Altered Bacterial Communities in Long-Term No-Till Soils Associated with Stratification of Soluble Aluminum and Soil pH
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Soil Sampling
2.2. Sample Preparation and Chemical Analyses
2.3. Soil Genomic DNA Extraction
2.4. Bacterial Community Sequencing and Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Chemistry of Soil Stratification
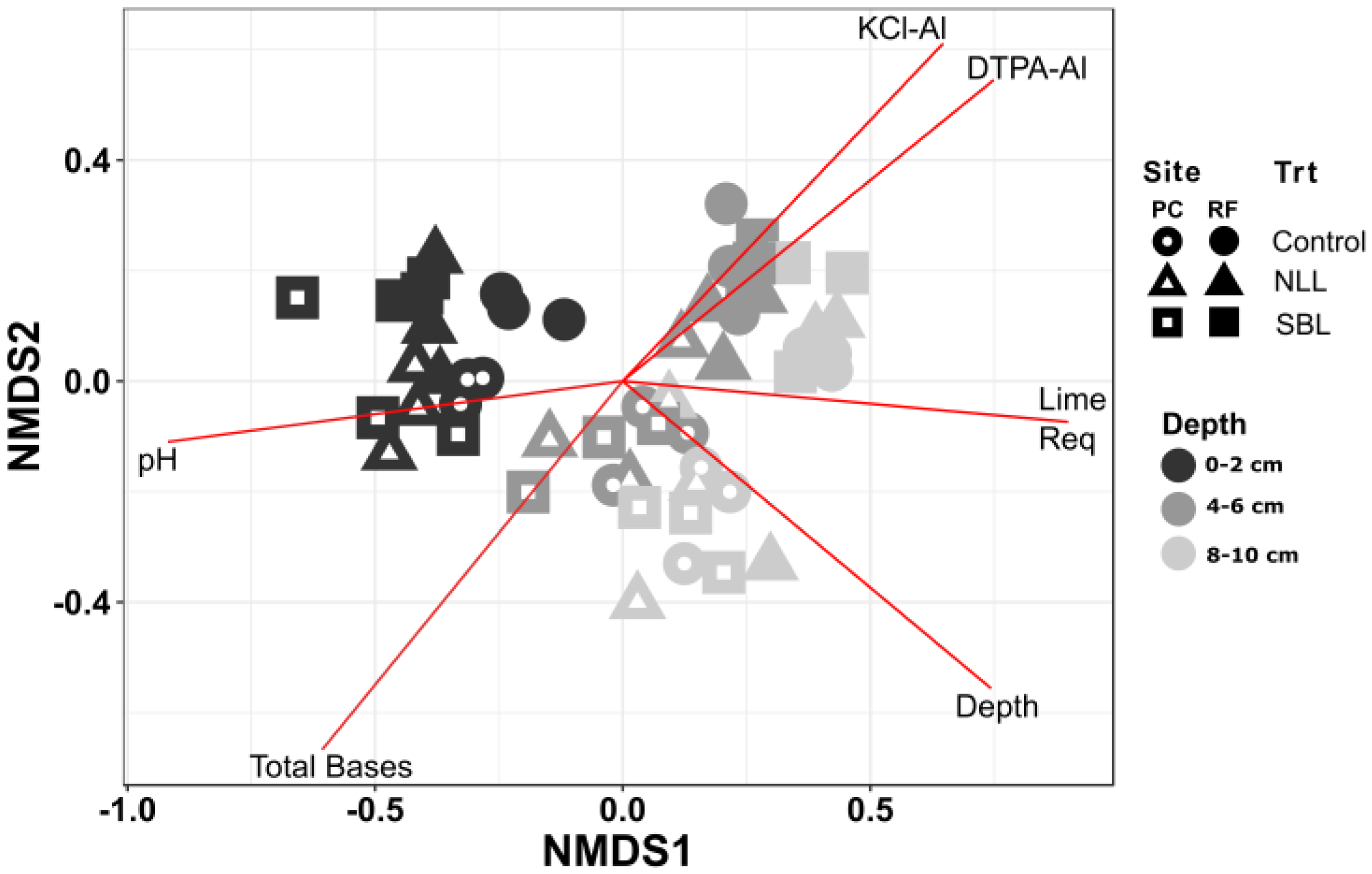
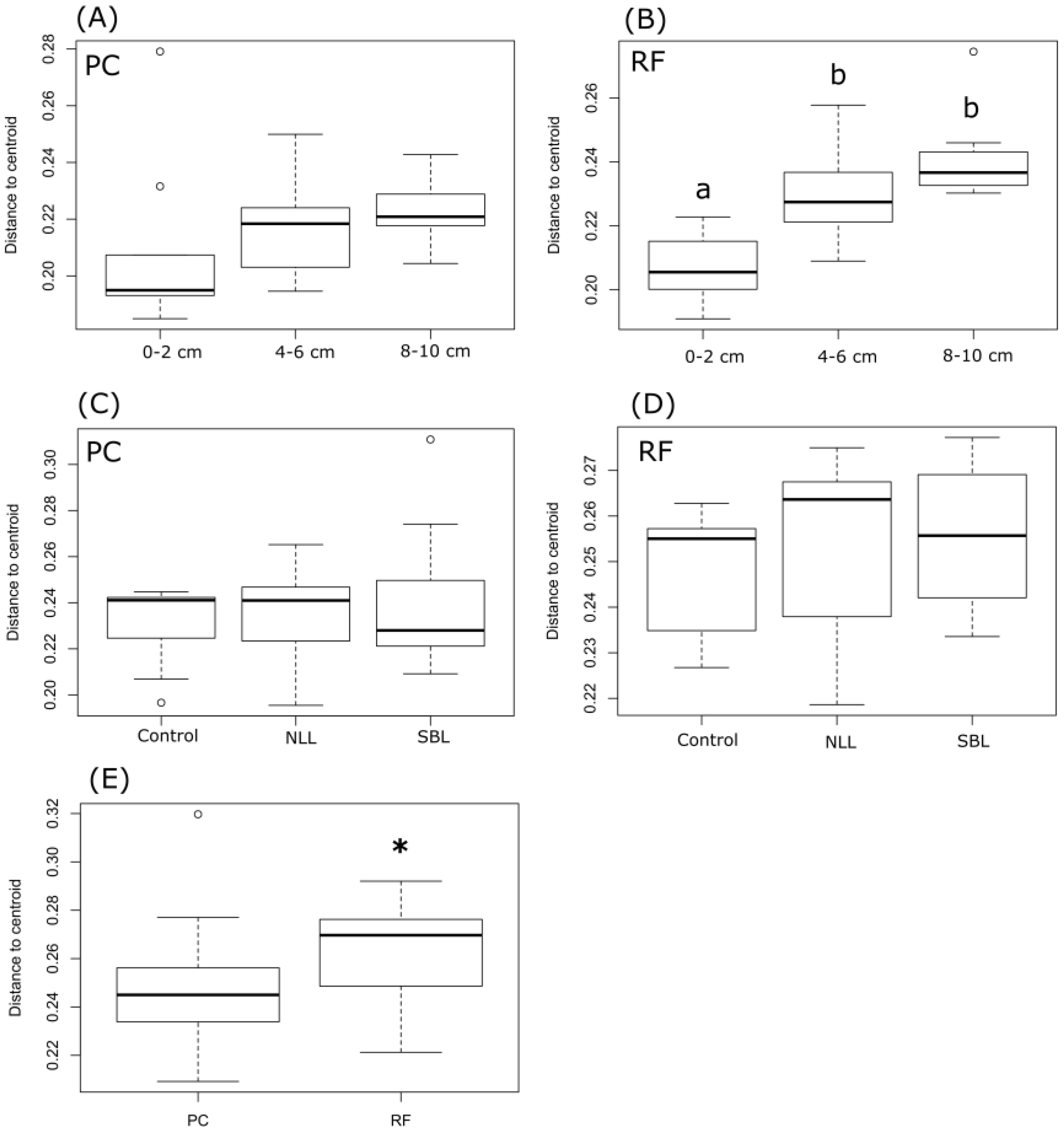
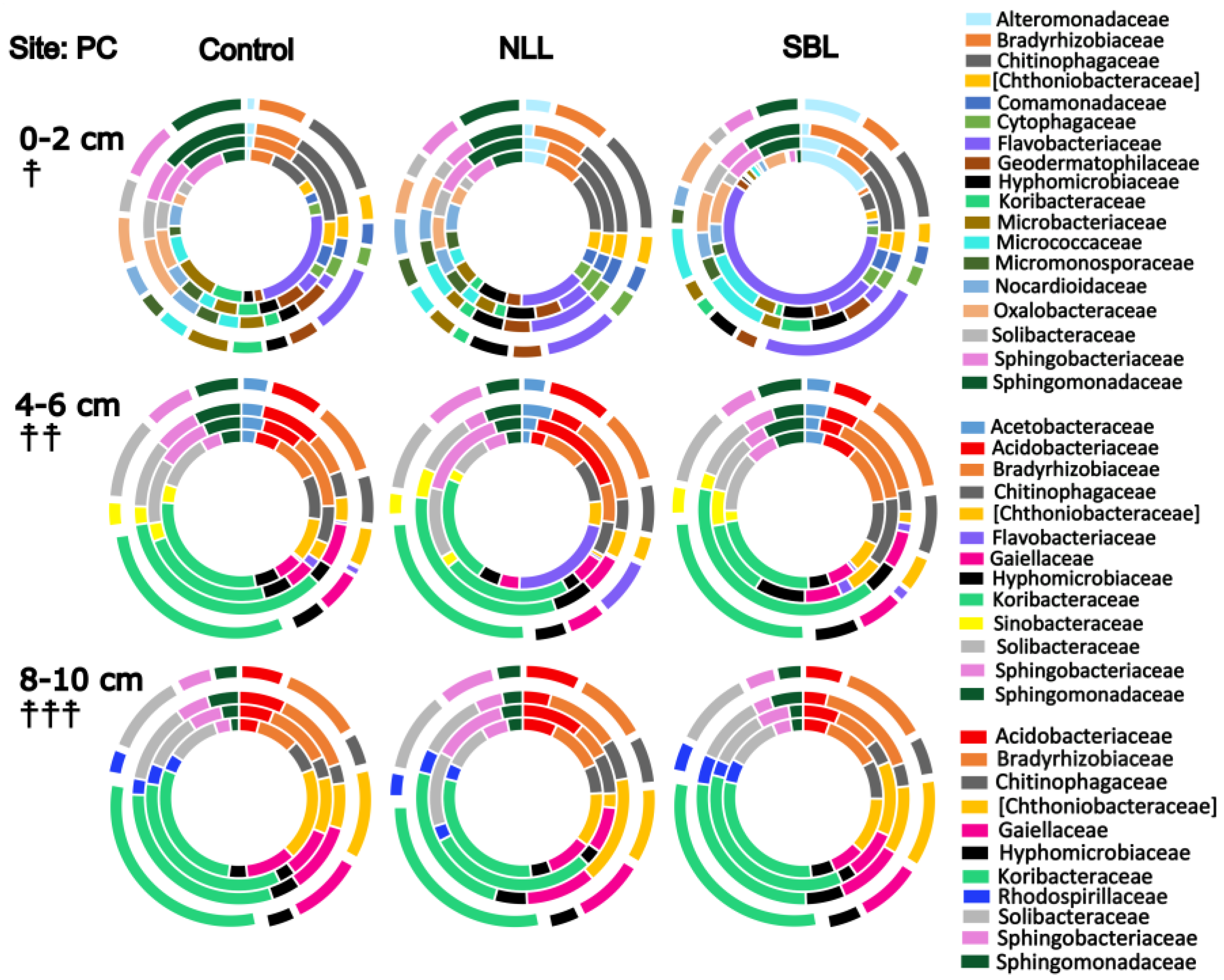
3.2. Soil Bacterial Community Composition
3.3. Taxonomic Stratification and Liming
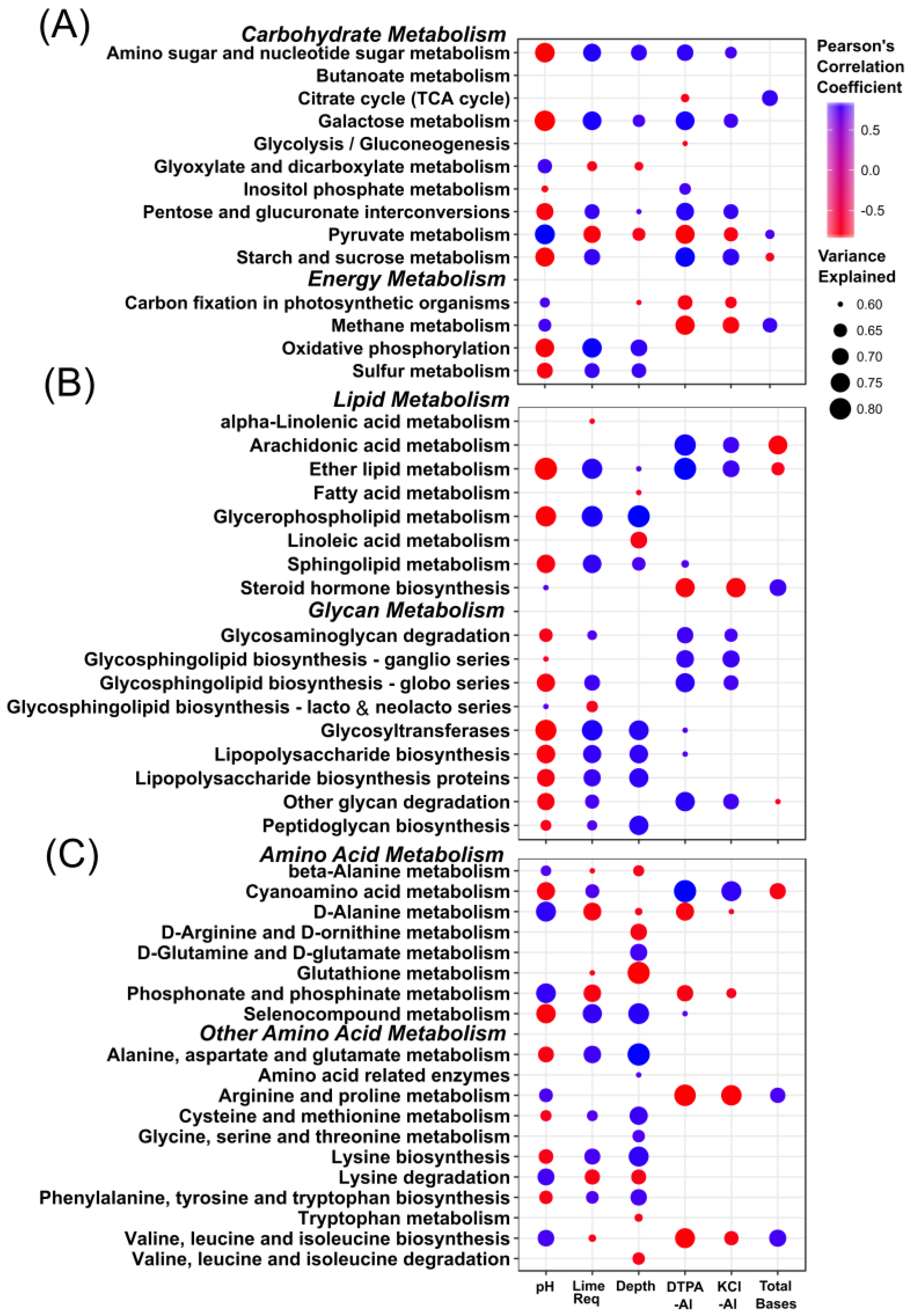
3.4. Stratification of Bacterial Function
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil pH, Lime, and Bacterial Community Composition
4.2. Stratification of Predicted Soil Community Function
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahler, R.L.; McDole, R.E. Effect of soil pH on crop yield in Northern Idaho1. Agron. J. 1987, 79, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Uexküll, H.R.; Mutert, E. Global extent, development and economic impact of acid soils. Plant Soil 1995, 171, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, J.H.; Ward, R.C.; Weil, R.R. Nutrient stratification in no-till soils. Agron. J. 2007, 65, 781–783. [Google Scholar]
- Sipilä, T.P.; Yrjälä, K.; Alakukku, L.; Palojärvi, A. Cross-site soil microbial communities under tillage regimes: Fungistasis and microbial biomarkers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8191–8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, F.; Lund, Z. Effect