Abstract
In recent years, accelerated global climate change has precipitated an increased frequency of wildfire events, with their devastating impacts on ecological systems and human populations becoming increasingly significant. Satellite remote sensing technology, leveraging its extensive spatial coverage and real-time monitoring capabilities, has emerged as a pivotal approach for wildfire early warning and comprehensive disaster assessment. To effectively detect subtle smoke signatures while minimizing background interference in remote sensing imagery, this paper introduces a novel dual-branch attention framework (CSFAttention) that synergistically integrates channel–spatial refinement with frequency spectral analysis to aggregate smoke features in remote sensing images. The channel–spatial branch implements an innovative triple-pooling strategy (incorporating average, maximum, and standard deviation pooling) across both channel and spatial dimensions to generate complementary descriptors that enhance distinct statistical properties of smoke representations. Concurrently, the frequency branch explicitly enhances high-frequency edge patterns, which are critical for distinguishing subtle textural variations characteristic of smoke plumes. The outputs from these complementary branches are fused through element-wise summation, yielding a refined feature representation that optimizes channel dependencies, spatial saliency, and spectral discriminability. The CSFAttention module is strategically integrated into the bottleneck structures of the ResNet architecture, forming a specialized deep network specifically designed for robust smoke recognition. Experimental validation on the USTC_SmokeRS dataset demonstrates that the proposed CSFResNet achieves recognition accuracy of 96.84%, surpassing existing deep networks for RS smoke recognition.
1. Introduction
Wildfires represent catastrophic natural phenomena that pose severe threats to human populations, infrastructure, and ecosystems. The frequency and intensity of wildfires have been significantly exacerbated by climate change in recent years, leading to devastating consequences worldwide. Among various indicators of wildfire onset, smoke is often the earliest observable signal, typically appearing before open flames. Therefore, timely and accurate smoke detection plays a critical role in early warning systems, enabling rapid response and the effective mitigation of fire-related damages. Remote sensing (RS) imagery has emerged as an invaluable resource in wildfire monitoring frameworks due to its extensive spatial coverage and temporal resolution capabilities, establishing it as an essential instrument for early detection and impact assessment. Consequently, the identification of wildfire smoke signatures through remote sensing imagery analysis has attracted significant scholarly interest, with researchers developing increasingly sophisticated methodologies to enhance detection accuracy and response efficiency [1,2].
The technological evolution in visual smoke detection has progressed through distinct developmental phases, transitioning from early feature-based algorithms to contemporary deep learning architectures. Initial methodologies primarily relied on handcrafted feature engineering to identify visual smoke signatures based on color, texture, and motion characteristics [3,4]. However, these approaches proved insufficient in addressing the inherent complexity of smoke patterns, which are characterized by significant variations in chromaticity, morphology, luminosity, and textural properties. This limitation spurred the adoption of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which have achieved remarkable success in visual smoke detection tasks [5,6]. Despite ongoing progress, smoke recognition in RS imagery remains a challenging and underexplored problem. Compared with conventional natural images, RS images exhibit more diverse backgrounds and lower image contrast. Smoke often shares visual similarities with clouds, haze, and dust, leading to high inter-class confusion. Moreover, smoke can appear faint, sparse, or diffuse, especially in the early stages of wildfires, which complicates its identification. These factors highlight the urgent need for robust feature extraction techniques that can distinguish subtle smoke patterns from similar visual elements in complex environments.
Attention mechanisms have become essential for dynamically recalibrating features, allowing modern CNN architectures to emphasize salient patterns while minimizing noise [7]. These mechanisms are now systematically integrated into smoke recognition frameworks to enhance perceptual sensitivity to smoke targets. Channel attention [8], spatial attention, and residual attention (RA) modules [9] were seamlessly integrated into the CNN architecture, enabling the proposed SmokeNet model to focus on label-specific information essential for accurate RS image classification [1]. A parallel design of channel and spatial attention mechanisms was employed to extract salient smoke-related features while suppressing irrelevant information [10]. Furthermore, leveraging the combined strengths of CNNs and visual Transformers [11], a novel forest fire smoke detection model, SR-Net, was developed to distinguish smoke from clouds in satellite remote sensing images [12]. Additionally, the adoption of depthwise separable convolution significantly reduced computational complexity, enhancing the model’s efficiency.
Despite the widespread adoption of attention mechanisms for feature discrimination, the existing methods primarily rely on channel and spatial attention strategies while often overlooking the importance of frequency-based feature refinement for capturing smoke texture patterns. This oversight limits the comprehensiveness of feature representation. To address this limitation, we propose a dual-branch attention mechanism (CSFAttention) that integrates channel–spatial refinement with frequency spectral analysis, providing a more holistic feature enhancement for improved smoke detection. The first branch, the channel–spatial module, sequentially applies channel and spatial attention operations to ensure precise localization of smoke regions while suppressing irrelevant noise. The channel attention mechanism employs a multi-pooling strategy—combining global average pooling, max pooling, and standard deviation pooling—to generate three complementary descriptors that refine distinct statistical properties of smoke features. The spatial attention module then applies the same triple-pooling strategy across the channel dimensions of feature maps, concatenates the outputs, and processes them through convolutional layers to create a spatially selective mask. The second branch, the frequency attention module, enhances spectral texture features using discrete cosine transform (DCT)-based frequency modulation. This approach compensates for the limitations of channel–spatial methods in capturing subtle smoke textures, which are crucial for early smoke recognition. The outputs from both branches are fused through element-wise summation, producing a final feature map enriched with channel, spatial, and frequency refinements. Furthermore, we integrate the CSFAttention module into a ResNet model [13] to construct a deep network optimized for smoke recognition. Experimental results indicate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance, reaching an accuracy of 96.84% on the USTC_SmokeRS dataset and outperforming existing deep learning models. The research framework of this paper is summarized in Figure 1.
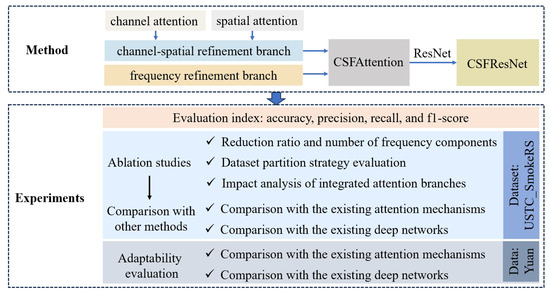
Figure 1.
The research framework of this paper. The proposed CSFAttention module integrates a channel–spatial refinement branch and a frequency refinement branch, and is inserted into the ResNet network to construct CSFResNet for remote sensing smoke recognition. The experiments first design ablation studies to evaluate the optimal hyperparameters and network structure, then compare the proposed method with existing attention mechanisms and deep networks to validate the effectiveness of the method proposed in this paper.
