ADEM as an Initial Presentation of SLE: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Description
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farag, E.A. Acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis (ADEM): Clinical characteristics and outcome. Pediatr. Ther. 2013, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Safadi, S.; Tizki, S.; Ouafik, I.; Ouhsousou, H.; Daoudi, A.; Nainia, K. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in children: What relationship? Glob. Pediatr. 2024, 8, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; Jayne, D.; Cervera, R.; et al. 2019 European League against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. In Arthritis & Rheumatology; U.S. National Library of Medicine: Hoboken, NJ, USA, September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Anilkumar, A.C.; Foris, L.A.; Tadi, P. Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 26 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A. Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis. White Matter Dis. 2020, 12, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.K.; Malhotra, H.S.; Kumar, N. Pathophysiology of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. In Multiple Sclerosis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 201–248. [Google Scholar]
- Postal, M.; Appenzeller, S. The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cytokine 2011, 56, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Xia, Y.M. Anti-double stranded DNA antibodies: Origin, pathogenicity, and targeted therapies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venner, A.A.; Ibañez, D.; Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.B.; MacKinnon, A.; Blasutig, I.M.; Yip, P.M. Comparison of three anti-dsdna assays: Performance and correlation with systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabayan, B.; Zolghadrasli, A. Vasculitis and rheumatologic diseases may play role in the pathogenesis of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM). Med. Hypotheses 2007, 69, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
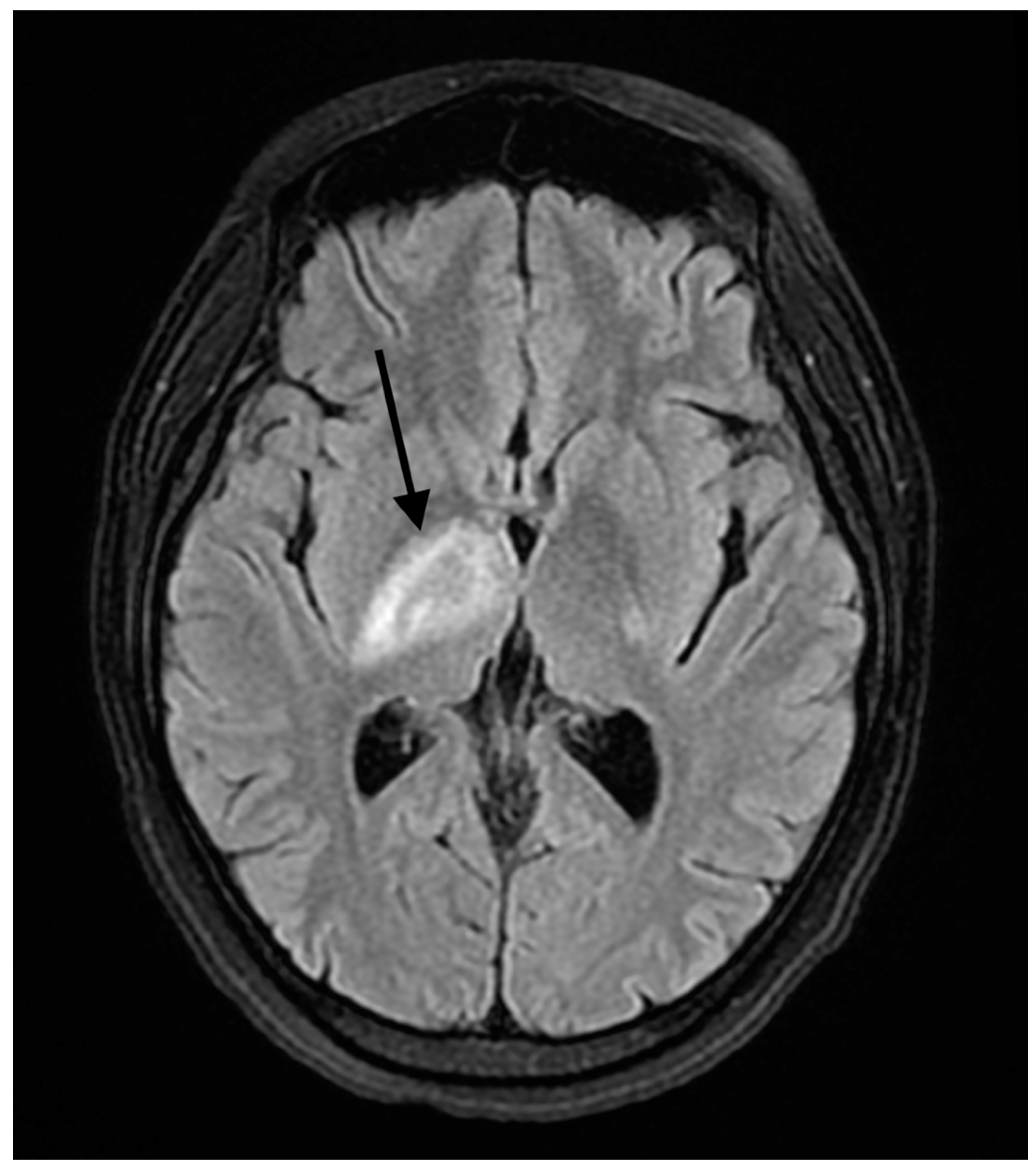
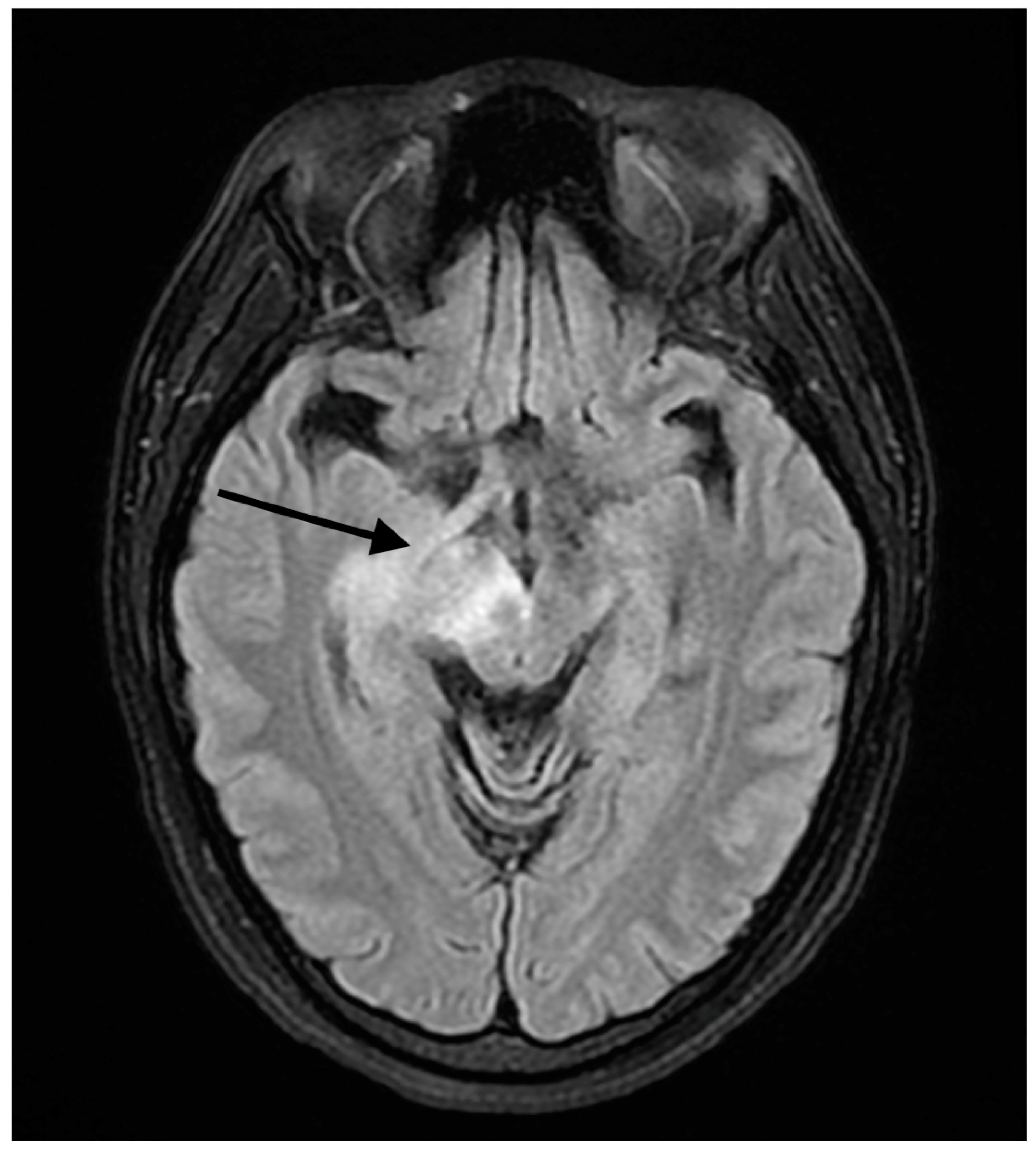
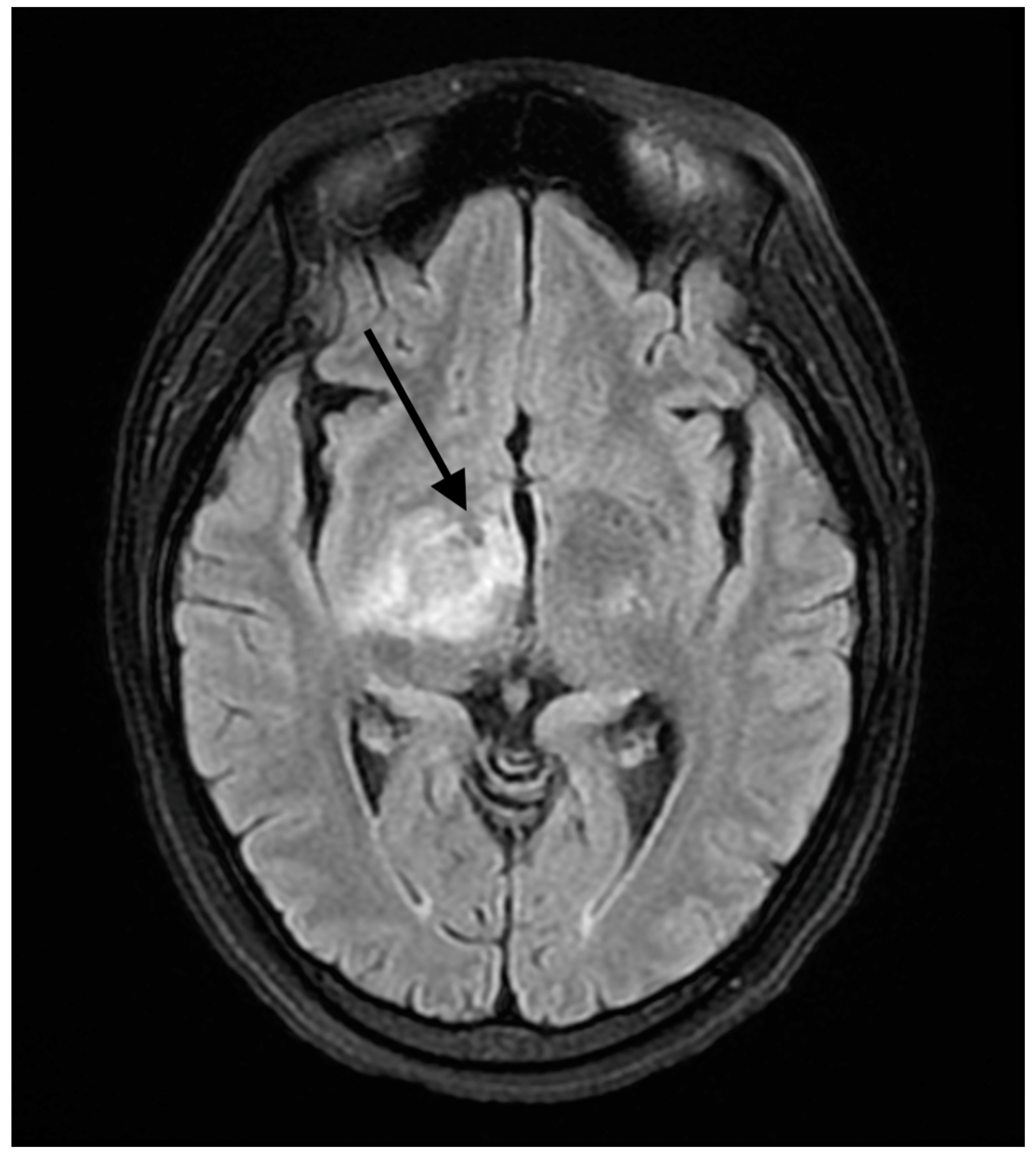

| Days Since Establishing with Rheumatology | Treatment | Anti-dsDNA(IU/mL) | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Prednisone 20 mg | 22 | Bilateral lower extremity weakness and facial droop |