of chemical activity of soil solution aluminum on cotton root penetration of acid subsoils. Soil Sci. 1966, 101, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, C.; Han, S.; Appanna, V.P.; Thomas, S.C.; Ulibarri, G.; Appanna, V.D. Metabolic reengineering invoked by microbial systems to decontaminate aluminum: Implications for bioremediation technologies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartain, J.; Kamprath, E. Effect of liming a highly Al-saturated soil on the top and root growth and soybean nodulation. Agron. J. 1975, 67, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shann, J.; Bertsch, P. Differential cultivar response to polynuclear hydroxo-aluminum complexes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, V.P.; Reardon, C.R.; Coffey, T.; Klein, A.M.; McFarland, C.L.; Huggins, D.R.; Sullivan, T.S. Stratification of soil chemical and microbial properties under no-till management after lime amendment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Kunito, T.; Isomura, I.; Sumi, H.; Park, H.-D.; Toda, H.; Otsuka, S.; Nagaoka, K.; Saeki, K.; Senoo, K. Aluminum and acidity suppress microbial activity and biomass in acidic forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joris, H.A.W.; Caires, E.F.; Bini, A.R.; Scharr, D.A.; Haliski, A. Effects of soil acidity and water stress on corn and soybean performance under a no-till system. Plant Soil 2013, 365, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, C.R.; Naderman, G.C.; Tucker, M.R.; Sugg, R.E. Nutrient and pH stratification with conventional and no-till management. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1999, 30, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, F.; Fortin, M.-C.; Staton, M. Periodic plowing effects on soil properties in a no-till farming system. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.A.; Dalal, R.C.; Standley, J. No-till effects on organic matter, pH, cation exchange capacity and nutrient distribution in a luvisol in the semi-arid subtropics. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, D.; Fontana, P.; De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Donati, C. Micca: A complete and accurate software for taxonomic profiling of metagenomic data. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Clemente, J.C.; Kuczynski, J.; Rideout, J.R.; Stombaugh, J.; Wendel, D.; Wilke, A.; Huse, S.; Hufnagle, J.; Meyer, F. The Biological Observation Matrix (BIOM) format or: How I learned to stop worrying and love the ome-ome. GigaScience 2012, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Oksanen, M.J.; Suggests, M. The vegan package. Community Ecol. Package 2007, 10, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. A layered grammar of graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2010, 19, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meron, D.; Atias, E.; Iasur Kruh, L.; Elifantz, H.; Minz, D.; Fine, M.; Banin, E. The impact of reduced pH on the microbial community of the coral acropora eurystoma. ISME J. 2011, 5, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.R.; Condron, L.M.; Clough, T.J.; Fiers, M.; Stewart, A.; Hill, R.A.; Sherlock, R.R. Biochar induced soil microbial community change: Implications for biogeochemical cycling of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Pedobiologia 2011, 54, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obia, A.; Cornelissen, G.; Mulder, J.; Dörsch, P. Effect of soil ph increase by biochar on NO, N2O and N2 production during denitrification in acid soils. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, R.; Chu, H.; Shen, R. Aluminum tolerance of wheat does not induce changes in dominant bacterial community composition or abundance in an acidic soil. Plant Soil 2013, 367, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielak, A.M.; Barreto, C.C.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; van Veen, J.A.; Kuramae, E.E. The ecology of acidobacteria: Moving beyond genes and genomes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Hulbert, S.H.; Schroeder, K.L.; Mavrodi, O.; Mavrodi, D.; Dhingra, A.; Schillinger, W.F.; Paulitz, T.C. Role of bacterial communities in the natural suppression of Rhizoctonia solani bare patch disease of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7428–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soman, C.; Li, D.; Wander, M.M.; Kent, A.D. Long-term fertilizer and crop-rotation treatments differentially affect soil bacterial community structure. Plant Soil 2017, 413, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendrula-Kotha, R.; Nkongolo, K.K. Microbial