Clinical and Sociodemographic Characterization of Mexican Cohort with Pseudoarthrosis: A Retrospective, Cross-Sectional, and Descriptive Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
- Patients with a clinical and/or radiological diagnosis of pseudoarthrosis.
- Patients treated at the “General Ignacio Zaragoza” Regional Hospital of the ISSSTE.
- Patients who agreed to and signed the consent form to participate in the study.
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
- Patients with bone infections caused by microbial agents.
- Patients with incomplete medical records.
- Patients with unstable fractures.
2.4. Pseudoarthrosis
2.5. Operational Definition of Overweight and Obesity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
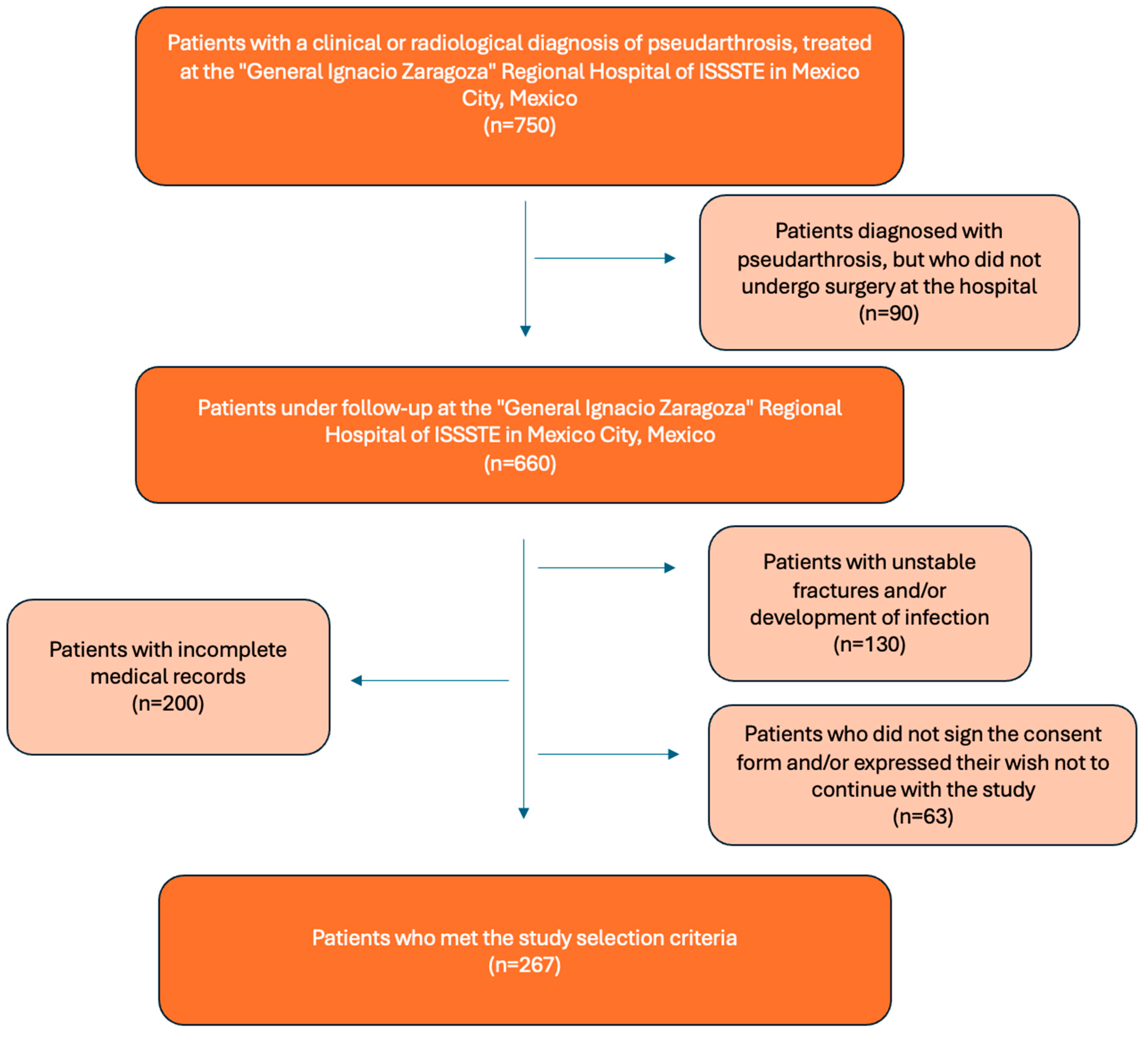
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escarpanter, B.J.C. Factores de riesgo para la aparición de seudoartrosis en las fracturas diafisarias. Rev. Cubana Ortop. Traumatol. 1996, 11, 50-55. [Google Scholar]
- Mogonza, E.B.; Vahamwiti, A.L.; Kaghoma, A.S.; Sikakulya, F.K.; Kamenge, E.K.; Akinja, S.U. Prevalence and risk factors for traumatic long bone pseudarthrosis at the Matanda Hospital, Butembo, eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2021, 40, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.S.; Jensen, N.M.; Gundtoft, P.H.; Kold, S.; Zura, R.; Viberg, B. Risk factors for nonunion following surgically managed, traumatic, diaphyseal fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EFORT Open Rev. 2022, 7, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunna, R.S.; Ostrov, P.B.; Ansari, D.; Dettori, J.R.; Godolias, P.; Elias, E.; Tran, A.; Oskouian, R.J.; Hart, R.; Abdul-Jabbar, A.; et al. The Risk of Nonunion in Smokers Revisited: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Glob. Spine J. 2022, 12, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zura, R.; Mehta, S.; Della Rocca, G.J.; Steen, R.G. Biological Risk Factors for Nonunion of Bone Fracture. JBJS Rev. 2016, 4, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicaiza, C.; Orellana, R.; Zambrano, J.; Andrea, D. Factores de riesgo de pseudoartrosis postraumática de diáfisis de tibia. Sinerg. Educ. 2022, E, Esp.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Moreno, J.; Casiano, G. Algoritmo del tratamiento de la pseudoartrosis diafisaria. Acta Ortop. Mex. 2019, 33, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lionel, L.; Barla, J.D.; Diego, C.; Danilo, T.; Sancineto, C.F.; Carabelli, G. Treatment of infected pseudoarthrosis in a subtrochanteric fracture in a patient with osteopetrosis. Case Rep. Orthop. 2020, 2020, 5630202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- How, N.E.; Street, J.T.; Dvorak, M.F.; Fisher, C.G.; Kwon, B.K.; Paquette, S.; Smith, J.S.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Ailon, T. Pseudarthrosis in adult and pediatric spinal deformity surgery: A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis of incidence, characteristics, and risk factors. Neurosurg. Rev. 2019, 42, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, E.; Illingworth, K.D.; Stephan, S.; Skaggs, D.L.; Andras, L.M. Rate and risk factors for pediatric cervical spine fusion pseudarthrosis: Opportunity for improvement. Spine Deform. 