| Day 180 | Prednisone 15 mg and Rituximab 1000 mg q4 week | 16 | Residual left lower extremity weakness. Resolution of facial droop |
| Day 360 | Prednisone 15 mg, Rituximab 1000 mg q4 week, and IVIG q3 weeks | 12 | Resolution of lower extremity weakness and facial droop |
| Differential Diagnosis | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Acute viral encephalitis | Fever, neck rigidity, and elevated acute phase reactants are typical. |
| Multiple sclerosis | First episode includes multifocal neurological deficits. Subsequent are usually not associated with acute encephalopathy. |
| Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein disease (MOGAD) | More typical in children. Optic neuritis, spinal cord symptoms, and demyelination similar to ADEM may be present. |
| Metastatic brain cancer | Headache, seizures, and stroke-like symptoms present. Symptoms varied according to lesion location. |
| Neurobrucellosis | Varied symptoms. Headaches, fever, and neck stiffness most common. Hearing loss, confusion, and possible extremity weakness can also be present. |
| Cardioembolic stroke | Sudden numbness or weakness involving the face and/or extremities is typical. Confusion headaches and dysphagia are also common. |
| Cavernous sinus syndrome | Severe headaches, confusion, coma, seizures, vision loss, diplopia, and ptosis are common manifestations. |
| Cerebral venous thrombosis | Severe headaches, confusion, coma, seizures, vision loss, diplopia, and ptosis are common manifestations. |
| NDMA receptor encephalitis | Rapid progression of neurocognitive symptoms including changes in behavior, seizures, coma, dysarthria, and autonomic dysfunction are typical. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sherwani, Y.; Alsaab, A.; Sengodan, M. ADEM as an Initial Presentation of SLE: A Case Report. Reports 2024, 7, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7030053
Sherwani Y, Alsaab A, Sengodan M. ADEM as an Initial Presentation of SLE: A Case Report. Reports. 2024; 7(3):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7030053
Chicago/Turabian StyleSherwani, Yousuf, Ayham Alsaab, and Mohan Sengodan. 2024. "ADEM as an Initial Presentation of SLE: A Case Report" Reports 7, no. 3: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7030053
APA StyleSherwani, Y., Alsaab, A., & Sengodan, M. (2024). ADEM as an Initial Presentation of SLE: A Case Report. Reports, 7(3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7030053





