Case Reports of Teprotumumab as Treatment for Monoclonal Antibody-Induced Thyroid Orbitopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction and Clinical Significance
2. Case Presentation
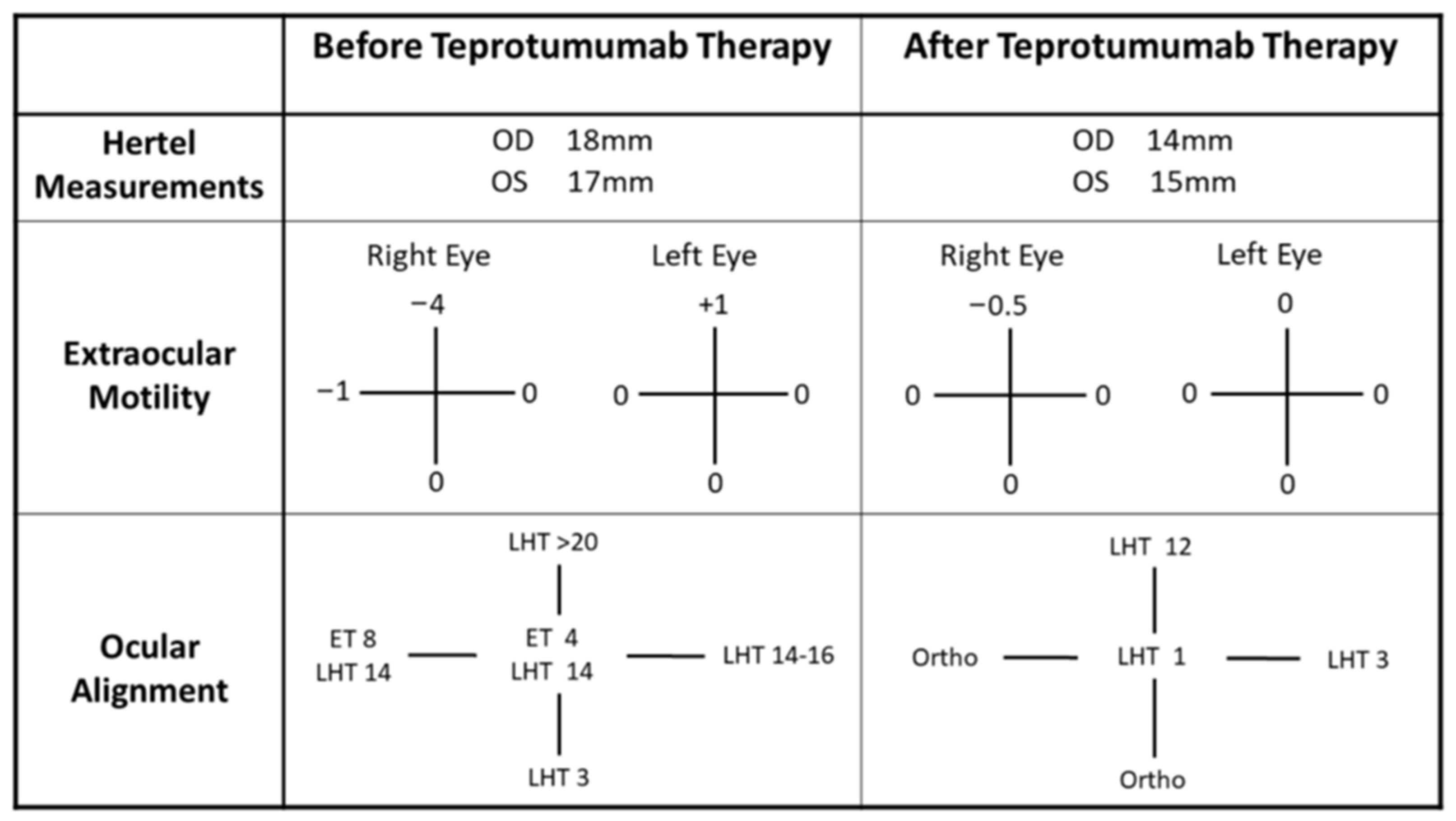
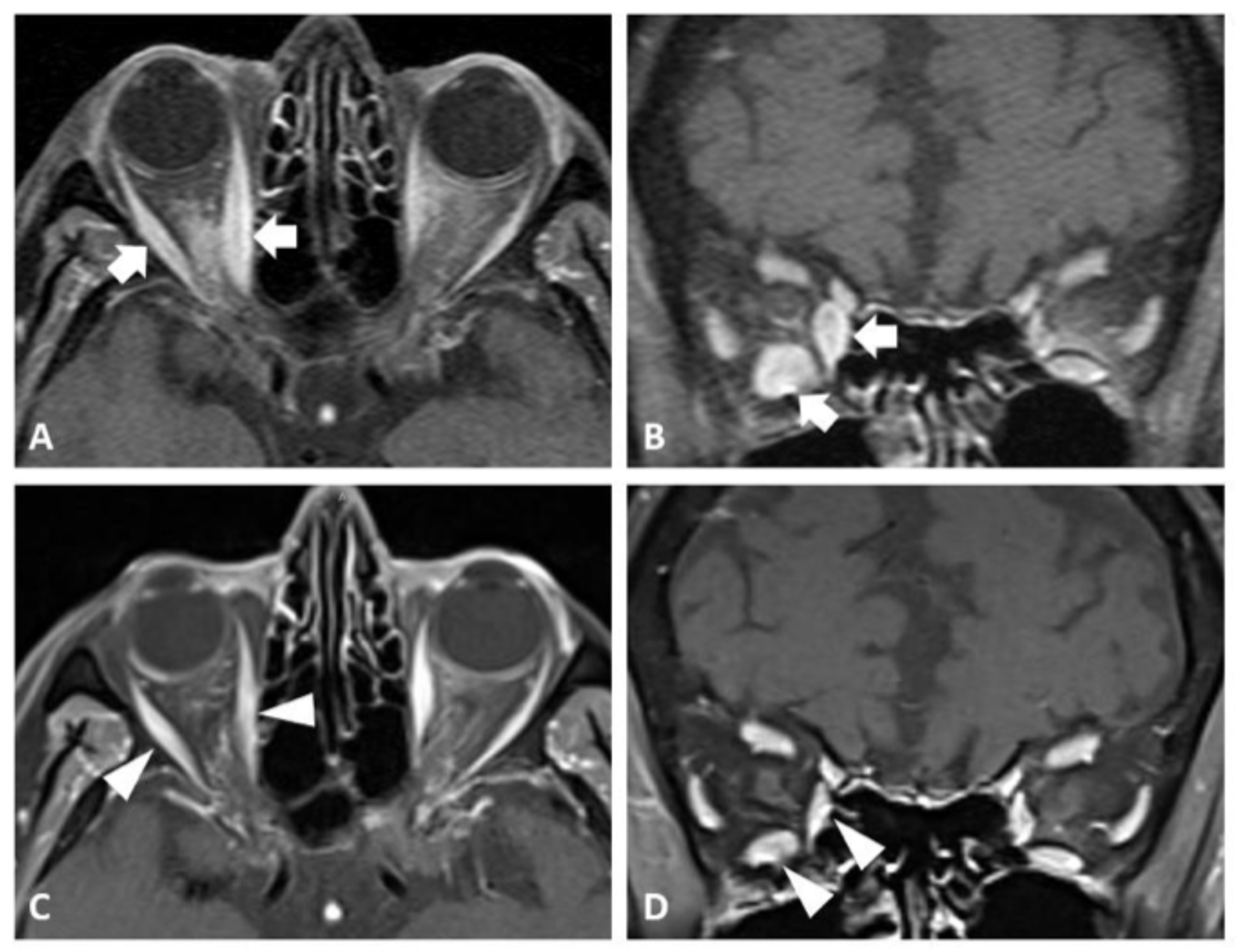
2.1. Case 1
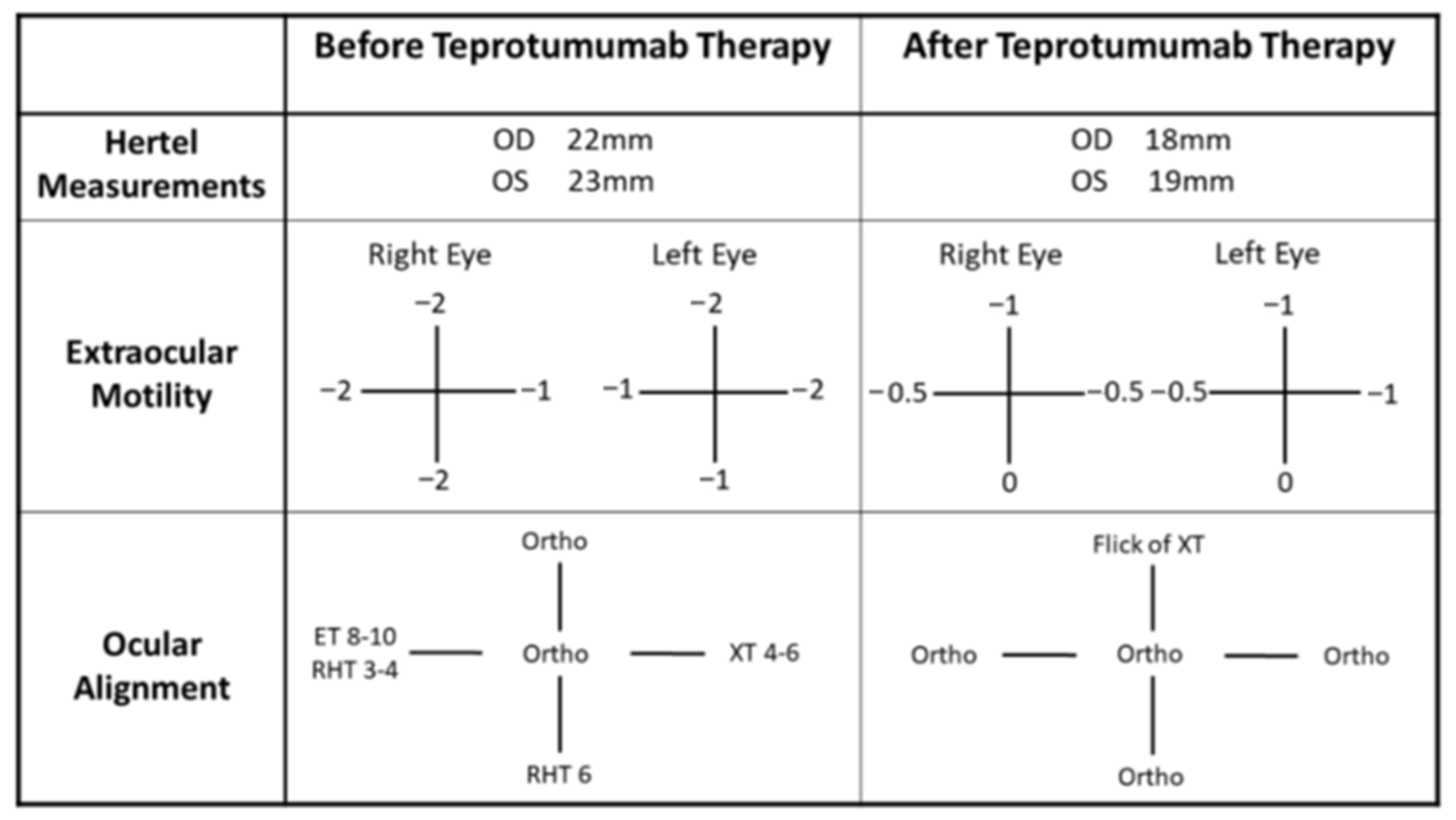
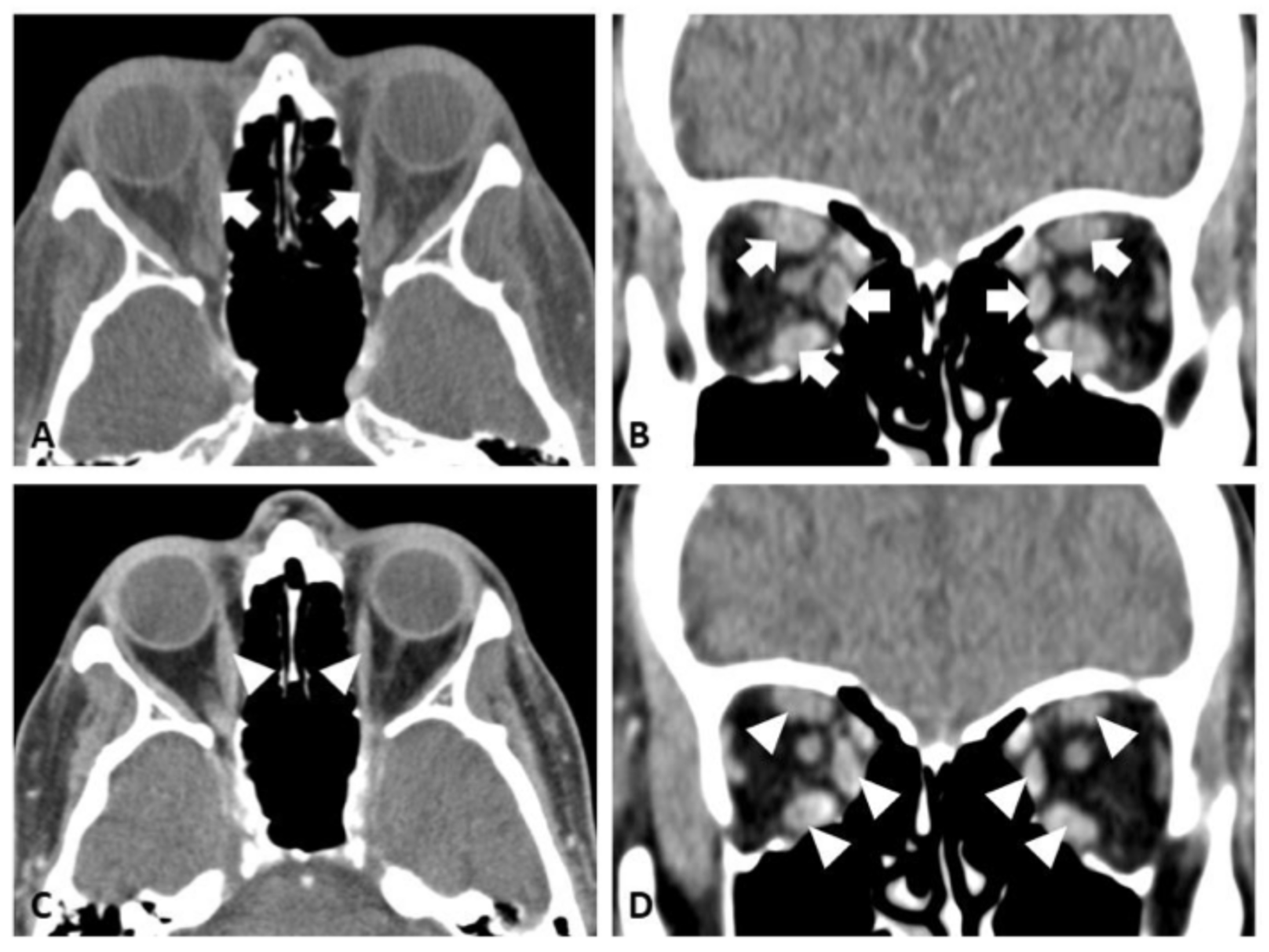
2.2. Case 2
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TED | Thyroid Eye Disease |
| IRAE | Immune-Related Adverse Events |
| mAb | Monoclonal Antibodies |
| IGF | Insulin-Like Growth Factor |
| TSH | Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone |
| CAS | Clinical Activity Score |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| TSI | Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulin |
| IV | Intravenous |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| TRAb | Thyrotropin Receptor Antibody |
| PD-1 | Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic Lymphocyte-Associated Protein-4 |
| AITD | Autoimmune Thyroid Disease |
| AITED | Autoimmune Thyroid Eye Disease |
References
- Castelli, M.S.; McGonigle, P.; Hornby, P.J. The pharmacology and therapeutic applications of monoclonal antibodies. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2019, 7, e00535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campredon, P.; Imbert, P.; Mouly, C.; Grunenwald, S.; Mazières, J.; Caron, P. Severe Inflammatory Ophthalmopathy in a Euthyroid Patient during Nivolumab Treatment. Eur. Thyroid J. 2018, 7, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, E.; Hadi, A.; Nair, G.; Bursztyn, L.L.; Fraser, J.A.; Ing, E.B. Incidence of alemtuzumab-induced thyroid-associated orbitopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Y.; Salem, J.E.; Cohen, J.V.; Chandra, S.; Menzer, C.