Significant Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum and Extensive Subcutaneous Emphysema in a COVID-19 Patient
Abstract
1. Background
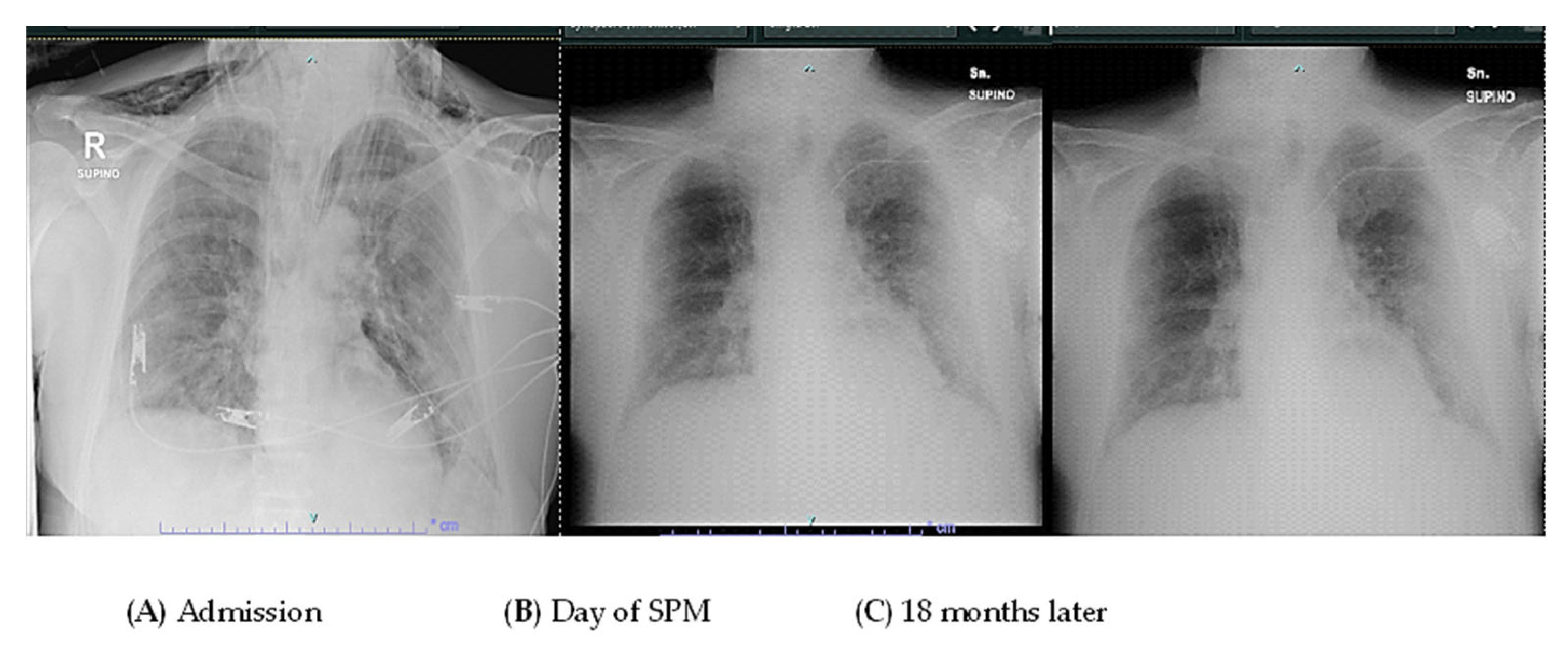
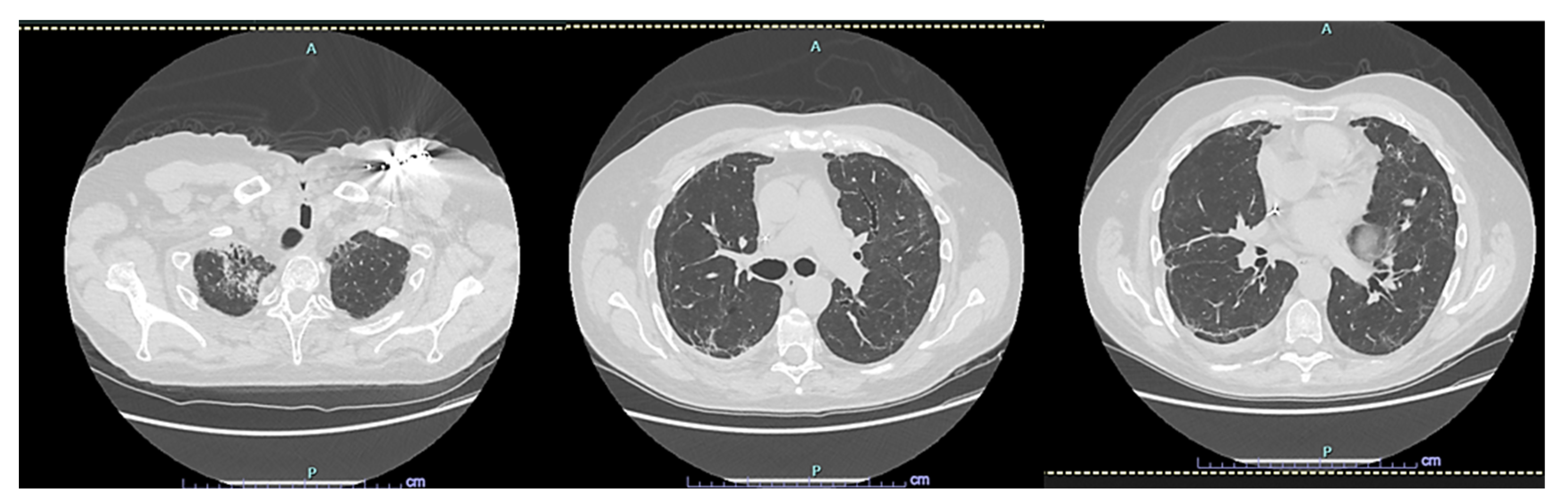
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Strength and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elhakim, T.S.; Abdul, H.S.; Pelaez Romero, C.; Rodriguez-Fuentes, Y. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax and subcutaneous emphysema in COVID-19 pneumonia: A rare case and literature review. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e239489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganessane, E.; Devendiran, A.; Ramesh, S.; Uthayakumar, A.; Chandrasekar, V.; Sadasivam, A.S.; Nathan, B.; Ayyan, M. Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19 disease: Clinical review with emphasis on emergency management. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Physicians Open 2023, 4, e12935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muley, M.; Finamore, P.; Pedone, C.; Margiotta, D.P.E.; Gilardi, E.; Sambuco, F.; De Vincentis, A.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U.; Travaglino, F.; Antonelli-Incalzi, R. Incidence and Outcome of Pneumomediastinum in Non-ICU Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 51, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberger, S.; Finkelstein, M.; Pagano, A.; Manna, S.; Toussie, D.; Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Concepcion, J.; Gupta, S.; Eber, C.; et al. Barotrauma in COVID 19: Incidence, pathophysiology, and effect on prognosis. Clin. Imaging 2022, 90, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manenti, A.; Roncati, L.; Melegari, G. Deepening Pathology of SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Explains Lung Ventilation Complications. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 113, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belletti, A.; Pallanch, O.; Bonizzoni, M.A.; Guidi, L.; De Cobelli, F.; Landoni, G.; Zangrillo, A.; De Bonis, M.; Palumbo, D. Clinical use of Macklin-like radiological sign (Macklin effect): A systematic review. Respir. Med. 2023, 210, 107178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternoster, G.; Belmonte, G.; Scarano, E.; Rotondo, P.; Palumbo, D.; Belletti, A.; Corradi, F.; Bertini, P.; Landoni, G.; Guarracino, F. Macklin effect on baseline chest CT scan accurately predicts barotrauma in COVID-19 patients. Respir. Med. 2022, 197, 106853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gao, C.; Xie, Y.; Xu, M. COVID-19 with spontaneous pneumomediastinum. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, S.; Roche, B.; Kazzaz, F.; Ocazionez, D.; Lal, A.P.; Estrada, Y.M.R.M.; Cherian, S.V. Pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum in COVID-19: A case series. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 363, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, W.; Kipkorir, V.; Marza, A.M.; Hamouri, S.; Albawaih, O.; Dhali, A.; Kim, W.; Udwadia, Z.F.; Nashwan, A.J.; Shaikh, N.; et al. Prognosis of Spontaneous Pneumothorax/Pneumomediastinum in Coronavirus Disease 2019: The CoBiF Score. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, A.; Nirwan, L.; Abi-Ghanem, A.S.; Arif, U.; Lahori, S.; Kassab, M.B.; Karout, S.; Itani, R.M.; Abdalla, R.; Naffaa, L.; et al. Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum in Patients Diagnosed with COVID-19: A Case Series with Review of Literature. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 28, 1586–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, S.; Maron, S.Z.; Cedillo, M.A.; Voutsinas, N.; Toussie, D.; Finkelstein, M.; Steinberger, S.; Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Eber, C.; et al. Spontaneous subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum in non-intubated patients with COVID-19. Clin. Imaging 2020, 67, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhon, M.S.; Thiara, S.; Kanji, H.D.; Ronco, J.J. Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19: The Macklin Effect? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 989–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Chun, W.; Lee, H.J.; Min, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Seo, J.Y.; Ahn, K.S.; Oh, S.R. The Role of Macrophages in the Development of Acute and Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Madotto, F.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; Bumbasirevic, V.; Piquilloud, L.; et al. Noninvasive Ventilation of Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Insights from the LUNG SAFE Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, L.D.J.; Ware, L.B. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: Causes, pathophysiology, and phenotypes. Lancet 2022, 400, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, K.E.; Swenson, E.R. Pathophysiology of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and COVID-19 Lung Injury. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 749–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M.A.; Arabi, Y.M.; Siegel, E.R.; Ware, L.B.; Bos, L.D.J.; Sinha, P.; Beitler, J.R.; Wick, K.D.; Curley, M.A.Q.; Constantin, J.M.; et al. Phenotypes and personalized medicine in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 2136–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, M.; Ali, S.Z.; Braud, R.; Weiman, D.; Garrett, H.E., Jr. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: A comparative study and review of the literature. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2008, 86, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños-Morales, F.V.; Santibáñez-Salgado, J.A.; Guadarrama-Pérez, C.; Herrera-Zamora, J.J.; Armas-Zárate, F.J.; Santillán-Doherty, P.J. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum in COVID-19 patients. Case series. Gac. Méd. Méx. 2021, 157, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Akhtar, J.; Nabzdyk, C. Pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2021, 91, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, A.; Todaro, G.; Valsecchi, G.; Losiggio, R.; Palumbo, D.; Landoni, G.; Zangrillo, A. Barotrauma in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients Undergoing Invasive Mechanical Ventilation: A Systematic Literature Review. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Pastores, S.M. Bursting at the Seams: Barotrauma in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marza, A.M.; Cindrea, A.C.; Petrica, A.; Stanciugelu, A.V.; Barsac, C.; Mocanu, A.; Critu, R.; Botea, M.O.; Trebuian, C.I.; Lungeanu, D. Non-Ventilated Patients with Spontaneous Pneumothorax or Pneumomediastinum Associated with COVID-19: Three-Year Debriefing across Five Pandemic Waves. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaspari, A.; Carrieri, F.; Villani, M.; Bertellini, E. Significant Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum and Extensive Subcutaneous Emphysema in a COVID-19 Patient. Reports 2024, 7, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7010015
Gaspari A, Carrieri F, Villani M, Bertellini E. Significant Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum and Extensive Subcutaneous Emphysema in a COVID-19 Patient. Reports. 2024; 7(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaspari, Arianna, Francesca Carrieri, Matteo Villani, and Elisabetta Bertellini. 2024. "Significant Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum and Extensive Subcutaneous Emphysema in a COVID-19 Patient" Reports 7, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7010015
APA StyleGaspari, A., Carrieri, F., Villani, M., & Bertellini, E. (2024). Significant Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum and Extensive Subcutaneous Emphysema in a COVID-19 Patient. Reports, 7(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7010015





