Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sites
2.2. Runoff Phosphorus Concentrations
2.3. Soil Test Phosphorus
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Test P
3.2. Surface Runoff and Tile Drainage Phosphorus Concentrations
3.3. Relationships between STP and FWM P Concentrations
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Test P
4.2. Relationships between STP and FWM P Concentrations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maccoux, M.J.; Dove, A.; Backus, S.M.; Dolan, D.M. Total and soluble reactive phosphorus loadings to Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1151–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavia, D.; David Allan, J.; Arend, K.K.; Bartell, S.; Beletsky, D.; Bosch, N.S.; Brandt, S.B.; Briland, R.D.; Daloğlu, I.; DePinto, J.V.; et al. Assessing and addressing the re-eutrophication of lake erie: Central basin hypoxia. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Johnson, L.T.; Wynne, T.T.; Baker, D.B. Forecasting annual cyanobacterial bloom biomass to inform management decisions in Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.A.; Ulén, B.; Stamm, C.; Bechmann, M. Incidental phosphorus losses–are they significant and can they be predicted? J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2003, 166, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, H.; Withers, P.J.A.; Baas, P.; Chan, N.I.; Doody, D.; Holiman, J.; Jacobs, B.; Li, H.; MacDonald, G.K.; McDowell, R.; et al. Integrating legacy soil phosphorus into sustainable nutrient management strategies for future food, bioenergy and water security. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2016, 104, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; Johnson, L.T.; Smith, D.R.; LaBarge, G.A.; Fausey, N.R. Phosphorus availability in western lake erie basin drainage waters: Legacy evidence across spatial scales. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; King, K.W.; Johnson, L.; Francesconi, W.; Richards, P.; Baker, D.; Sharpley, A.N. Surface runoff and tile drainage transport of phosphorus in the midwestern USA. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Esbroeck, C.J.; Macrae, M.L.; Brunke, R.I.; McKague, K. Annual and seasonal phosphorus export in surface runoff and tile drainage from agricultural fields with cold temperate climates. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, L.A.; King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; LaBarge, G.A.; Duncan, E.W.; Fausey, N.R. Phosphorus export from artificially drained fields across the eastern corn belt. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetstra, M.A.; Tellez, C.; Wilson, R. 4R Nutrient Stewardship in the Western Lake Erie Basin Part II: A Panel Study; The Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vitosh, M.L.; Johnson, J.W.; Mengel, D.B. Tri-State Fertilizer Recommendations for Corn, Soybeans, Wheat, and Alfalfa; Ohio State University Agricultural Extension Bulletin E-2567: Columbus, OH, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Dayton, E.; LaBarge, G.A. Sensitivity analysis of the ohio phosphorus risk index. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Buda, A.R.; Easton, Z.M.; Lory, J.A.; Osmond, D.L.; Radcliffe, D.E.; Nelson, N.O.; Veith, T.L.; Doody, D.G. The promise, practice, and state of planning tools to assess site vulnerability to runoff phosphorus loss. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, K.; Schneider, K.; McConkey, B. Components of phosphorus loss from agricultural landscapes, and how to incorporate them into risk assessment tools. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraski, T.W.; Bundy, L.G. Relationships between phosphorus levels in soil and in runoff from corn production systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djodjic, F. Phosphorus leaching in relation to soil type and soil phosphorus content. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, P.A.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Turner, B.L. Relating soil phosphorus to dissolved phosphorus in runoff: A single extraction coefficient for water quality modeling. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.B.; Johnson, L.T.; Confesor, R.B.; Crumrine, J.P. Vertical stratification of soil phosphorus as a concern for dissolved phosphorus runoff in the Lake Erie basin. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, E.W.; King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; LaBarge, G.; Pease, L.A.; Smith, D.R.; Fausey, N.R. Linking soil phosphorus to dissolved phosphorus losses in the midwest. Agric. Environ. Lett. 2017, 2, 170004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterholz, W.R.; Hanrahan, B.R.; King, K.W. Legacy Phosphorus concentration–discharge relationships in surface runoff and tile drainage from Ohio crop fields. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N. Soil mixing to decrease surface stratification of phosphorus in manured soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messiga, A.J.; Ziadi, N.; Morel, C.; Grant, C.; Tremblay, G.; Lamarre, G.; Parent, L.-E. Long term impact of tillage practices and biennial p and n fertilization on maize and soybean yields and soil P status. Field Crops Res. 2012, 133, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Huang, C.; Haney, R.L. Phosphorus fertilization, soil stratification, and potential water quality impacts. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 72, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, L.R.; Sharpley, A.N.; Yamamoto, M.; Menzel, R.G. The depth of rainfall-runoff-soil interaction as determined by 32 P. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C.; Edwards, D.R.; Sharpley, A.N. Effect of extractable soil surface phosphorus on runoff water quality. Trans. ASAE 1993, 36, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbert, H.A.; Daniel, T.C.; Lemunyon, J.L.; Jones, R.M. Relationship of soil test phosphorus and sampling depth to runoff phosphorus in calcareous and noncalcareous soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.; Sharpley, A.; Buda, A.; McDowell, R.; Allen, A. Soil Controls of phosphorus in runoff: Management barriers and opportunities. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 91, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gächter, R.; Ngatiah, J.M.; Stamm, C. Transport of phosphate from soil to surface waters by preferential flow. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Ford, W.; Buda, A.R.; Kennedy, C.D. Effect of tillage on macropore flow and phosphorus transport to tile drains: Tillage, macropore flow, and phosphorus. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 2868–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plach, J.M.; Macrae, M.L.; Williams, M.R.; Lee, B.D.; King, K.W. Dominant glacial landforms of the lower great lakes region exhibit different soil phosphorus chemistry and potential risk for phosphorus loss. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Duncan, E.W.; Pease, L.A.; Penn, C.J. Fertilizer placement and tillage effects on phosphorus concentration in leachate from fine-textured soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Ford, W.; Fausey, N.R. Edge-of-Field research to quantify the impacts of agricultural practices on water quality in Ohio. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 9A–12A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; LaBarge, G.A.; Smith, D.R.; Reutter, J.M.; Duncan, E.W.; Pease, L.A. Addressing agricultural phosphorus loss in artificially drained landscapes with 4R nutrient management practices. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, C.J.; Kryskalla, J.R. Methods of Analysis by the U.S. Geological Survey National Water Quality Laboratory: Evaluation of Alkaline Persulfate Digestion as an Alternative to Kjeldahl Digestion for the Determination of Total and Dissolved Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Water; Water Resources Investigations Report 03-4174; United States Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2003.
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Macrae, M.L.; Ford, W.; Van Esbroeck, C.; Brunke, R.I.; English, M.C.; Schiff, S.L. Uncertainty in nutrient loads from tile-drained landscapes: Effect of sampling frequency, calculation algorithm, and compositing strategy. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallarino, A.P. Spatial variability patterns of phosphorus and potassium in no-tilled soils for two sampling scales. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzon, J.D.; O’Halloran, I.P.; Fallow, D.J.; von Bertoldi, A.P.; Aspinall, D. Spatial variability of soil test phosphorus, potassium, and ph of ontario soils. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandt, S.; Ketterings, Q.M.; Lembo, A.J.; Vermeylen, F. In-field variability of soil test phosphorus and implications for agronomic and environmental phosphorus management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallarino, A.P.; Borges, R. Phosphorus and potassium distribution in soil following long-term deep-band fertilization in different tillage systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, J.R.; Mallarino, A.P. Soil-Test phosphorus and crop grain yield responses to long-term phosphorus fertilization for corn-soybean rotations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulford, A.M.; Culman, S.W. Over-fertilization does not build soil test phosphorus and potassium in ohio. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboski, C.A.M.; Lamb, J.A. Changes in soil test phosphorus concentration after application of manure or fertilizer. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Moyer, B.G.; Elwinger, G.F. Effect of mineral and manure phosphorus sources on runoff phosphorus. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, M.L.; English, M.C.; Schiff, S.L.; Stone, M. Intra-annual variability in the contribution of tile drains to basin discharge and phosphorus export in a first-order agricultural catchment. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 92, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrahan, B.R.; King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; Duncan, E.W.; Pease, L.A.; LaBarge, G.A. Nutrient balances influence hydrologic losses of nitrogen and phosphorus across agricultural fields in northwestern Ohio. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 113, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deubel, A.; Hofmann, B.; Orzessek, D. Long-term effects of tillage on stratification and plant availability of phosphate and potassium in a loess chernozem. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchi, L.; Wendling, M.; Amossé, C.; Jeangros, B.; Sinaj, S.; Charles, R. Long and short term changes in crop yield and soil properties induced by the reduction of soil tillage in a long term experiment in Switzerland. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 174, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.S.; Beetstra, M.A.; Reutter, J.M.; Hesse, G.; Fussell, K.M.D.; Johnson, L.T.; King, K.W.; LaBarge, G.A.; Martin, J.F.; Winslow, C. Commentary: Achieving phosphorus reduction targets for Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.; Elliott, J.; Macrae, M.; Glenn, A. Near-surface soils as a source of phosphorus in snowmelt runoff from cropland. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.R.; Cornish, P.S. Soil sample depth in pasture soils for environmental soil phosphorus testing. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 42, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, P.D.; Radcliffe, D.E.; Cabrera, M.L. Rainfall timing and poultry litter application rate effects on phosphorus loss in surface runoff. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 2201–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pote, D.H.; Daniel, T.C.; Sharpley, A.N.; Moore, P.A.; Edwards, D.R.; Nichols, D.J. Relating extractable soil phosphorus to phosphorus losses in runoff. SOIL Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.; Foster, G.; Weesies, G.; McCool, D.; Yoder, D. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agriculture Handbook; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington DC, USA, 1997.
- Smith, D.R.; Francesconi, W.; Livingston, S.J.; Huang, C. Phosphorus losses from monitored fields with conservation practices in the Lake Erie basin, USA. AMBIO 2015, 44, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.R.; Hendricks, S.E. Soil test phosphorus and clay content effects on runoff water quality. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Mullins, G.L.; Zelazny, L.W. Mineralogy in relation to phosphorus sorption and dissolved phosphorus losses in runoff. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, J.D.; Findlay, W.I. Soil and phosphorus loss from conservation and conventional tillage in corn production. J. Environ. Qual. 1995, 24, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Johnson, L.T.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, D.R.; Baker, D.B.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Confesor, R. Increased soluble phosphorus loads to Lake Erie: Unintended consequences of conservation practices? J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidon, P.; Cuadra, P.E. Phosphorus dynamics in tile-drain flow during storms in The US Midwest. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Baker, D.B.; Johnson, L.T.; Smith, D.R.; Fausey, N.R. Hydrologic and biogeochemical controls on phosphorus export from western Lake Erie tributaries. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, L.A.; Fausey, N.R.; Martin, J.F.; Brown, L.C. Weather, landscape, and management effects on nitrate and soluble phosphorus concentrations in subsurface drainage in the western Lake Erie basin. Trans. ASABE 2018, 61, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, A.R.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; Srinivasan, M.S.; Bryant, R.B.; Feyereisen, G.W. Effects of hydrology and field management on phosphorus transport in surface runoff. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.; Jarvie, H.P.; Buda, A.; May, L.; Spears, B.; Kleinman, P. Phosphorus legacy: Overcoming the effects of past management practices to mitigate future water quality impairment. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1308–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipitalo, M.J.; Gibbs, F. Potential of earthworm burrows to transmit injected animal wastes to tile drains. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 2103–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.K.; Rudolph, D.L.; Conant, B. Bromide and chloride tracer movement in macroporous tile-drained agricultural soil during an annual climatic cycle. J. Hydrol. 2012, 460–461, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Bryant, R.B.; Needelman, B.; Kleinman, P. Spatial distribution of soil phosphorus across selected New York dairy farm pastures and hay fields. Soil Sci. 2007, 172, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Surface Runoff * | Tile Drainage * | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Median | Min. | Max. | Mean | Median | Min. | Max. | ||
| STP (mg P kg−1) | 0–5 cm | 61 | 54 | 19 | 145 | 66 | 57 | 19 | 202 |
| 0–20 cm | 40 | 35 | 12 | 121 | 44 | 37 | 12 | 150 | |
| STP coefficient of variation (%) | 0–5 cm | 35 | 31 | 6 | 83 | 32 | 29 | 2 | 83 |
| 0–20 cm | 39 | 34 | 7 | 108 | 36 | 33 | 1 | 108 | |
| Pstrat † | 1.98 | 1.90 | 1.18 | 3.35 | 1.88 | 1.80 | 1.25 | 3.35 | |
| FWM DRP Conc (mg L−1) | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.66 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.27 | |
| FWM TP Conc (mg L−1) | 0.65 | 0.53 | 0.25 | 1.91 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.64 | |
| Total discharge (mm) | 283 | 242 | 20 | 735 | 87 | 64 | 9 | 279 | |
| Observed Increases (#) | Observed Decreases (#) | Mean of Absolute Values * | Largest Decrease * | Largest Increase * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STP | 0–5 cm | 30 | 18 | 14 | −52 | 102 |
| 0–20 cm | 31 | 17 | 9 | −32 | 25 | |
| STP coefficient of variation | 0–5 cm | 30 | 18 | 14 | −53 | 37 |
| 0–20 cm | 25 | 23 | 15 | −78 | 53 | |
| Pstrat † | 25 | 23 | 0.43 | −1.55 | 1.87 | |
| DRP | TP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Slope * | Regression Intercept * | R2 | RMSE | Regression Slope * | Regression Intercept * | R2 | RMSE | |
| Surface runoff | ||||||||
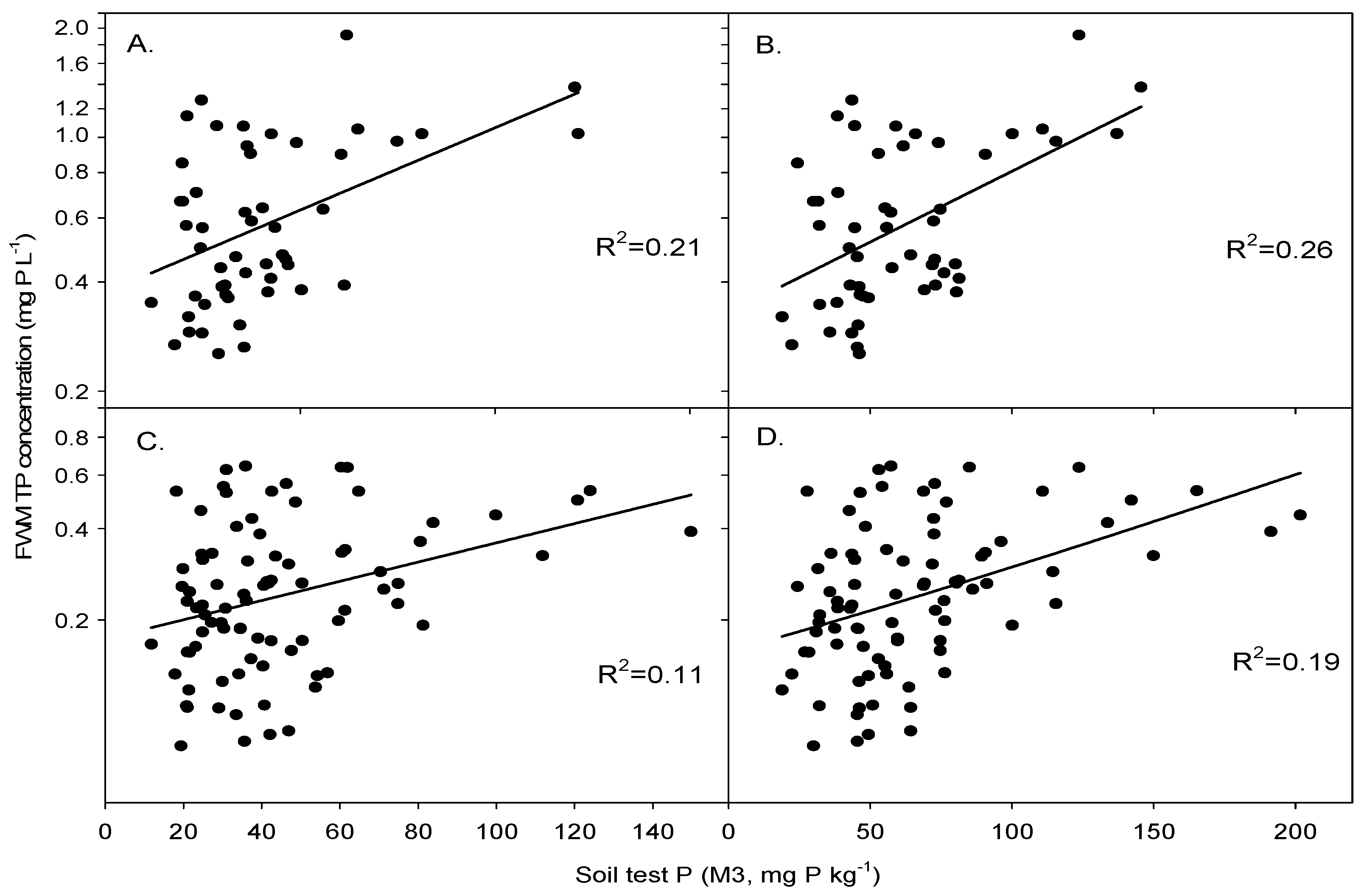
| 0–5 cm samples | 0.015 | −2.90 | 0.31 | 0.66 | 0.009 | −1.11 | 0.26 | 0.44 |
| 0–20 cm samples | 0.016 | −2.59 | 0.19 | 0.72 | 0.01 | −0.98 | 0.21 | 0.45 |
| Tile drainage | ||||||||
| 0–5 cm samples | 0.014 | −3.90 | 0.44 | 0.56 | 0.007 | −1.87 | 0.19 | 0.50 |
| 0–20 cm samples | 0.016 | −3.73 | 0.32 | 0.62 | 0.007 | −1.75 | 0.11 | 0.53 |
| Model * | R2 | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface runoff | |||
| FWM DRP | 0.020 × STP + 0.59 × Pstrat − 3.92 | 0.34 | 0.66 |
| FWM TP | 0.010 × STP − 0.98 | 0.21 | 0.45 |
| Tile drainage | |||
| FWM DRP | 0.019 × STP + 0.53 × Pstrat − 4.81 | 0.46 | 0.56 |
| FWM TP | 0.009 × STP + 0.38 × Pstrat − 2.53 | 0.24 | 0.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osterholz, W.; King, K.; Williams, M.; Hanrahan, B.; Duncan, E. Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4040067
Osterholz W, King K, Williams M, Hanrahan B, Duncan E. Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge. Soil Systems. 2020; 4(4):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4040067
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsterholz, William, Kevin King, Mark Williams, Brittany Hanrahan, and Emily Duncan. 2020. "Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge" Soil Systems 4, no. 4: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4040067
APA StyleOsterholz, W., King, K., Williams, M., Hanrahan, B., & Duncan, E. (2020). Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge. Soil Systems, 4(4), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4040067




