Wildfire Effects on the Soil Respiration and Bacterial Microbiota Composition in Mediterranean-Type Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Sampling
2.2. Measurements of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Soil Respiration Rates
2.4. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of Soil Physico-Chemical Characteristics as Affected by Wildfire
3.2. Soil Respiration
3.3. Influence of Fire on Bacterial Phyla and Their Correlation with Vegetation
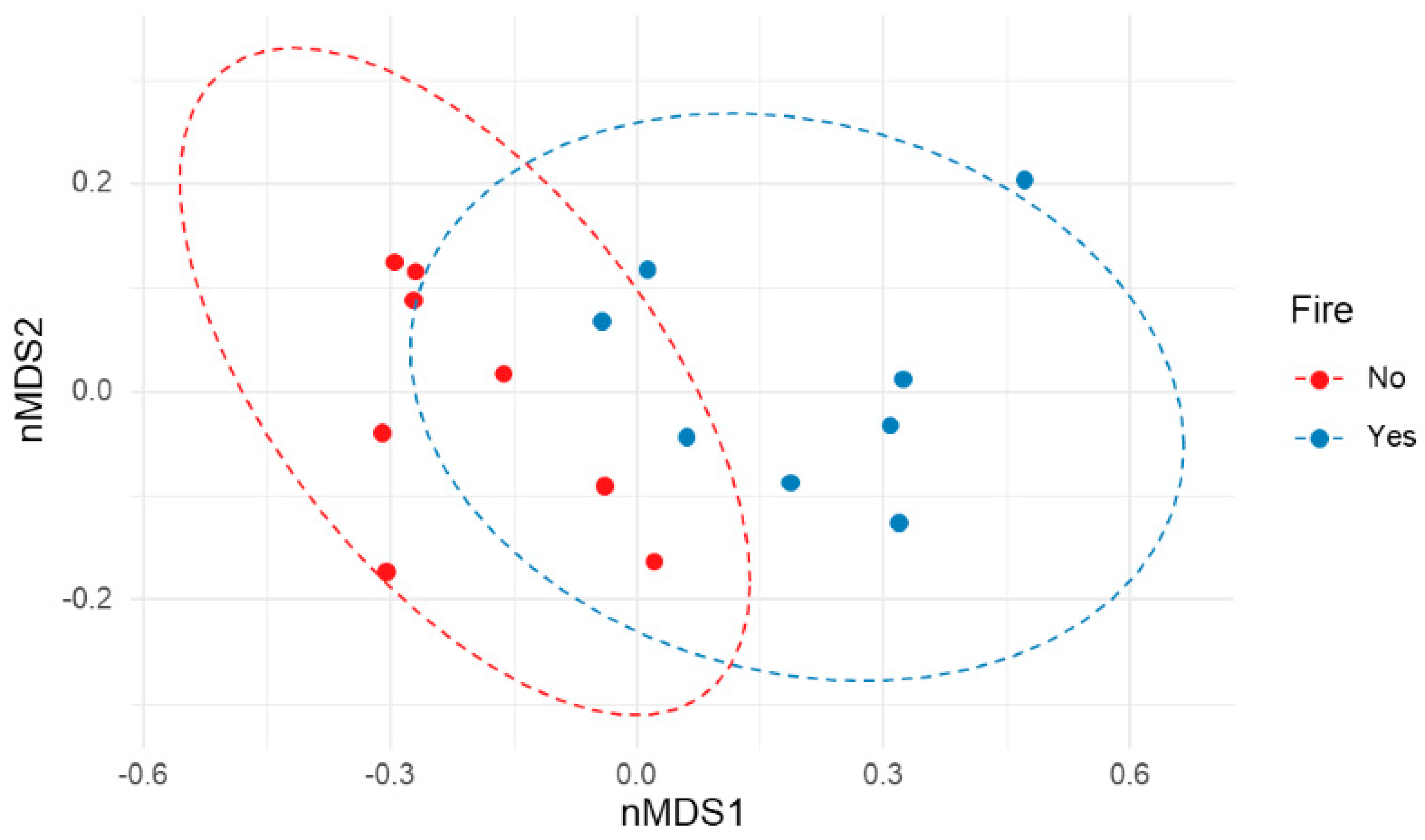
3.4. Wildfire Influence on Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, P.T.; Hanley, H.; Mahesh, A.; Reed, C.; Strenfel, S.J.; Davis, S.J.; Kochanski, A.K.; Clements, C.B. Climate warming increases extreme daily wildfire growth risk in California. Nature 2023, 621, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.; Skea, J.; Shukla, P.R. Global Warming of 1.5 C: IPCC Special Report on Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 C above Pre-Industrial Levels in Context of Strengthening Response to Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, R.; Corringham, T.; Gershunov, A.; Benmarhnia, T. Wildfire smoke impacts respiratory health more than fine particles from other sources: Observational evidence from Southern California. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Butry, D.; Gilbert, S.; Webb, D.; Fung, J. The costs and losses of wildfires. NIST Spec. Publ. 2017, 1215, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Vogler, K.C.; Ager, A.A.; Day, M.A.; Jennings, M.; Bailey, J.D. Prioritization of forest restoration projects: Tradeoffs between wildfire protection, ecological restoration and economic objectives. Forests 2015, 6, 4403–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Alonso, P.; Saiz, G.; García, R.A.; Pauchard, A.; Ferreira, A.; Merino, A. Post-fire ecological restoration in Latin American forest ecosystems: Insights and lessons from the last two decades. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 509, 120083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certini, G. Effects of fire on properties of forest soils: A review. Oecologia 2005, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Jayakumar, S. Impact of forest fire on physical, chemical and biological properties of soil: A review. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 2, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Francos, M.; Pereira, P.; Alcañiz, M.; Úbeda, X. Post-wildfire management effects on short-term evolution of soil properties (Catalonia, Spain, SW-Europe). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, H. Effects of a wildfire on selected physical, chemical and biochemical soil properties in a Pinus massoniana forest in South China. Forests 2014, 5, 2947–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francos, M.; Úbeda, X.; Pereira, P.; Alcañiz, M. Long-term impact of wildfire on soils exposed to different fire severities. A case study in Cadiretes Massif (NE Iberian Peninsula). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francos Quijorna, M. Wildfire and Forest Management Effects on Soil Properties; Universitat de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Castaldi, S.; De Grandcourt, A.; Rasile, A.; Skiba, U.; Valentini, R. CO2, CH4 and N2O fluxes from soil of a burned grassland in Central Africa. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Raghubanshi, A.; Singh, R.; Srivastava, S. Microbial biomass acts as a source of plant nutrients in dry tropical forest and savanna. Nature 1989, 338, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxbury, J.; Lauren, J.; Fruci, J. Measurement of the biologically active soil nitrogen fraction by a 15N technique. