Abstract
Fire whirls are reported to occur frequently in the wilderness and in urban areas due to the influence of ambient winds. Fire whirls that occur on sloped fuel surfaces are common in the wilderness and have received less attention despite their potential to significantly alter fire behavior. Particularly in terms of frequency and height, previous studies have been performed on flatlands but less so on slopes. This paper presents an experimental study of fire whirls in sidewind line fires, focusing on the frequency of occurrence and the height of fire whirls. Regarding the effect of a side wind, it is shown that a side wind increases the frequency of occurrence, while the velocity component parallel or perpendicular to the line fire has a competing effect. In contrast, an increase in the slope reduces the height of the fire whirl; this phenomenon has been justified on the basis of experimental data from our work and the literature and explained in terms of the mechanism of vortex generation and movement.
1. Introduction
Fire whirls are vertically oriented, violently rotating columns of fire. They have been observed in urban areas, in oil spill fires, in the wild, and in volcanic eruptions. Dynamically, they are closely related to other rotating atmospheric phenomena such as dust storms and tornadoes [1]. All fire whirls, especially the larger ones, are considerable safety hazards for firefighters because they increase the intensity of fires, have unstable rates and directions of spread, and cause wind damage [2].
The formation of fire whirls can lead to a significant increase in the rate of fire expansion, and the powerful cyclones (the maximum speed of which may reach 60–80 m/s) can also cause severe damage [3,4]. It is important to determine the frequency of fire whirlwinds induced by different slopes for firefighting.
As examined in an uphill fire spread experiment [5,6], the concentrated vortex required to form a fire vortex is created by the interaction between the airflow and the fire plume. A leeward slope provides the vortex source for flame vortex formation due to the blocking effect of the mountain on the wind [7]. The interaction of multiple fires with an applied shear flow [8] or the interaction of crosswinds with line fires [9,10] also tends to induce a fire vortex. In particular, the wind speed required to form a flame vortex is related to the heat release rate [7,9,10,11,12,13,14].
Numerous experimental observations and studies have been carried out on highly sloping terrains, with Graham [15] pointing out that the most likely conditions for the generation of fire whirls occur on leeward slopes with strong winds blowing over the top of the ridge and that the obstruction of airflow by the ridge leads to the formation of natural eddies on the leeward side. Umscheid [16] documented fire whirlwinds and their evolution with photographs. Furthermore, examination of synoptic and local meteorological environments revealed that pre-existing frontal boundaries contribute to the formation of fire whirls during their combustion motion.
Dupuy [5] measured the effects of fire behavior variables (diffusion rate, fuel consumption, flame lingering time, temperature, and the geometry of the flame) using the fuel bed, finding that the uphill fire line developed from an initially straight line to a line with a sharp shape, while the no-slope fire line had a smooth, curved shape.
It has been demonstrated that increasing the inclination considerably increases the diffusion rate and changes the shape of the flame front, and vortexes perpendicular to the burning surface have been systematically observed in 30° upslope fires. These fire vortexes move upward along the lateral flanks of the narrow-tip fire line towards the fire head and are attributed to the strong effect observed when the slope angle is increased to 30°.
Subsequently, Morandini [17] performed simultaneous heat flow measurements at the edge of the fuel bed at high scan rates by using a combination of particle image velocimetry and video imaging. From the data collected, it was determined that the increase in diffusivity is due to a significant change in the fluid dynamics around the flame with the increase in slope.
Under slope-free conditions, the preheating of the fuel pellets is mainly controlled by the radiation from the flame. The air flow is characterized by a vertical buoyancy-driven plume and balanced lateral entrainment of fresh air on both sides of the flame. During the upward spread of the flame, a significant increase in air entrainment on the burning side of the flame was observed compared to the horizontal case. The wind generated by the flame plume blows away from the fire and the flame is partially attached to the inclined surface. The downstream heating of the unburned fuel was shown to depend on both radiant and convective heating mechanisms. The rate of heat transfer received at the front increases with an increasing slope and fuel load. Periodic turbulent bursts of the flame, guided by airflow, were also identified as a mechanism by which convective heating occurs even away from the fire line, favoring further spread of the flame in the upslope direction [17].
