Multimodality Imaging of Moyamoya Disease: A Practical Guide for Neuroradiologists Based on a Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction and Clinical Significance
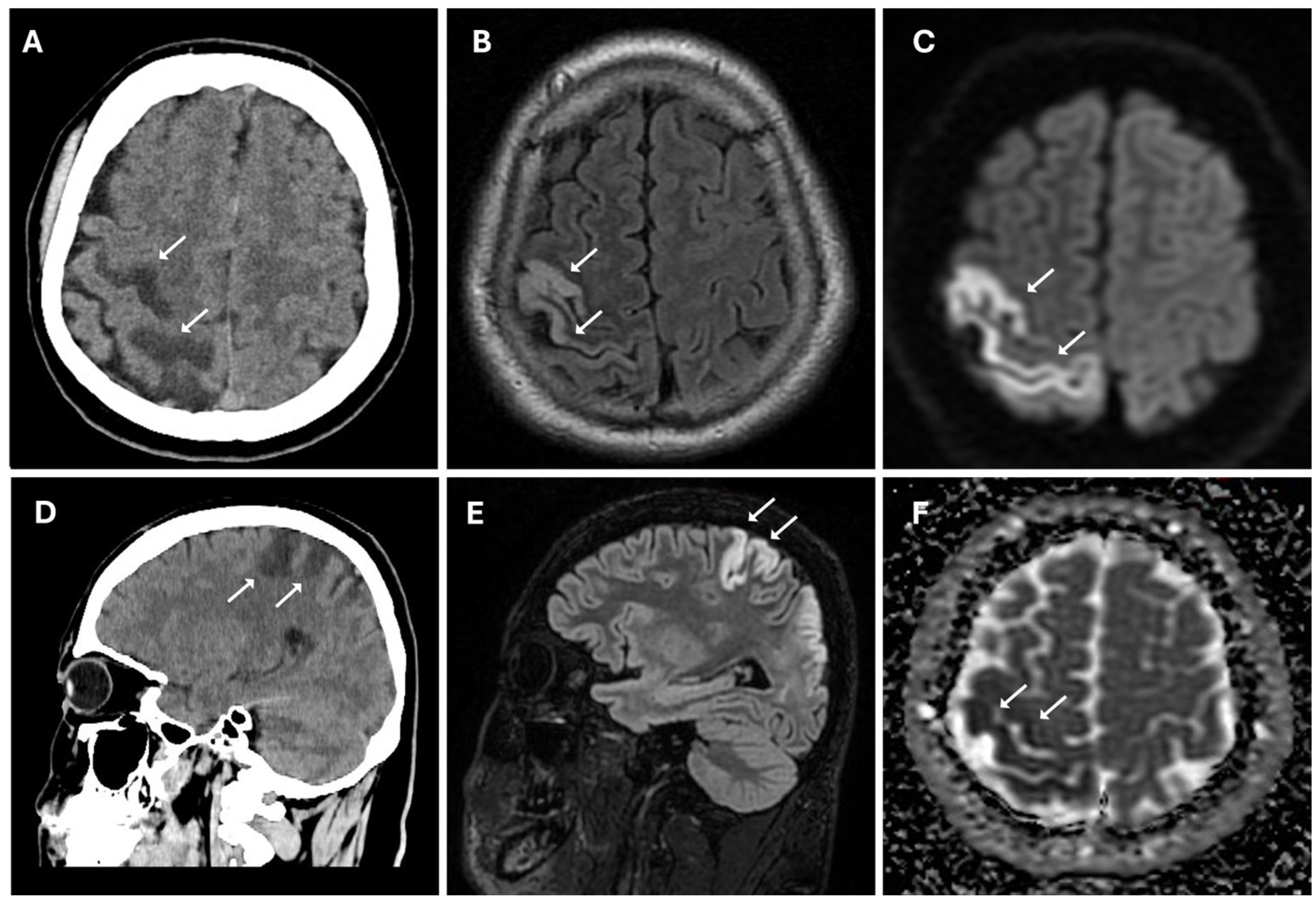
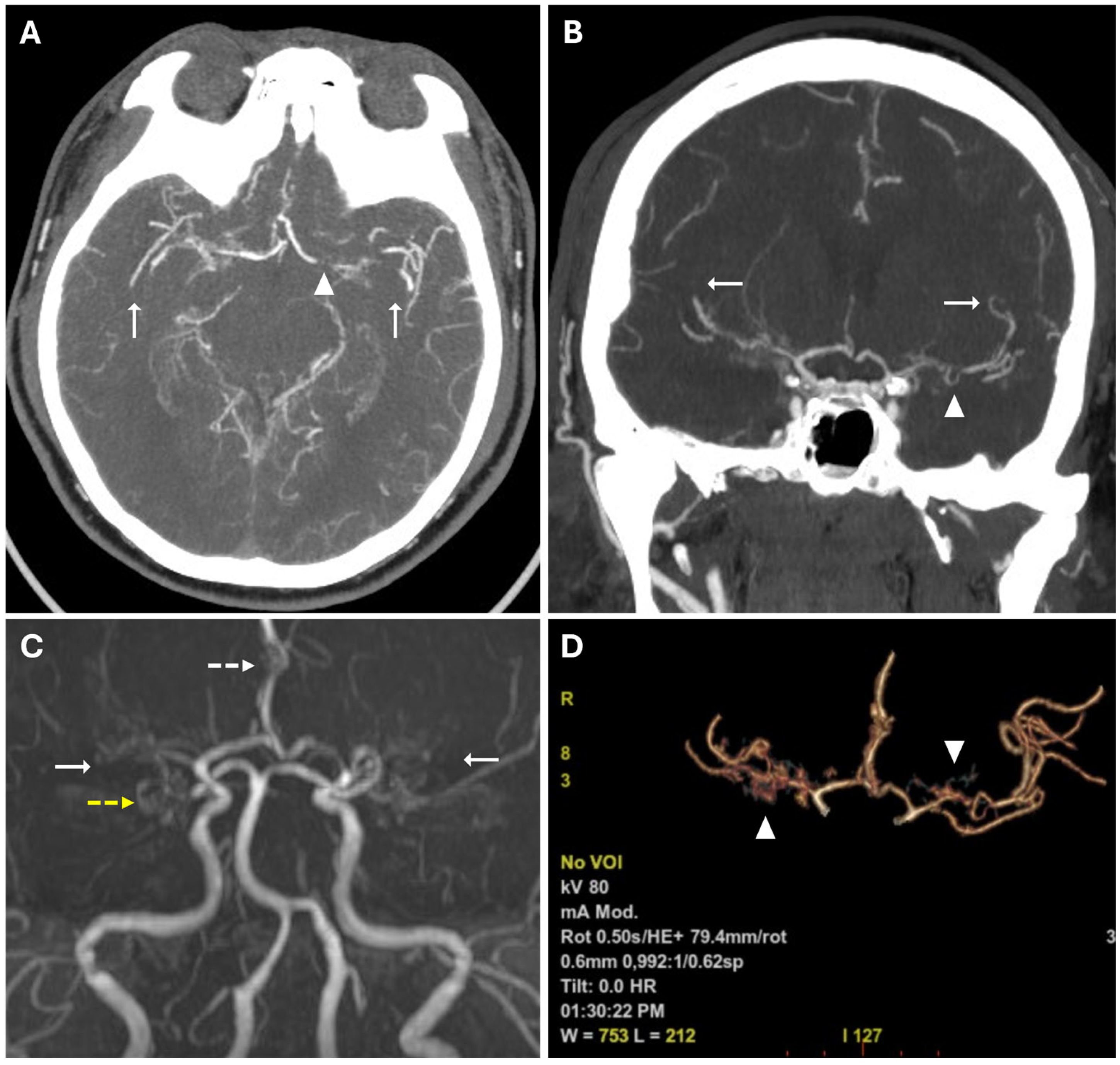
