Cognitive Evolution of a Patient Who Suffered a Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Eight Years Ago, after Being Treated with Growth Hormone, Melatonin and Neurorehabilitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation Section
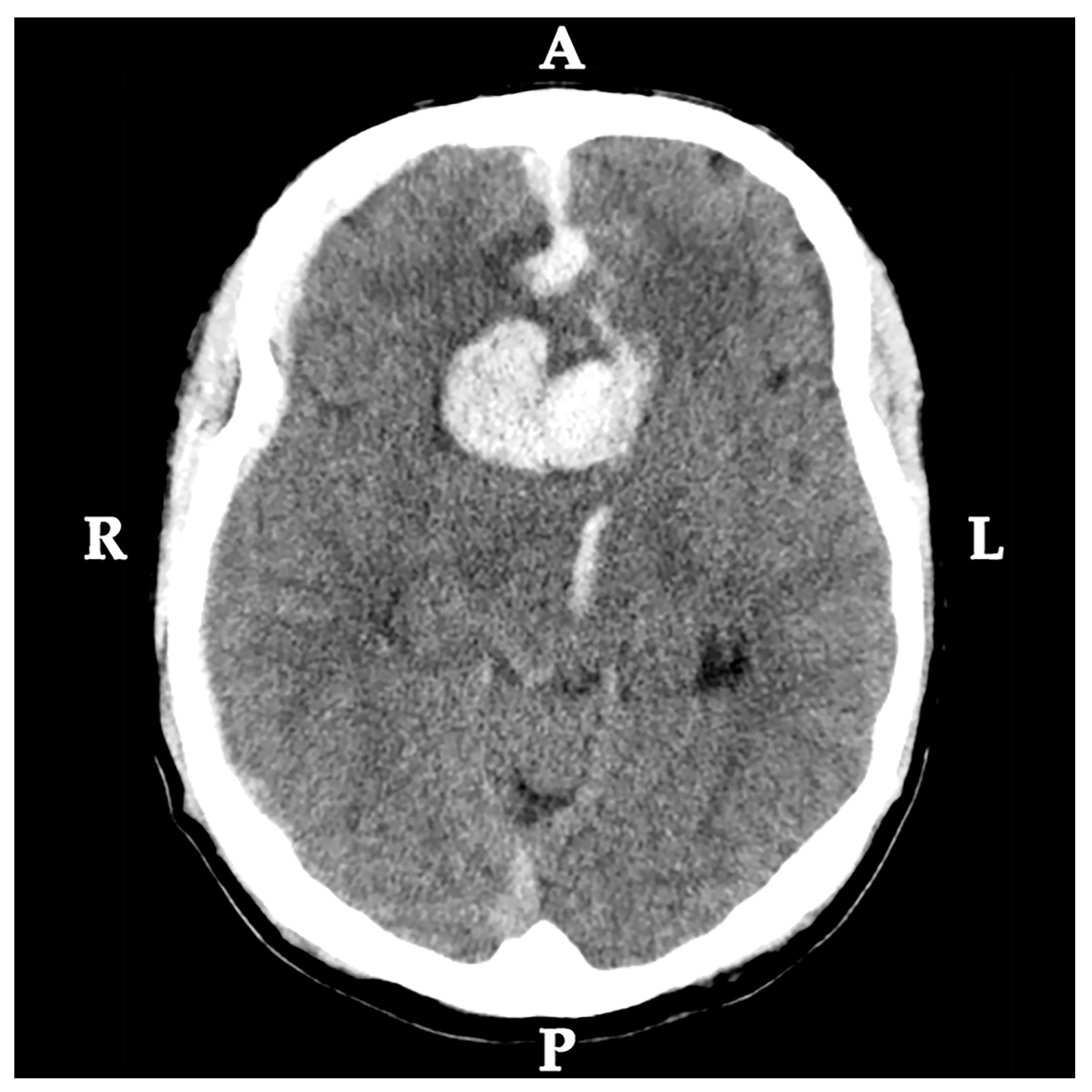
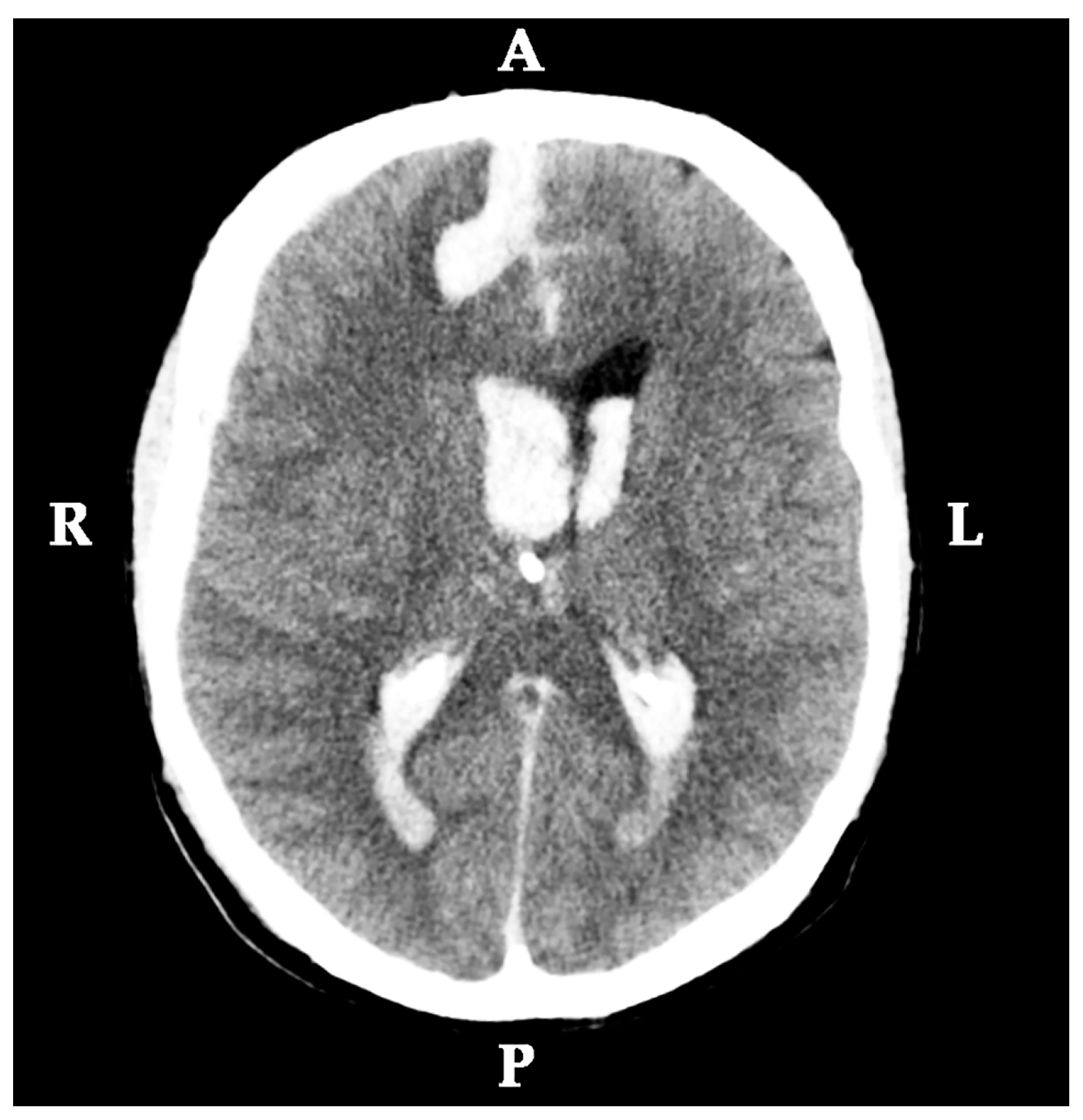
2.1. Medical History