Further thermal measurements and an image analysis conducted by Silvani [6] showed that the flame spread state and its associated behavior changed with an increasing slope. This is observed by the propagation of the flame and its contact surface on the fuel bed. As the slope increases, the flame structure changes from U-shaped to V-shaped, and the radiation-dominated thermal environment at the front of the flame gradually changes to a mixed convection–radiation environment, where convection eventually dominates in a steep slope. In addition, periodic fire whirls roll along the flame front from the bottom to the top and occur more frequently as the angle of the slope increases. When the slope reaches 30°, an increase in the flame front curvature is associated with the appearance of fire spins that roll in sheets along the flame front, indicating a significant change in the hydrodynamics and heat transfer.
Himoto [18] conducted an experimental study of fire whirls generated around an L-shaped fire source in a wind tunnel, distinguishing stable fire vortexes from intermittently generated fire vortexes. They also investigated the frequency of fire vortex generation in flat ground conditions without further considering the hydrodynamic mechanisms of fire vortex generation or exploring the effect of frequency with slope. The frequency of occurrence of straight-line fire whirls was also quantified [19], but the slope factor was missing.
Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of typical fire whirlwind-induced crosswinds and slope on the integrated systematic variation in fire whirlwind occurrence frequency and height of fire whirls on the windward slope. Our previous work [20] found that the emphasis is on initial flame vortex formation. In contrast, this study explored the frequency of fire vortex occurrence mainly through statistical methods. Test images were acquired by sampling the signal at a frequency of 10 Hz. Extracted flame images with a significant rotational motion were created. The burner length was used as a scale to measure the height of fire whirls. The frequency of occurrence of fire whirls at different flame heights was determined by the proportion of rotating flame images in all images. Specifically, we randomly extracted 2 min videos and converted them into images of each frame, which contained images of fire whirls and images without fire whirls. We counted the fire cyclones with obvious rotations and those that were vertically independent, and compared the statistics with the total number of images to obtain the frequency of fire whirls.
This work not only determines the frequency of fire whirls occurrence induced by the fire source system under different crosswind conditions, but also extended it to fire whirls induced on slopes. This was achieved using a fire source system in conjunction with a slope lifting device, applying statistical methods to slope fire and interpreting the results obtained based on the vortex movement and generation mechanisms.
2. Experimental
Simulation experiments of the fire whirl phenomenon were performed by a system consisting of a mechanical wind wall, slope apparatus, a gas burner system, and a fire line (Figure 1). In particular, the fire line was used to induce the fire whirl.
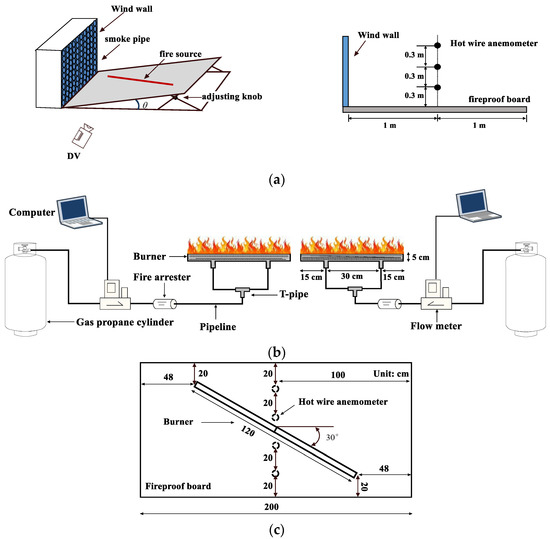
Figure 1.
Schematic for experimental setup. (a) Layout of the experimental set-up and hot-wire anemometer; (b) gas burner system for producing fire lines; (c) layout of fireproof panels and burners.
A propane cylinder, a flow meter, a fire arrester, and a pipeline burner connected by stainless steel piping compose the gas combustion system (Figure 1b). Inside the gas burner is a thin ceramic fiber blanket at the bottom, one thick layer of glass beads of 3 mm in diameter in the middle, and another thin ceramic fiber blanket at the top. The nearly 5 cm thick layer of glass beads completely reduces the flow momentum of propane from the cylinder. Linear holes were drilled through the fireproof board to place the liner burner. The burner top was flush with the upper surface of the fireproof board, and the slit was filled with plasticine between the hole and the burner rim. The wall surface is made of extremely hard fireproof board, so it is necessary to cut the fireproof board to insert the burner and ensure it is flush with the board surface. Therefore, after the process of cutting and installing the burner, there will be gaps of a few millimeters between the board and the burner. In order to make the fit between the burner and the board more ideal, we use plastic glue to fill the gaps to ensure that the effect of the gaps is minimal.