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1991, 34, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certini, G.; Moya, D.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Mastrolonardo, G. The impact of fire on soil-dwelling biota: A review. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 488, 118989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, F.J.; Acea, M.J.; Carballas, T. Soil microbial populations after wildfire. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1993, 13, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, S.R.; Rogers, B.M.; Treseder, K.K.; Randerson, J.T. Fire severity influences the response of soil microbes to a boreal forest fire. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goberna, M.; García, C.; Insam, H.; Hernández, M.; Verdú, M. Burning fire-prone Mediterranean shrublands: Immediate changes in soil microbial community structure and ecosystem functions. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiqi, L.; Zhou, X. Soil Respiration and the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Fu, S. Biological indices for soil quality evaluation: Perspectives and limitations. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatica-Saavedra, P.; Aburto, F.; Rojas, P.; Echeverría, C. Soil health indicators for monitoring forest ecological restoration: A critical review. Restor. Ecol. 2023, 31, e13836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Álvarez, P.A.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Sagra, J.; Moya, D.; Fontúrbel, T.; De las Heras, J. Soil respiration changes after prescribed fires in Spanish black pine (Pinus nigra Arn. ssp. salzmannii) monospecific and mixed forest stands. Forests 2017, 8, 248. [Google Scholar]
- Concilio, A.; Ma, S.; Li, Q.; LeMoine, J.; Chen, J.; North, M.; Moorhead, D.; Jensen, R. Soil respiration response to prescribed burning and thinning in mixed-conifer and hardwood forests. Can. J. For. Res. 2005, 35, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fest, B.J.; Livesley, S.J.; von Fischer, J.C.; Arndt, S.K. Repeated fuel reduction burns have little long-term impact on soil greenhouse gas exchange in a dry sclerophyll eucalypt forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Rojas, M.; Lewandrowski, W.; Erickson, T.E.; Dixon, K.W.; Merritt, D.J. Soil respiration dynamics in fire affected semi-arid ecosystems: Effects of vegetation type and environmental factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tüfekçioğlu, A.; Küçük, M.; Bilmiş, T.; Altun, L.; Yılmaz, M. Soil respiration and root biomass responses to burning in Calabrian pine (Pinus brutia) stands in Edirne, Turkey. J. Environ. Biol. 2010, 31, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Piao, S.; Janssens, I.A.; Tang, J.; Liu, W.; Chi, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, S. Soil respiration under climate warming: Differential response of heterotrophic and autotrophic respiration. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3229–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Todd-Brown, K.E.; Bailey, V.L.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, C. A moisture function of soil heterotrophic respiration that incorporates microscale processes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, P.R. Fractionation and particle size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part I. Agronomy 9; Black, C.A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 545–567. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard, D.; Kalra, Y.; Crumbaugh, J. Nitrate and exchangeable ammonium nitrogen. Soil Sampl. Methods Anal. 1993, 1, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, C.; Hart, M.; Brookes, P.C. Laboratory manual of the soil microbial biomass group. Rothamsted Res. 2006, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Alef, K. Estimation of soil respiration. In Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Alef, K., Nannipieri, P., Eds.; Academic: London, UK, 1995; pp. 215–216. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.; Taka, J.; Kluyver, T.; Konovalov, A.; Ragan-Kelley, M.; Thiéry, N.M.; Fangohr, H. Using Jupyter for reproducible scientific workflows. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2021, 23, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Oksanen, M.J.; Suggests, M. The vegan package. Community Ecol. Package 2007, 10, 719. [Google Scholar]
- Cáceres, M.D.; Legendre, P. Associations between species and groups of sites: Indices and statistical inference. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 90, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-García, C.; Santin, C.; Doerr, S.H.; Strydom, T.; Urbanek, E. Wildland fire ash enhances short-term CO2 flux from soil in a Southern African savannah. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Liu, H.; Pu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhou, B.; Yuan, R.; Wang, F. Bacterial response to soil property changes caused by wood ash from wildfire in forest soils around mining areas: Relevance of bacterial community composition, carbon and nitrogen cycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Song, J.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Hao, Y.; Di, M.; Wan, S. Understanding the effects of fire and nitrogen addition on soil respiration of a field study by combining observations with a meta-analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 292, 108106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A.; Gentile, A.E.; Arena, C.; De Santo, A.V. Organic matter, nutrient content and biological activity in burned and unburned soils of a Mediterranean maquis area of southern Italy. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, C.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Gómez, I.; García-Orenes, F.; Jordán, M.M. Microbial recolonization and chemical changes in a soil heated at different temperatures. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, C.; Inclán, R.; Sánchez, D.; Clavero, M.; Fernández, A.; Morante, R.; Cardeña, A.; Blanco, A.; Van Miegroet, H. Effect of wildfires on soil respiration in three typical Mediterranean forest ecosystems in Madrid, Spain. Plant Soil 2013, 369, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, T.; Garcia, C.; Reinhardt, I. Short-term effect of wildfire on the chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties of Mediterranean pine forest soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1997, 25, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schill, M.L. Severe Wildfires Reduce Soil Microbial Exoenzyme Production and Fungal Abundances in the Southern Appalachian Mountains. Ph.D. Dissertation, The University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ling, L.; Singh, B.P.; Luo, Y.; Jeewani, P.H.; Xu, J. Decomposition of substrates with recalcitrance gradient, primed CO2, and its relations with soil microbial diversity in post-fire forest soils. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; González-Pérez, J.A.; Turmero, A.; Hernández, M.; Ball, A.S.; González-Vila, F.J.; Arias, M.E. Physico-chemical and microbial perturbations of Andalusian pine forest soils following a wildfire. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas-Borja, M.; Miralles, I.; Ortega, R.; Plaza-Álvarez, P.; Gonzalez-Romero, J.; Sagra, J.; Soriano-Rodríguez, M.; Certini, G.; Moya, D.; Heras, J. Immediate fire-induced changes in soil microbial community composition in an outdoor experimental controlled system. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 134033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.R.; Narrowe, A.B.; Rhoades, C.C.; Fegel, T.S.; Daly, R.A.; Roth, H.K.; Chu, R.K.; Amundson, K.K.; Young, R.B.; Steindorff, A.S. Wildfire-dependent changes in soil microbiome diversity and function. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephanou, C.; Omirou, M.; Philippot, L.; Zissimos, A.M.; Christoforou, I.C.; Trajanoski, S.; Oulas, A.; Ioannides, I.M. Land use in urban areas impacts the composition of soil bacterial communities involved in nitrogen cycling. A case study from Lefkosia (Nicosia) Cyprus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Miera, L.E.S.; Pinto, R.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, J.J.; Calvo, L.; Ansola, G. Wildfire effects on diversity and composition in soil bacterial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Woolet, J.; Yedinak, K.M.; Whitman, T. Experimentally determined traits shape bacterial community composition one and five years following wildfire. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 7, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido-Chavez, M.F.; Randolph, J.W.J.; Zalman, C.; Larios, L.; Homyak, P.M.; Glassman, S.I. Rapid bacterial and fungal successional dynamics in first year after chaparral wildfire. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2023, 32, 1685–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sansupa, C.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R. Short-term response of soil bacterial and fungal communities to fire in rotational shifting cultivation, northern Thailand. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 196, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, B.; Tang, C.; Yu, H.; Lv, X.; Rodrigues, J.L.M.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Xu, J. Habitat heterogeneity induced by pyrogenic organic matter in wildfire-perturbed soils mediates bacterial community assembly processes. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.F.; Lockhart, J.S.; Charaska, E.; Aho, K.; Lohse, K.A. Bacterial composition of soils in ponderosa pine and mixed conifer forests exposed to different wildfire burn severity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| pH | EC dS/m | C % | Inorganic N (μg g−1) | CaCO3 % | Sand % | Silt % | Clay % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OGB | 7.64 ± 0.22 | 0.64 ± 0.13 | 1.64 ± 0.11 | 18.97 ± 18.89 | 8.27 ± 1.10 | 66.24 | 14.77 | 18.99 |
| OGCn | 7.00 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 1.44 ± 0.05 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 6.42 ± 0.40 | 66.84 | 14.47 | 18.69 |
| OGCf | 7.09 ± 0.05 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 1.41 ± 0.04 | 4.12 ± 4.19 | 6.37 ± 0.52 | 67.60 | 14.65 | 18.75 |
| PFB | 7.82 ± 0.06 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.61 ± 0.03 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 9.84 ± 0.91 | 83.44 | 5.20 | 11.36 |
| PFC | 7.58 ± 0.05 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.45 ± 0.02 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 5.56 ± 0.43 | 74.24 | 12.10 | 13.66 |
| MVB | 7.82 ± 0.04 | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 1.71 ± 0.08 | 7.63 ± 4.78 | 10.91 ± 0.88 | 63.84 | 18.65 | 17.51 |