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S.; Das, S.; Beckermann, K.E.; Ha, L.; et al. Fatal Toxic Effects Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michot, J.; Bigenwald, C.; Champiat, S.; Collins, M.; Carbonnel, F.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Berdelou, A.; Varga, A.; Bahleda, R.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. Immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint blockade: A comprehensive review. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 54, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, O.; Oweira, H.; Petrausch, U.; Helbling, D.; Schmidt, J.; Mannhart, M.; Mehrabi, A.; Schöb, O.; Giryes, A. Immune-related ocular toxicities in solid tumor patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2017, 17, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvin, L.A.; Shields, C.L.; Orloff, M.; Sato, T.; Shields, J.A. Checkpoint Inhibitor Immune Therapy: Systemic Indications and Ophthalmic Side Effects. Retina 2018, 38, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Rutkowski, P.; Grob, J.-J.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Wagstaff, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Ferrucci, P.F.; et al. Overall Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoushtari, A.N.; Friedman, C.F.; Navid-Azarbaijani, P.; Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Momtaz, P.; Panageas, K.S.; Wolchok, J.D.; Chapman, P.B. Measuring Toxic Effects and Time to Treatment Failure for Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Melanoma. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomze, D.; Meirson, T.; Hasan Ali, O.; Goldman, A.; Flatz, L.; Habot-Wilner, Z. Ocular Adverse Events Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2022, 30, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, L.-S.; Cheng, J.-W.; Cai, J.-P.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.-Y.; Wei, R.-L. Meta-analysis of Association Between the +49A/G Polymorphism of Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen-4 and Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy. Curr. Eye Res. 2015, 40, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.P.; Chu, Y.C.; Wen, Y.H.; Lin, W.T.; Hour, A.L.; Wang, W.T. Investigation of the Correlation between Graves’ Ophthalmopathy and CTLA4 Gene Polymorphism. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, T.; Hidaka, Y.; Guimaraes, V.; Soliman, M.; DeGroot, L.J. CTLA-4 gene polymorphism associated with Graves’ disease in a Caucasian population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmar, M.; Kahaly, G.J. Immunoregulatory and Susceptibility Genes in Thyroid and Polyglandular Autoimmunity. Thyroid 2005, 15, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodic, G.; Hinkle, D.M.; Cia, Y. Drug-Induced Graves Disease From CTLA-4 Receptor Suppression. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 27, e87–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, A.J.; Twyman, C.L.; Arnold, D.L.; Cohen, J.A.; Confavreux, C.; Fox, E.J.; Hartung, H.-P.; Havrdova, E.; Selmaj, K.W.; Weiner, H.L.; et al. Alemtuzumab for patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis after disease-modifying therapy: A randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Bian, K.; Li, C. Alemtuzumab for haematological malignancies. Ann. Hematol. 