2023, 11, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora Ríos, F.G.; Antonio Romero, C.E.; Mejía Rohenes, L.C.; Hernández Martínez, S.; Isunza Ramírez, A.; Mota González, E. Incidencia de pseudoartrosis en el Hospital Regional General Ignacio Zaragoza del ISSSTE. Rev. Esp. Méd. Quir. 2012, 17, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, C.; Rey, D. Descripción de los factores de riesgo biológicos para pseudoartrosis. Repert. Med. Cirugía 2018, 26, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretell Mazzini, J.A.; Ruiz Semba, C.; Rodriguez, M.J. Trastornos de la consolidación: Retardo y pseudoartrosis. Rev. Med. Hered. 2009, 20, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konomi, T.; Yasuda, A.; Fujiyoshi, K.; Yato, Y.; Asazuma, T. Incidences and Risk Factors for Postoperative Non-Union after Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Closed-Box Titanium Spacers. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsifaki, A.; Kalouda, G.; Maroulaki, S.; Foukas, A.; Armakolas, A. The Genetic and Biological Basis of Pseudoarthrosis in Fractures: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Diseases 2025, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, G.; González, A. Retardo de Consolidación y Pseudoartrosis. Available online: https://unitia.secot.es/web/manual_residente/CAPITULO%2011.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Gustilo, R.B.; Mendoza, R.M.; Williams, D.N. Problems in the management of type III (severe) open fractures: A new classification of type III open fractures. J. Trauma 1984, 24, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Overweight and Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- Brinker, M.R.; Trivedi, A.; O’Connor, D.P. Debilitating Effects of Femoral Nonunion on Health-Related Quality of Life. J. Orthop. Trauma 2017, 31, e37–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, W.H.; de Steiger, R.; Richardson, M.; Gruen, R.; Balogh, Z.J. Health outcomes of delayed union and nonunion of femoral and tibial shaft fractures. Injury 2014, 45, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolini, E.; West, R.; Giannoudis, P.V. Risk factors for long bone fracture non-union: A stratification approach based on the level of the existing scientific evidence. Injury 2015, 46, S8–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, F.C.; Dos Reis, J.M.; Dos Reis, S.P.; Bartelega, L.A.; De Melo, N.F.; Mundim Araújo, C.D. Epidemiology of open fractures and degree of satisfaction of initial care. Acta Ortop. Bras. 2022, 30, e245221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouraria, G.G.; Santos Júnior, J.A.S.; Kikuta, F.K.; Zogbi, D.R.; Brigatto, R.M.; de Paula Coelho, S.; Cruz, M.A.; Etchebehere, M. Prevalence and risk factors for pseudarthrosis in humeral shaft fractures treated by minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis: A 10-year review. Shoulder Elb. 2022, 14, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, K.; Ito, M.; Abumi, K.; Haba, H.; Taneichi, H.; Kaneda, K. Radiological risk factors of pseudoarthrosis and/or instrument breakage after PLF with the pedicle screw system in isthmic spondylolisthesis. J. Spinal. Disord Tech. 2006, 19, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollern, D.A.; Woods, B.I.; Shah, N.V.; Schroeder, G.D.; Kepler, C.K.; Kurd, M.F.; Kaye, I.D.; Millhouse, P.W.; Diebo, B.G.; Paulino, C.B.; et al. Risk Factors for Pseudarthrosis After Surgical Site Infection of the Spine. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2019, 13, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raizman, N.M.; O’Brien, J.R.; Poehling-Monaghan, K.L.; Yu, W.D. Pseudarthrosis of the spine. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2009, 17, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.F.; Fiere, V.; Obeid, I.; Charles, Y.P.; El-Youssef, K.; Lahoud, A.; Faddoul, J.; Ferrero, E.; Riouallon, G.; Silvestre, C.; et al. Pseudarthrosis in adult spine deformity surgery: Risk factors and treatment options. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 3225–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bydon, M.; De la Garza-Ramos, R.; Abt, N.B.; Macki, M.; Sciubba, D.M.; Wolinsky, J.P.; Bydon, A.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Witham, T.F. Durotomy is associated with pseudoarthrosis following lumbar fusion. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.; Sharma, M.; Dietz, N.; Dettori, J.; Ugiliweneza, B.; Nuno, M.; Boakye, M.; Drazin, D. Demographics and Outcomes of Spine Surgery in Octogenarians and Nonagenarians: A Comparison of the National Inpatient Sample, MarketScan and National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Databases. Cureus 2019, 11, e6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, Z.; Mehta, V.A.; Lubelski, D.; Elliott, C.; Miller, J.A.; Benzel, E.C.; Mroz, T.E. Quality of Life and Cost Implications of Pseudarthrosis After Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion and its Subsequent Revision Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2020, 133, e592–e599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Frequency (n) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Female | 124 | 46.4% |
| Age (years) | ||
| 4–18 | 22 | 8.2% |
| 19–45 | 83 | 31.0% |
| 46–75 | 134 | 50.1% |
| >76 | 28 | 10.48% |
| Schooling | ||
| Elementary | 39 | 14.6% |
| Secondary school | 39 | 14.6% |
| High school | 88 | 33.0% |
| Bachelor’s degree | 98 | 36.7% |
| Without schooling | 3 | 1.12% |
| Nutritional status | ||
| Overweight | 114 | 42.7% |
| Obesity | 90 | 33.7% |
| Comorbidity | ||
| Osteoporosis | 84 | 31.5% |
| Systemic arterial hypertension | 59 | 22.1% |
| Diabetes mellitus | 71 | 26.6% |
| Alcoholism | 39 | 14.6% |
| Smoking | 141 | 52.8% |
| Variable | Frequency (n) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Affected bone | ||
| Humerus | 53 | 19.9% |
| Femur | 53 | 19.9% |
| Tibia | 65 | 24.3% |
| Fibula | 15 | 5.6% |
| Radius | 54 | 20.2% |
| Ulna | 10 | 3.7% |
| Other | 17 | 6.4% |
| Open fracture | ||
| Yes | 47 | 17.65% |
| No | 220 | 82.4% |
| Grade of fracture exposure | ||
| I | 13 | 27.75 |
| II | 22 | 46.8% |
| IIIa | 2 | 4.3% |
| IIIb | 10 | 21.3% |
| Surgical lead time (days) | ||
| 0–7 | 38 | 14.2% |
| 8–14 | 143 | 53.6% |
| 15–21 | 86 | 32.2% |