The primary highlights of this paper are as follows:
- We design a novel triple-pooling strategy (average, max, and standard deviation) for both channel and spatial attention modules. This approach captures complementary statistical properties, including central tendency, peak responses, and distribution variability, to generate robust descriptors that comprehensively characterize smoke features under diverse conditions.
- We propose a novel dual-branch architecture that integrates channel–spatial attention with frequency-domain analysis to enhance smoke feature representation. To complement the channel–spatial attention function, the frequency attention branch incorporates discrete cosine transform (DCT) to refine multi-frequency smoke texture patterns, resulting in a robust smoke representation.
- We conduct a systematic evaluation of our framework using the widely acknowledged USTC_SmokeRS dataset, achieving state-of-the-art recognition accuracy. To assess generalizability, we further examine the adaptability of the proposed methodology on the popular Yuan smoke dataset. The consistent performance demonstrated across these diverse datasets substantiates the effectiveness of the CSFAttention module in constructing comprehensive smoke representations through the strategic integration of hybrid attention mechanisms.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Hand-Crafted Features for Smoke Detection
Traditional smoke detection methodologies predominantly rely on handcrafted feature engineering to identify candidate regions, followed by machine learning-based verification processes. Commonly utilized features include color attributes, texture patterns, spatial–temporal dynamics, and motion characteristics, all of which help in generating candidate smoke regions within an image [14,15,16].
Color features frequently serve as fundamental components in multimodal frameworks, synergistically combined with complementary visual cues to enhance smoke characterization [17,18,19]. Early implementations demonstrated progressive refinement through multi-feature fusion strategies. For instance, optical flow dynamics were integrated with chromatic analysis to mitigate false positives in wildfire scenarios [15], while motion-color-area feature combinations were proposed to optimize detection precision [16]. Subsequent advancements introduced comprehensive feature ensembles incorporating static attributes (color irregularity, wavelet energy, and edge orientation histograms) and dynamic properties (motion vectors and directional changes) to improve environmental adaptability [19].
Edge-aware detection paradigms have evolved through sophisticated texture analysis techniques, with Local Binary Patterns (LBPs) [20] emerging as a pivotal framework for smoke pattern recognition. Hierarchical implementations combining LBP variants with neural classifiers demonstrated enhanced multi-scale texture discrimination through pyramid decomposition strategies [21]. Contemporary approaches further optimized feature discriminability by fusing local LBP descriptors with global chromatic-statistical features through SVM-based classification architectures [22]. Hybrid methodologies integrating LBP-based texture analysis with optical flow motion features achieved robust performance across diverse environmental conditions while maintaining computational efficiency [23].
Frequency domain analysis has been systematically explored through transform-based feature extraction, particularly leveraging Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) and Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) for multi-resolution smoke characterization. Early implementations employed DWT for spectral decomposition and correlation analysis of smoke’s transient patterns [24], while block-based DCT-DWT fusion strategies enhanced classification robustness through complementary frequency representations [25]. Advanced fractal analysis using DCT coefficients improved smoke growth pattern detection [26], with recursive DCT implementations optimizing computational efficiency in real-time systems [27]. Wavelet-based background separation techniques further advanced early smoke detection capabilities by analyzing transient spectral components [28,29]. These frequency-domain approaches demonstrated particular effectiveness when fused with spatial features, establishing comprehensive multi-domain analysis frameworks for smoke detection.
2.2. Deep Feature Refinement by Attention Mechanisms
The emergence of deep learning (DL) techniques, which autonomously extract robust features from raw image data and optimize feature representations, has catalyzed substantial performance enhancements across various computer vision tasks [30]. Building upon these DL foundations, contemporary research has increasingly embraced biological visual paradigms to further optimize computational efficiency and perceptual accuracy. Specifically, the human visual system’s selective processing paradigm, which prioritizes salient regions through sequential partial observations rather than holistic scene analysis, has inspired fundamental advancements in attention mechanisms for computer vision systems [31,32]. These mechanisms implement dynamic feature weighting strategies to enhance discriminative representation learning, demonstrating broad applicability across image classification [8,13,33], object detection [34,35,36], object segmentation [37,38], image restoration [39], and 3D vision tasks [40,41,42].
Channel attention architectures have evolved through progressive refinements of the seminal Squeeze-and-Excitation Network (SENet) framework [8]. Subsequent innovations introduced higher-order statistical modeling through global second-order pooling [43], style-based feature recalibration [44], and efficient cross-channel interaction via adaptive 1D convolutions [45]. Spectral analysis perspectives revealed fundamental connections between channel attention and frequency-domain transformations, leading to multi-spectral attention designs [46]. Channel–spatial co-attention mechanisms emerged through architectures like CBAM [33] and BAM [47], which synergistically combine channel-wise and spatial feature recalibration. Advanced variants further optimized cross-domain interactions through triplet attention [48], coordinate-aware position encoding [49], and parameter-free 3D attention estimation [50].
The introduction of Transformer architectures [51] brought self-attention mechanisms capable of modeling long-range dependencies, addressing the local receptive field limitations of traditional CNNs. Vision Transformer variants [11] and hybrid CNN–Transformer designs [52,53] have proven particularly effective in capturing global contextual relationships. Additionally, these models improved computational efficiency by incorporating depthwise separable convolutions and multi-scale pyramid structures [12].
2.3. Attention Mechanisms for Smoke Recognition
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) [13,54,55,56] have become foundational for smoke recognition due to their hierarchical feature extraction capabilities, driving advancements in fire detection systems [5]. However, conventional CNNs often exhibit limited discriminative power for subtle smoke patterns due to their reliance on local receptive fields, which may overemphasize irrelevant background textures. This limitation has motivated the integration of attention mechanisms to dynamically prioritize critical regions and channels while suppressing noise [6].
Channel attention mechanisms, which adaptively weight feature maps through learnable scaling factors, have proven pivotal for smoke detection. Foundational research demonstrated that multi-scale channel attention, combined with implicit deep supervision, enhances feature selectivity for smoke [57]. Subsequent innovations integrated dilated convolutions with efficient channel attention to model multi-scale smoke patterns [58], while hybrid modules combining local and global channel dependencies further improved robustness against adversarial interference [59]. Complementary spatial attention mechanisms address region-specific feature modulation, and concurrent channel-wise recalibration and spatial prioritization achieve comprehensive feature refinement. For instance, hybrid channel–spatial modules integrated into EfficientNet variants significantly boost smoke recognition accuracy by suppressing irrelevant backgrounds [60], while residual attention mechanisms, combined with channel–spatial operations, enhanced label-specific feature concentration [9]. To address the inherent locality of CNNs, recent hybrid architectures effectively combine self-attention mechanisms with the inductive bias of CNNs. Techniques such as convolutional token embedding bridged the gap between CNNs and transformers’ domains, enabling cascaded feature learning that preserves both micro-textures and macro-patterns [53].