A flow meter (Alicat mass flow controller) was used to monitor the mass flow rate of propane with an accuracy of ±0.2% over a measurement range of 0–50 SLPM. The heat of combustion is 46.3 MJ/kg. The product of mass flow rate and combustion heat is the heat release rate () of the fire line.
Constant temperature hot wire anemometers (HWAs, model 0963-00 of Kanomax Inc. Japan) were placed away from the wind wall exit without the fire line (see the twelve measuring points in Figure 1a,c). The HWA probe had a data acquisition frequency of 10 Hz. The average wind speed (Ua) over time and space was linearly plotted against the fan output frequency, as shown in Figure 2. The slope angle increases the air flow velocity at the measuring points.
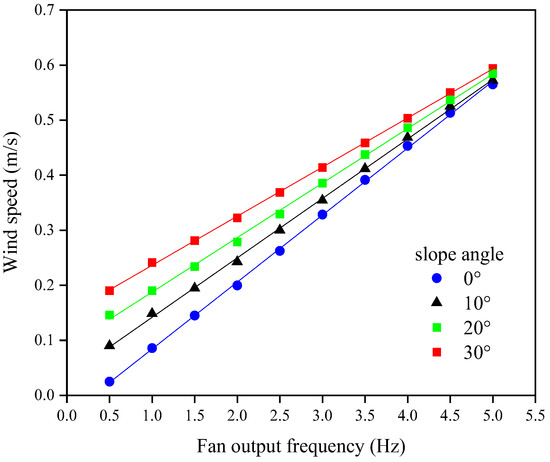
Figure 2.
Average wind speed versus fan frequency.
The line burner was set to be straight, as shown in Figure 1c, and the fire line was 120 cm in length and 4 cm in width. A reasonable angle between the wind direction and the fire source and an appropriate wind speed within the critical wind speed range are important factors in generating fire whirls. In actual wildland line fires, there is a certain angle between the wind direction and most of the line fire sources. In order to successfully generate a fire cyclone, we choose 30° as the angle between the wind direction and the fire direction. Figure 1c shows the relative position of the burner on the fireproof board in detail. Table 1 shows the details of the test conditions. is the inclined angle of the slope apparatus and is the heat release rate per wire or burner length. The test conditions used in this paper are detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of test conditions.
Laboratory studies of steadily generated fire whirls generally use mechanical devices, such as pool fires with slits or fixed frames [14], which generally use baffles and slits to generate fire whirls in a confined space for studying the parameter changes during their steady state. The disadvantage of this is that these experimental setups cannot be used to study the characteristics of fire whirls in open space fires. Fire whirls on slopes are a special combustion phenomenon formed by the interaction of wind and terrain. The slope increases the difficulty of conducting research and also increases scholarly interest, as it also possesses a different pattern from fire whirls occurring in flat fires.
This device for simulating open space line fires has the feasibility to simulate fire whirls induced by line fire sources in the field due to the ability to control the slope and heat release rate with the crosswind wind speed. Therefore, the results generated by this device can help us to understand the behavior of fire whirls in real wildland fires.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Observation
Figure 3 shows the movement of a fire whirl on the line fire source, with arrows representing the direction of rotation. For a 120 cm long burner on a flat surface, fire whirls were observed, with the flame being vertical and independent, rotating counterclockwise, moving along the line fire, and coming to rest or moving towards the leeward end before it disappeared. As shown in Figure 3b, the flame initially has a weak swirl and a downwind tilt, undergoes a transition, becomes strongly rotating and upright, and then moves down the linear burner.

Figure 3.
Photos of fire whirl formation and evolution at relative time moments between 0 and 6 s. = 0 degree; = 20 kW/m; Ua = 0.34 m/s. The arrows represent the direction of rotation of the fire whirl.
When the wind speed is in the critical range [11], the fire whirl maintains a high intensity and then moves downwind driven by the wind. When it reaches the leeward end, the vortex intensity increases slightly, as shown in Figure 3c. After increasing the heat release rate, the height and size of the fire whirl increases significantly. In contrast, when the wind speed increases over a certain level, no fire whirl appears. It is noteworthy that all the observed fire whirls rotated counterclockwise. Occasionally, more than two fire whirls were observed at the same time, but their duration was rather limited.