| Females (95% CI) | Obesity (95% CI) | Overweight (95% CI) | Osteoporosis (95% CI) | SAH (95% CI) | DM (95% CI) | Alcoholism (95% CI) | Smoking (95% CI) | Open Fracture (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humerus | 7.9% (4.64–11.10%) | 9.7% (6.19–13.29%) | 7.9% (4.64–11.10%) | 2.2% (0.47–4.03%) | 3.0% (0.96–5.04%) | 4.5% (2.00–6.98%) | 4.9% (2.28–7.46%) | 13.9% (9.72–18.00%) | 1.1% (0.00–2.37%) |
| Femur | 9.0% (5.56–12.42%) | 5.2% (2.57–7.91%) | 7.9% (4.64–11.10%) | 5.6% (2.86–8.38%) | 6.7% (3.74–9.74%) | 8.6% (5.24–11.98%) | 1.5% (0.04–2.96%) | 6.4% (3.45–9.29%) | 4.1% (1.73–6.51%) |
| Tibia | 13.5% (9.38–17.58%) | 9.0% (5.56–12.42%) | 12.7% (8.73–16.73%) | 18.0% (13.37–22.59%) | 6.0% (3.15–8.83%) | 5.2% (2.57–7.91%) | 4.9% (2.28–7.46%) | 14.2% (10.04–18.42%) | 7.1% (4.04–10.20%) |
| Fibula | 3.4% (1.21–5.53%) | 1.1% (0.00–2.37%) | 3.4% (1.21–5.53%) | 1.5% (0.04–2.96%) | 0.4% (0.07–2.09%) | 0.4% (0.07–2.09%) | 0.7% (0.21–2.69%) | 3.4% (1.21–5.53%) | 0.7% (0.21–2.69%) |
| Radius | 9.4% (5.87–12.85%) | 5.6% (2.86–8.38%) | 6.4% (3.45–9.29%) | 3.0% (0.95–5.04%) | 2.6% (0.71–4.54%) | 5.2% (2.57–7.91%) | 1.5% (0.04–2.96%) | 10.1% (6.50–13.72%) | 3.7% (1.48–6.02%) |
| Ulna | 1.5% (0.04–2.96%) | 1.1% (0.00–2.37%) | 1.5% (0.04–2.96%) | 0.0% (0.00–1.42%) | 0.4% (0.07–2.09%) | 0.4% (0.07–2.095) | 0.7% (0.21–2.69%) | 2.2% (0.47–4.03%) | 0.7% (0.21–2.69%) |
| Another affected bone | 1.9% (0.61–4.30%) | 1.9% (0.61–4.30%) | 3.0% (1.30–5.86%) | 1.1% (0.23–3.25%) | 3.0% (1.30–5.86%) | 2.2% (0.83–4.81%) | 0.4% (0.01–2.08%) | 2.6% (1.06–5.29%) | 0.0% (0–1.12%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez, E.I.P.; Mora Ríos, F.G.; Muñoz Hernández, B.M.; Ramos Texta, J.; Domínguez González, R.C.; Pérez Figueroa, J.A.; García-Benavides, P.; Castro-Fuentes, C.A. Clinical and Sociodemographic Characterization of Mexican Cohort with Pseudoarthrosis: A Retrospective, Cross-Sectional, and Descriptive Study. Reports 2025, 8, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040227
Jiménez EIP, Mora Ríos FG, Muñoz Hernández BM, Ramos Texta J, Domínguez González RC, Pérez Figueroa JA, García-Benavides P, Castro-Fuentes CA. Clinical and Sociodemographic Characterization of Mexican Cohort with Pseudoarthrosis: A Retrospective, Cross-Sectional, and Descriptive Study. Reports. 2025; 8(4):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040227
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez, Emilio Ignacio Pérez, Félix Gustavo Mora Ríos, Brian Misael Muñoz Hernández, Josué Ramos Texta, Roberto Carlos Domínguez González, Joan Artemio Pérez Figueroa, Pedro García-Benavides, and Carlos Alberto Castro-Fuentes. 2025. "Clinical and Sociodemographic Characterization of Mexican Cohort with Pseudoarthrosis: A Retrospective, Cross-Sectional, and Descriptive Study" Reports 8, no. 4: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040227
APA StyleJiménez, E. I. P., Mora Ríos, F. G., Muñoz Hernández, B. M., Ramos Texta, J., Domínguez González, R. C., Pérez Figueroa, J. A., García-Benavides, P., & Castro-Fuentes, C. A. (2025). Clinical and Sociodemographic Characterization of Mexican Cohort with Pseudoarthrosis: A Retrospective, Cross-Sectional, and Descriptive Study. Reports, 8(4), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040227