2.2. Neurorehabilitation 1
2.3. Neurorehabilitation 2
2.3.1. Neurostimulation
2.3.2. Occupational Therapy
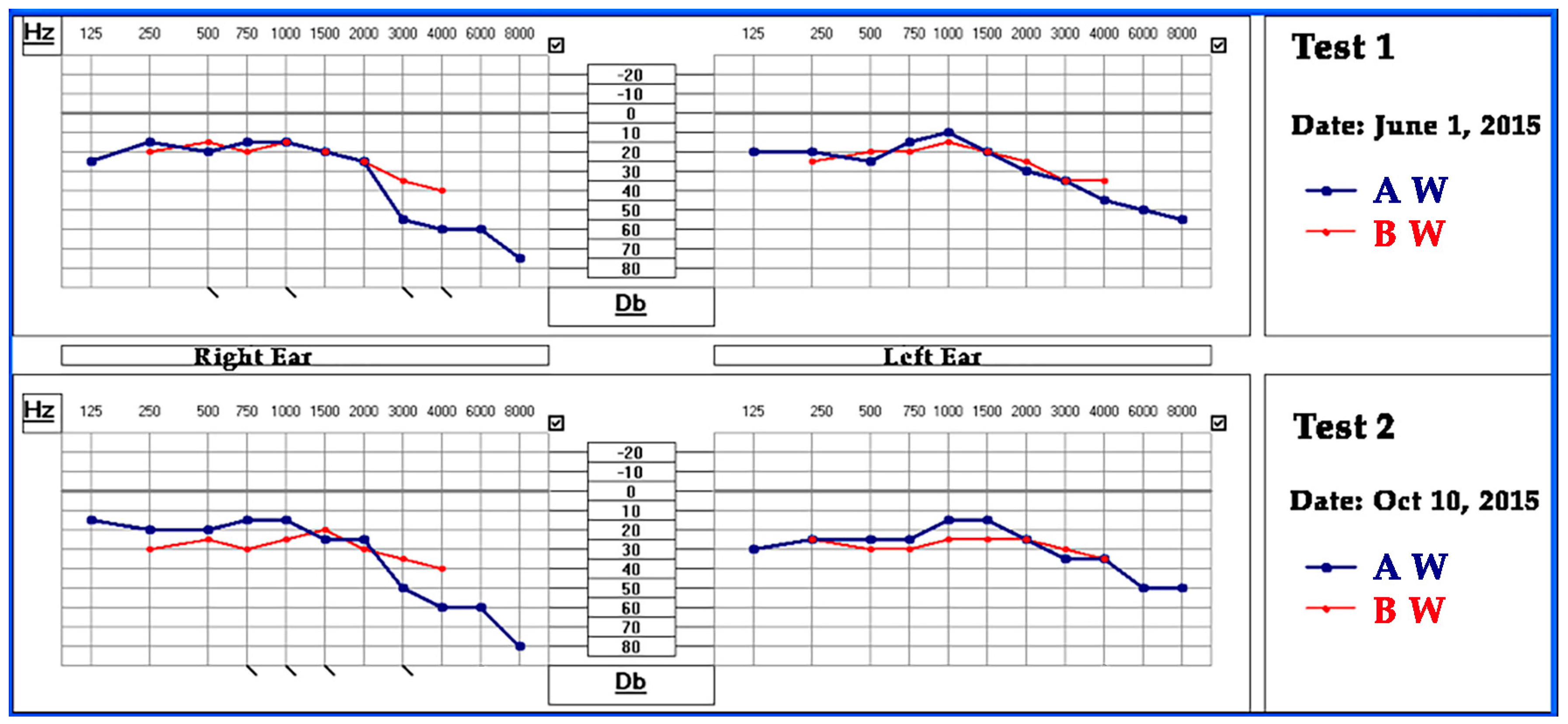
2.3.3. EINA
- (A)
- Aerial listening.
- (B)
- Selectivity.
- (C)
- Bone listening.
- (D)
- Spatialization errors.
- (E)
- Laterality.
- (1)
- First block: the combinations were made between Mozart music, specific Pass Bands (to work on balance, postural control) and Gregorian chants, reaching a total of 40 sessions.
- (2)
- Second block: consisted on 40 sessions of Mozart music, specific Pass Bands (for language, attention and memory) and Gregorian chants.
- (3)
- Third block: consisted on 50 sessions combining Mozart music, Dense Music and Gregorian chants.