Remote sensing (RS) imagery has emerged as a foundational technology in disaster surveillance due to its extensive spatial coverage, real-time data acquisition capabilities, and cost effectiveness. Wildfires, distinguished by their devastating impacts, pose significant threats to both ecological equilibrium and socioeconomic frameworks. As smoke constitutes a primary indicator of wildfire initiation, it represents a critical signal for early detection systems. Consequently, the scientific community has increasingly focused on leveraging RS imagery for wildfire identification and monitoring. Recent developments in smoke recognition based on remote sensing categorize images into six classes: cloud, dust, haze, land, seaside, and smoke. The integration of attention mechanisms has introduced a new impetus for extracting the most informative features from smoke in RS images, thereby contributing significantly to the effectiveness of wildfire monitoring and management. Ref. [1] highlighted the importance of attention mechanisms and introduced an innovative SmokeNet for RS-based smoke classification. To refine feature extraction, channel attention [8], spatial attention, and residual attention (RA) modules [9] were seamlessly integrated into the CNN framework, enabling the model to emphasize label-specific information crucial for precise classification. Expanding upon this concept, ref. [10] focused on extracting both global contextual information and salient features in RS images, proposing a self-adaptive feature aggregation (SAFA) network with dual pathways for smoke recognition. The global information extraction pathway (GIEP) strengthened multi-level feature interaction by establishing links between low-level and high-level representations. Meanwhile, the salient feature extraction pathway (SFEP) incorporated channel–spatial attention modules into ResBlocks [13] to highlight key discriminative features. The final classification result was obtained by weighting and aggregating the outputs from both subnetworks. Additionally, ref. [12] leveraged the combined strengths of CNNs and visual Transformers [11] to introduce SR-Net, an advanced forest fire smoke detection model capable of distinguishing smoke from clouds in satellite RS images. Furthermore, the adoption of depthwise separable convolution significantly optimized computational efficiency, reducing processing complexity while maintaining model accuracy.
Despite these advancements, existing attention mechanisms primarily focus on channel–spatial interactions while overlooking frequency-domain discriminators, which are crucial for smoke recognition. To address this limitation, we propose a dual-branch architecture that integrates channel–spatial refinement with frequency analysis. This design is further enhanced by an innovative triple-pooling (average, max, and standard deviation) module, which optimizes feature preservation and improves discriminatory capability.
3. The Proposed Method
In this section, we first introduce the proposed CSFAttention mechanism module in detail. Then, we present a deep network that integrates the CSFAttention module to improve smoke recognition.
3.1. CSFAttention Mechanism Module
As illustrated in Figure 2, the proposed CSFAttention mechanism utilizes two parallel processing branches to refine discriminative smoke features through complementary perceptual dimensions. The channel–spatial refinement branch first applies channel attention weighting to adaptively recalibrate feature responses at the channel level. This is followed by spatial attention, which enhances class-specific semantic regions within the feature tensor. Simultaneously, the frequency analysis branch employs discrete cosine transformation (DCT) to decompose input features into multi-scale frequency components. It then applies frequency-domain modifications to aggregate characteristic spectral signatures of smoke patterns. Detailed mathematical formulations and implementation specifications for each subsystem are presented in the subsequent sections.
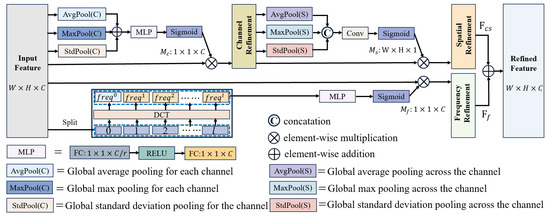
Figure 2.
The proposed CSFAttention module. The channel–spatial attention branch sequentially performs channel attention feature restoration followed by spatial attention feature refinement. The frequency attention branch utilizes frequency spectral components to aggregate smoke features. The results from these complementary branches are fused through element-wise summation.
3.1.1. Revisit Squeeze-and-Excitation Block
The Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) block [8] creates channel inter-dependencies in feature maps, enhancing the model’s sensitivity to informative channels that significantly contribute to the final classification decision. Structurally, the SE block consists of two main steps: squeeze and excitation. The squeeze step is responsible for embedding global information, while the excitation step focuses on the adaptive recalibration of channel relationships. Given an input feature map , the squeeze step for the c-th channel can be formulated as follows:
where represents the output associated with the c-th channel. The input comes directly from a convolutional layer with a fixed kernel size, representing a collection of local descriptors. The squeeze operation allows for the collection of global information and is typically implemented using global average pooling (GAP).
The second step, excitation, aims to fully capture channel-wise dependencies, which can be formulated as
where ⊙ refers to channel-wise multiplication, is the sigmoid function, and is the result generated by a transformation function of multi-layer perceptron (MLP), which is formulated as follows:
Here, and are two linear transformations that can be learned to capture the importance of each channel.
The SE block has been widely adopted in recent CNNs and has proven to be a key component in achieving state-of-the-art performance. However, it primarily focuses on reweighing the importance of each channel by modeling channel relationships, while overlooking spatial and frequency aggregation. To address this limitation, we propose a novel dual-branch attention module that integrates both channel–spatial refinement and frequency recalibration.
3.1.2. Channel–Spatial Refinement Branch
Given an intermediate feature map as input, the channel–spatial refinement branch sequentially infers a 1D channel attention and a 2D spatial attention . The overall attention process can be summarized as
where ⊙ refers to channel-wise multiplication, ⊗ denotes element-wise multiplication, and is the final refined output. The following describes the details of each attention module.
Channel attention. Channel attention mechanisms assign importance weights to different channels and have gained popularity in the deep learning community due to their simplicity and effectiveness in feature modeling. A key aspect of many channel attention approaches is the use of a single scalar per channel, which minimizes the computational overhead. As a result, global average pooling (GAP) is widely adopted for its efficiency and straightforward implementation. However, while GAP is computationally inexpensive, its simplicity restricts its ability to capture complex variations across different inputs. In particular, critical channel feature information may be lost when computing the mean value during GAP operations. In contrast, max pooling identifies the most salient regions of the feature map, providing additional cues for distinguishing object features and enabling more refined channel-wise attention [33,47]. Furthermore, since GAP functions as a channel-wise mean statistic for smoke images, incorporating standard deviation statistics can better characterize the data distribution within feature channels [44,61]. This enhancement is particularly valuable for extracting texture features in smoke-related imagery. Therefore, we propose integrating multiple pooling operations (average pooling, max pooling, and standard deviation pooling), and combining their results through element-wise summation. This approach leverages the strengths of each pooling method, improving feature representation and enhancing the effectiveness of channel attention.
Specifically, we first calculate the importance weights from the feature map using three pooling operations: global average pooling, max pooling, and standard deviation pooling. This results in three different 1D coefficients: , , and , derived from the input feature . These coefficients are then summed and passed through a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) with one hidden layer to produce the final channel attention coefficient . To reduce the parameter overhead, the hidden activation size in MLP is set to , where r is the reduction ratio. In short, the channel attention is computed as
where denotes the sigmoid function, , and is two linear transformations in MLP.