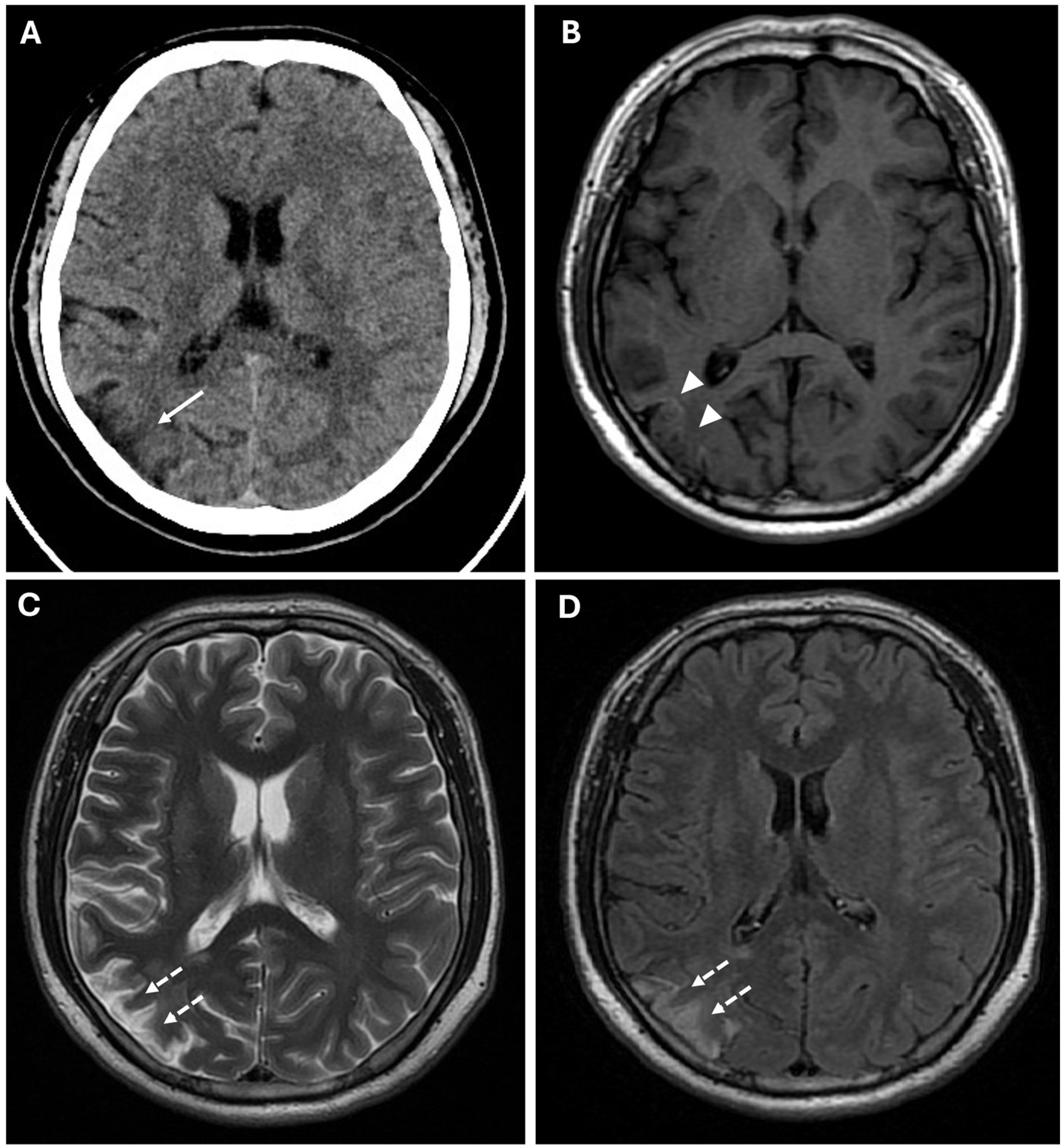
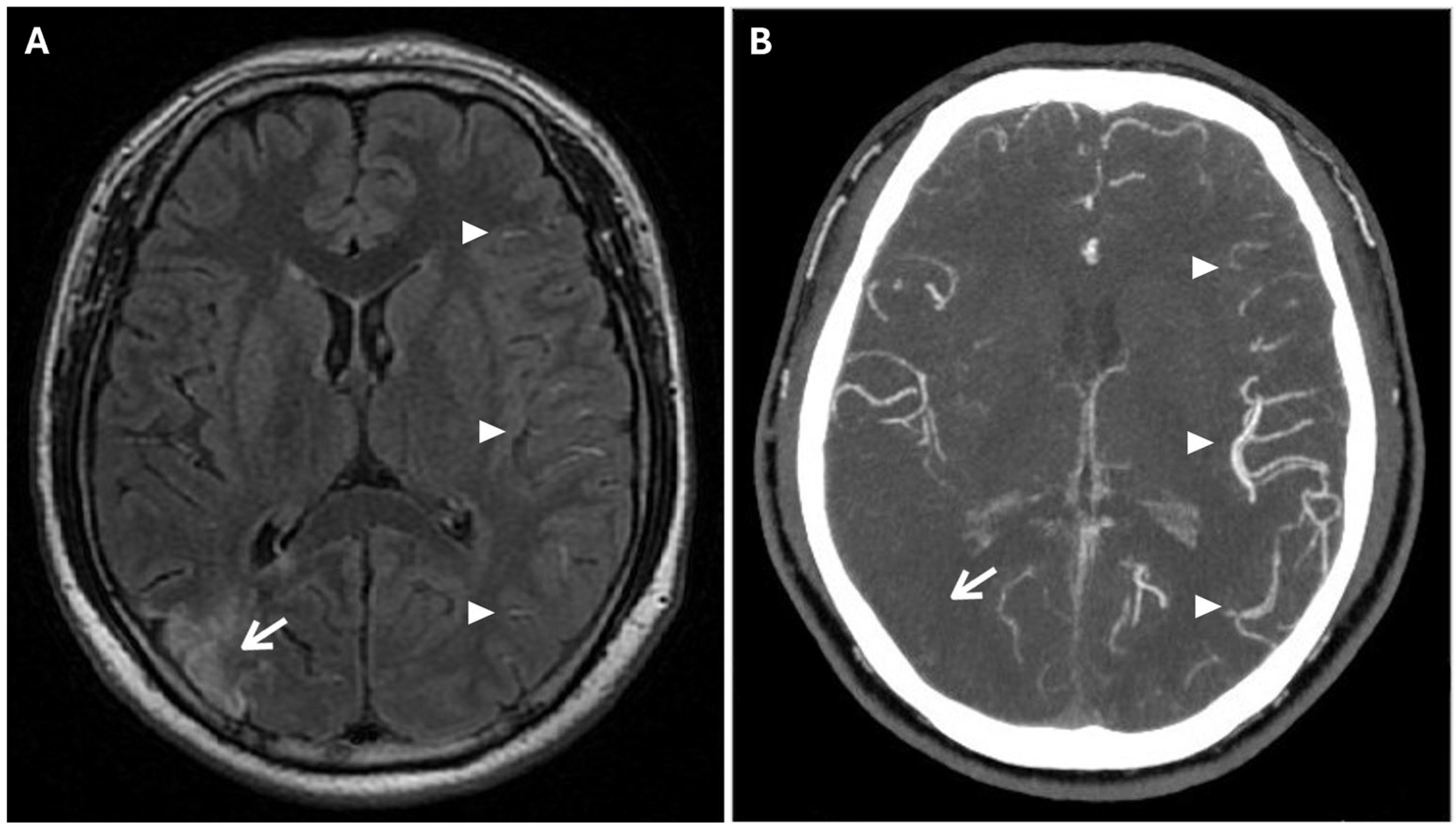
