomography to characterize the pore network of reservoir rocks: A case study on carbonates. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 95, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Weil, R.R.; Hill, R.L. Effects of compaction and cover crops on soil least limiting water range and air permeability. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 136, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, P.; Leitner, D.; Kammerer, G.; Loiskandl, W.; Kaul, H.P.; Bodner, G. Root induced changes of effective 1D hydraulic properties in a soil column. Plant Soil 2014, 381, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, S.R.; Black, C.R.; Roberts, J.A.; Mooney, S.J. Soil compaction: A review of past and present techniques for investigating effects on root growth. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Mani, I.; Sundaram, P.K. Effect of subsoil compaction on rooting behavior and yields of wheat. J. Terramechanics 2020, 92, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.; Silk, W.K.; Schurr, U. Environmental effects on spatial and temporal patterns of leaf and root growth. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 279–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzesiak, S.; Grzesiak, M.T.; Hura, T.; Marcińska, I.; Rzepka, A. Changes in root system structure, leaf water potential and gas exchange of maize and triticale seedlings affected by soil compaction. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 88, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Sha, L.; Yang, H.; Guo, Z.; Sun, R. Quantification of traffic-induced compaction based on soil and agricultural implement parameters. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengough, A.G.; McKenzie, B.M.; Hallett, P.D.; Valentine, T.A. Root elongation, water stress, and mechanical impedance: A review of limiting stresses and beneficial root tip traits. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, B.K.; Hasan, M.; Wade, L.J. Penetration of hardpans by rice lines in the rainfed lowlands. Field Crops Res. 2002, 76, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Fan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, R. Evaluation of soil macro-aggregate characteristics in response to soil macropore characteristics investigated by X-ray computed tomography under freeze-thaw effects. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 225, 105559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.F.; Bourrie, G.; Trolard, F. Soil compaction impact and modelling. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udawatta, R.P.; Anderson, S.H.; Gantzer, C.J.; Garrett, H.E. Influence of prairie restoration on CT-measured soil pore characteristics. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogunovic, I.; Pereira, P.; Kisic, I.; Sajko, K.; Sraka, M. Tillage management impacts on soil compaction, erosion and crop yield in Stagnosols (Croatia). Catena 2018, 160, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D.; Wang, G.; Li, G.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of two typical plantations in the karst ecosystem of southwestern China. Forests 2018, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Velde, B.; Zhang, T. Quantitative estimation of pore variability and complexity in soils by digital image method. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2003, 40, 678–682. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Horn, R.; Hallett, P. Soil structure and its functions in ecosystems: Phase matter & scale matter. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, S. Applicability of fractal models in estimating soil water retention characteristics from particle-size distribution data. Pedosphere 2002, 2002, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Qin, Q.; Bai, Z. Characterizing the effects of opencast coal-mining and land reclamation on soil macropore distribution characteristics using 3D CT scanning. Catena 2018, 171, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, N.; Larsbo, M.; Koestel, J. Connectivity and percolation of structural pore networks in a cultivated silt loam soil quantified by x-ray tomography. Geoderma 2017, 287, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Moldrup, P.; Schaap, M.G.; Tuller, M.; Kulkarni, R.; Vogel, H.J.; Wollesen de Jonge, L. Prediction of biopore-and matrix-dominated flow from X-ray CT-derived macropore network characteristics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 4017–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Maity, P.P.; Das, T.K.; Krishnan, P.; Chakraborty, D.; Bhatia, A.; Ray, M.; Kund, A.; Bhattacharyya, R. Characterization of soil pores through X-ray computed microtomography and carbon mineralization under contrasting tillage and land configurations in the indo-gangetic plains of India. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 898249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, I.G.; Martín-Sotoca, J.J.; Losada, J.C.; López, P.; Tarquis, A.M. Scaling properties of binary and greyscale images in the context of X-ray soil tomography. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Lin, H.; Li, S. Quantification of 3-D soil macropore networks in different soil types and land uses using computed tomography. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Han, X.Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Yan, J.; Feng, Y.; Gan, J.; Zou, W.; Liu, G. Effects of organic amendment depths on black soil pore structure using CT scanning technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Kumar, S.; Udawatta, R.P.; Anderson, S.H.; de Jonge, L.W.; Katuwal, S. X-ray micro-computed tomography characterized soil pore network as influenced by long-term application of manure and fertilizer. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alskaf, K.; Mooney, S.J.; Sparkes, D.L.; Wilson, P.; Sjögersten, S. Short-term impacts of different tillage practices and plant residue retention on soil physical properties and greenhouse gas emissions. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierret, A.; Capowiez, Y.; Belzunces, L.; Moran, C.J. 3D reconstruction and quantification of macropores using X-ray computed tomography and image analysis. Geoderma 2002, 106, 247–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroselli, C.; Williams, K.A.; Ghosh, A.; McKay Fletcher, D.; Ruiz, S.A.; Gerheim Souza Dias, T.; Scotson, C.P.; Roose, T. Space and time-resolved monitoring of phosphorus release from a fertilizer pellet and its mobility in soil using microdialysis and X-ray computed tomography. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, L.F.; Auler, A.C.; Roque, W.L.; Mooney, S.J. X-ray microtomography analysis of soil pore structure dynamics under wetting and drying cycles. Geoderma 2020, 362, 114103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shein, E.V.; Skvortsova, E.B.; Dembovetskii, A.V.; Abrosimov, K.N.; Il’In, L.I.; Shnyrev, N.A. Pore-size distribution in loamy soils: A comparison between microtomographic and capillarimetric determination methods. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2016, 49, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, X. Bio-tillage: A new perspective for sustainable agriculture. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.J.; He, B.H.; Chen, Y.F. Disturbance function for soil disturbed state strength based on X-ray computed tomography triaxial test. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Han, Q.; Pan, X.; He, F.; Chen, C. Assessment of the responses of soil pore properties to combined soil structure amendments using X-ray computed tomography. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yan, X.; Peng, X. Effects of straw incorporation on paddy soil structure in rice-wheat rotation system. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Schlüter, S.; Albrecht, L.; Schwärzel, K.; Kreiselmeier, J. Long-term effects of conventional tillage and no-tillage on saturated and near-saturated hydraulic conductivity–Can their prediction be improved by pore metrics obtained with X-ray CT? Geoderma 2020, 361, 114082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Becker, E.; Liang, G.; Houssou, A.A.; Wu, H.; Wu, X.; Cai, D.; Degré, A. Effect of different tillage systems on aggregate structure and inner distribution of organic carbon. Geoderma 2017, 288, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer-Landefeld, L.; Brandhuber, R.; Fenner, S.; Koch, H.J.; Stockfisch, N. Effects of agricultural machinery with high axle load on soil properties of normally managed fields. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 75, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivarajan, S.; Maharlooei, M.; Bajwa, S.G.; Nowatzki, J. Impact of soil compaction due to wheel traffic on corn and soybean growth, development and yield. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.; Sandin, M.; Colombi, T.; Horn, R.; Or, D. Historical increase in agricultural machinery weights enhanced soil stress levels and adversely affected soil functioning. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iassonov, P.; Gebrenegus, T.; Tuller, M. Segmentation of X-ray computed tomography images of porous materials: A crucial step for characterization and quantitative analysis of pore structures. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W09415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunpandian, M.; Arunprasath, T.; Vishnuvarthanan, G.; Pallikonda Rajasekaran, M. Soil porosity analysis using combined maximum entropy and class variance thresholding. In Microelectronics, Electromagnetics and Telecommunications: Proceedings of the Fourth ICMEET 2018, Visakhapatnam, India, 3–4 February 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 641–650. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, K.C.; Buchan, G.D. Porosity and pore size distribution. Encycl. Soil Sci. 2006, 1, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Peng, X.; Peth, S.; Xiao, T.Q. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil aggregate microstructure quantified with synchrotron-based micro-computed tomography. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Reading, L.; Jing, Z. Three-dimensional quantification of macropore networks of different compacted soils from opencast coal mine area using X-ray computed tomography. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebron, I.; Suarez, D.L.; Schaap, M.G. Soil pore size and geometry as a result of aggregate-size distribution and chemical composition. Soil Sci. 2002, 167, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, R.; Fan, H. Evaluation of the impact of freeze-thaw cycles on pore structure characteristics of black soil using X-ray computed tomography. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Feng, C.; Niu, S.; Xu, P.; Chen, C. Analysis of the pore network structure of microbial solidification of construction residue soil based on CT scanning. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöhlitz, J.; Rücknagel, J.; Schlüter, S.; Vogel, H.J.; Christen, O. Computed tomography as an extension of classical methods in the analysis of soil compaction, exemplified on samples from two tillage treatments and at two moisture tensions. Geoderma 2019, 346, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, F. Evaluation of soil microbial indices along a revegetation chronosequence in grassland soils on the Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 41, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, P.; Feeney, D.; Bengough, A.; Rillig, M.; Scrimgeour, C.; Young, I. Disentangling the impact of AM fungi versus roots on soil structure and water transport. Plant Soil 2009, 314, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffih-Hdadi, K.; Défossez, P.; Richard, G.; Cui, Y.J.; Tang, A.M.; Chaplain, V. A method for predicting soil susceptibility to the compaction of surface layers as a function of water content and bulk density. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottinelli, N.; Hallaire, V.; Goutal, N.; Bonnaud, P.; Ranger, J. Impact of heavy traffic on soil macroporosity of two silty forest soils: Initial effect and short-term recovery. Geoderma 2014, 217, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berisso, F.E.; Schjønning, P.; Keller, T.; Lamandé, M.; Etana, A.; de Jonge, L.W.; Iversen, B.V.; Arvidsson, J.; Forkman, J. Persistent effects of subsoil compaction on pore size distribution and gas transport in a loamy soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 122, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Cai, C. Linking aggregate stability to the characteristics of pore structure in different soil types along a climatic gradient in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Wu, Y.; Geng, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Cai, C. Soil pore dynamics and infiltration characteristics as affected by cultivation duration for Mollisol in northeast China. Geoderma 2024, 449, 117021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Peng, X.; Yu, X. Characterization of aggregate microstructures of paddy soils under different patterns of fertilization with synchrotron radiation micro-CT. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2014, 51, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, H. Effects of long-term fertilization on the microstructure and stability of cinnamon soil aggregates in cropland of North China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Tao, P.; Li, H. Exploring the pore structure of reconstructed soils and its effects on water and salt transport based on CT scanning. Coal Geol. Explor. 2024, 52, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, T. Soil pore structure and its research methods: A review. Soil Water Res. 2024, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

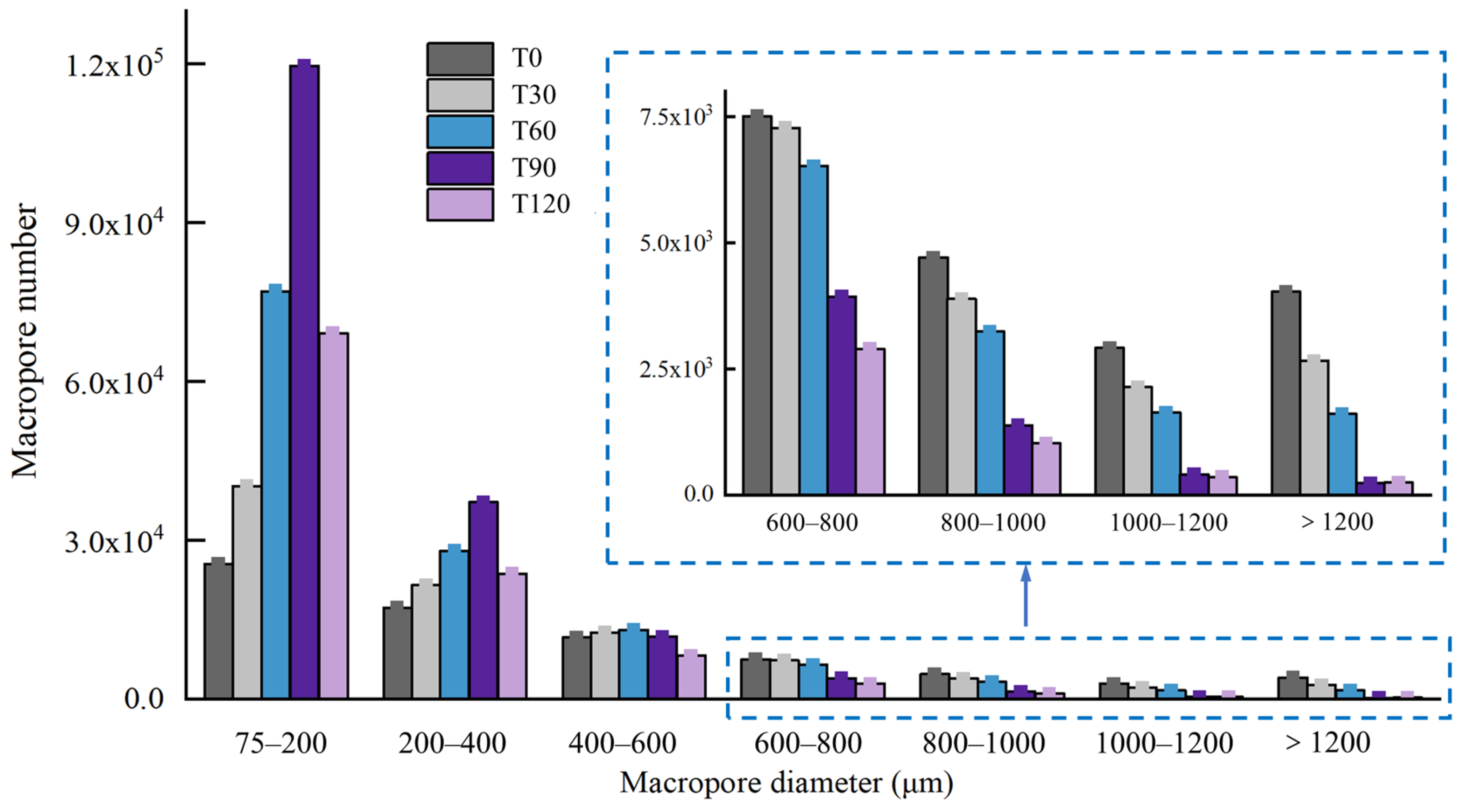
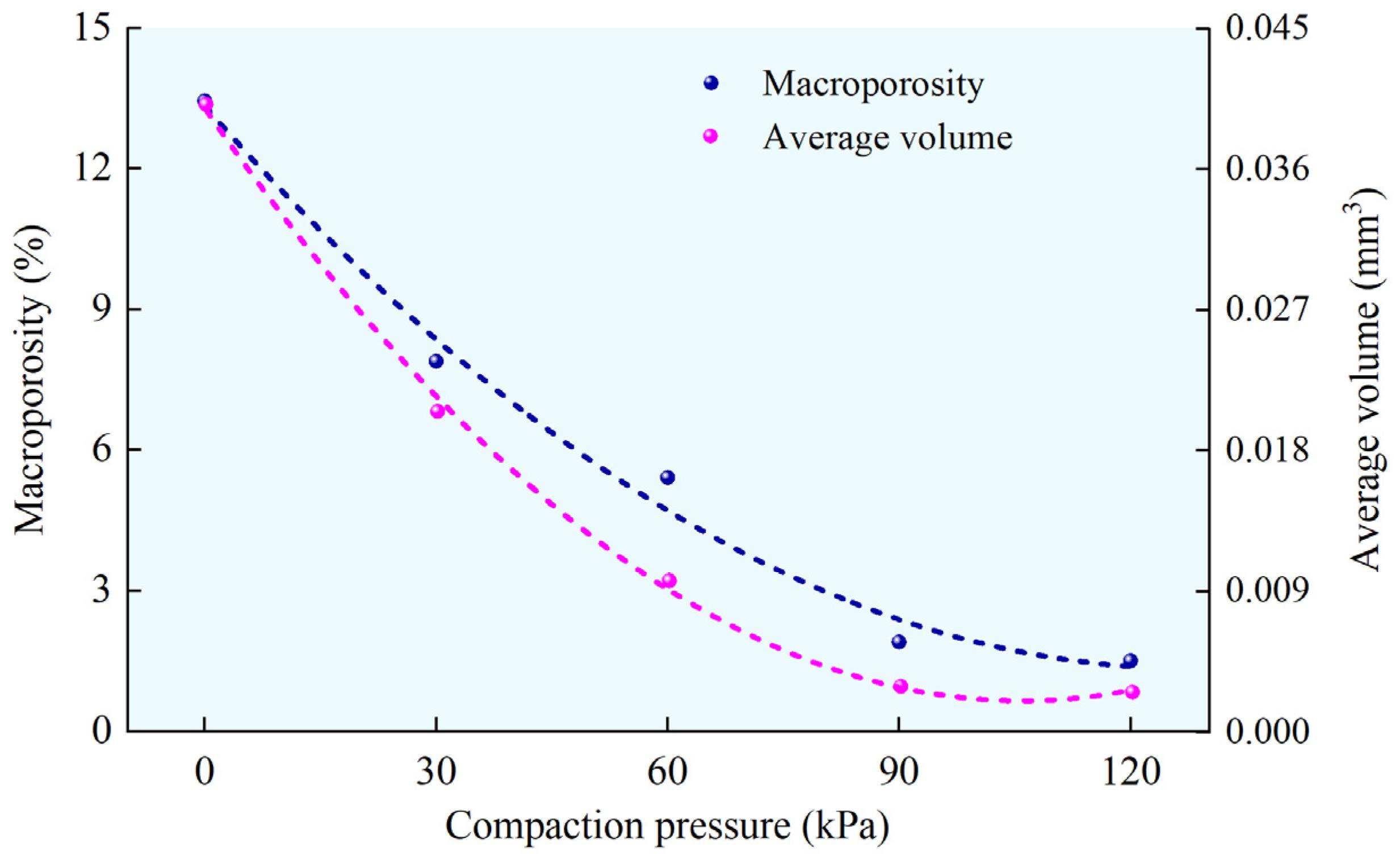
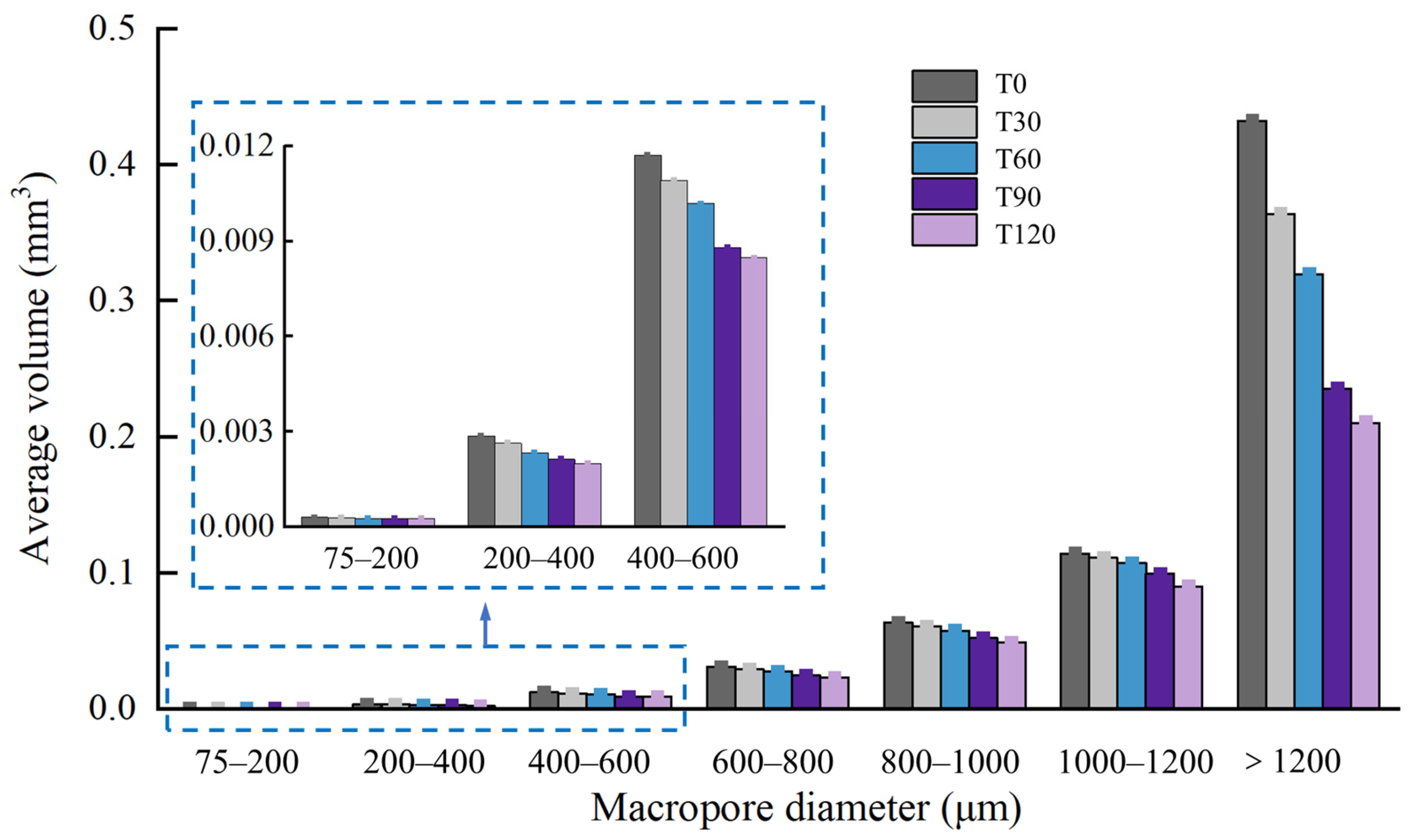
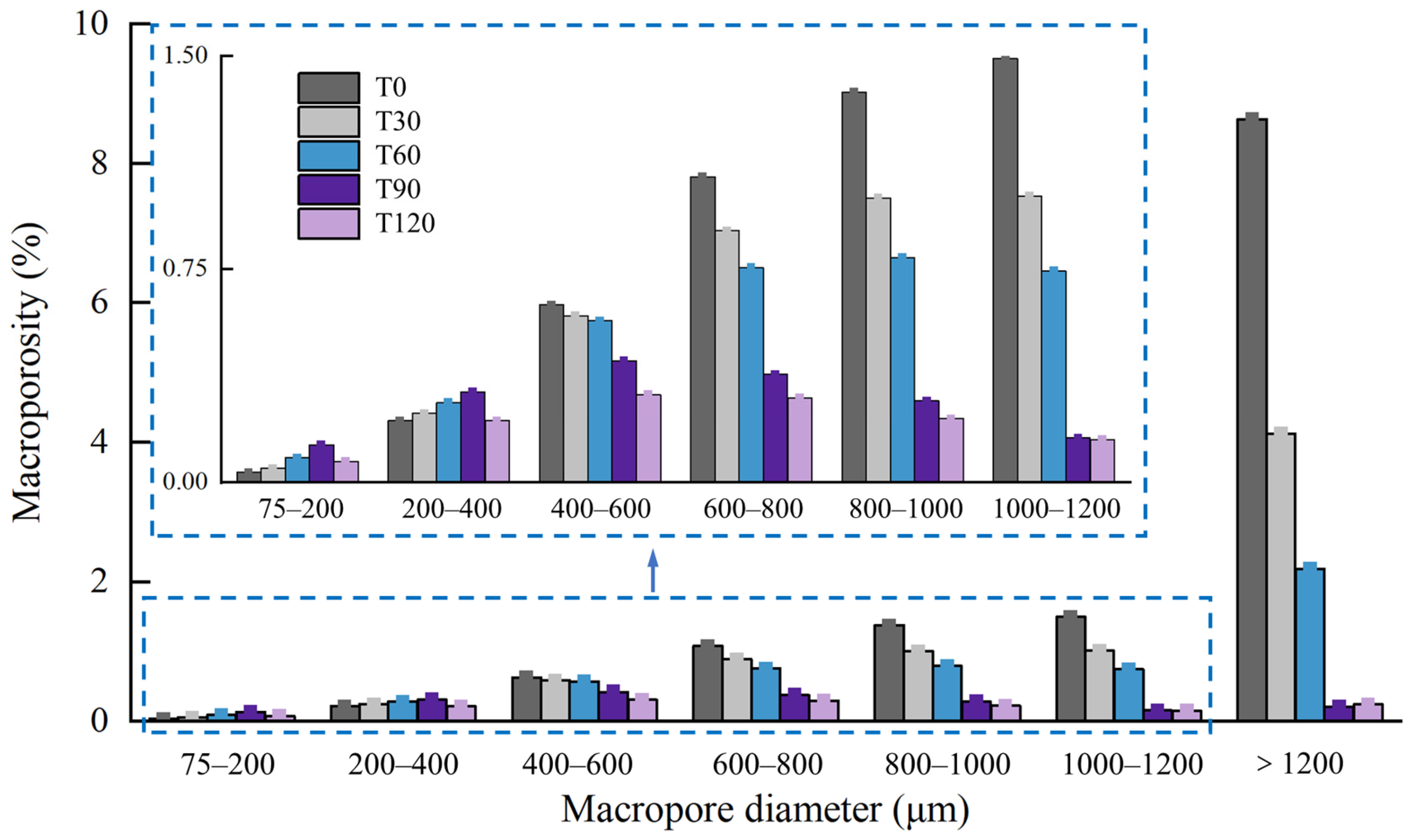
| Treatment Means | T0 | T30 | T60 | T90 | T120 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Number | 73,685 (4774) b | 90,257 (5270) b | 131,293 (7744) ab | 174,643 (9467) a | 105,594.5 (6956) ab |
| Total Volume (mm3) | 3151.9 (115.4) a | 1850.4 (15.3) b | 1268.8 (113.4) c | 446.9 (191.6) d | 354.6 (42.5) e |
| Macroporosity (%) | 13.448 (0.865) a | 7.894 (0.505) b | 5.413 (0.148) c | 1.906 (0.495) d | 1.513 (0.084) d |