The channel refined feature map is denoted as
where ⊙ refers to channel-wise multiplication.
Spatial attention. Unlike channel attention, which emphasizes the importance of different channels, spatial attention focuses on identifying the most informative regions within the feature map. This makes spatial attention complementary to channel attention. In our channel–spatial refinement branch, channel attention and spatial attention are placed in a sequential manner. Mirroring the design of the channel attention block, we employ mixed pooling operations in the spatial attention to capture complementary statistical properties of smoke features. Based on the channel-refined feature map , we aggregate spatial information using triple-pooling operations, generating three 2D attention coefficients: , , and . These coefficient matrices are then concatenated and passed through a standard convolutional layer to produce the 2D spatial attention mask . In short, the spatial attention is computed as
where denotes the sigmoid function, and represents a convolution operation with the filter size of .
Thus, the designed channel–spatial branch sequentially applies channel and spatial attention modules, emphasizing meaningful features along those two principal dimensions. The refined feature map from the input feature is calculated as
where ⊙ refers to channel-wise multiplication, and ⊗ denotes element-wise multiplication.
3.1.3. Frequency Refinement Branch
The discrete cosine transform (DCT) is an orthogonal transform that decomposes an image into spectral sub-bands of varying importance, which are related to the image’s visual quality [62]. The 2D discrete cosine transform is typically expressed as follows:
where is the 2D DCT frequency spectrum, is the input signal, and h and w represent the frequency components of 2D DCT.
With the proof [46], GAP in the SE module [8] is a special case of 2D DCT and is proportional to the lowest frequency component of 2D DCT, namely
Characterizing smoke is particularly challenging due to its unpredictable behavior. Low-frequency components typically correspond to smooth and flat regions, while high-frequency components capture texture and fine details. In channel attention mechanisms, GAP primarily retains low-frequency information while neglecting higher-frequency components. However, these higher-frequency components provide valuable details that enhance smoke feature representation. To address this limitation, extending GAP to incorporate multiple frequency components from the 2D DCT can be beneficial. This approach enables a more comprehensive representation of relevant features, improving the model’s ability to characterize smoke effectively. The complete frequency attention refinement branch can be formulated as follows.
The input feature map is split into l parts along the channel dimension, i.e., , where each part and . For each part, a corresponding 2D DCT frequency component is implemented:
where is the frequency component corresponding to , and is the -dimensional vector after the transformation. The whole transformation coefficients for the input feature can be obtained by concatenation and MLP operation:
in which denotes the sigmoid function, and is the obtained multi-spectral weights. The refined features by frequency attention branch can be written as
where ⊙ refers to channel-wise multiplication.
In the frequency attention mechanism module, selecting appropriate frequency components is crucial for smoke feature representation. We adopt a strategy that evaluates the importance of each frequency component to guide the selection process. Specifically, we first analyze the impact of each individual frequency component on smoke recognition accuracy. Then, we select the top l frequency components that achieve the highest accuracy and integrate them for enriching smoke feature representation.
We fuse the results of both branches through the simple element-wise summation operation, generating a final feature map enriched with channel, spatial, and frequency refinements:
where ⊕ refers to element-wise summation.
3.2. The Network with CSFAttention for Smoke Recognition
ResNet [13] is a deep convolutional neural network designed to overcome the vanishing gradient problem by using skip connections, and it has achieved remarkable success in image recognition tasks. We integrate the CSFAttention module into the bottleneck of ResNet50, resulting in a modified deep network (CSFResNet) for smoke recognition. The input to this new bottleneck passes through three convolutional layers before entering the attention module. The output of the attention module is then combined with the identity mapping of the bottleneck input to produce the final output. Figure 3 illustrates the detailed structure of the proposed network for smoke recognition.
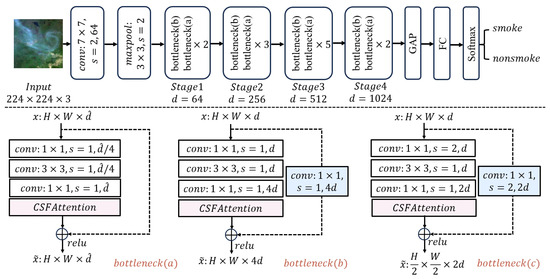
Figure 3.
The structure of CSFResNet. The proposed CSFAttention mechanism is strategically incorporated into the bottleneck structures of ResNet architecture to facilitate the sophisticated refinement of smoke-related features.
The input image is initially resized to . After passing through a convolutional layer and a max pooling layer, a feature map of size is obtained. Four stages with different numbers of bottlenecks are sequentially arranged to form a hierarchical network structure, which is used to extract multi-scale feature representations of smoke in the image. The four stages contain 3, 4, 6, and 3 bottlenecks, respectively. The bottleneck (b) structure at the front of Stage 1 is used to handle feature dimension matching during skip connections, increasing the feature dimension from 64 to 256. It is then passed through two consecutive bottleneck (a) structures to obtain a feature map of size . The bottleneck (c) structure at the front of Stage 2 reduces the feature map size to of the original dimensions while doubling the number of feature map channels. It is then processed through three consecutive bottleneck (a) structures to obtain a feature map of size . Stages 3 and 4 follow a similar process to Stage 2, progressively refining features and ultimately generating a feature map of size . Finally, it ends with global average pooling, a fully connected layer, and a softmax function for classification, determining whether the image contains smoke or not.
4. Experimental Results
We will conduct experiments to evaluate the performance of the proposed CSFResNet and demonstrate its superiority compared with state-of-the-art competitors in this section. All experiments are conducted in the Ubuntu 20.04 operation system with an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 3080 GPU.
4.1. Dataset
Wildfires are highly destructive natural disasters, and detecting them early is crucial. Smoke emission serves as a key indicator of wildfire occurrence and is essential for fire detection. To enhance smoke identification capabilities in remote sensing (RS) imagery, the USTC_SmokeRS satellite dataset was developed specifically to distinguish smoke from other visually similar scenes. MODIS data were selected as the principal source for USTC_SmokeRS construction due to their comprehensive spectral and temporal characteristics. The original MODIS Level 1B data underwent preprocessing in ENVI software version 5.3, including geometric correction to the Universal Transverse Mercator projection and radiometric calibration to obtain reflectance and radiance data. For image composition, MODIS bands 1, 4, and 3 were selected to represent the red, green, and blue channels, respectively. The resulting true-color RGB images were then used to build the USTC_SmokeRS dataset. The utilization of true-color RGB imagery offers substantial methodological advantages. Ref. [1] leveraged this approach because most optical satellite sensors can generate RGB images, making them more accessible than multi-spectral data. Furthermore, convolutional neural network (CNN) models trained on true-color RGB imagery exhibit enhanced transferability, allowing the model to be effectively utilized with RGB images from other satellite sensors without requiring significant architectural modifications.