2025, 104, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnera, C.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Alemtuzumab: A review of efficacy and risks in the treatment of relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twyman, C.; Oyuela, P.; Palmer, J.; Margolin, D.; Dayan, C. Thyroid Autoimmune Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Alemtuzumab for Relapsing-remitting Multiple Sclerosis: Four-year Follow-up of the CARE-MS Studies (P2.199). Neurology 2014, 82 (Suppl. 10), P2.199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scappaticcio, L.; Castellana, M.; Virili, C.; Bellastella, G.; Centanni, M.; Cannavò, S.; Campennì, A.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Giovanella, L.; Trimboli, P. Alemtuzumab-induced thyroid events in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, J.; Muller, I.; Mian, C. Clinical management of alemtuzumab-induced autoimmune thyroid diseases: A narrative review. Eur. Thyroid J. 2025, 14, e250007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Thompson, S.A.J.; Loh, P.; Davies, J.L.; Tuohy, O.C.; Curry, A.J.; Azzopardi, L.; Hill-Cawthorne, G.; Fahey, M.T.; Compston, A.; et al. Human autoimmunity after lymphocyte depletion is caused by homeostatic T-cell proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20200–20205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Phuah, C.-L.; Cox, A.L.; Thompson, S.A.; Ban, M.; Shawcross, J.; Walton, A.; Sawcer, S.J.; Compston, A.; Coles, A.J. IL-21 drives secondary autoimmunity in patients with multiple sclerosis, following therapeutic lymphocyte depletion with alemtuzumab (Campath-1H). J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pariani, N.; Willis, M.; Muller, I.; Healy, S.; Nasser, T.; McGowan, A.; Lyons, G.; Jones, J.; Chatterjee, K.; Dayan, C.; et al. Alemtuzumab-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction Exhibits Distinctive Clinical and Immunological Features. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3010–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, J.C.P.; Moran, C.; Chatterjee, V.K.; Jones, J.; Coles, A.; Murthy, R. Immune reconstitution after alemtuzumab therapy for multiple sclerosis triggering Graves’ orbitopathy: A case series. Eye 2019, 33, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, A.R.; Clarke, A.M.; Wooldridge, T.; Waldmann, H.; Hale, G.; Symmons, D.; Hazleman, B.L.; Isaacs, J.D. Morbidity and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis patients with prolonged therapy-induced lymphopenia: Twelve-year outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinari, L.; Lapalombella, R.; Andritsos, L.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Lin, T.S.; Byrd, J.C. Alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3644–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinblatt, M.E.; Maddison, P.J.; Bulpitt, K.J.; Hazleman, B.L.; Urowitz, M.B.; Sturrock, R.D.; Coblyn, J.S.; Maier, A.L.; Spreen, W.R.; Manna, V.K.; et al. Campath-1h, a humanized monoclonal antibody, in refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmalan, A.; Blecher, N.; Hyder, S.; Couch, S.M.; Godfrey, K.J.; Stan, M.N.; Bradley, E.A.; Wagner, L.H.; Tooley, A.A. Alemtuzumab-Induced Thyroid Eye Disease: A Comprehensive Case Series and Review of the Literature. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 39, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez De Vera Gómez, P.; Méndez Muros, M.; Torres Cuadro, A.; de Miera, F.J.T.S.; Ruiz, R.L.; Vázquez, R.G.; González, J.J.G.; Hermosilla, A.M.G.; Hernández, T.M. Alemtuzumab induces severe orbitopathy in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.M.; Jesus, G.G.J.; Cuadrado, A.T.; Manuel, G.H.A. Graves’ orbitopathy caused by alemtuzumab: A case series. Endocr. Abstr. 2022, 81, ep959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, R.S.; Kahaly, G.J.; Patel, A.; Sile, S.; Thompson, E.H.; Perdok, R.; Fleming, J.C.; Fowler, B.T.; Marcocci, C.; Marinò, M.; et al. Teprotumumab for the Treatment of Active Thyroid Eye Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, J.; Duncan, N.; Yorio, J.; Meltzer, E.; Aung, M.H. Case Reports of Teprotumumab as Treatment for Monoclonal Antibody-Induced Thyroid Orbitopathy. Reports 2025, 8, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040246
Moon J, Duncan N, Yorio J, Meltzer E, Aung MH. Case Reports of Teprotumumab as Treatment for Monoclonal Antibody-Induced Thyroid Orbitopathy. Reports. 2025; 8(4):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040246
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Jared, Nicole Duncan, Jeff Yorio, Ethan Meltzer, and Moe H. Aung. 2025. "Case Reports of Teprotumumab as Treatment for Monoclonal Antibody-Induced Thyroid Orbitopathy" Reports 8, no. 4: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040246
APA StyleMoon, J., Duncan, N., Yorio, J., Meltzer, E., & Aung, M. H. (2025). Case Reports of Teprotumumab as Treatment for Monoclonal Antibody-Induced Thyroid Orbitopathy. Reports, 8(4), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040246