Fire whirls can still occur on low-gradient slopes, as shown in Figure 4, where at various moments at = 20 kW/m and Ua = 0.31 m/s, the fire whirls appear above the line fire, moving in the windward direction with the rotating online fire source. The fire whirls maintain a fixed strong rotation at the tail end of the line fire, in contrast to flat ground, which is thus though to be a effect of the slope.

Figure 4.
Photos of fire whirl formation and evolution at relative time moments between 0 and 4 s. = 10 degree; = 20 kW/m; Ua = 0.31 m/s.
Under slope conditions, a counterclockwise rotating fire whirl is still generated in the line fire and, as can be seen from the velocity vector field in the numerical simulation shown in Figure 5, the counterclockwise fire whirl rotates while moving along the wind direction, and its influence can extend beyond the line fire.
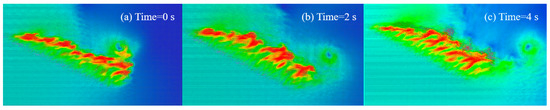
Figure 5.
Counterclockwise rotation of the fire whirls in numerical simulations. = 30 degree; = 20 kW/m; Ua = 0.39 m/s.
3.2. Fire Whirl Generation Frequency and Height
Figure 6 shows the frequency of occurrence with wind speed for different slopes. In a line fire with a heat release rate of 20 kW/m per unit length, the frequency of fire whirls occurrence increases and then decreases with increasing wind speed, while the frequency is at a maximum between 0.2 and 0.3 m/s for three different slopes and the frequency of fire whirls is higher for high slopes than low slopes.
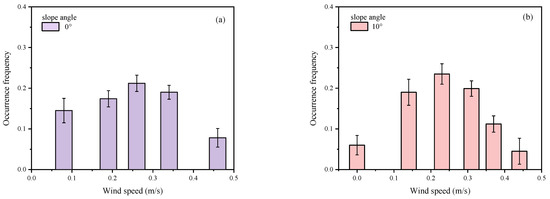
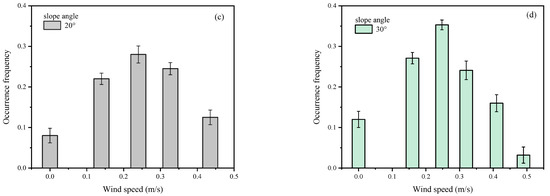
Figure 6.
The relationship between the frequency of fire whirls and wind speed at different slope angles. = 20 kW/m. (a) 0°; (b) 10°; (c) 20°; (d) 30°.
Recall that fire whirls can be generated by the interaction of multiple fires and, typically, an applied shear flow contributes to an increase in the frequency of fire whirls [8]. Jagged flames on the fire line were observed in our tests, which essentially formed a multiple fire system where the crosswind could be decomposed into a sum of two component velocity vectors parallel and perpendicular to the fire line. The parallel velocity vector acts as a shear flow, increasing the frequency of flame vortices, while the perpendicular velocity vector exerts pressure on the flame surface, disrupting the multi-fire system. Thus, it can be deduced that the frequency of fire whirls increases before it decreases [8]. In addition, the setting of a fixed controllable heat release rate leads to the existence of partial pyrolysis and phase change processes downwind, such as evaporation of volatiles. The increase in slope certainly accelerates the whole process, making periodic flame outbreaks [17] more frequent and potentially contributing to the frequency of fire whirls.
Note also that at a 30° slope, even in the absence of wind, a lower frequency of fire whirls is occasionally produced, which is hypothesized to be caused by the upslope component of the buoyancy of the flame heat plume [21]. This suggests that for linear fires, a fire whirl can be generated at high slopes in the absence of wind. This is consistent with the experimental results of Silvani [6], who found that the radiation-dominated thermal environment at the front of the flame gradually changed to a mixed convection–radiation environment, where convection eventually dominates in the steep slope configuration. Periodic fire whirlwinds roll along the flame front from the bottom to the top and occur more frequently as the slope angle increases. Fires spread up to 30° on the slope and the increase in curvature of the flame front was associated with the appearance of fire whirlwinds rolling along the sheet of the flame front, suggesting a remarkable change in hydrodynamics and heat transfer.
