Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinity, Growth, and Productivity of Triticale in Sandy Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
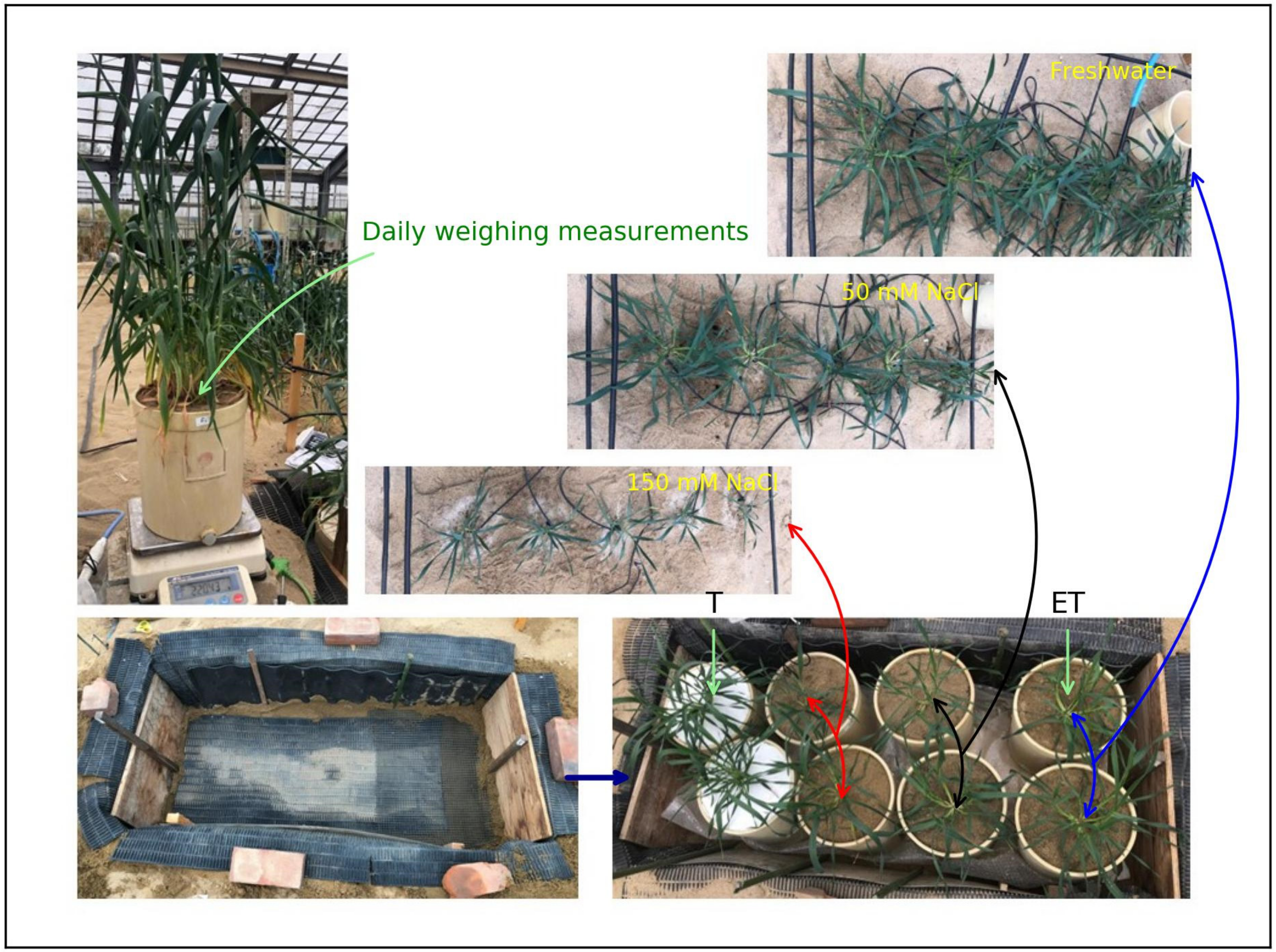
2.1. Experiment Design
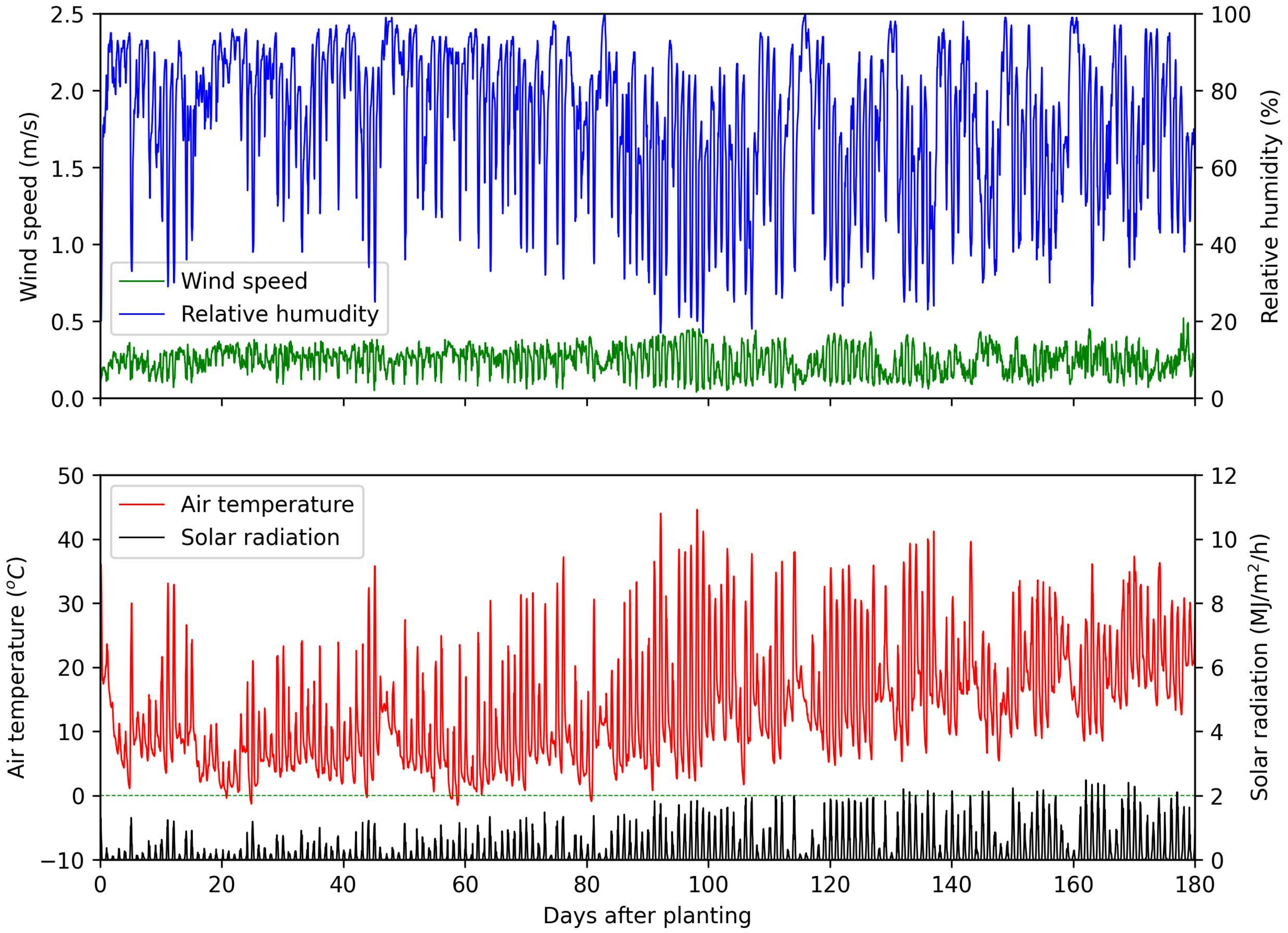
2.2. Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
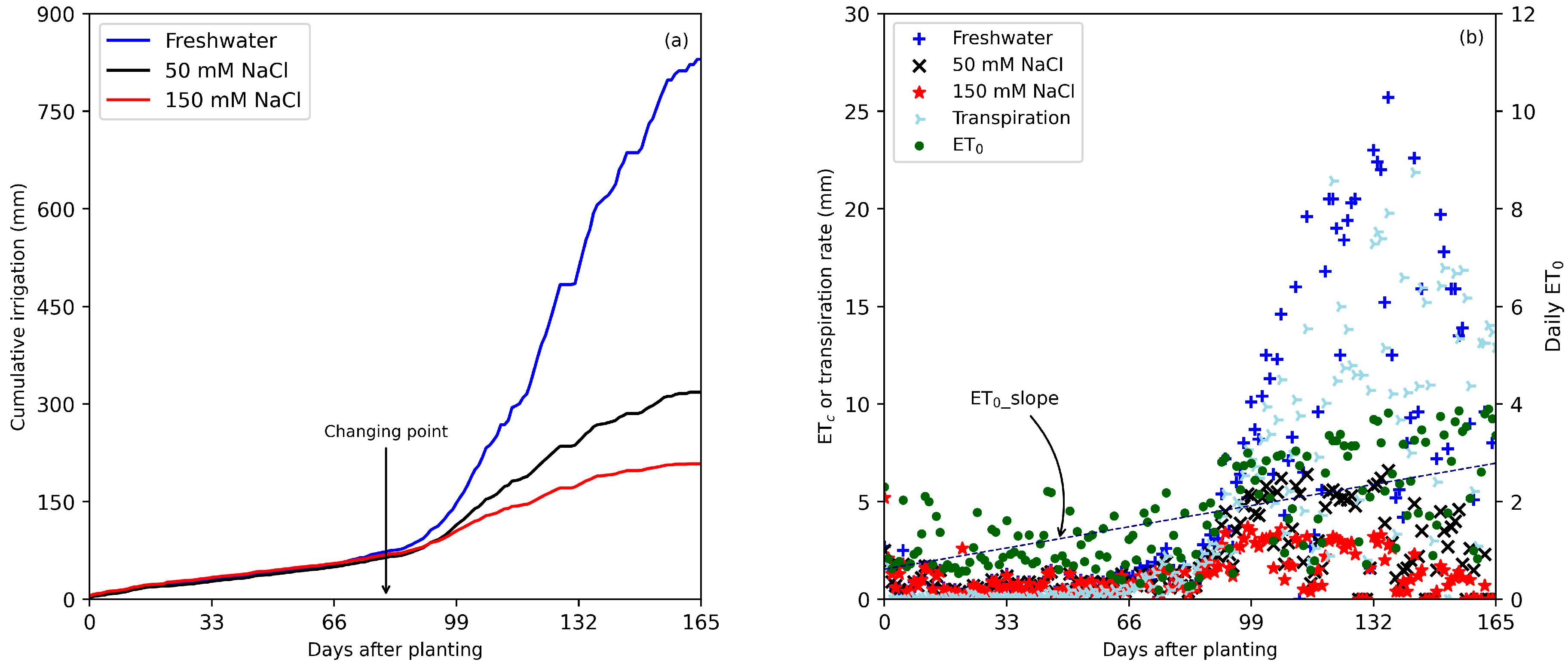
3.1. Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Crop Water Demand
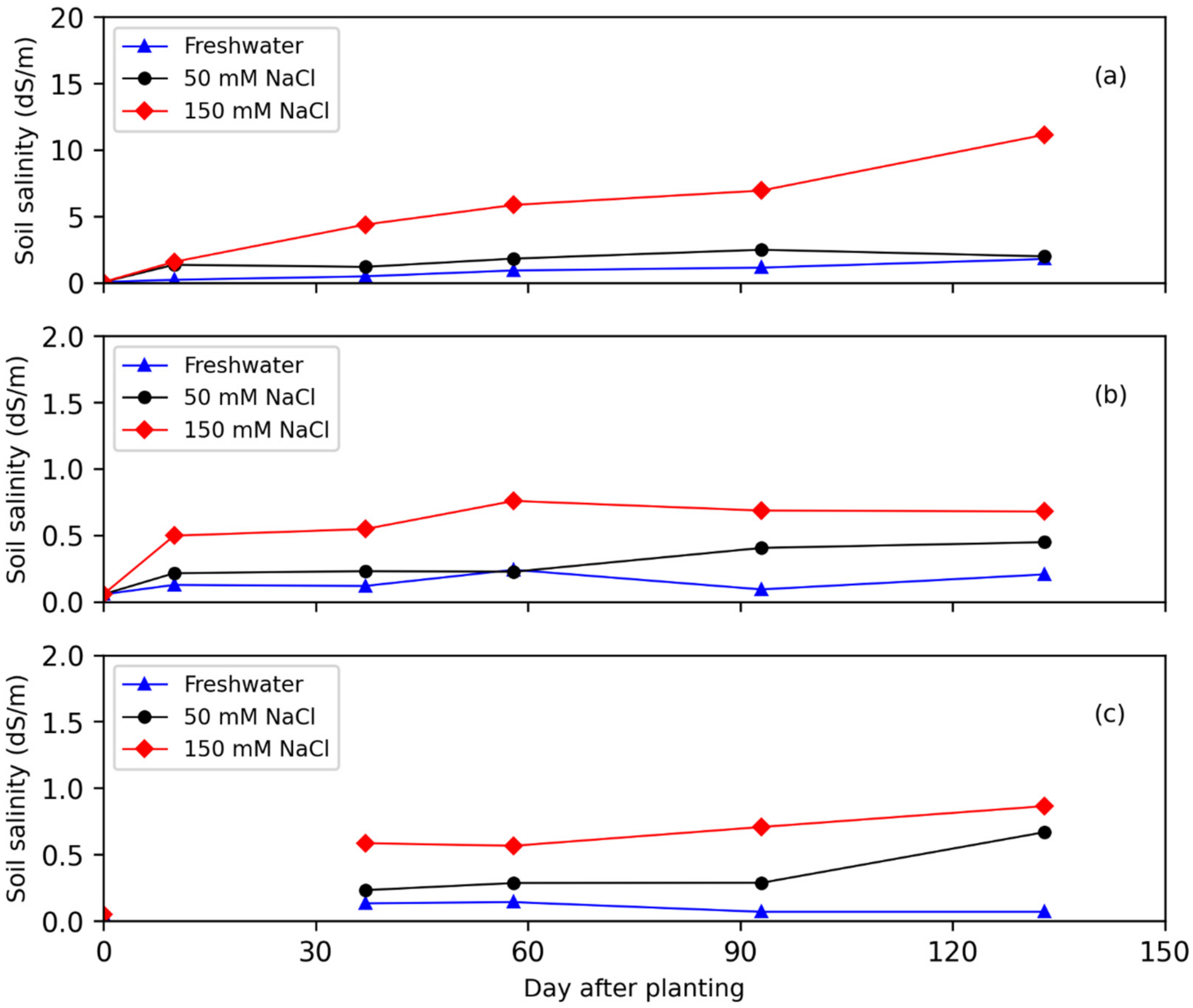
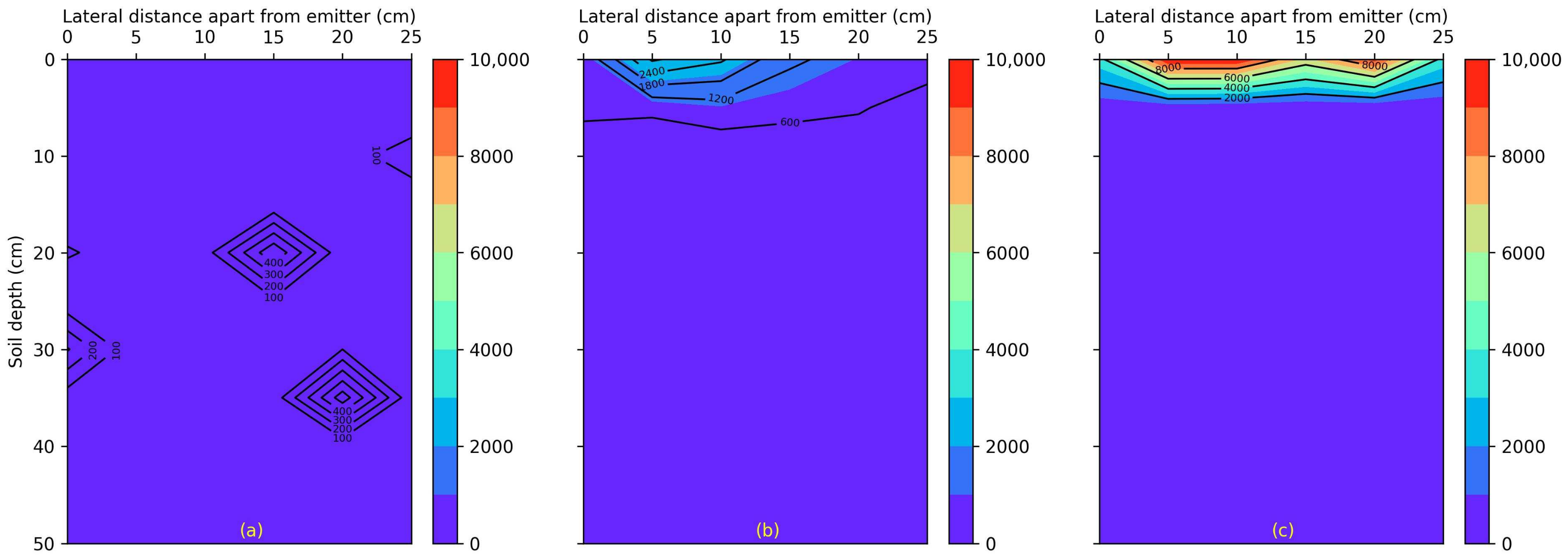
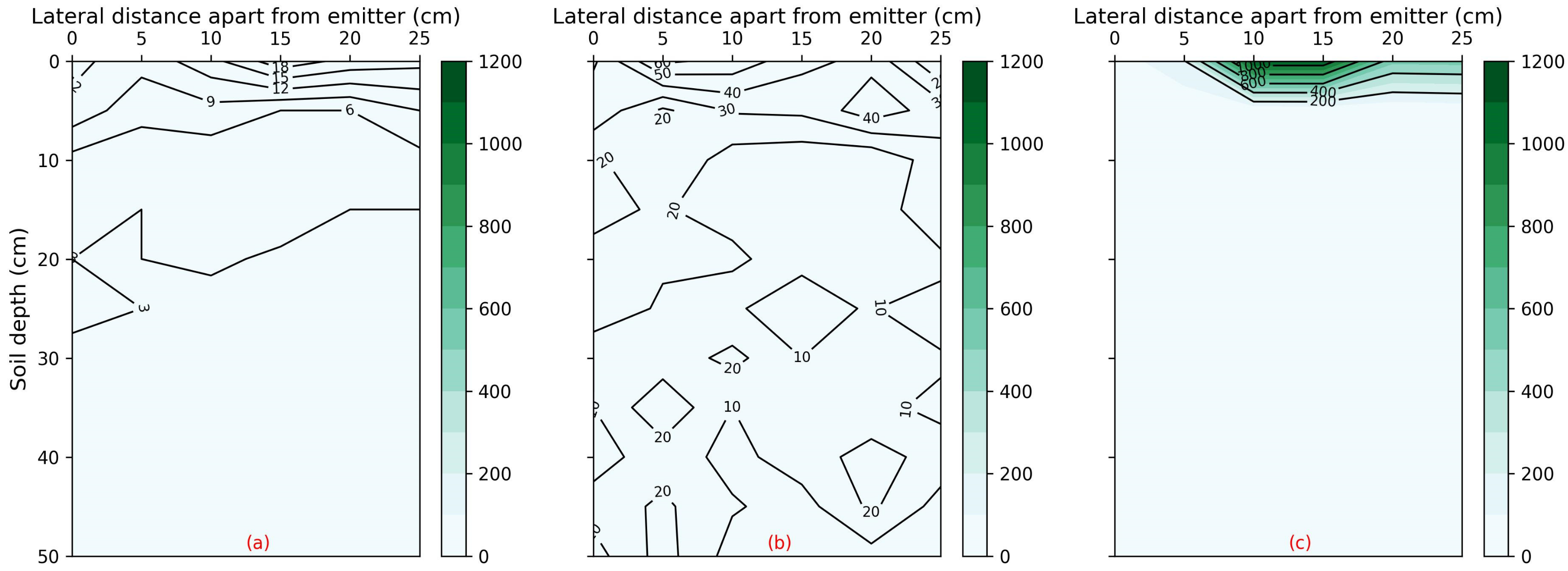
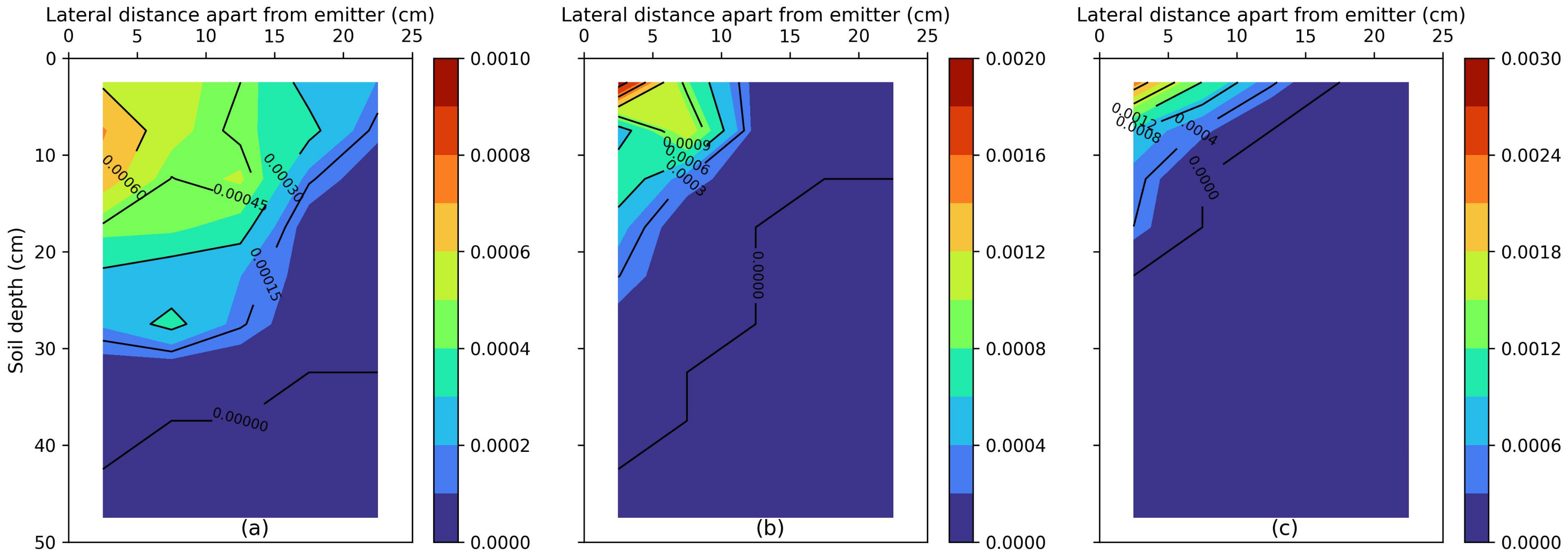
3.2. Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinity and Nutrients Fate
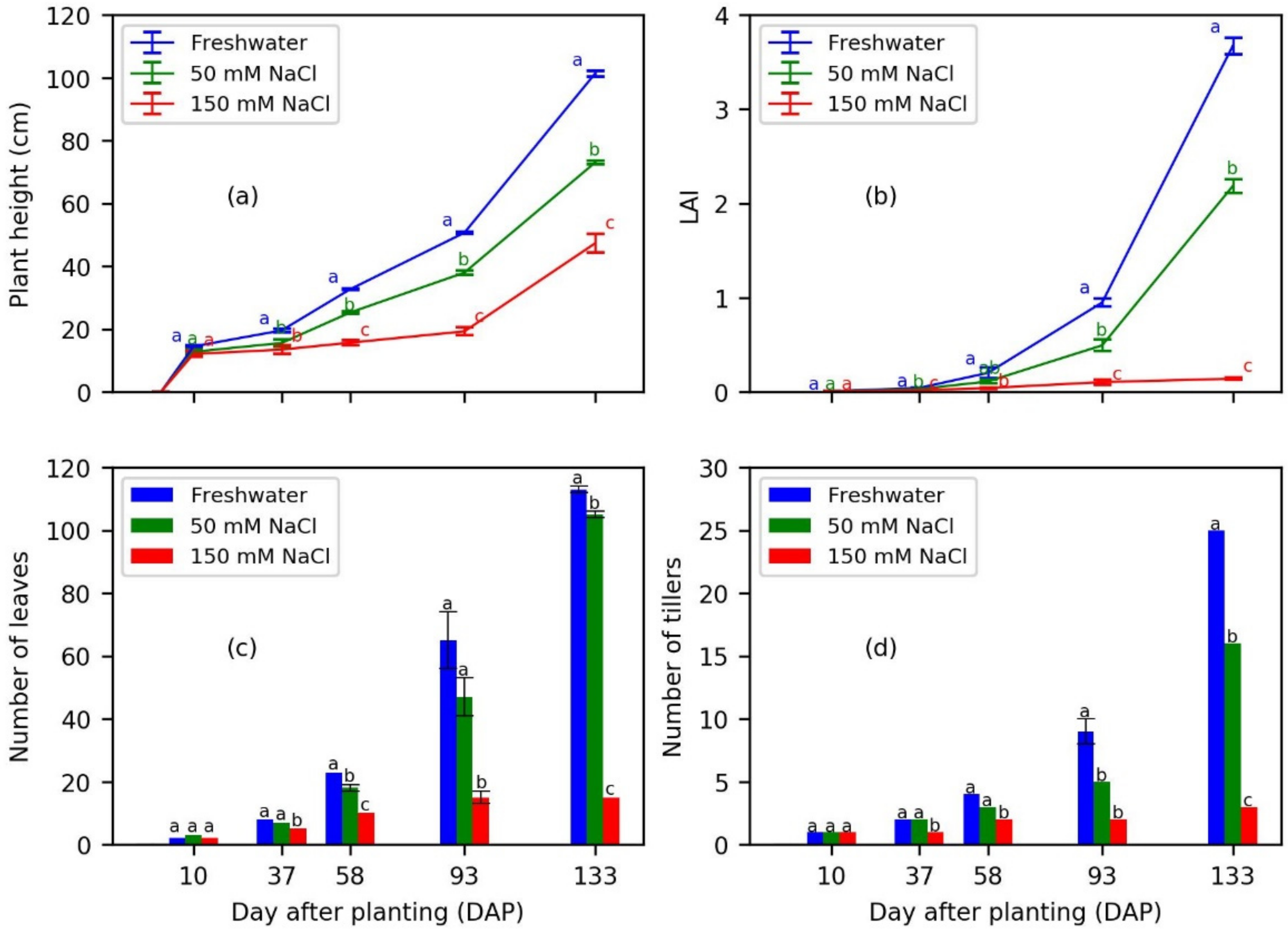
3.3. Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Plant Growth
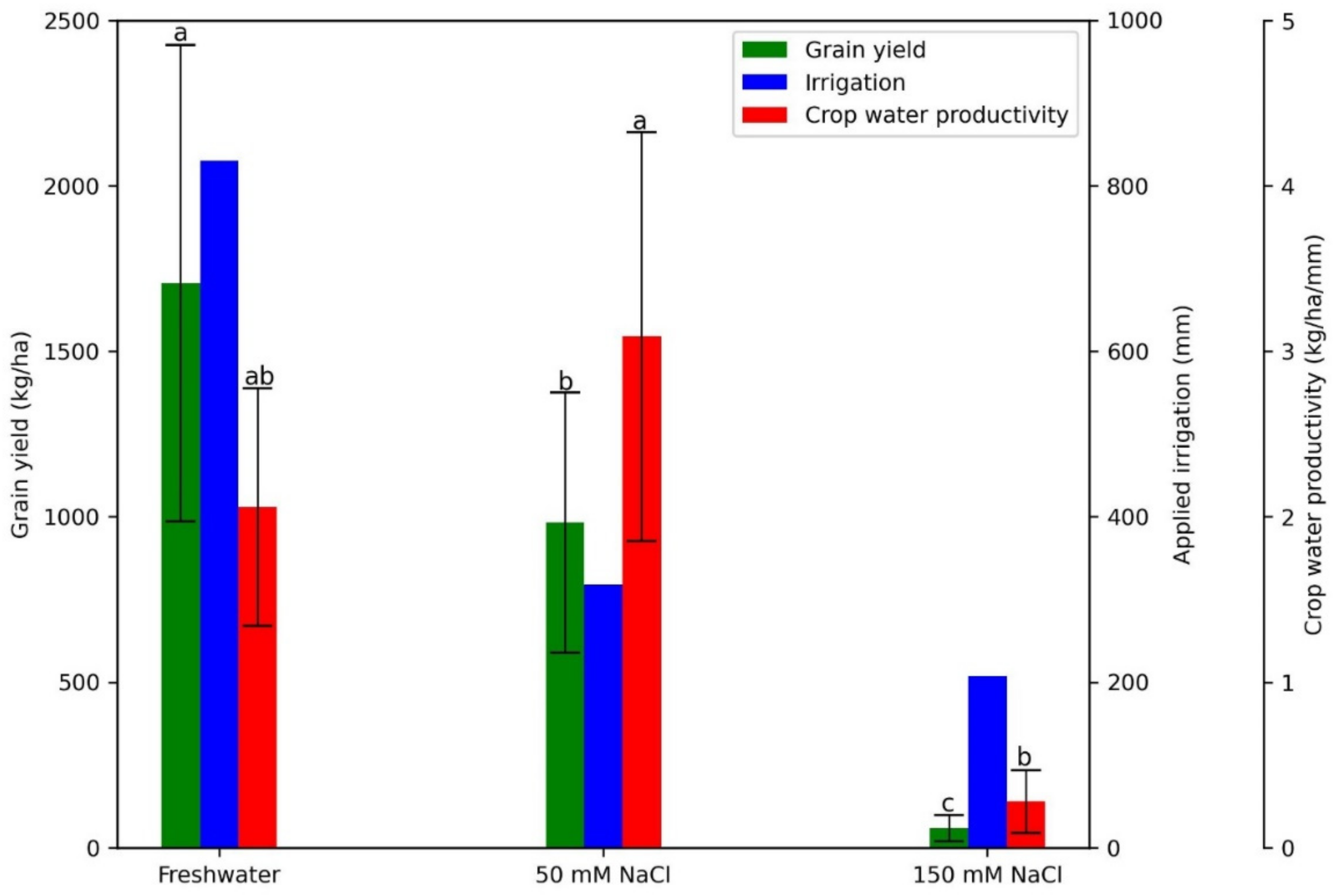
3.4. Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Yield, Yield Components, and Crop Productivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global Predictions of Primary Soil Salinization under Changing Climate in the 21st Century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Quillérou, E.; Nangia, V.; Murtaza, G.; Singh, M.; Thomas, R.J.; Drechsel, P.; Noble, A.D. Economics of Salt-Induced Land Degradation and Restoration. Nat Resour Forum 2014, 38, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.I.; Farooq, M.; Muscolo, A.; Rehman, A. Crop Diversification and Saline Water Irrigation as Potential Strategies to Save Freshwater Resources and Reclamation of Marginal Soils—A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28695–28729. [Google Scholar]
- Erkan, I.E.; Aras, Ö.E. Effects of Salicylic Acid on Triticale under Salt Stress. Bilge Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2021, 5, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelley, T. Triticale: A low-Input Cereal with Untapped Potential. In Genetic Resources, Chromosome Engineering, and Crop Improvement: Cereals; Singh, R.J., Jauhar, P.P., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2006; Volume 