The USTC_SmokeRS has been widely used to evaluate smoke recognition performance in satellite remote sensing applications [63,64,65]. It consists of six categories, smoke, seaside, land, haze, dust, and cloud, with the following image distribution: 1016 smoke images, 1007 seaside images, 1027 land images, 1002 haze images, 1009 dust images, and 1164 cloud images. Smoke is selected as the target category for wildfire detection. Dust and haze have a great similarity in color and texture with smoke, and they increase the difficulty of recognition. Clouds frequently manifest in satellite images and may be erroneously classified as smoke plumes during wildfire events, further complicating accurate identification. The land and seaside are used as the backgrounds of fire wildfire smoke. The representative images are shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
The representative images from USTC_SmokeRS datasets. The images in the first row to the sixth row belong to smoke, cloud, dust, haze, land, and seaside.
The smoke recognition problem is typically regarded as a binary classification task, where remote sensing images are classified as either smoke (to trigger an alarm) or background. To facilitate binary classification, the seaside, land, haze, dust, and cloud categories are merged into a single non-smoke (background) class, resulting in 5209 images. To balance the dataset, various data augmentation techniques, including brightness and contrast enhancement, rotation, scaling, cropping, and flipping, are applied, expanding the original 1016 smoke images to 5080. The balanced USTC_SmokeRS dataset is used to evaluate the performance of different networks.
4.2. Evaluation Index
Smoke recognition results are typically evaluated using the following metrics: true positives (TP), false positives (FP), false negatives (FN), and true negatives (TN). Specifically, TP refers to cases where smoke is correctly identified in both the predictions and ground-truth observations, while TN indicates correct classification of non-smoke scenarios. FP errors occur when non-smoke instances are incorrectly labeled as smoke, and FN errors happen when actual smoke events are misclassified as non-smoke. Evaluation metrics, such as accuracy, precision, recall, and f1-score, are derived from TP, FP, FN, and TN, and are commonly used to assess the performance of smoke recognition techniques. These metrics are defined as follows:
Accuracy. This metric represents the proportion of correct predictions among all predictions made:
Precision. It is calculated as the ratio of true positives to the total number of samples predicted as positives, reflecting the accuracy of positive predictions:
Recall. It represents the ratio between true positives and the total number of actual positive samples, indicating the model’s ability to identify positive instances accurately:
F1-score. It provides a balanced evaluation of precision and recall metrics:
4.3. Network Train
The balanced USTC_SmokeRS dataset is divided into training, validation, and test sets to facilitate the evaluation of the smoke recognition algorithm’s performance. Smoke recognition is a binary classification task that categorizes images as either smoke or non-smoke. To optimize classification performance, we use the cross-entropy loss function, which measures the discrepancy between true and predicted label distributions. The mathematical formulation of the cross-entropy loss is as follows:
where y and are the true and predicted labels, respectively.
We train the proposed CSFResNet model from scratch using the SGD optimizer for 100 epochs with a batch size of 32 on a single GPU. The initial learning rate is set to 0.0125 and is reduced by a factor of 10 at the 50th and 80th epochs, resulting in two reductions overall. To enhance training stability and prevent convergence to local optima, we apply momentum and learning rate decay, with weight decay and momentum set to 0.0001 and 0.9, respectively. For a fair and consistent comparison, all competing models are trained using the same protocols and hyperparameters as CSFResNet.
4.4. Ablation Studies
This subsection empirically validates the effectiveness of key design choices in our framework. First, we examine two critical hyperparameters in the CSFAttention module: the reduction ratio (r) in the MLP layers of the channel and frequency attention modules, which controls feature compression, and the number of frequency components (l), which determines the extent of spectral information utilization. Next, we evaluate the impact of different training-validation-test partitioning strategies on model performance, and select the optimal configuration for all subsequent experiments. Finally, we assess the impact of integrating the channel–spatial and frequency branches, evaluating whether their combined operation improves feature representation compared to using each branch independently.
Reduction ratio and number of frequency components. To systematically optimize our attention module, we first investigate two critical hyperparameters, which are reduction ratio r in the MLP operation and number of components l in the frequency attention branch. The reduction ratio r governs feature compression efficiency, directly balancing model capacity and computational cost. The balanced USTC_SmokeRS dataset is partitioned into training, validation, and test sets in a 6:2:2 ratio, a common practice in machine learning training strategies based on dataset size, in order to evaluate the impact of the reduction ratio r and the number of components l on model performance. We evaluate r across candidate values {2, 4, 8, 16, 32} to identify optimal configurations. For frequency components selection in the frequency refinement branch, we divide the whole 2D DCT frequency space into parts since the smallest feature map size of CSFResNet is . To investigate the effects of different frequency components, we conduct 49 independent experiments, each activating a single frequency component. Based on performance rankings, we select the top-l components (with ) for final integration. We perform the grid search to determine the optimal combinations of r and l for USTC_SmokeRS datasets. As shown in Figure 5, the USTC_SmokeRS dataset achieves peak performance with and , which are adopted uniformly in subsequent experiments.
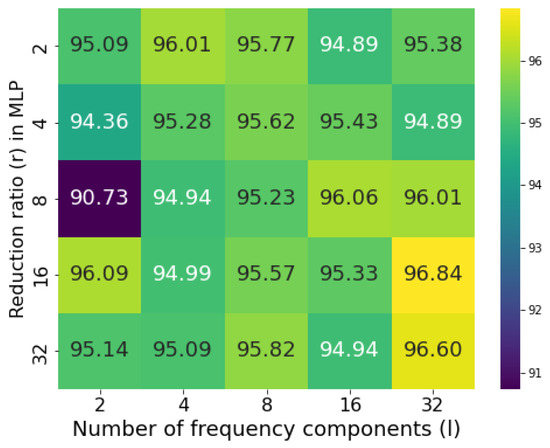
Figure 5.
Accuracy of different combinations of reduction ratio (r) and number of frequency components (l).
Dataset partition strategy evaluation. In order to evaluate the impact of different data partitioning strategies on model performance, we divide the balanced USTC_SmokeRS dataset into training, validation, and test sets using four commonly adopted ratios: 5:2.5:2.5, 6:2:2, 7:1.5:1.5, and 8:1:1. For each partitioning strategy, we conduct five-fold cross-validation experiments to obtain reliable statistical results.
The experimental outcomes, including accuracy, precision, recall, and f1-score, are summarized in Table 1. As shown, the proposed method consistently achieves competitive performance across all partitioning schemes. Notably, the 6:2:2 split yields the highest accuracy of 96.25%, along with balanced values for other metrics, indicating its effectiveness in preserving generalization capability while maintaining adequate data for both training and evaluation.

Table 1.
Experimental results of the proposed method on the USTC_SmokeRS dataset partitioned with different percentages.