Since wind speed has a significant impact on the frequency of fire whirls, we chose to conduct a comparison of the height of fire whirls at different heat release rates at a similar fixed wind speed of 0.24 m/s (in the critical wind speed range). The height of fire whirls is defined as the vertical distance between the apex of the fire whirl and the wall when the fire whirl is perpendicular to the wall. When the ground is flat, we determined the height of fire whirls perpendicular to the horizontal, and when there is a slope, we determined the height of fire whirls perpendicular to the wall, as shown in Figure 7. Additionally, the burner length was used as a scale to measure the height of fire whirl.

Figure 7.
Height of fire whirls (H).
It can be seen from Figure 8, the height of fire whirl gradually decreases as the slope increases, while the heights of fire whirls at a high heat release rate are greater than those at a low heat release rate.
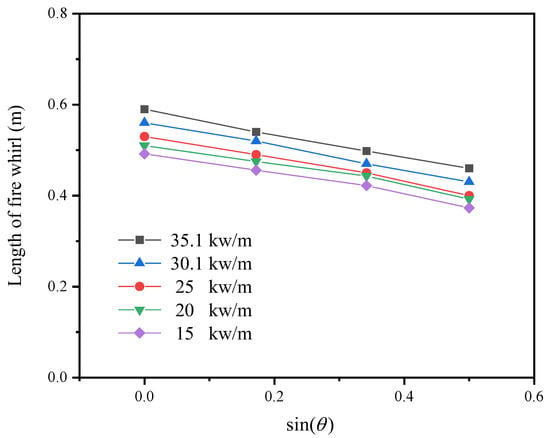
Figure 8.
Relationship between the height of fire whirls and slope. Ua = 0.24 m/s.
On the one hand, as the slope increases, it becomes more difficult to combine the horizontal vortex lines with the thermally buoyant plume, leading to a decrease in flame stability. On the other hand, the increase in slope increases the effect of the gravity component, making gsinθ larger while gcosθ decreases, leading to a decrease in the ring volume [22], which further leads to a decrease in flame stability.
Measurements by Sasaki [10] using particle image velocimetry (PIV) showed that the rotational velocity component decreases near the bottom of the wall [7] and that the radial inflow at the wall enhances the heat transfer between the flame and the burner, resulting in the formation of higher intensity vortices [7]. The effect of the slope increases the wall wind velocity component, making it is extremely easy to exceed the critical range of crosswind velocity and thus its influence, increasing instability [23,24].
At the same slope incline, as the heat release rate increases, the ring volume increases [25] and the effect of the slope on the rotating flame decreases [26] to a lesser extent. For a fire whirl formed by a liquid fuel, an increase in the ring volume improves the heat transmission to the fuel surface, increases the combustion rate, and reduces air entrainment, thereby increasing the flame height of fire whirls [27].
3.3. Condition and Mechanism of Fire Whirl Formation
The formation of flame vortexes demands a source of environmental vorticity. A concentration mechanism is generally considered to exist in the formation of fire whirls [28,29]. Ambient vorticity in the atmosphere can be created by the surface boundary layer of the wind, wind shear from inhomogeneous level densities, and the rotation of the Earth. This redirect horizontal vorticity to the vertical and induces vortex stretching.
Byram and Martin [30] suggested that three conditions are necessary for the formation of thermally driven rotating vortices such as fire whirls: firstly, the existence of a generating vortex; secondly, the presence of a fluid sink within the vortex; and thirdly, frictional or dragging force at a surface. Generating vortices provide the angular momentum required for rotational motion, fluid sinks are created by buoyancy or other forced flows that pool ambient vortical volumes into the center by coiled suction to form a high-speed rotating vortex core, and frictional forces are applied by impermeable walls to the air on horizontal surfaces to create a stable bottom boundary layer.
The mechanism for the generation of rotating vortexes can also be explained by the vorticity Equation (1):
where is the vortex vector; V is the volume; f is the thrust force; ρ is the local gas density; and v is the kinematic viscosity.
The last three terms on the right-hand side of the equation represent the generation of vorticity, which is a non-conservative force; the oblique pressure fluid; and the viscous force. The second term on the left-hand side of the equation represents the vorticity transmission due to wind, which indicates that the horizontal vorticity generated upwind exerts an influence on the behavior of the combustion downwind. The first term on the right-hand side of the equation indicates that the velocity gradient in the flow field stretches and bends the vortex lines that are already present, thus changing the magnitude and direction of the vortex volume. This means that when a horizontal vortex line near the wall meets a rising fire plume, the horizontal vortex line becomes a vertical vortex line and the vortex volume increases due to stretching, creating a vertical concentration of vortices.