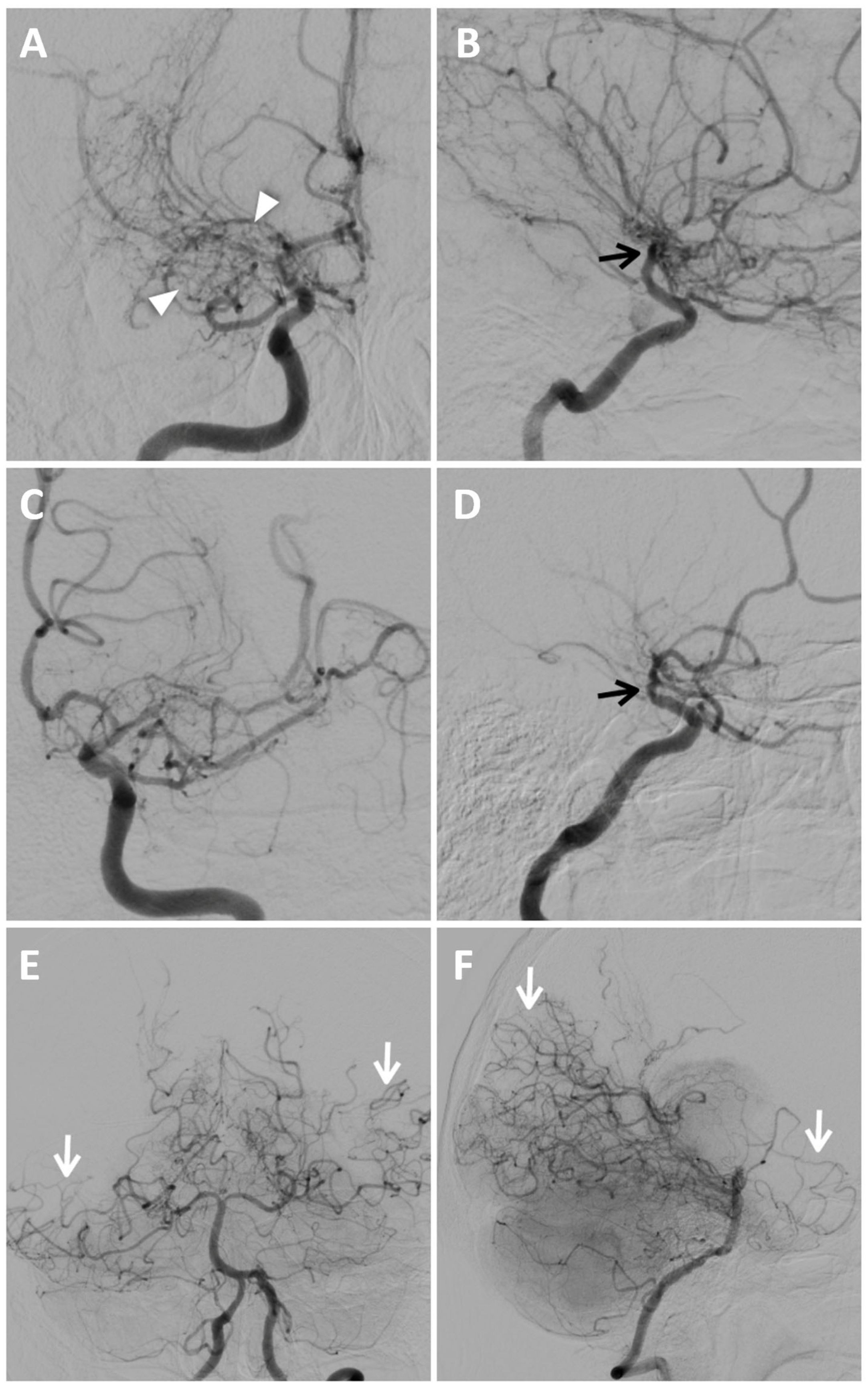
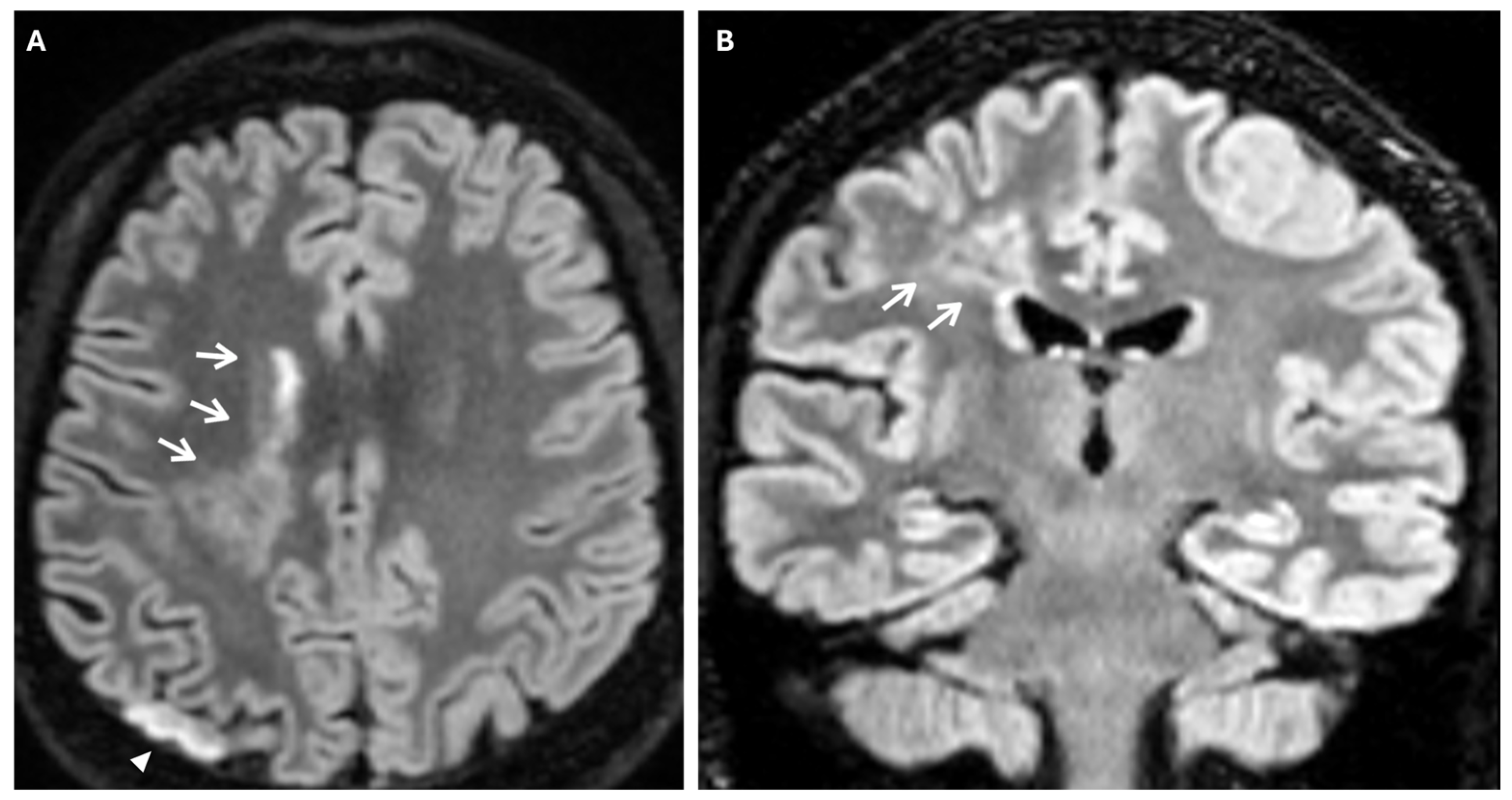
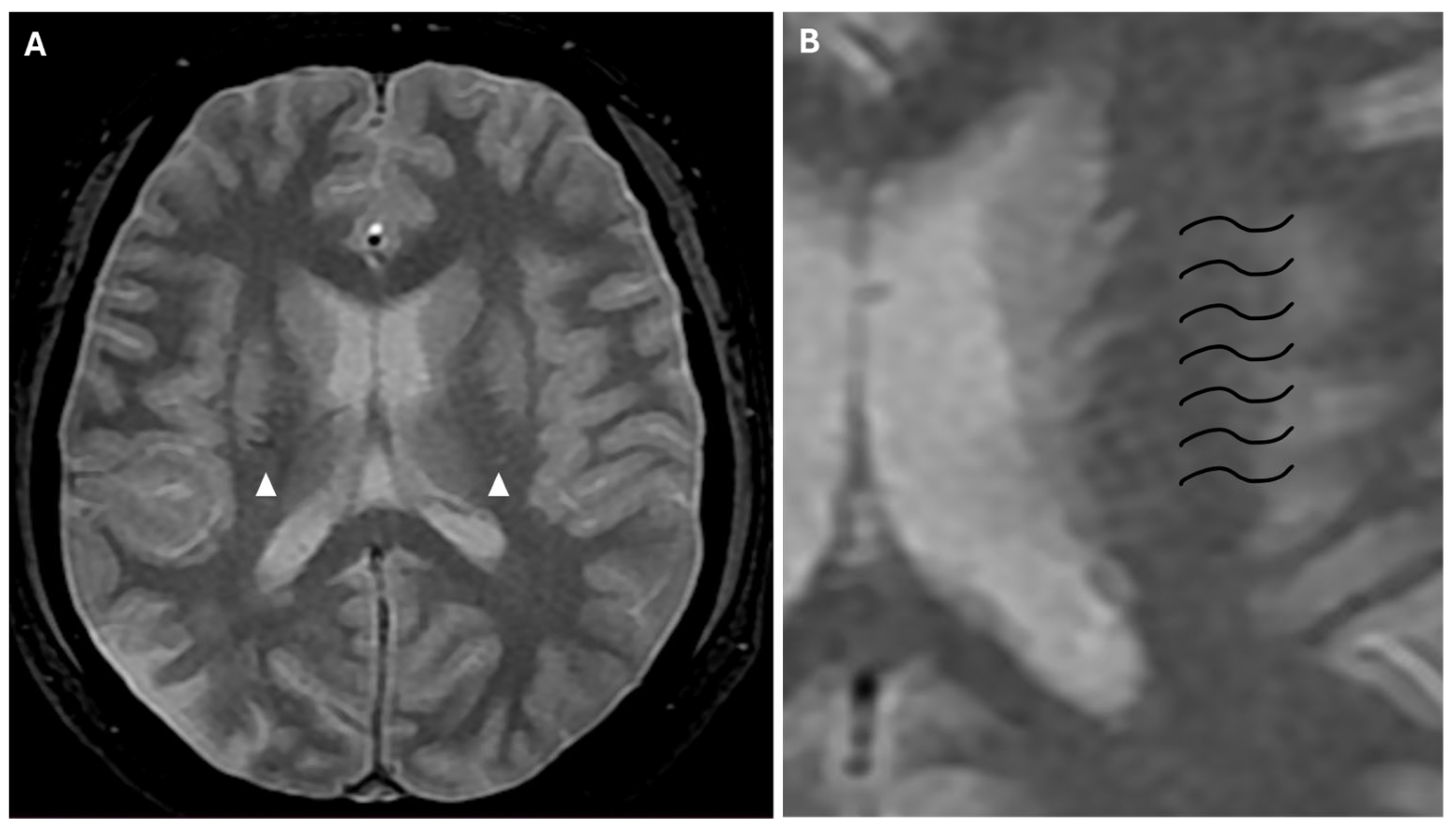