Based on these experimental results, we adopt the 6:2:2 split ratio with five-fold cross-validation for all subsequent experiments in this study, as it provides the optimal balance between training data volume and validation/test set representativeness for our proposed method.
Impact analysis of integrated attention branches. We demonstrate the necessity of integrating the channel–spatial attention branch with the frequency attention branch by incorporating the proposed CSFAttention module into the bottleneck structure of ResNet50, thereby constructing the CSFResNet network for smoke recognition. To validate our design choices, we conduct an ablation study, removing each branch individually to assess the effectiveness of using both attention branches. Specifically, the network that includes only the channel–spatial attention branch is denoted as CSFResNet-cs, while the one incorporating only the frequency attention branch is labeled as CSFResNet-f. The experimental results are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Performance evaluation of dual-branch attention design on the USTC_SmokeRS dataset.
The proposed CSFResNet demonstrates superior performance over both the baseline ResNet50 and single-branch variants (CSFResNet-cs, CSFResNet-f). As shown in Table 2, CSFResNet, CSFResNet-cs, and CSFResNet-f significantly outperform the base ResNet50 model, highlighting the effectiveness of the attention mechanisms in improving the performance for smoke recognition. Furthermore, CSFResNet attains 96.25% accuracy, surpassing ResNet50 (82.39%) by 13.86% and outperforming CSFResNet-cs (92.67%) and CSFResNet-f (92.46%) by 3.58% and 3.79%, respectively. As illustrated in Figure 6, CSFResNet achieves consistent improvements in precision, recall, and f1-score. This demonstrates that the dual-branch design synergistically captures complementary smoke features, yielding greater discriminative power than isolated branches.
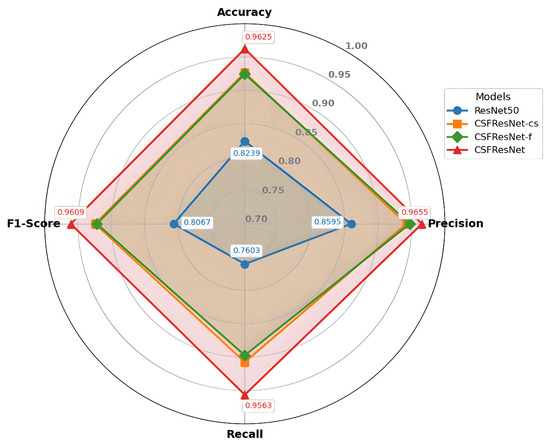
Figure 6.
Performance evaluation of dual-branch structure. CSFResNet outperforms the baseline and single-branch variants in accuracy, precision, recall, and f1-score.
4.5. Comparison with the Other Methods
We first compare CSFAttention with common attention mechanisms to highlight its advantages. We then evaluate the CSFResNet, which integrates CSFAttention module, against popular deep networks to demonstrate that our proposed network outperforms both convolution-based and Transformer-based models.
4.5.1. Comparison with the Existing Attention Mechanisms
This subsection compares the proposed CSFAttention module with popular attention mechanisms, including SE [8], CBAM [33], SRM [44], FCA [46], and SimAM [50]. Each attention mechanism replaces the CSFAttention module in CSFResNet, resulting in a new network (denoted as [Attention Mechanism]ResNet) for smoke recognition evaluation. As reported in Table 3, the proposed CSFResNet demonstrates significant superiority over other attention-enhanced ResNet variants in smoke recognition tasks.

Table 3.
Performance comparison of different attention mechanisms on the USTC_SmokeRS dataset.
CSFResNet achieves the highest accuracy (96.25%), precision (96.55%), recall (95.63%), and f1-score (96.09%), significantly outperforming the other networks. For instance, FCAResNet, which is one of the leading methods, achieves an accuracy of 93.09%, while SEResNet and SimAMResNet achieve accuracies of 92.64% and 92.27%, respectively. Notably, the SRMResNet model shows a lower performance across all metrics, with an accuracy of 86.17%.
To better understand how well-learned representations capture smoke information in an image, we select images from the USTC_SmokeRS dataset. Using Grad-CAM [66], we visualize heatmaps at the networks’ final convolutional layers to gain insights into their feature representation behaviors. For comparison, we also generate heatmaps for the corresponding counterparts. As shown in Figure 7, CSFAttention-enhanced networks more accurately focus on smoke regions than their competitors. In scenarios characterized by minimal smoke coverage within the image, the proposed CSFResNet demonstrates exceptional efficacy in detecting subtle smoke signatures while substantially mitigating background interference effects. Concurrently, in instances where smoke plumes dominate the spatial extent of the imagery, the methodology exhibits robust capabilities in accurately perceiving dense smoke formations. This dual functionality underscores the model’s adaptability across varying smoke concentrations, facilitating comprehensive wildfire detection capabilities regardless of the spatial distribution characteristics of smoke manifestations.
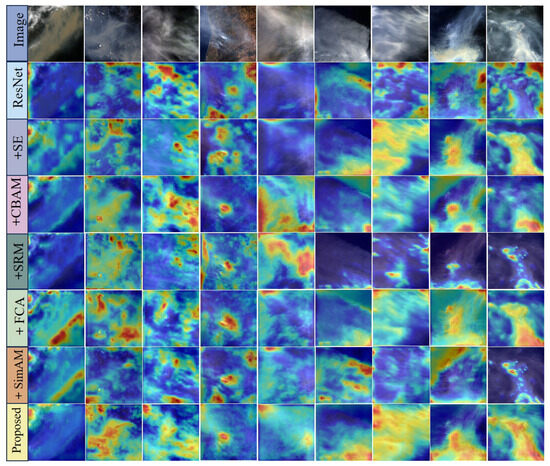
Figure 7.
Visualization of heatmaps generated by GradCAM [66]. The first row represents images from USTCSmokeRS; the second row shows results based on ResNet; and rows 3 through 8 demonstrate the effects of different attention mechanisms.
4.5.2. Comparison with the Existing Deep Networks
We compare our CSFResNet with widely used deep networks for smoke recognition, including both CNN-based models (AlexNet [54], ResNet [13], DenseNet [67], EfficientNet [68], RepVGG [69]) and Transformer-based models (ViT [11], DeiT [70], Swin Transformer [71], MViT [72]). As summarized in Table 4, CSFResNet outperforms these state-of-the-art models in smoke recognition, demonstrating its effectiveness in this task.

Table 4.
Performance evaluation of different deep networks for USTC_SmokeRS smoke recognition.
As shown in Table 4, CSFResNet achieves an accuracy of 96.25%, outperforming all other networks in the comparison. These results confirm that integrating the dual-branch attention module into the ResNet architecture to form CSFResNet significantly enhances smoke recognition performance compared to both CNN-based and Transformer-based models.
4.6. Adaptability Evaluation
We further validate the performance of the proposed method on the generic smoke recognition dataset, demonstrating the strong adaptability of our approach.
