Screening for Cluster Headache—Introduction of the SMARTED Scale
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Logistic Regression Results
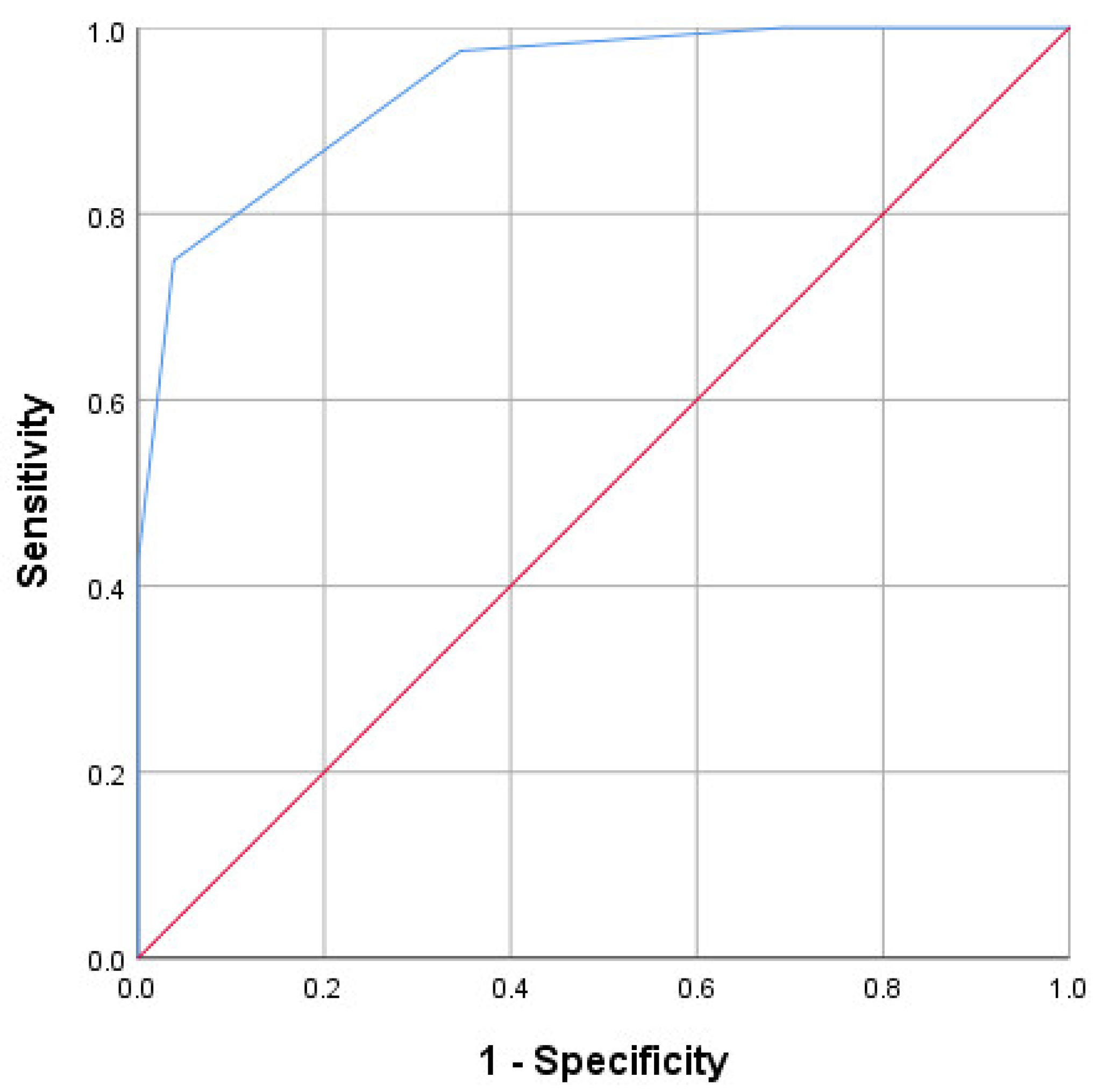
3.3. Development and Testing of the Scale
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary and Contributions
4.2. Future Work
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CH | cluster headache |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| TAC | trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia |
| n.r. | not reported (i.e., missing data) |
References
- Pohl, H.; Gantenbein, A.R.; Sandor, P.S.; Schoenen, J.; Andree, C. Interictal Burden of Cluster Headache: Results of the EUROLIGHT Cluster Headache Project, an Internet-Based, Cross-Sectional Study of People with Cluster Headache. Headache 2020, 60, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, L.; Cavers, D. ‘A cry in the dark’: A qualitative exploration of living with cluster headache. Br. J. Pain 2021, 15, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jürgens, T.P.; Gaul, C.; Lindwurm, A.; Dresler, T.; Paelecke-Habermann, Y.; Schmidt-Wilcke, T.; Lürding, R.; Henkel, K.; Leinisch, E. Impairment in episodic and chronic cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, A.; Leone, M.; Afra, J.; Linde, M.; Sandor, P.S.; Evers, S.; Goadsby, P.J. EFNS guidelines on the treatment of cluster headache and other trigeminal-autonomic cephalalgias. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederiksen, H.H.; Lund, N.L.; Barloese, M.C.; Petersen, A.S.; Jensen, R.H. Diagnostic delay of cluster headache: A cohort study from the Danish Cluster Headache Survey. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapper, J.A.; Klapper, A.; Voss, T. The misdiagnosis of cluster headache: A nonclinic, population-based, Internet survey. Headache 2000, 40, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.B. Epidemiology and genetics of cluster headache. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischera, M.; Marziniak, M.; Gralow, I.; Evers, S. The incidence and prevalence of cluster headache: A meta-analysis of population-based studies. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeier, M.S.; Stattmann, M.; Wegener, S.; Gantenbein, A.R.; Pohl, H. Interrater agreement in headache diagnoses. Cephalalgia Rep. 2022, 5, 25158163221115391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.J.; Antonaci, F.; Jensen, R.; Lainez, M.J.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Valade, D. Recommendations for headache service organisation and delivery in Europe. J. Headache Pain 2011, 12, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, H.; Gantenbein, A.R.; Sandor, P.S.; Andrée, C. A Survey on Probable and Improbable Decisions About Headache Treatment. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, H. Red flags in headache care. Headache 2022, 62, 534–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbrink, L.A.; Weller, C.M.; Cheung, C.; Stijnen, T.; Haan, J.; Ferrari, M.D.; Terwindt, G.M. Stepwise web-based questionnaires for diagnosing cluster headache: LUCA and QATCH. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.S.; Obermann, M.; Fritsche, G.; Slomke, M.; Dommes, P.; Schilf, C.; Diener, H.C.; Katsarava, Z. Population-based validation of a German-language self-administered headache questionnaire. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parakramaweera, R.; Evans, R.W.; Schor, L.I.; Pearson, S.M.; Martinez, R.; Cammarata, J.S.; Amin, A.J.; Yoo, S.H.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Y.; et al. A brief diagnostic screen for cluster headache: Creation and initial validation of the Erwin Test for Cluster Headache. Cephalalgia 2021, 41, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buture, A.; Boland, J.W.; Dikomitis, L.; Huang, C.; Ahmed, F. Development and Evaluation of a Screening Tool to Aid the Diagnosis of a Cluster Headache. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, P.W.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, M.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, J.W.; Kim, B.S.; Oh, K.; Moon, H.S.; et al. Development and Validation of the Cluster Headache Screening Questionnaire. J. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 15, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousset, V.; Laporte, A.; Legoff, M.; Traineau, M.H.; Dartigues, J.F.; Brochet, B. Validation of a brief self-administered questionnaire for cluster headache screening in a tertiary center. Headache 2009, 49, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, G.; Hueppe, M.; Kukava, M.; Dzagnidze, A.; Schuerks, M.; Yoon, M.S.; Diener, H.C.; Katsarava, Z. Validation of a german language questionnaire for screening for migraine, tension-type headache, and trigeminal autonomic cephalgias. Headache 2007, 47, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, P.; Beghi, E.; Manzoni, G.C. Validation of a questionnaire for the detection of cluster headache. Headache 2005, 45, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows; Version 26.0; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pergolizzi, J.V., Jr.; Magnusson, P.; LeQuang, J.A.; Wollmuth, C.; Taylor, R., Jr.; Breve, F. Exploring the Connection Between Sleep and Cluster Headache: A Narrative Review. Pain Ther. 2020, 9, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, T.D.; Fishman, R.S. Cluster headache in the United States of America: Demographics, clinical characteristics, triggers, suicidality, and personal burden. Headache 2012, 52, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, P.W.; Kim, B.S.; Park, J.W.; Sohn, J.H.