2, pp. 395–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F. Triticale: Nutritional Composition and Food Uses. Food Chem. 2017, 241, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantale, C.; Petrazzuolo, F.; Correnti, A.; Farneti, A.; Felici, F.; Latini, A.; Galeffi, P. Triticale for Bioenergy Production. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 8, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankarla, V.; Shukla, M.K.; Picchioni, G.A.; VanLeeuwen, D.; Schutte, B.J. Germination and Emergence Responses of Alfalfa, Triticale and Quinoa Irrigated with Brackish Groundwater and Desalination Concentrate. Agronomy 2020, 10, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluışık, S.; Oney-Birol, S. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of 13 Cultivars of Triticale (× Triticosecale Wittmack) to Salt Stress. Gesunde Pflanz. 2021, 73, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, H.; Doneva, S. Analysis on some qualitative traits of Bulgarian triticale cultivars. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 59, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Gołębiowska, G.; Dyda, M.; Wajdzik, K. Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes Associated with Cold-Acclimation and Microdochium Nivale Tolerance/Susceptibility in Winter Triticale (× Triticosecale). Plants 2021, 10, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonbani, M.; Arzani, A. Morpho-Physiological Traits Associated with Terminal Drought—Stress Tolerance in Triticale and Wheat. Agron. Res. 2011, 9, 315–329. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, S.; Tian, X.; Du, W. Morphological and Physiological Traits of Triticale as Affected by Drought Stress. Chil J. Agric. Res. 2023, 83, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanazari, M.; Golkar, P.; Mirmohammady Maibody, A.M. Effects of Drought Stress on Some Agronomic and Bio-Physiological Traits of Trititicum Aestivum, Triticale, and Tritipyrum Genotypes. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2018, 64, 2005–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankarla, V.; Shukla, M.K.; VanLeeuwen, D.; Schutte, B.J.; Picchioni, G.A. Growth, Evapotranspiration, and Ion Uptake Characteristics of Alfalfa and Triticale Irrigated with Brackish Groundwater and Desalination Concentrate. Agronomy 2019, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, O.F.; Shukla, M.K.; Stringam, B.; Picchioni, G.A.; Gard, C. Irrigation with brackish water changes evapotranspiration, growth and ion uptake of halophytes. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 195, 142–153. [Google Scholar]
- Grieve, C.M.; Grattan, S.R.; Maas, E.V. Chapter 13 Plant salt tolerance. Agric. Ultural Salin. Assess. Manag. 2012, 71, 405–459. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A. Assessment of Genetic Parameters for Yield and Yield Attributes of Triticale and Wheat Genotype under Salt Affected Condition. J. Pharm. Innov. 2021, 10, 337–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Dias, M.C.; Freitas, H. Drought and Salinity Stress Responses and Microbe-Induced Tolerance in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 591911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 29; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Ayub, Q. Effect of Salinity on Physiological and Biochemical Attributes of Different Brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) Cultivars. Pure Appl. Biol. 2020, 9, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankarla, V.; Shukla, M.K.; Picchioni, G.A. Root Growth, Architecture, and Ion Uptake of Alfalfa and Triticale Irrigated with Brackish Groundwater and Reverse Osmosis Concentrate. Agrosystems Geosci. Environ. 2021, 4, e20180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Day, D.A.; Fricke, W.; Watt, M.; Arsova, B.; Barkla, B.J.; Bose, J.; Byrt, C.S.; Chen, Z.; Foster, K.J.; et al. Energy Costs of Salt Tolerance in Crop Plants. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimaki, H.; Shimano, T.; Inoue, M.; Nakane, K. Effect of a Salt Crust on Evaporation from a Bare Saline Soil. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimaki, H.; Shiozawa, S.; Inoue, M. Effect of Salty Crust on Soil Albedo. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2003, 118, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.; Verma, S.B.; Singh, A.K. Sustainable Management of Soil Salinity with Special Reference to Smart Fertigation Systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2024, 94, 705–718. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Du, S.; Guo, H.; Min, W. Long-Term Saline Water Drip Irrigation Alters Soil Physicochemical Properties, Bacterial Community Structure, and Nitrogen Transformations in Cotton. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 182, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Modeling Strategies to Balance Salt Leaching and Nitrogen Loss for Drip Irrigation with Saline Water in Arid Regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahtouh, J.; Mohtar, R.; Assi, A.; Schwab, P.; Jantrania, A.; Deng, Y.; Munster, C. Impact of Brackish Groundwater and Treated Wastewater on Soil Chemical and Mineralogical Properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 647, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ali, A.R.; Yang, H.; Shukla, M. Brackish Groundwater and Reverse Osmosis Concentrate Influence Soil Physical and Thermal Properties and Pecan Evapotranspiration. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 1519–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney, H.F.; Criddle, W.D. Determining Water Requirements in Irrigated Areas from Climatological and Irrigation Data; Soil conservation service technical paper 96; Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereire, L.S.; Rase, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration. In Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage paper number 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pütz, T.; Kiese, R.; Wollschläger, U.; Groh, J.; Rupp, H.; Zacharias, S.; Priesack, E.; Gerke, H.H.; Gasche, R.; Bens, O.; et al. TERENO-SOILCan: A Lysimeter-Network in Germany Observing Soil Processes and Plant Diversity Influenced by Climate Change. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ma, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J. A Simple Method for Estimating Field Crop Evapotranspiration from Pot Experiments. Water 2018, 10, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Octura, J.E.; Gadiaware, P.; Octura, E. Estimating Evapotranspiration and Crop Coefficient of Vegetable Crops Using Pot Micro-Lysimeters. Philipp J. Sci. 2020, 149, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Salinity; Management. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Hillel, D., Hatfield, J.H., Powlson, D.S., Rosenzweig, C., Scow, K.M., Singer, M.J., Sparks, D.L., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 435–442. [Google Scholar]
- Nana, J.B.; Abd El Baki, H.M.; Fujimaki, H. Determining Drought and Salinity Stress Response Function for Garlic. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimaki, H. SimpleDigitizer Software; Version 3.2; Arid Land Research Center: Tottori, Japan, 2011; Available online: https://www.alrc.tottori-u.ac.jp/fujimaki/ (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Newman, E. A Method of Estimating the Total Length of Root in a Sample. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 3, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ali, A.R.; Shukla, M.K.; Marsalis, M.; Khan, N. Irrigation with Desalinated and Raw Produced Waters: Effects on Soil Properties, and Germination and Growth of Five Forages. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goet, G.; Sonkar, I.; Kumar, S.; Prasad, K.S.H.; Ojha, C.S.P. Effect of Salinity on Crop Growth and Soil Moisture Dynamics: A Study with Root Water Uptake Model. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2024, 28, 04024009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, S.M.; Fujimaki, H. Soil Salinity Resistance Effect on Evaporation. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, F. Effects of Evolving Salt Precipitation on the Evaporation and Temperature of Sandy Soil with a Fixed Groundwater Table. Vadose Zone J. 2021, 20, e20122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, A.; Gawde, A.; Cantrell, C.L.; Baxter, H.L.; Joyce, B.L.; Stewart, C.N.; Zheljazkov, V.D. Effects of Produced Water on Soil Characteristics, Plant Biomass, and Secondary Metabolites. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, Z.; Dai, S.; Ding, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Ding, G.; Wang, P.; Guan, Y.; Liu, W. Integrative analyses of transcriptomics and metabolomics upon seed germination of foxtail millet in response to salinity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13660. [Google Scholar]
- Alkharabsheh, H.M.; Seleiman, M.F.; Hewedy, O.A.; Battaglia, M.L.; Jalal, R.S.; Alhammad, B.A.; Schillaci, C.; Ali, N.; Al-Doss, A. Field Crop Responses and Management Strategies to Mitigate Soil Salinity in Modern Agriculture: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atak, M.; Kaya, M.D.; Kaya, G.; Çikili, Y.; Çiftçi, C.Y. Effects of NACL on the Germination, Seedling Growth and Water Uptake of Triticale. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2006, 30, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Alagoz, S.M.; Hadi, H.; Toorchi, M.; Pawłowski, T.A.; Shishavan, M.T. Effects of Water Deficiency at Different Phenological Stages on Oxidative Defense, Ionic Content, and Yield of Triticale (× Triticosecale Wittmack) Irrigated with Saline Water. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 22, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, F.; Yun, P.; Kiani-Pouya, A.; Movahedi, A.; Rasouli, M.; Salehi, M.; Shabala, S. One Size Does Not Fit All: Different Strategies Employed by Triticale and Barley Plants to Deal with Soil Salinity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 218, 105585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgün, İ.; Kara, B.; Altindal, D. Effect of Salinity (NaCl) on Germination, Seedling Growth and Nutrient Uptake of Different Triticale Genotypes. Turk. J. Field Crops 2011, 16, 225–232. Available online: https://www.field-crops.org/assets/pdf/product51338591945e6.