2.3.4. Medical Treatment
3. Results
3.1. Neurorehabilitation 1
3.1.1. Blood Analysis
3.1.2. Neurostimulation
3.2. Neurorehabilitation 2
3.2.1. Neurostimulation
3.2.2. Occupational Therapy
3.2.3. EINA
3.2.4. Blood Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
EINA
References
- Guerrero, F.; de la Linde, C.M.; Pino, F.I. General Management in intensive care of patient with spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage. Med. Intensiv. 2008, 32, 342–353. [Google Scholar]
- Kellner, P.; Stoevesandt, D.; Soukup, J.; Bucher, M.; Raspé, C. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anaesthesist 2012, 61, 792–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gijn, J.; Kerr, R.S.; Rinkel, G.J. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. Lancet 2007, 369, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivancos, J.; Gilo, F.; Frutos, R.; Maestre, J.; García-Pastor, A.; Quintana, F.; Roda, J.M.; Ximénez-Carrillo, A.; por el Comité ad hoc del Grupo de Estudio de Enfermedades Cerebrovasculares de la SEN; Díez Tejedor, E.; et al. Clinical managements for subarachnoid haemorrhage. Diagnosis and treatment. Neurologia 2014, 29, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisman, J.L.; Song, J.K.; Newell, D.W. Cerebral aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caicedo, D.; Devesa, P.; Arce, V.M.; Requena, J.; Devesa, J. Chronic limb-threatening ischemia could benefit from growth hormone therapy for wound healing and limb salvage. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 12, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Ren, X.L.; Huang, H.; Guo, X.J.; Ma, A.G.; Li, D. Circulating long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid and incidence of stroke: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 83781–83791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, K.J.; Harris, W.S.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease: Are There Benefits? Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 18, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, J.I.; Tarr, R.W.; Selman, W.R. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shahi, R.; White, P.M.; Davenport, R.J.; Lindsay, K.W. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. BMJ 2006, 333, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koenig, M.A. Management of delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Continuum 2012, 18, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabel, H.H.; Pedersen, A.R.; Johnsen, S.P.; Nielsen, J.F. Rupture of a non-traumatic anterior communicating artery aneurysm: Does location of aneurysm associate with functional independence following post-acute in-patient neurorehabilitation? Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2017, 24, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almqvist, O.; Thorén, M.; Sääf, M.; Eriksson, O. Effects of growth hormone substitution on mental performance in adults with growth hormonedeficiency: A pilot study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1986, 11, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, P.; Broman, J.E.; Hetta, J.; Wiklund, I.; Erfurth, E.M.; Hagg, E.; Karlsson, F.A. Quality of life in adults with growth hormone (GH) deficiency: Response to treatment with recombinant human GH in a placebo-controlled 21-month trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 3585–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deijen, J.B.; de Boer, H.; van der Veen, E.A. Cognitive changes during growth hormone replacement in adult men. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1998, 23, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.D.; Musolino, N.R.; Cunha Neto, M.; Caires, M.A.; Rosenthal, M.C.; Camargo, C.P.; Bronstein, M.D. Impact of recombinant human growth hormone (RH-GH) treatment on psychiatric, neuropsychological and clinical profiles of GH deficient adults. A placebo-controlled trial. Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria 1999, 57, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertel, H.; Schneider, H.J.; Stalla, G.K.; Holsboer, F.; Zhil, J. The effect of growth hormone substitution on cognitive performance in adult patients with hypopituitarism. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2004, 29, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arwert, L.I.; Deijen, J.B.; Müller, M.; Drent, M.L. Long-term growth hormone treatment preserves GH-induced memory and mood improvements: A 10-year follow-up study in GH-deficient adult men. Horm. Behav. 