| Total Surface area (mm2) | 59,037 (3868) a | 45,380 (1087) b | 38,110 (839) c | 22,371 (1203) d | 17,925 (1743) e |
| Average diameter (mm) | 0.4487 (0.0069) a | 0.2736 (0.0826) b | 0.2343 (0.0323) bc | 0.2213 (0.0027) bc | 0.1947 (0.0049) c |
| Number of pore throats | 28,735 (275) a | 19,640 (624) b | 10,579 (328) c | 6449 (1787) d | 4317 (499) e |
| Pore throat surface area (mm2) | 11.24 (0.14) a | 7.48 (0.22) b | 3.89 (0.24) c | 2.45 (0.68) d | 1.63 (0.18) e |
| Connectivity (%) | 14.258 (0.478) a | 7.178 (0.056) b | 2.430 (0.276) c | 0.1293 (0.005) d | 0.1290 (0.055) d |
| Maximum path length (mm) | 8.082 (0.991) b | 12.305 (0.625) a | 7.401 (0.652) b | 6.476 (0.702) b | 4.647 (0.519) b |
| Average path length (mm) | 0.385 (0.0126) a | 0.331 (0.0166) b | 0.289 (0.0168) c | 0.271 (0.0026) c | 0.244 (0.0006) d |
| Average path branch | 1350 (145) c | 8143 (1640) c | 64,848 (2689) b | 166,184 (7143) a | 67,313 (1571) b |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 1.333 (0.026) d | 1.497 (0.013) c | 1.598 (0.016) b | 1.671 (0.025) a | 1.723 (0.0219) a |
| Fractal dimension | 1.3285 (0.0055) c | 1.3455 (0.0065) b | 1.3520 (0.0011) b | 1.3540 (0.0012) ab | 1.3623 (0.0055) a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, Z.; Jiang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Jin, M.; Jiang, D. Characterizing the Effects of Compaction on Agricultural Tilled Soil Macropore Characteristics Using X-Ray Computed Tomography. Soil Syst. 2025, 9, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9040126
Guan Z, Jiang T, Li H, Zhang M, Jin M, Jiang D. Characterizing the Effects of Compaction on Agricultural Tilled Soil Macropore Characteristics Using X-Ray Computed Tomography. Soil Systems. 2025; 9(4):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9040126
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Zhuohuai, Tao Jiang, Haitong Li, Min Zhang, Mei Jin, and Dong Jiang. 2025. "Characterizing the Effects of Compaction on Agricultural Tilled Soil Macropore Characteristics Using X-Ray Computed Tomography" Soil Systems 9, no. 4: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9040126
APA StyleGuan, Z., Jiang, T., Li, H., Zhang, M., Jin, M., & Jiang, D. (2025). Characterizing the Effects of Compaction on Agricultural Tilled Soil Macropore Characteristics Using X-Ray Computed Tomography. Soil Systems, 9(4), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9040126