The role of crosswinds in flame vortex height can be explained by the vorticity and transport caused by the interaction between the wind speed, the ground, and the upward flame plume [19]. Viscous shear can produce horizontal vortex lines near the ground as the wind blows across it, which under the action of wind pressure in the downwind direction finally transform into vertical vortex lines when they encounter an upward floating flame plume. In addition, the strength of the vertical vortex lines can be enhanced due to the stretching effect of the upwardly buoyant flow plume.
The vortex between the wind power and the wall provides a source of vorticity for an increase in flame height. However, as the crosswind increases, the upward linear flame plume will gradually tilt towards the horizontal. When a horizontal vortex line encounters a horizontal flame plume, it will never become a vertical vortex line, so the fire whirls will disappear as the crosswind increases beyond the critical conditions. Note that the above analysis is physically invalid after the formation of a flame vortex, as the flame vortex can have a significant effect on the local flow fields.
However, when fire whirls occur on a slope, the formation pattern is slightly different from that on flat ground. Nelson [21] suggested that when the uphill component of the fire buoyancy velocity is used in combination with the velocity and direction of the ambient wind to produce effective values of the wind speed and direction that determine the propagation velocity vector, the uphill component of the fire buoyancy increases the wind speed at the wall.
The increased wind speed will cause the original vortex on a flat surface to stretch and extend more closely, increasing the frequency of the vertical vortex. However, the slope effect will also make it more difficult to combine the vertical vortices on the slope and increase the flame height, thus reducing its height, while the horizontal vortex line will be stretched by the upslope component of the heat flow on the slope, causing the vertical vortex to move upslope. Additionally, this confirms Simpson’s [31] experimental model, which showed that while fire whirlwinds move towards the slope side as the slope angle increases, they have a significant impact on the fire wind field when the fire is small. As the fire size increases, multiple fire whirls usually form, but become smaller in size.
Note that Chuah [32] clearly showed with scale model experiments that if the flame vortex is strong enough, its structure will be predominantly rotational and entrained rather than buoyant. This suggests that strong rotation will be generated perpendicular to the slope when it occurs on an inclined slope, as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9.
Photos of fire whirl formation and evolution at relative time moments between 0 and 4 s. Straight line fire; = 30°; = 30.1 kW/m; Ua = 0.32 m/s.
These experimental findings can only determine the relationship between the frequency and height of fire whirls occurring on the windward slope, while the actual fire whirl in a fireground will be more complex and variable than those under experimental conditions. The angle between the crosswind and the line fire source, turbulence, and other variables will also have an impact on the results, and this dependence of frequency and height on slope is not representative of what may occur in nature, but only for these experiments.
4. Conclusions
Experiments triggering fire whirls on slopes were studied in this paper. The focus is on the frequency of fire whirls on different slopes. The experimental results show that wind has a significant effect on the frequency of fire whirls in line fires, and, in particular, the frequency of fire whirls was found to increase and then decrease with increasing wind speed. This was deduced to be caused by the competing effects of two velocity vectors; the velocity vector parallel to the line fire plays a positive role mainly as a shear flow to increase the frequency of occurrence of flame spins, while the vertical velocity vector plays a negative role.
The increase in slope, on the other hand, has a positive effect on the frequency of fire whirls under the same operating conditions. Viscous shear can produce horizontal vortex lines near the ground, which are then transported downwind under wind pressure. The presence of a slope increases the transport of horizontal vortex lines at the wall under downwind conditions, which binds them more closely to the flame plume floating on the line and thus increases the frequency of flame vortices.