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
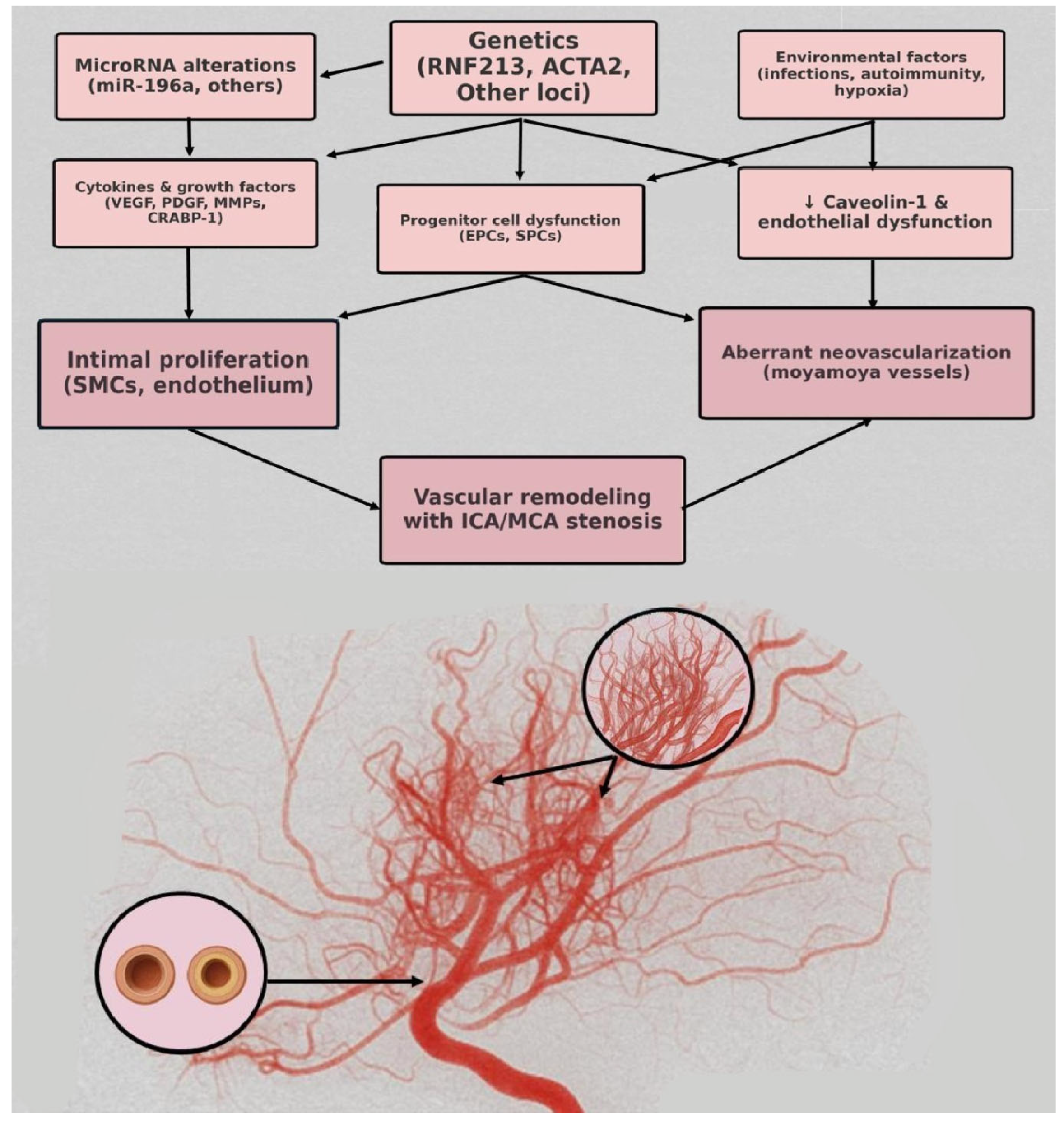
3.1. Pathophysiology and Differential Diagnosis
3.2. Clinical Aspects and Radiological Features
- – Stenosis or occlusion involving the terminal segment of the ICA.