response to soil liming of damaged ecosystems revealed by pyrosequencing and phospholipid fatty acid analyses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalenberger, A.; O’Sullivan, O.; Gahan, J.; Cotter, P.D.; Courtney, R. Bacterial communities established in bauxite residues with different restoration histories. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7110–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemire, J.; Mailloux, R.; Auger, C.; Whalen, D.; Appanna, V.D. Pseudomonas fluorescens orchestrates a fine metabolic-balancing act to counter aluminium toxicity. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wood, M. A mechanism of aluminium toxicity to soil bacteria and possible ecological implications. Plant Soil 1995, 171, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lu, C.; Jiang, H.; Peng, J. Global transcriptome analysis reveals distinct aluminum-tolerance pathways in the al-accumulating species Hydrangea macrophylla and marker identification. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Depth | KCl-Al | Total Bases | Lime Req | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCl-Al | 0.34 | ||||
| Total Bases | 0.21 | 0.71 | |||
| Lime Req | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.52 | ||
| pH | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.64 | 0.96 | |
| DTPA-Al | 0.34 | 0.76 | 0.90 | 0.67 | 0.73 |
| Depth (cm) | RF Soil pH | RF DTPA-Al | RF KCl-Al | PC Soil pH | PC DTPA-Al | PC KCl-Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |||
| Control | ||||||