The Yuan smoke dataset [73] is widely used for training and evaluating smoke recognition models. It is divided into four subsets: Set1, Set2, Set3, and Set4. Set1 contains 1383 images, including 552 smoke and 831 non-smoke images. Set2 comprises 1505 images, with 699 smoke and 817 non-smoke images. Set3 consists of 10,712 images, including 2201 smoke and 8511 non-smoke images, while Set4 contains 10,617 images, with 2254 smoke and 8363 non-smoke images. To address the imbalance between smoke and non-smoke images, data augmentation techniques—including horizontal and vertical flips and random rotations—are applied to the 2201 smoke images in Set3. This augmentation results in a more balanced dataset with 8804 smoke and 8851 non-smoke images. Similarly, augmentation is performed on the 2254 smoke images in Set4, yielding 9016 smoke and 8363 non-smoke images. By merging Set1, Set2, the augmented Set3, and the extended Set4, a larger dataset is created, comprising 19,071 smoke and 18,862 non-smoke images. The dataset is partitioned in a 6:2:2 ratio to create training, validation, and test sets, and a five-fold cross-validation strategy is implemented to evaluate the performance of deep networks.
Based on the Yuan dataset, we demonstrate that our proposed CSFAttention module outperforms other attention mechanisms, while also showing the superiority of the CSFResNet architecture over other deep networks. The experimental results are comprehensively summarized in Table 5.

Table 5.
The performance comparison of the proposed method with its competitors on the Yuan dataset.
As shown in Table 5, the proposed CSFResNet method achieves outstanding performance on the Yuan dataset, with an accuracy of 98.94%, precision of 98.80%, recall of 99.15%, and f1-score of 98.97%, outperforming all other attention-based ResNet variants. Compared with SEResNet, CBAMResNet, SRMResNet, FCAResNet, and SimAMResNet, CSFResNet consistently achieves higher scores across all evaluation metrics, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed fusion attention mechanism.
When compared to conventional convolutional neural networks and Transformer-based architectures, CSFResNet also demonstrates remarkable performance. Our method significantly outperforms traditional CNNs such as AlexNet [54] (95.62 ± 0.72% accuracy), ResNet50 [13] (95.80 ± 0.42% accuracy), and DenseNet-121 [67] (96.49 ± 0.33% accuracy). The performance gap is even more pronounced when compared to Transformer-based models, including ViT-B dosovitskiy2020image (95.29 ± 0.20% accuracy), Deit-Small [70] (93.77 ± 0.37% accuracy), and Swin-small [71] (94.63 ± 0.72% accuracy). Among all tested networks, only EfficientNet-b1 [68] (99.15 ± 0.17% accuracy) and RepVGG-A1 [69] (99.09 ± 0.11% accuracy) achieve comparable results to our proposed method. The difference between CSFResNet and EfficientNet-b1 is merely 0.21% in accuracy, which is not statistically significant considering the standard deviations.
Experimental results validate the effectiveness of the proposed CSFAttention module in enhancing smoke recognition performance, demonstrating consistent improvements across various metrics and datasets. This adaptability makes the developed CSFResNet model a robust and reliable tool for smoke recognition application.
5. Conclusions
This research introduces a novel dual-branch attention framework (CSFAttention) that synergistically integrates channel–spatial feature refinement with frequency analysis to enhance remote sensing (RS) smoke recognition capabilities. The channel–spatial refinement module, augmented by a comprehensive triple-pooling strategy (incorporating average, maximum, and standard deviation pooling operations), effectively captures the multifaceted statistical characteristics of smoke features across heterogeneous environmental conditions. Concurrently, the frequency refinement branch employs spectral attention mechanisms to enhance the textural representation of smoke signatures. Through the strategic fusion of these complementary branches, the framework achieves holistic feature optimization that systematically balances channel dependencies, spatial saliency, and spectral discriminability. The proposed CSFAttention mechanism is strategically integrated into the bottleneck modules of the ResNet architecture to recognize RS smoke images. Experimental validation on the widely used USTC_SmokeRS dataset demonstrates the framework’s superiority, achieving state-of-the-art accuracies of 96.84%.
In comparison to existing attention mechanisms, which typically focus solely on channel or spatial dimensions, CSFAttention’s dual-branch structure introduces frequency-domain information—a key differentiator that proves particularly effective in remote sensing contexts where subtle texture variations and background noise pose significant challenges. This design choice contributes directly to the performance gains observed across multiple evaluation metrics and datasets.
While the proposed framework demonstrates significant advancements, several limitations necessitate further research:
Computational complexity limitations. While our dual-branch architecture delivers superior performance, it introduces additional computational overhead compared to single-branch attention mechanisms. This increased complexity may present challenges for deployment on resource-constrained edge devices in remote monitoring stations. Future work will focus on model compression and optimization techniques to reduce computational requirements while maintaining recognition accuracy.
Attention-driven RS smoke location. The method presented in this paper is primarily designed for classifying remote sensing smoke images into two categories: smoke and non-smoke. However, it does not perform target localization within the images. To address this limitation, future research will focus on annotating the data with both category labels and precise location information necessary for object detection tasks. Additionally, a multi-attention mechanism integration strategy will be applied to the object detection framework to enhance the accuracy of smoke classification and localization in remote sensing images.
Multi-temporal feature integration. The current framework does not exploit the temporal dimension of satellite imagery, which could provide valuable contextual information for distinguishing smoke plumes from other phenomena based on their evolution patterns. Developing a spatiotemporal extension of CSFAttention that incorporates time-series data represents a promising direction for future research.