- – The presence of moyamoya vessels, in proximity to the stenotic artery during the arterial phase.
- Stage I: narrowing of the internal carotid artery bifurcation.
- Stage II: presence of visible moyamoya collateral vessels, dilated ACAs, MCAs, and narrowed ICA bifurcation.
- Stage III: augmentation of moyamoya vessels and narrowed ACA and MCA.
- Stage IV: diminished number of moyamoya vessels, deterioration of ICA, ACA, MCA, and presence of collateral from external carotid artery.
- Stage V: occlusion of ICA, ACA and MCA; further deterioration of moyamoya vessels; and increased collateral from extracranial vessels.
3.3. Management and Outcome
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MMD | moyamoya disease |
| MDCT | multi-detector computed tomography |
| CTA | computed tomography angiography |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRA | magnetic resonance angiography |
| DSA | digital subtraction angiography |
| ICA | internal carotid artery |
| MCA | middle cerebral artery |
| ACA | anterior cerebral artery |
| PCA | posterior cerebral artery |
| SPECT | single-photon emission CT |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| TIA | transient ischemic attack |
| FLAIR | fluid attenuated inversion recovery |
| DWI | diffusion weighted imaging |
| ADC | apparent diffusion coefficient |
| SWI | susceptibility weighted imaging |
| FFE | fast field echo |
| TOF | time of flight |
References
- Suzuki, J.; Takaku, U. Cerebrovascular “Moyamoya” Disease. Arch. Neurol. 1969, 20, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S. Moyamoya disease: Epidemiology, clinical features, and diagnosis. J. Stroke 2016, 18, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, R.M.; Smith, E.R. Moyamoya Disease and Moyamoya Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Bao, X.Y.; Yang, W.Z.; Shi, W.C.; Li, D.S.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zong, R.; Han, C.; Zhao, F.; Feng, J. Moyamoya disease in China: Its clinical features and outcomes. Stroke 2012, 43, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, S.; Kusaka, Y.; Fujimura, M.; Wakai, K.; Tamakoshi, A.; Hashimoto, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Yoshimoto, T. Prevalence and clinicoepidemiological features of moyamoya disease in Japan: Findings from a nationwide epidemiological survey. Stroke 2008, 39, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasów, E.; Kułakowska, A.; Łukasiewicz, A.; Kapica-Topczewska, K.; Korneluk-Sadzyńska, A.; Brzozowska, J.; Drozdowski, W. Moyamoya disease: Diagnostic imaging. Pol. J. Radiol. 2011, 76, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jin, M.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Xi, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Huang, Y. Imaging of Moyamoya Disease and Moyamoya Syndrome: Current Status. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2019, 43, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, N.; Tominaga, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Nagata, I.; Houkin, K.; Suzuki, N.; Takagi, Y. Research Committee on the Pathology and Treatment of Spontaneous Occlusion of the Circle of Willis; Health Labour Sciences Research Grant for Research on Measures for Infractable Diseases. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of moyamoya disease (spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis). Neurol. Med. Chir. 2012, 52, 245–266. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, M.Y.; Hao, X.; Chiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Ye, X.; Wang, R.; et al. Advances in moyamoya disease: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic interventions. MedComm 2025, 6, e7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Luo, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Xue, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. CARE-radiology statement explanation and elaboration: Reporting guideline for radiological case reports. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2024, 29, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, S.; Fujimura, M.; Takahashi, J.; Kataoka, H.; Ogasawara, K.; Iwama, T.; Tominaga, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Research Committee on Moyamoya Disease (Spontaneous Occlusion of Circle of Willis) of the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, Japan. Diagnostic Criteria for Moyamoya Disease—2021 Revised Version. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2022, 62, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, R.; Foti, P.V.; Pennisi, I.; Conti, A.; Meli, G.A.; Vasile, T.; Gozzo, C.; Tallamona, E.; Inì, C.; Palmucci, S.; et al. Stylo-Jugular Venous Compression Syndrome: Lessons Based on a Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, e932035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phi, J.H.; Wang, K.