2005, 47, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, P.S. Neurocognitive function in adults with growth hormone deficiency. Horm. Res. 2005, 64 (Suppl. S3), 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- High, W.M., Jr.; Briones-Galang, M.; Clark, J.A.; Gilkison, C.; Mossberg, K.A.; Zgaljardic, D.J.; Masel, B.E.; Urban, R.J. Effect of growth hormone replacement therapy on cognition after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimunde, P.; Quintana, A.; Castañón, B.; Casteleiro, N.; Vilarnovo, Z.; Otero, A.; Devesa, A.; Otero-Cepeda, X.L.; Devesa, J. Effects of growth hormone (GH) replacement and cognitive rehabilitation in patients with cognitive disorders after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2011, 25, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, O.K.; Cortet-Rudelli, C.; Yollin, E.; Merlen, E.; Daveluy, W.; Rousseaux, M. Growth hormone replacement therapy in patients with traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Park, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. The effect of recombinant human growth hormone therapy in patients with completed stroke: A pilot trial. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arce, V.M.; Devesa, P.; Devesa, J. Role of growth hormone (GH) in the treatment on neural diseases: From neuroprotection to neural repair. Neurosci. Res. 2013, 76, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, F.; Hallberg, M. Growth hormone and cognitive function. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 6, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devesa, J.; Reimunde, P.; Devesa, P.; Barberá, M.; Arce, V. Growth hormone (GH) and brain trauma. Horm. Behav. 2013, 63, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devesa, J.; Díaz-Getino, G.; Rey, P.; García-Cancela, J.; Loures, I.; Nogueiras, S.; Hurtado de Mendoza, A.; Salgado, L.; González, M.; Pablos, T.; et al. Brain Recovery after a Plane Crash: Treatment with Growth Hormone (GH) and Neurorehabilitation: A Case Report. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30470–30482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; BaHammam, A.S.; Brown, G.M.; Spence, D.W.; Bharti, V.K.; Kaur, C.; Hardeland, R.; Cardinali, D.P. Melatonin antioxidative defense: Therapeutical implications for aging and neurodegenerative processes. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 23, 267–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackowski, A.; Crockard, A.; Burnstock, G.; Russell, R.R.; Kristek, F. The time course of intracranial pathophysiological changes following experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage in the rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1990, 10, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, T.J.; Brismar, J.; Svendgaard, N.A. Subarachnoid haemorrhage in the rat: Angiography and fluorescence microscopy of the major cerebral arteries. Stroke 1985, 16, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehba, F.A.; Schwartz, A.Y.; Chereshnev, I.; Bederson, J.B. Acute decrease in cerebral nitric oxide levels after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2000, 20, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.M.; Afshar, J.K.; Boock, R.J.; Oldfield, E.H. Temporal changes in perivascular concentrations of oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, and methemoglobin after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 88, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignarro, L.J. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1990, 30, 535–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, M.J.; Blackmore, D.G. Growth hormone (GH), brain development and neural stem cells. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2011, 9, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberg, N.D.; Brywe, K.G.; Isgaard, J. Aspects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I related to neuroprotection, regeneration and functional plasticity in the adult brain. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 53–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia, M.; Fuente, A.; Criado, J.; Yajeya, J.; Devesa, J.; Riolobos, A.S. Early growth hormone (GH) treatment promotes relevant motor functional improvement after severe frontal cortex lesion in adult rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 247, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devesa, J.; Almengló, C.; Devesa, P. Multiple Effects of Growth Hormone in the Body: Is it Really the Hormone for Growth? Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes 2016, 12, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, F. Growth hormone in the brain: Characteristics of specific brain targets for the hormone and their functional significance. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2000, 21, 330–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, P.S. Somatropin therapy and cognitive functions in adults with growth hormone deficiency: A critical review. Treat. Endocrinol. 2006, 5, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arwert, L.I.; Veltman, D.J.; Deijen, J.B.; van Dam, P.S.; Drent, M.L. Effects of growth hormone substitution therapy on cognitive functioning in growth hormone deficient patients: A functional MRI study. Neuroendocrinology 2006, 83, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quik, E.H.; van Dam, P.S.; Kenemans, J.L. Growth hormone and selective attention: A review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wass, J.A.; Reddy, R. Growth hormone and memory. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 207, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deijen, J.B.; Arwert, L.I.; Drent, M.L. The GH/IGF-I Axis and Cognitive Changes across a 4-Year Period in Healthy Adults. ISRN Endocrinol. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devesa, J.; Lema, H.; Zas, E.; Munín, B.; Taboada, P.; Devesa, P. Learning and Memory Recoveries in a Young Girl Treated with Growth Hormone and Neurorehabilitation. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caicedo, D.; Díaz, O.; Devesa, P.; Devesa, J. Growth Hormone (GH) and Cardiovascular System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devesa, P.; Reimunde, P.; Gallego, R.; Devesa, J.; Arce, V.M. Growth hormone (GH) treatment may cooperate with locally-produced GH in increasing the proliferative response of hippocampal progenitors to kainate-induced injury. Brain Inj. 2011, 25, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLenachan, S.; Lum, M.G.; Waters, M.J.; Turnley, A.M. Growth hormone promotes proliferation of adult neurosphere cultures. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2009, 19, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David Aberg, N.; Lind, J.; Isgaard, J.; Georg Kuhn, H. Peripheral growth hormone induces cell proliferation in the intact adult rat brain. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2010, 20, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathipati, P.; Gorba, T.; Scheepens, A.; Goffin, V.; Sun, Y.; Fraser, M. Growth hormone and prolactin regulate human neural stem cell regenerative activity. Neuroscience 2011, 190, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Antiinflammatory activity of melatonin in central nervous system. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.J.; Wu, C.; Niu, H.J.; Wang, K.; Mo, L.J.; Shao, A.W.; Dixon, B.J.; Zhang, J.M.; Yang, S.X.; Wang, Y.R. Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Melatonin in Hemorrhagic Stroke. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.B. Multisensory Stimulation in Stroke Rehabilitation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Särkämö, T.; Tervaniemi, M.; Laitinen, S.; Forsblom, A.; Soinila, S.; Mikkonen, M.; Autti, T.; Silvennoinen, H.M.; Erkkilä, J.; Laine, M.; et al. Music listening enhances cognitive recovery and mood after middle cerebral artery stroke. Brain 2008, 131, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauscher, F.H.; Shaw, G.L.; Ky, K.N. Music and spatial task performance. Nature 1993, 365, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasenzer, E.R.; Kanat, A.; Neugebauer, E. Neurosurgery and Music; Effect of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. World Neurosurg. 2017, 102, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrusio, W.; Ettorre, E.; Vicenzini, E.; Vanacore, N.; Cacciafesta, M.; Mecarelli, O. The Mozart Effect: A quantitative EEG study. Conscious Cogn. 2015, 35, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Toro, A.; Operto, F.F.; Ferrarioli, G.; Pisano, S.; Viggiano, A.; Verrotti, A. Mozart’s music in children with drug-refractory epileptic encephalopathies. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 50, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, P.; Giuglietti, M.; Baglioni, A.; Verdolini, N.; Murgia, N.; Piccirilli, M.; Elisei, S. Effects of music on seizure frequency in institutionalized subjects with severe/profound intellectual disability and drug-resistant epilepsy. Psychiatr. Danub. 2017, 29 (Suppl. S3), 399–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Operto, F.F.; Caprio, F.; Ferraioli, G.; Pisano, S.; Viggiano, A.; Verrotti, A. Mozart’s music in children with drug-refractory epileptic encephalopathies: Comparison of two protocols. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 78, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devesa, J.; Alonso, A.; López, N.; García, J.; Puell, C.I.; Pablos, T.; Devesa, P. Growth Hormone (GH) and Rehabilitation Promoted Distal Innervation in a Child affected by Caudal Regression Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poidvin, A.; Touzé, E.; Ecosse, E.; Landier, F.; Béjot, Y.; Giroud, M.; Rothwell, P.M.; Carel, J.C.; Coste, J. Growth hormone treatment for childhood short stature and risk of stroke in early adulthood. Neurology 2014, 83, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, A.; Gravholt, C.H.; Olsen, M.S.; Christiansen, J.S.; Stochholm, K. Growth hormone replacement does not increase mortality in patients with childhood-onset growth hormone deficiency. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 83, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stochholm, K.; Kiess, V. Long-term safety of growth hormone-A combined registry analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia, M.; Palomero, J.; Fuente, A.; Criado, J.M.; Yajeya, J.; Decesa, J. Motor improvement of skilled forelimb use induced by treatment with growth hormone and rehabilitation is dependent on the onset of the treatment after cortical ablation. Neural Plast. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
| PRE | DISCHARGE | |
|---|---|---|
| Date | 2010/02/14 | 2010/05/14 |
| Subtest WAIS I | Typical Score | Typical Score |
| Arithmetic | 11 | 12 |
| Similarities | 12 | 15 |
| Digits | 11 | 13 |
| Number key | 9 | 10 |
| Incomplete figures | 12 | 15 |
| Cubes | 10 | 13 |
| Puzzles | 12 | 15 |
| Date | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tests | 2015/05/20 | 2017/05/22 | ||
| Pc | Pc | |||
| ATTENTION | D2 | TR | 45 | 45 |
| TA | 30 | 40 | ||
| O | 20 | 20 | ||
| C | 30 | 15 | ||
| TOT | 45 | 45 | ||
| CON | 42 | 49 | ||
| VAR | 67 | 75 | ||
| Typical Score | Typical Score | |||
| PROCESSING SPEED | Stroop test of words and colors | P | 34 | 26 |
| C | 30 | 31 | ||
| Scalar Score | Scalar Score | |||
| Subtests of the WAIS III Scale | Number key | 9 | 11 | |
| Symbol search | 9 | 13 | ||
| Index | Index | |||
| Processing speed | 89 | 111 | ||
| Scalar Score | Scalar Score | |||
| MEMORY | Subtests of the WMS-III Scale | Tests I | 2 | 9 |
| Couples I | 3 | 6 | ||
| Tests II | 1 | 7 | ||
| Couples II | 1 | 6 | ||
| DAM | 1 | 7 | ||
| Pc | Pc | |||
| Complex Figure of Rey | 1 | 5 | ||
| Scalar Score | Scalar Score | |||
| EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONS | Subtest cubes WAIS III | 10 | 16 | |
| Subtest digits WAIS III | 8 | 12 | ||
| Subtest of letters and numbers. WMS-III | 11 | 13 | ||
| Space location subtest. WMS-III | 10 | 12 | ||
| Index | Index | |||
| Work memory index. WMS-III | 101 | 115 | ||
| Pc | Pc | |||
| Complex Figure of Rey | Time | 75 | 95 | |
| Accuracy | 75 | 95 | ||
| Typical Score | Typical Score | |||
| Stroop Interference Test | 52 | 59 | ||
| PRE | DISCHARGE | |
|---|---|---|
| Date | 2015/06/01 | 2015/09/01 |
| Test | Scores | Scores |
| BARTHEL | 95/100 | 100/100 |
| LAWTON and BRODY | 20/31 | 15/31 |
| FIM/FAM | 178/210 | 192/210 |
| MINI MENTAL STATE | 20/37 | 28/37 |
| LOTCA | 80/87 | 85/87 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quintana, A.; Agra, C.; Outeiral, L.; Devesa, A.; Llorente, D.; Devesa, J. Cognitive Evolution of a Patient Who Suffered a Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Eight Years Ago, after Being Treated with Growth Hormone, Melatonin and Neurorehabilitation. Reports 2018, 1, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports1010002
Quintana A, Agra C, Outeiral L, Devesa A, Llorente D, Devesa J. Cognitive Evolution of a Patient Who Suffered a Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Eight Years Ago, after Being Treated with Growth Hormone, Melatonin and Neurorehabilitation. Reports. 2018; 1(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports1010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuintana, Ana, Carlos Agra, Lucía Outeiral, Ana Devesa, David Llorente, and Jesús Devesa. 2018. "Cognitive Evolution of a Patient Who Suffered a Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Eight Years Ago, after Being Treated with Growth Hormone, Melatonin and Neurorehabilitation" Reports 1, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports1010002
APA StyleQuintana, A., Agra, C., Outeiral, L., Devesa, A., Llorente, D., & Devesa, J. (2018). Cognitive Evolution of a Patient Who Suffered a Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Eight Years Ago, after Being Treated with Growth Hormone, Melatonin and Neurorehabilitation. Reports, 1(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports1010002