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Miao, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, C.; Ye, C.; Yan, Y.; Wang, H. What Factors Control Plant Height? J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 1803–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ke, W.; Hou, H. Effect of Salt Stress on Growth, Physiological Parameters, and Ionic Concentration of Water Dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) Cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 660409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Bano, A.; Khan, N. Climate Change and Salinity Effects on Crops and Chemical Communication Between Plants and Plant Growth-Promoting Microorganisms Under Stress. Front. Sustain Food Syst. 2021, 5, 618092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, N.; Kafkafi, U. Root Growth Under Salinity Stress; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 787–805. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.B.; Sperry, J.S.; Dawson, T.E. Root Water Uptake and Transport: Using Physiological Processes in Global Predictions. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.A.; Nawata, E.; Shigenaga, S. Effects of Salinity and Water Stress on the Growth, Yield and Physiological Characteristics in Hexaploid Triticale. Nettai Nogyo/Nettai Nougyou 1993, 37, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzążewska, E.; Gąsiorowska, B. Yield components of spring triticale as affected by cultivar and multi-nutrient fertiliser type and rate. Folia Pomeranae Univ. Technol. Stetin. Agric. Aliment. Piscaria Zootech. 2023, 369, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A. The Abiotic Stress Response and Adaptation of Triticale-A Review. Cereal. Res. Commun. 2014, 42, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, B.J. Triticale: Overview. In Encyclopedia of Food Grains; Wrigley, C.W., Corke, H., Seetharaman, K., Faubion, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 168–172. [Google Scholar]