Language-guided RS smoke recognition. The currently available USTC_SmokeRS dataset is limited in scale, containing only a little over 1000 smoke images. Acquiring larger-scale datasets incurs significantly higher costs. With the extensive research on vision language models (VLMs), an alternative approach is to utilize textual descriptions to guide the model through few-shot training, offering a potential solution to data limitations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.C.; methodology, G.C. and L.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, G.C. and L.Y.; writing—review and editing, G.C. and G.F.; validation, L.Y. and Z.Y.; data curation, Z.Y.; visualization, L.Y.; funding acquisition, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Tianjin Municipal College Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (202410069063), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62205243).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available at https://github.com/syx-a11y/remote-sensing-smoke-recognition (accessed on 7 May 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ba, R.; Chen, C.; Yuan, J.; Song, W.; Lo, S. Smokenet: Satellite smoke scene detection using convolutional neural network with spatial and channel-wise attention. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Coogan, S.C.; Subramanian, S.G.; Crowley, M.; Taylor, S.; Flannigan, M.D. A review of machine learning applications in wildfire science and management. Environ. Rev. 2020, 28, 478–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, J.A.; Oladosu, J.A. Video-based smoke detection algorithms: A chronological survey. Comput. Eng. Intell. Syst. 2014, 5, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- Matlani, P.; Shrivastava, M. A survey on video smoke detection. In Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development: Proceedings of ICT4SD 2016; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Khanna, P.; Ojha, A. A survey on vision-based outdoor smoke detection techniques for environmental safety. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2022, 185, 158–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Xian, B.; Yu, H. Visual fire detection using deep learning: A survey. Neurocomputing 2024, 596, 127975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.-H.; Xu, T.-X.; Liu, J.-J.; Liu, Z.-N.; Jiang, P.-T.; Mu, T.-J.; Zhang, S.-H.; Martin, R.R.; Cheng, M.-M.; Hu, S.-M. Attention mechanisms in computer vision: A survey. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Residual attention network for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Cao, Y.; Feng, X.; Lu, X. Global2salient: Self-adaptive feature aggregation for remote sensing smoke detection. Neurocomputing 2021, 466, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tan, S.; Yang, Z.; Wen, D.; Xiao, H. A forest fire smoke detection model combining convolutional neural network and vision transformer. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6, 1136969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Piccinini, P.; Calderara, S.; Cucchiara, R. Reliable smoke detection in the domains of image energy and color. In Proceedings of the 2008 15th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 October 2008; pp. 1376–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Chunyu, Y.; Jun, F.; Jinjun, W.; Yongming, Z. Video fire smoke detection using motion and color features. Fire Technol. 2010, 46, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, T.X.; Kim, J.-M. An effective four-stage smoke-detection algorithm using video images for early fire-alarm systems. Fire Saf. J. 2011, 46, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Bai, Z.; Chen, H.; Bohush, R.; Ablameyko, S. An effective algorithm to detect both smoke and flame using color and wavelet analysis. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 2017, 27, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; He, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, J. Video smoke detection using shape, color and dynamic features. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 33, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, L. Using popular object detection methods for real time forest fire detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID), Hangzhou, China, 8–9 December 2018; Volume 1, pp. 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikainen, M.; Maenpaa, T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F. Video-based smoke detection with histogram sequence of lbp and lbpv pyramids. Fire Saf. J. 2011, 46, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgir, N.; Nguyen, K.; Chandran, V.; Boles, W. Combining multi-channel color space with local binary co-occurrence feature descriptors for accurate smoke detection from surveillance videos. Fire Saf. J. 2018, 102, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Li, W.; Dong, N. Fire smoke detection based on texture features and optical flow vector of contour. In Proceedings of the 2016 12th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA), Guilin, China, 12–15 June 2016; pp. 2879–2883. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.-Y.; Han, N.; Luo, Q.-J. A smoke detection algorithm based on discrete wavelet transform and correlation analysis. In Proceedings of the 2012 Fourth International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking and Security, Nanjing, China, 2–4 November 2012; pp. 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Gubbi, J.; Marusic, S.; Palaniswami, M. Smoke detection in video using wavelets and support vector machines. Fire Saf. J. 2009, 44, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazza-Benyahia, A.; Hamouda, N.; Tlili, F.; Ouerghi, S. Early smoke detection in forest areas from dct based compressed video. In Proceedings of the 2012 20th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Bucharest, Romania, 27–31 August 2012; pp. 2752–2756. [Google Scholar]
- Millan-Garcia, L.; Sanchez-Perez, G.; Nakano, M.; Toscano-Medina, K.; Perez-Meana, H.; Rojas-Cardenas, L. An early fire detection algorithm using ip cameras. Sensors 2012, 12, 5670–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töreyin, B.U.; Dedeoğlu, Y.; Cetin, A.E. Wavelet based real-time smoke detection in video. In Proceedings of the 2005 13th European Signal Processing Conference, Antalya, Turkey, 4–8 September 2005; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Huang, T. Wavelet based smoke detection method with rgb contrast-image and shape constrain. In Proceedings of the 2013 Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Kuching, Malaysia, 17–20 November 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Wang, P.; Abbas, K. A survey on deep learning and its applications. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.H.; Chelazzi, L. Attentional modulation of visual processing. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 27, 611–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, M.M.; Golomb, J.D.; Turk-Browne, N.B. A taxonomy of external and internal attention. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2011, 62, 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.01497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Ocnet: Object context network for scene parsing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.00916. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Lu, L.; Qi, P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Q.; Hu, H.; Zhai, J.; Li, X. Cascaded frameworks in underwater optical image restoration. Inf. Fusion 2025, 117, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Gool, L.V. Temporal segment networks for action recognition in videos. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 2740–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Tu, Z. Attentional shapecontextnet for point cloud recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4606–4615. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.-H.; Cai, J.-X.; Liu, Z.-N.; Mu, T.-J.; Martin, R.R.; Hu, S.-M. Pct: Point cloud transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2021, 7, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, P. Global second-order pooling convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3024–3033. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H.-E.; Nam, H. Srm: A style-based recalibration module for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1854–1862. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. Eca-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Li, X. Fcanet: Frequency channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 783–792. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J. Bam: Bottleneck attention module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, D.; Nalamada, T.; Arasanipalai, A.U.; Hou, Q. Rotate to attend: Convolutional triplet attention module. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 3139–3148. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.-Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. Simam: A simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11863–11874. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jung, H.-K.; Jin, Y.; Hua, D.; Xu, S. Lightweight smoke recognition based on deep convolution and self-attention. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1218713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Yu, H. Convolution-enhanced vision transformer network for smoke recognition. Fire Technol. 2023, 59, 925–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yan, Q.; Liu, P. An efficient fire detection method based on multiscale feature extraction, implicit deep supervision and channel attention mechanism. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 8467–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yu, J.; He, Z. Deca: A novel multi-scale efficient channel attention module for object detection in real-life fire images. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 1362–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J. Adversarial fusion network for forest fire smoke detection. Forests 2022, 13, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, S.; Alenezi, F.; Masood, S.; Ahmad, M.; Gündüz, E.S.; Polat, K. Attention based cnn model for fire detection and localization in real-world images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 189, 116114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Belongie, S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1501–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.R.; Yip, P. Discrete Cosine Transform: Algorithms, Advantages, Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Qu, J.J.; Hao, X.; Liu, Y.; Sommers, W.T. An improved algorithm for small and cool fire detection using modis data: A preliminary study in the southeastern united states. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, W.; Lian, L.; Wei, X. Forest fire smoke detection using back-propagation neural network based on modis data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4473–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, R.; Song, W.; Li, X.; Xie, Z.; Lo, S. Integration of multiple spectral indices and a neural network for burned area mapping based on modis data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Maaten, L.V.D.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Han, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J. Repvgg: Making vgg-style convnets great again. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13733–13742. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jégou, H. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 10347–10357. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Xiong, B.; Mangalam, K.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Malik, J.; Feichtenhofer, C. Multiscale vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 6824–6835. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Wan, B.; Yuan, F.; Xia, X.; Shi, J. A deep normalization and convolutional neural network for image smoke detection. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18429–18438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).