Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sites
2.2. Runoff Phosphorus Concentrations
2.3. Soil Test Phosphorus
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Test P
3.2. Surface Runoff and Tile Drainage Phosphorus Concentrations
3.3. Relationships between STP and FWM P Concentrations
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Test P
4.2. Relationships between STP and FWM P Concentrations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maccoux, M.J.; Dove, A.; Backus, S.M.; Dolan, D.M. Total and soluble reactive phosphorus loadings to Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1151–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scavia, D.; David Allan, J.; Arend, K.K.; Bartell, S.; Beletsky, D.; Bosch, N.S.; Brandt, S.B.; Briland, R.D.; Daloğlu, I.; DePinto, J.V.; et al. Assessing and addressing the re-eutrophication of lake erie: Central basin hypoxia. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Johnson, L.T.; Wynne, T.T.; Baker, D.B. Forecasting annual cyanobacterial bloom biomass to inform management decisions in Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.A.; Ulén, B.; Stamm, C.; Bechmann, M. Incidental phosphorus losses–are they significant and can they be predicted? J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2003, 166, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, H.; Withers, P.J.A.; Baas, P.; Chan, N.I.; Doody, D.; Holiman, J.; Jacobs, B.; Li, H.; MacDonald, G.K.; McDowell, R.; et al. Integrating legacy soil phosphorus into sustainable nutrient management strategies for future food, bioenergy and water security. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2016, 104, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; Johnson, L.T.; Smith, D.R.; LaBarge, G.A.; Fausey, N.R. Phosphorus availability in western lake erie basin drainage waters: Legacy evidence across spatial scales. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; King, K.W.; Johnson, L.; Francesconi, W.; Richards, P.; Baker, D.; Sharpley, A.N. Surface runoff and tile drainage transport of phosphorus in the midwestern USA. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Esbroeck, C.J.; Macrae, M.L.; Brunke, R.I.; McKague, K. Annual and seasonal phosphorus export in surface runoff and tile drainage from agricultural fields with cold temperate climates. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, L.A.; King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; LaBarge, G.A.; Duncan, E.W.; Fausey, N.R. Phosphorus export from artificially drained fields across the eastern corn belt. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetstra, M.A.; Tellez, C.; Wilson, R. 4R Nutrient Stewardship in the Western Lake Erie Basin Part II: A Panel Study; The Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vitosh, M.L.; Johnson, J.W.; Mengel, D.B. Tri-State Fertilizer Recommendations for Corn, Soybeans, Wheat, and Alfalfa; Ohio State University Agricultural Extension Bulletin E-2567: Columbus, OH, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Dayton, E.; LaBarge, G.A. Sensitivity analysis of the ohio phosphorus risk index. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Buda, A.R.; Easton, Z.M.; Lory, J.A.; Osmond, D.L.; Radcliffe, D.E.; Nelson, N.O.; Veith, T.L.; Doody, D.G. The promise, practice, and state of planning tools to assess site vulnerability to runoff phosphorus loss. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reid, K.; Schneider, K.; McConkey, B. Components of phosphorus loss from agricultural landscapes, and how to incorporate them into risk assessment tools. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andraski, T.W.; Bundy, L.G. Relationships between phosphorus levels in soil and in runoff from corn production systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djodjic, F. Phosphorus leaching in relation to soil type and soil phosphorus content. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, P.A.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Turner, B.L. Relating soil phosphorus to dissolved phosphorus in runoff: A single extraction coefficient for water quality modeling. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, D.B.; Johnson, L.T.; Confesor, R.B.; Crumrine, J.P. Vertical stratification of soil phosphorus as a concern for dissolved phosphorus runoff in the Lake Erie basin. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, E.W.; King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; LaBarge, G.; Pease, L.A.; Smith, D.R.; Fausey, N.R. Linking soil phosphorus to dissolved phosphorus losses in the midwest. Agric. Environ. Lett. 2017, 2, 170004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterholz, W.R.; Hanrahan, B.R.; King, K.W. Legacy Phosphorus concentration–discharge relationships in surface runoff and tile drainage from Ohio crop fields. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N. Soil mixing to decrease surface stratification of phosphorus in manured soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messiga, A.J.; Ziadi, N.; Morel, C.; Grant, C.; Tremblay, G.; Lamarre, G.; Parent, L.-E. Long term impact of tillage practices and biennial p and n fertilization on maize and soybean yields and soil P status. Field Crops Res. 2012, 133, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Huang, C.; Haney, R.L. Phosphorus fertilization, soil stratification, and potential water quality impacts. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 72, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahuja, L.R.; Sharpley, A.N.; Yamamoto, M.; Menzel, R.G. The depth of rainfall-runoff-soil interaction as determined by 32 P. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C.; Edwards, D.R.; Sharpley, A.N. Effect of extractable soil surface phosphorus on runoff water quality. Trans. ASAE 1993, 36, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torbert, H.A.; Daniel, T.C.; Lemunyon, J.L.; Jones, R.M. Relationship of soil test phosphorus and sampling depth to runoff phosphorus in calcareous and noncalcareous soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.; Sharpley, A.; Buda, A.; McDowell, R.; Allen, A. Soil Controls of phosphorus in runoff: Management barriers and opportunities. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 91, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gächter, R.; Ngatiah, J.M.; Stamm, C. Transport of phosphate from soil to surface waters by preferential flow. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Ford, W.; Buda, A.R.; Kennedy, C.D. Effect of tillage on macropore flow and phosphorus transport to tile drains: Tillage, macropore flow, and phosphorus. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 2868–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plach, J.M.; Macrae, M.L.; Williams, M.R.; Lee, B.D.; King, K.W. Dominant glacial landforms of the lower great lakes region exhibit different soil phosphorus chemistry and potential risk for phosphorus loss. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Duncan, E.W.; Pease, L.A.; Penn, C.J. Fertilizer placement and tillage effects on phosphorus concentration in leachate from fine-textured soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Ford, W.; Fausey, N.R. Edge-of-Field research to quantify the impacts of agricultural practices on water quality in Ohio. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 9A–12A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; LaBarge, G.A.; Smith, D.R.; Reutter, J.M.; Duncan, E.W.; Pease, L.A. Addressing agricultural phosphorus loss in artificially drained landscapes with 4R nutrient management practices. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, C.J.; Kryskalla, J.R. Methods of Analysis by the U.S. Geological Survey National Water Quality Laboratory: Evaluation of Alkaline Persulfate Digestion as an Alternative to Kjeldahl Digestion for the Determination of Total and Dissolved Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Water; Water Resources Investigations Report 03-4174; United States Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2003.
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Macrae, M.L.; Ford, W.; Van Esbroeck, C.; Brunke, R.I.; English, M.C.; Schiff, S.L. Uncertainty in nutrient loads from tile-drained landscapes: Effect of sampling frequency, calculation algorithm, and compositing strategy. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallarino, A.P. Spatial variability patterns of phosphorus and potassium in no-tilled soils for two sampling scales. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzon, J.D.; O’Halloran, I.P.; Fallow, D.J.; von Bertoldi, A.P.; Aspinall, D. Spatial variability of soil test phosphorus, potassium, and ph of ontario soils. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandt, S.; Ketterings, Q.M.; Lembo, A.J.; Vermeylen, F. In-field variability of soil test phosphorus and implications for agronomic and environmental phosphorus management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallarino, A.P.; Borges, R. Phosphorus and potassium distribution in soil following long-term deep-band fertilization in different tillage systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, J.R.; Mallarino, A.P. Soil-Test phosphorus and crop grain yield responses to long-term phosphorus fertilization for corn-soybean rotations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulford, A.M.; Culman, S.W. Over-fertilization does not build soil test phosphorus and potassium in ohio. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laboski, C.A.M.; Lamb, J.A. Changes in soil test phosphorus concentration after application of manure or fertilizer. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Moyer, B.G.; Elwinger, G.F. Effect of mineral and manure phosphorus sources on runoff phosphorus. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, M.L.; English, M.C.; Schiff, S.L.; Stone, M. Intra-annual variability in the contribution of tile drains to basin discharge and phosphorus export in a first-order agricultural catchment. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 92, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrahan, B.R.; King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; Duncan, E.W.; Pease, L.A.; LaBarge, G.A. Nutrient balances influence hydrologic losses of nitrogen and phosphorus across agricultural fields in northwestern Ohio. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 113, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deubel, A.; Hofmann, B.; Orzessek, D. Long-term effects of tillage on stratification and plant availability of phosphate and potassium in a loess chernozem. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchi, L.; Wendling, M.; Amossé, C.; Jeangros, B.; Sinaj, S.; Charles, R. Long and short term changes in crop yield and soil properties induced by the reduction of soil tillage in a long term experiment in Switzerland. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 174, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.S.; Beetstra, M.A.; Reutter, J.M.; Hesse, G.; Fussell, K.M.D.; Johnson, L.T.; King, K.W.; LaBarge, G.A.; Martin, J.F.; Winslow, C. Commentary: Achieving phosphorus reduction targets for Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.; Elliott, J.; Macrae, M.; Glenn, A. Near-surface soils as a source of phosphorus in snowmelt runoff from cropland. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, M.R.; Cornish, P.S. Soil sample depth in pasture soils for environmental soil phosphorus testing. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 42, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, P.D.; Radcliffe, D.E.; Cabrera, M.L. Rainfall timing and poultry litter application rate effects on phosphorus loss in surface runoff. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 2201–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pote, D.H.; Daniel, T.C.; Sharpley, A.N.; Moore, P.A.; Edwards, D.R.; Nichols, D.J. Relating extractable soil phosphorus to phosphorus losses in runoff. SOIL Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.; Foster, G.; Weesies, G.; McCool, D.; Yoder, D. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agriculture Handbook; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington DC, USA, 1997.
- Smith, D.R.; Francesconi, W.; Livingston, S.J.; Huang, C. Phosphorus losses from monitored fields with conservation practices in the Lake Erie basin, USA. AMBIO 2015, 44, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, F.R.; Hendricks, S.E. Soil test phosphorus and clay content effects on runoff water quality. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Mullins, G.L.; Zelazny, L.W. Mineralogy in relation to phosphorus sorption and dissolved phosphorus losses in runoff. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaynor, J.D.; Findlay, W.I. Soil and phosphorus loss from conservation and conventional tillage in corn production. J. Environ. Qual. 1995, 24, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Johnson, L.T.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, D.R.; Baker, D.B.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Confesor, R. Increased soluble phosphorus loads to Lake Erie: Unintended consequences of conservation practices? J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vidon, P.; Cuadra, P.E. Phosphorus dynamics in tile-drain flow during storms in The US Midwest. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Baker, D.B.; Johnson, L.T.; Smith, D.R.; Fausey, N.R. Hydrologic and biogeochemical controls on phosphorus export from western Lake Erie tributaries. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pease, L.A.; Fausey, N.R.; Martin, J.F.; Brown, L.C. Weather, landscape, and management effects on nitrate and soluble phosphorus concentrations in subsurface drainage in the western Lake Erie basin. Trans. ASABE 2018, 61, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, A.R.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; Srinivasan, M.S.; Bryant, R.B.; Feyereisen, G.W. Effects of hydrology and field management on phosphorus transport in surface runoff. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpley, A.; Jarvie, H.P.; Buda, A.; May, L.; Spears, B.; Kleinman, P. Phosphorus legacy: Overcoming the effects of past management practices to mitigate future water quality impairment. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1308–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shipitalo, M.J.; Gibbs, F. Potential of earthworm burrows to transmit injected animal wastes to tile drains. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 2103–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.K.; Rudolph, D.L.; Conant, B. Bromide and chloride tracer movement in macroporous tile-drained agricultural soil during an annual climatic cycle. J. Hydrol. 2012, 460–461, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Bryant, R.B.; Needelman, B.; Kleinman, P. Spatial distribution of soil phosphorus across selected New York dairy farm pastures and hay fields. Soil Sci. 2007, 172, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Surface Runoff * | Tile Drainage * | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Median | Min. | Max. | Mean | Median | Min. | Max. | ||
| STP (mg P kg−1) | 0–5 cm | 61 | 54 | 19 | 145 | 66 | 57 | 19 | 202 |
| 0–20 cm | 40 | 35 | 12 | 121 | 44 | 37 | 12 | 150 | |
| STP coefficient of variation (%) | 0–5 cm | 35 | 31 | 6 | 83 | 32 | 29 | 2 | 83 |
| 0–20 cm | 39 | 34 | 7 | 108 | 36 | 33 | 1 | 108 | |
| Pstrat † | 1.98 | 1.90 | 1.18 | 3.35 | 1.88 | 1.80 | 1.25 | 3.35 | |
| FWM DRP Conc (mg L−1) | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.66 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.27 | |
| FWM TP Conc (mg L−1) | 0.65 | 0.53 | 0.25 | 1.91 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.64 | |
| Total discharge (mm) | 283 | 242 | 20 | 735 | 87 | 64 | 9 | 279 | |
| Observed Increases (#) | Observed Decreases (#) | Mean of Absolute Values * | Largest Decrease * | Largest Increase * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STP | 0–5 cm | 30 | 18 | 14 | −52 | 102 |
| 0–20 cm | 31 | 17 | 9 | −32 | 25 | |
| STP coefficient of variation | 0–5 cm | 30 | 18 | 14 | −53 | 37 |
| 0–20 cm | 25 | 23 | 15 | −78 | 53 | |
| Pstrat † | 25 | 23 | 0.43 | −1.55 | 1.87 | |
| DRP | TP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Slope * | Regression Intercept * | R2 | RMSE | Regression Slope * | Regression Intercept * | R2 | RMSE | |
| Surface runoff | ||||||||
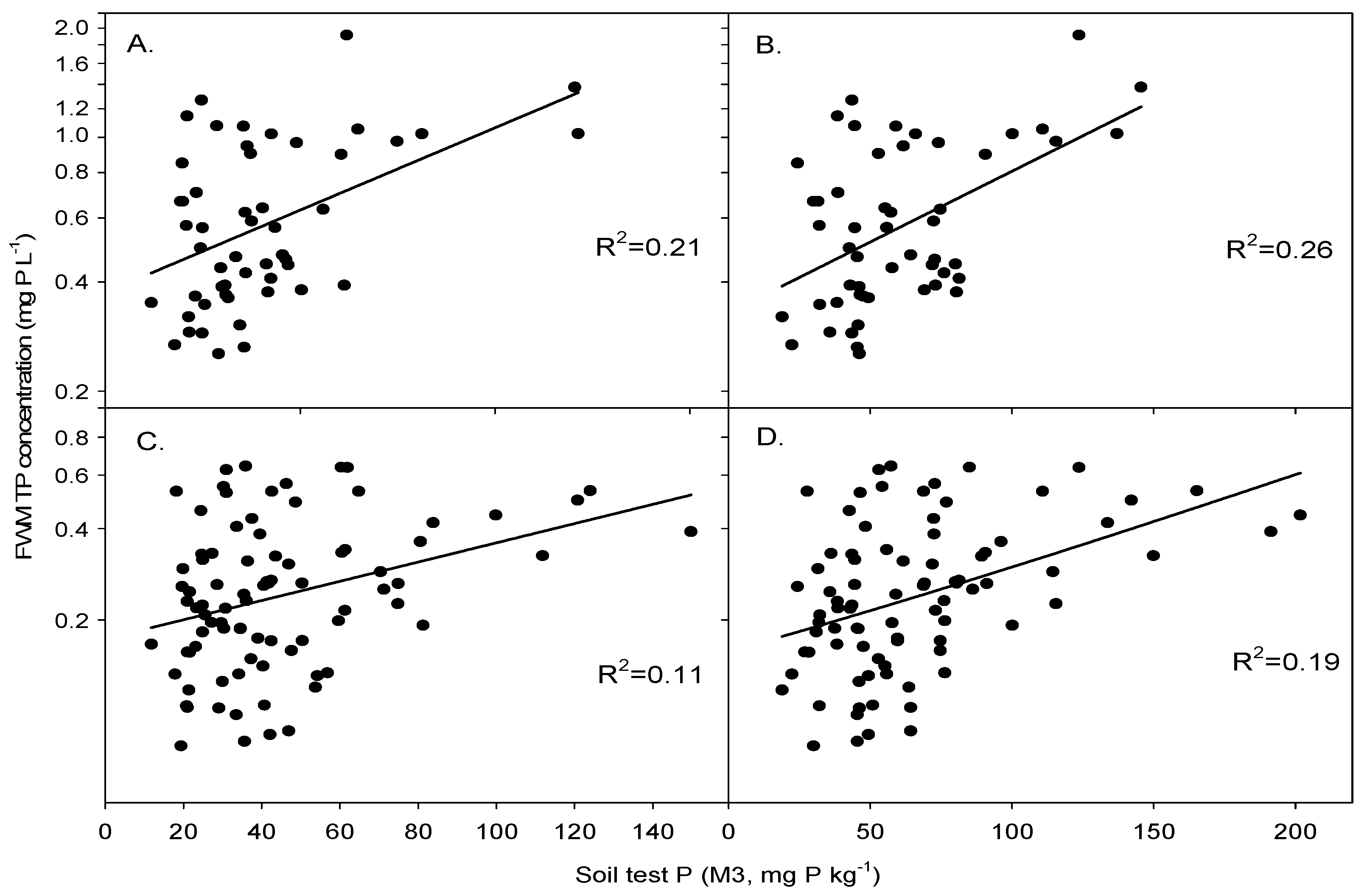
| 0–5 cm samples | 0.015 | −2.90 | 0.31 | 0.66 | 0.009 | −1.11 | 0.26 | 0.44 |
| 0–20 cm samples | 0.016 | −2.59 | 0.19 | 0.72 | 0.01 | −0.98 | 0.21 | 0.45 |
| Tile drainage | ||||||||
| 0–5 cm samples | 0.014 | −3.90 | 0.44 | 0.56 | 0.007 | −1.87 | 0.19 | 0.50 |
| 0–20 cm samples | 0.016 | −3.73 | 0.32 | 0.62 | 0.007 | −1.75 | 0.11 | 0.53 |
| Model * | R2 | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface runoff | |||
| FWM DRP | 0.020 × STP + 0.59 × Pstrat − 3.92 | 0.34 | 0.66 |
| FWM TP | 0.010 × STP − 0.98 | 0.21 | 0.45 |
| Tile drainage | |||
| FWM DRP | 0.019 × STP + 0.53 × Pstrat − 4.81 | 0.46 | 0.56 |
| FWM TP | 0.009 × STP + 0.38 × Pstrat − 2.53 | 0.24 | 0.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osterholz, W.; King, K.; Williams, M.; Hanrahan, B.; Duncan, E. Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4040067
Osterholz W, King K, Williams M, Hanrahan B, Duncan E. Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge. Soil Systems. 2020; 4(4):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4040067
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsterholz, William, Kevin King, Mark Williams, Brittany Hanrahan, and Emily Duncan. 2020. "Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge" Soil Systems 4, no. 4: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4040067
APA StyleOsterholz, W., King, K., Williams, M., Hanrahan, B., & Duncan, E. (2020). Stratified Soil Sampling Improves Predictions of P Concentration in Surface Runoff and Tile Discharge. Soil Systems, 4(4), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4040067