| 0–2 | 5.1 ± 0.04 (a, x) | 23 ± 3 (a, x) | 14 ± 5 (a, x) | 5.4 ± 0.3 (a, x) | 11 ± 2 (a, x) | 2 ± 2 (a, x) |
| 4–6 | 4.4 ± 0.1 (b, x) | 40 ± 4 (a, x) | 132 ± 7 (a, x) | 4.9 ± 0.1 (b, x) | 19 ± 4 (a, x) | 34 ± 19 (a, x) |
| 8–10 | 4.4 ± 0.2 (b, x) | 40 ± 4 (a, x) | 143 ± 6 (a, x) | 4.8 ± 0.2 (b, x) | 16 ± 5 (a, x) | 37 ± 24 (a, x) |
| NLL | ||||||
| 0–2 | 6.2 ± 0.2 (a, y) | 9 ± 4 (a, y) | 1 ± 2 (a, x) | 6.7 ± 0.2 (a, y) | 2 ± 1 (a, y) | 1 ± 0 (a, x) |
| 4–6 | 4.7 ± 0.1 (b, x) | 36 ± 4 (a, x) | 70 ± 15 (a, y) | 5.2 ± 0.1 (a, y) | 14 ± 3 (a, x) | 6 ± 6 (a, x) |
| 8–10 | 4.4 ± 0.2 (c, x) | 36 ± 6 (a, x) | 127 ± 34 (a, x) | 4.9 ± 0.1 (a,x) | 17 ± 3 (a, x) | 30 ± 22 (a, x) |
| SBL | ||||||
| 0–2 | 6.4 ± 0.2 (a, y) | 5 ± 2(a, y) | 3 ± 2 (a, x) | 6.7 ± 0.2 (a, y) | 1 ± 0 (a, y) | 1 ± 1 (a, x) |
| 4–6 | 4.5 ± 0.2 (a, x) | 36 ± 3 (a, x) | 106 ± 43 (a, xy) | 5.3 ± 0.4 (a, y) | 13 ± 3 (a, x) | 6 ± 9 (a, x) |
| 8–10 | 4.3 ± 0.1 (a, x) | 41 ± 1 (a, x) | 200 ± 31 (a, y) | 4.9 ± 0.2 (a, x) | 17 ± 3 (a, x) | 19 ± 19 (a, x) |
| Depth (cm) | RF Observed | RF Shannon’s Index | PC Observed | PC Shannon’s Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | ||||
| 0–2 | 2504 ± 64 (a) | 6.5 ± 0.1 (a) | 2607 ± 125 (a) | 6.6 ± 0.2 (a) |
| 4–6 | 1915 ± 59 (b) | 5.5 ± 0.2 (b) | 2294 ± 265 (b) | 6.2 ± 0.2 (b) |
| 8–10 | 1754 ± 49 (b) | 5.2 ± 0.2 (b) | 2139 ± 132 (b) | 5.9 ± 0.2 (b) |
| NLL | ||||
| 0–2 | 2726 ± 318 (a) | 6.6 ± 0.4 (a) | 2902 ± 240 (a) | 6.9 ± 0.1 (a) |
| 4–6 | 1975 ± 135 (b) | 5.7 ± 0.2 (b) | 2362 ± 363 (b) | 6.1 ± 0.4 (b) |