The slope component of the flame plume also causes the fire whirl to move downwind towards the slope. However, the slope effect also makes it more difficult for the horizontal vortex lines to combine closely with the flame plume on the slope to form a vertical vortex and form a higher intensity vertical vortex line, which results in a lower height of fire whirls.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.W.; software, Y.W.; validation, K.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, K.Z.; visualization, Y.W.; supervision, K.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
No ethical approval required.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Forthofer, J.M.; Goodrick, S.L. Review of Vortices in Wildland Fire. J. Combust. 2011, 2011, 984363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodrat, M.; Shakeriaski, F.; Nelson, D.J.; Simeoni, A. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Formation and Flame Precession of Fire Whirls: A Review. Fire 2021, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazunori, K. Fire Whirls: Why Are They Tall, and When Do They Occur? J. Combust. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 61, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, J.; Scott, R.B. 12b.4 strategic directions for wsr-88d doppler weather surveillance radar in the period Strategic Directions for WSR-88D Doppler Weather Surveillance Radar in the Period 2007–2025. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy, J.L.; Maréchal, J.; Portier, D.; Valette, J.C. The effects of slope and fuel bed width on laboratory fire behaviour. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2011, 20, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvani, X.; Morandini, F.; Dupuy, J.-L. Effects of slope on fire spread observed through video images and multiple-point thermal measurements. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2012, 41, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.D.; Rajamanickam, P.; Coenen, W.; Sánchez, A.L.; Williams, F.A. A model for the constant-density boundary layer surrounding fire whirls. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 900, A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Z.; Kohyu, S.; Zhu, J. Burn-out time data analysis on interaction effects among multiple fires in fire arrays. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 2589–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, K.; Sekimoto, K.; Minami, T.; Tashiro, T.; Saito, K. Scale-model experiments of moving fire whirl over a line fire. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Igari, M.; Kuwana, K. Fire whirls behind an L-shaped wall in a crossflow. Combust. Flame 2018, 197, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, K.; Sekimoto, K.; Saito, K.; Williams, F.A. Scaling fire whirls. Fire Saf. J. 2008, 43, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, M. Vortex strength and size of fire whirls without flames around a long narrow fire source. Fire Saf. J. 2022, 129, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, A.; Bradley, D. Wildfires and the generation of fire whirls. Combust. Flame 2021, 239, 111664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi, A.; Gollner, M.J.; Xiao, H. Fire Whirls. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2018, 50, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, H.E. Fire-whirlwind formation as favored by topography and upper winds: Fire whirlwinds studied in the lab [reprinted from 1957]. 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Umscheid, M.E.; Monteverdi, J.P.; Davies, J.M. Photographs and Analysis of an Unusually Large and Long-Lived Firewhirl. E J. Sev. Storms Meteorol. 2006, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandini, F.; Silvani, X.; Dupuy, J.L.; Susset, A. Fire spread across a sloping fuel bed: Flame dynamics and heat transfers. Combust. Flame 2018, 190, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himoto, K.; Naruse, T. Probabilistic aspect of fire whirl generation around an L-shaped fire source in a crosswind. Fire Saf. J. 2017, 88, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, N.; Yuan, X. Effect of wind on fire whirl over a line fire. Fire Technol. 2016, 52, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, N.; Yin, P.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, J. Fire Whirl due to Interaction between Line Fire and Cross Wind. Fire Saf. Sci. 2014, 11, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.M. An effective wind speed for models of fire spread. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2002, 11, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Chow, W.K.; Chow, C.L. Generation and characteristics of internal fire whirl in a shaft model with two corner slits under microgravity conditions. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 3058–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, K.A.; Smits, A.J. Stereo PIV measurements in fire whirls. Exp. Fluids 2019, 60, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, K.A.; Smits, A.J. Scaling of a small scale burner fire whirl. Combust. Flame 2016, 163, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, W.; Kolb, E.J.; Sánchez, A.L.; Williams, F.A. Observed dependence of characteristics of liquid-pool fires on swirl magnitude. Combust. Flame 2019, 205, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yao, Q.; Law, C.K. The bottom boundary-layer structure of fire whirls. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 4277–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, K.H.; Kushida, G. The prediction of flame heights and flame shapes of small fire whirls. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmons, H.W.; Ying, S.-J. The fire whirl. Symp. (Int.) Combust. 1967, 11, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroney, R.N. Fire whirls, fire tornadoes, and fire storms: Physical and numerical modeling. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Physical Modelling of Flow and Dispersion Phenomena, Prato, Italy, 3–5 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Byram, G.M.; Martin, R.E. The modeling of fire whirlwinds. For. Sci. 1970, 16, 386–399. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, C.C.; Sharples, J.J.; Evans, J.P. Sensitivity of atypical lateral fire spread to wind and slope. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, K.H.; Kuwana, K.; Saito, K.; Williams, F.A. Inclined fire whirls. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 2417–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).