| MVCn | 7.53 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 1.47 ± 0.05 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 6.20 ± 0.33 | 71.84 | 8.80 | 19.36 |
| MVCf | 7.50 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.08 | 1.55 ± 0.05 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 6.35 ± 0.41 | 68.44 | 12.54 | 20.02 |
 |
| Soil | Average Daily Respiration | % Increase in Relation to Control Cn | % Increase in Relation to Control Cf |
|---|---|---|---|
| OGB | 0.0273 | 174 | 270 |
| OGCn | 0.0099 | ||
| OGCf | 0.0074 | ||
| MVB | 0.0264 | 180 | 9 |
| MVCn | 0.0094 | ||
| MVCf | 0.0242 |
| ASV | Taxon | Association with Samples | Association Strength | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASV22 | ASV22 Proteobacteria:Rhodoplanes | Unburned | 0.791 | 0.0220 |
| ASV66 | ASV66 Verrucomicrobiota:Candidatus_Udaeobacter | Unburned | 0.866 | 0.0090 |
| ASV72 | ASV72 Verrucomicrobiota:uncultured | Unburned | 0.866 | 0.0050 |
| ASV75 | ASV75 Verrucomicrobiota:Ellin517 | Unburned | 0.791 | 0.0260 |
| ASV250 | ASV250 Bacteroidota:Flavisolibacter | Unburned | 1.000 | 0.0010 |
| ASV353 | ASV353 Actinobacteriota:Arthrobacter | Unburned | 0.866 | 0.0060 |
| ASV404 | ASV404 Actinobacteriota:MB-A2-108 | Unburned | 0.791 | 0.0260 |
| ASV498 | ASV498 Proteobacteria:Massilia | Unburned | 0.866 | 0.0130 |
| ASV513 | ASV513 Proteobacteria:MND1 | Unburned | 0.791 | 0.0280 |
| ASV522 | ASV522 Proteobacteria:TRA3-20 | Unburned | 0.935 | 0.0010 |
| ASV533 | ASV533 Proteobacteria:Acidibacter | Unburned | 0.866 | 0.0080 |
| ASV589 | ASV589 Proteobacteria:Reyranella | Unburned | 0.866 | 0.0050 |
| ASV12 | ASV12 Proteobacteria:Psychroglaciecola | Burned | 0.845 | 0.0100 |
| ASV30 | ASV30 Proteobacteria:uncultured | Burned | 0.756 | 0.0430 |
| ASV195 | ASV195 Bacteroidota:Mucilaginibacter | Burned | 0.845 | 0.0080 |
| ASV199 | ASV199 Bacteroidota:Pedobacter | Burned | 0.756 | 0.0230 |
| ASV337 | ASV337 Acidobacteriota:Paludibaculum | Burned | 0.756 | 0.0310 |
| ASV389 | ASV389 Actinobacteriota:Kribbella | Burned | 0.845 | 0.0060 |
| ASV503 | ASV503 Proteobacteria:Noviherbaspirillum | Burned | 0.845 | 0.0050 |
| ASV540 | ASV540 Proteobacteria:Novosphingobium | Burned | 0.845 | 0.0070 |
| ASV580 | ASV580 Proteobacteria:uncultured | Burned | 0.756 | 0.0220 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalias, P.; Hadjisterkotis, E.; Omirou, M.; Michaelidou, O.; Ioannides, I.M.; Neocleous, D.; Christou, A. Wildfire Effects on the Soil Respiration and Bacterial Microbiota Composition in Mediterranean-Type Ecosystems. Fire 2024, 7, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7070213
Dalias P, Hadjisterkotis E, Omirou M, Michaelidou O, Ioannides IM, Neocleous D, Christou A. Wildfire Effects on the Soil Respiration and Bacterial Microbiota Composition in Mediterranean-Type Ecosystems. Fire. 2024; 7(7):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7070213
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalias, Panagiotis, Eleftherios Hadjisterkotis, Michalis Omirou, Ourania Michaelidou, Ioannis M. Ioannides, Damianos Neocleous, and Anastasis Christou. 2024. "Wildfire Effects on the Soil Respiration and Bacterial Microbiota Composition in Mediterranean-Type Ecosystems" Fire 7, no. 7: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7070213
APA StyleDalias, P., Hadjisterkotis, E., Omirou, M., Michaelidou, O., Ioannides, I. M., Neocleous, D., & Christou, A. (2024). Wildfire Effects on the Soil Respiration and Bacterial Microbiota Composition in Mediterranean-Type Ecosystems. Fire, 7(7), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7070213