| Yield Attribute | Unit | Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freshwater | 50 mM NaCl | 150 mM NaCl | ||
| Plant height | cm | 109 ± 1.9 a | 83 ± 2.3 b | 59 ± 9.3 c |
| Num. tillers | - | 47 ± 5 a | 14 ± 1 b | 2 ± 0 c |
| Number of spikes | - | 14 ± 2 a | 6 ± 0 b | 1 ± 0 c |
| Spike length | cm | 15.9 ± 0.5 a | 14.8 ± 0.4 a | 9.5 ± 0.4 b |
| Spike width | cm | 1.1 ± 0.1 a | 0.9 ± 0 a | 0.8 ± 0.3 a |
| 100 grain weight | g | 3 ± 0.3 a | 2.7 ± 0.1 a | 1.8 ± 0.1 b |
| Total fresh biomass | g | 189.8 ± 18.1 a | 64.6 ± 6.9 b | 7.3 ± 1.8 c |
| Total dry biomass | g | 133.3 ± 14.2 a | 59.1 ± 6.1 b | 4 ± 0.9 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd El Baki, H.M.; Fujimaki, H.; Toderich, K.; Nana, J.B.; Qureshi, A.S. Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinity, Growth, and Productivity of Triticale in Sandy Soil. Soil Syst. 2025, 9, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020028
Abd El Baki HM, Fujimaki H, Toderich K, Nana JB, Qureshi AS. Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinity, Growth, and Productivity of Triticale in Sandy Soil. Soil Systems. 2025; 9(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd El Baki, Hassan M., Haruyuki Fujimaki, Kristina Toderich, Jean Bosco Nana, and Asad S. Qureshi. 2025. "Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinity, Growth, and Productivity of Triticale in Sandy Soil" Soil Systems 9, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020028
APA StyleAbd El Baki, H. M., Fujimaki, H., Toderich, K., Nana, J. B., & Qureshi, A. S. (2025). Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinity, Growth, and Productivity of Triticale in Sandy Soil. Soil Systems, 9(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020028