| 8–10 | 1956 ± 366 (b) | 5.6 ± 0.5 (b) | 2283 ± 262 (b) | 6.0 ± 0.2 (b) |
| SBL | ||||
| 0–2 | 2708 ± 169 (a) | 6.6 ± 0.2 (a) | 2631 ± 608 (a) | 6.0 ± 1.4 (a) |
| 4–6 | 1823 ± 45 (b) | 5.5 ± 0.03 (b) | 2528 ± 353 (b) | 6.4 ± 0.5 (b) |
| 8–10 | 1786 ± 122 (b) | 5.2 ± 0.3 (b) | 2194 ± 95 (b) | 5.9 ± 0.1 (b) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lewis, R.W.; Barth, V.P.; Coffey, T.; McFarland, C.; Huggins, D.R.; Sullivan, T.S. Altered Bacterial Communities in Long-Term No-Till Soils Associated with Stratification of Soluble Aluminum and Soil pH. Soil Syst. 2018, 2, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils2010007
Lewis RW, Barth VP, Coffey T, McFarland C, Huggins DR, Sullivan TS. Altered Bacterial Communities in Long-Term No-Till Soils Associated with Stratification of Soluble Aluminum and Soil pH. Soil Systems. 2018; 2(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils2010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLewis, Ricky W., Victoria P. Barth, Todd Coffey, Carol McFarland, David R. Huggins, and Tarah S. Sullivan. 2018. "Altered Bacterial Communities in Long-Term No-Till Soils Associated with Stratification of Soluble Aluminum and Soil pH" Soil Systems 2, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils2010007
APA StyleLewis, R. W., Barth, V. P., Coffey, T., McFarland, C., Huggins, D. R., & Sullivan, T. S. (2018). Altered Bacterial Communities in Long-Term No-Till Soils Associated with Stratification of Soluble Aluminum and Soil pH. Soil Systems, 2(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils2010007