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Moyamoya Syndrome: A Window of Moyamoya Disease. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2015, 57, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, O.Y.; Fujimura, M.; Kim, S.K. The Pathophysiology of Moyamoya Disease: An Update. J. Stroke 2016, 18, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Li, B.; Xu, L.-J.; Xiao, X.-L. High-resolution MR imaging of the arterial wall in moyamoya disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, D.; Gao, P.; Su, J.; Yang, H.; Gao, X.; Ni, W.; Lei, Y.; et al. Progression in Moyamoya Disease: Clinical Features, Neuroimaging Evaluation, and Treatment. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, V.T.; Cogswell, P.M.; Rinaldo, L.; Brinjikji, W.; Huston, J.; Klaas, J.P.; Lanzino, G. Contemporary and emerging magnetic resonance imaging methods for evaluation of moyamoya disease. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeda, S.; Korogi, Y.; Hiai, Y.; Ohnari, N.; Sato, T.; Hirai, T. Pitfalls of 3D FLAIR brain imaging: A prospective comparison with 2D FLAIR. Acad. Radiol. 2012, 19, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivrioglu, A.K.; Saglam, M.; Yildiz, B.; Anagnostakou, V.; Kizilkilic, O. Ivy Sign in Moyamoya Disease. Eurasian J. Med. 2016, 48, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.V.; Killingsworth, M.C.; Bhaskar, S. Cerebral collaterals in acute ischaemia: Implications for acute ischaemic stroke patients receiving reperfusion therapy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 1238–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Xia, C.; Tan, J.; Xiao, A.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y. Ivy Sign: Usefulness in Diagnosis and Prognosis Prediction of Moyamoya Disease. World Neurosurg. 2024, 181, e1012–e1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nah, H.W.; Kwon, S.U.; Kang, D.W.; Ahn, J.S.; Kwun, B.D.; Kim, J.S. Moyamoya disease-related versus primary intracerebral: Hemorrhage location and outcomes are different. Stroke 2012, 43, 1947–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xiao, W.-M.; Luo, G.-P.; Liu, Y.-L.; Qu, J.-F.; Fang, X.-W.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.-K. Asymmetrical cortical vein sign predicts early neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke patients with severe intracranial arterial stenosis or occlusion. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, J.; Kodama, N. Moyamoya disease—A review. Stroke 1983, 14, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Oh, C.W.; Bang, J.S.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, W.S. Moyamoya Disease: Treatment and Outcomes. J. Stroke 2016, 18, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Kimiwada, T.; Karibe, H.; Shirane, R.; Sasaki, T.; Metoki, H.; Tominaga, T. Preoperative Risks of Cerebral Infarction in Pediatric Moyamoya Disease. Stroke 2021, 52, 2302–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, Y.; Miyawaki, S.; Imai, H.; Hongo, H.; Teranishi, Y.; Dofuku, S.; Ishigami, D.; Ohara, K.; Koizumi, S.; Ono, H.; et al. Differences in Clinical Features among Different Onset Patterns in Moyamoya Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Radiological Findings | CT/CTA | MRI | DSA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bottle neck sign | + + + | + + | + + + |
| Ivy sign | + | + + + | + |
| Puff of smoke sign | + | + | + + + |
| Medullary streak sign | + | + + + | + + |
| Prominent vessel sign | + | + + + | + |
| Cortical vein sign | + | + + + | + + |
| Brush sign | + | + + + | + + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferraro, E.; Amaduri, A.; Ini’, C.; Travali, M.; Tiralongo, F.; Foti, P.V.; Cristaudo, C.; Basile, A. Multimodality Imaging of Moyamoya Disease: A Practical Guide for Neuroradiologists Based on a Case Report. Reports 2025, 8, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040232
Ferraro E, Amaduri A, Ini’ C, Travali M, Tiralongo F, Foti PV, Cristaudo C, Basile A. Multimodality Imaging of Moyamoya Disease: A Practical Guide for Neuroradiologists Based on a Case Report. Reports. 2025; 8(4):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040232
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerraro, Elisa, Agata Amaduri, Corrado Ini’, Mario Travali, Francesco Tiralongo, Pietro Valerio Foti, Concetto Cristaudo, and Antonio Basile. 2025. "Multimodality Imaging of Moyamoya Disease: A Practical Guide for Neuroradiologists Based on a Case Report" Reports 8, no. 4: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040232
APA StyleFerraro, E., Amaduri, A., Ini’, C., Travali, M., Tiralongo, F., Foti, P. V., Cristaudo, C., & Basile, A. (2025). Multimodality Imaging of Moyamoya Disease: A Practical Guide for Neuroradiologists Based on a Case Report. Reports, 8(4), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040232