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, B.K.; Chu, M.K.; Ahn, J.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Song, T.J.; et al. Smoking History and Clinical Features of Cluster Headache: Results from the Korean Cluster Headache Registry. J. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 17, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbanti, P.; Aurilia, C.; Dall’Armi, V.; Egeo, G.; Fofi, L.; Bonassi, S. The phenotype of migraine with unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms documents increased peripheral and central trigeminal sensitization. A case series of 757 patients. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.; Lipton, R.B. Classification of Headache. In The Headaches, 3rd ed.; Olesen, J., Goadsby, P.J., Ramadan, N.M., Tfelt-Hansen, P., Welch, K.M.A., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Torelli, P.; Manzoni, G.C. Behavior during cluster headache. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2005, 9, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosbrugger, H.; Kelava, A. Testtheorie und Fragebogenkonstruktion; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Pereda, S.; Madera, J.; Gonzalez-Quintanilla, V.; Drake-Perez, M.; Marzal Espi, C.N.; Serrano Munuera, C.; Garcia, S.C.; Aguilella Linares, C.; Fernandez Recio, M.; Velamazan Delgado, G.; et al. Is conventional brain MRI useful for the diagnosis of cluster headache in patients who meet ICHD-3 criteria? Experience in three hospitals in Spain. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 434, 120122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdulle, A.M.; Abera, S.F.; Abyu, G.Y.; Ahmed, M.B.; Aichour, A.N.; Aichour, I.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 877–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutjes, A.W.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Glas, A.S.; Bossuyt, P.M.M. Case-control and two-gate designs in diagnostic accuracy studies. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
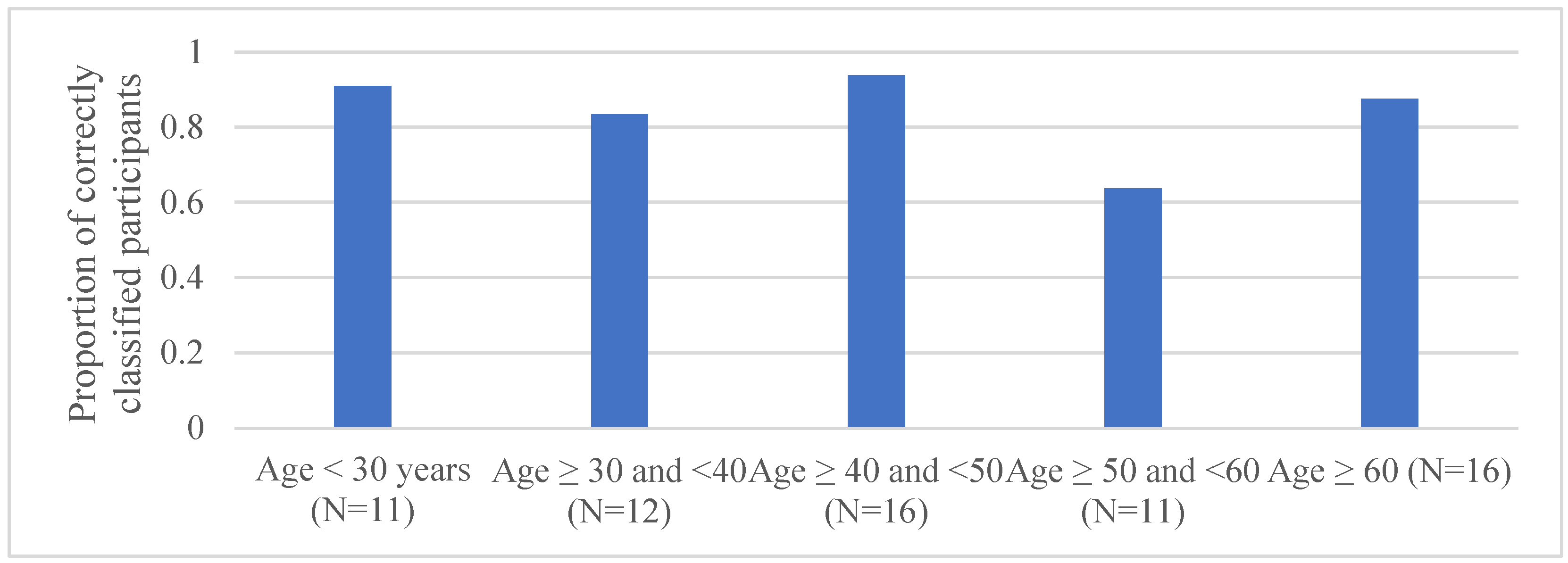
| No. | Question | Sensi-Tivity | Speci-Ficity | p Value | Odds Ratio | n.r. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | “My headaches are usually excruciating.” | 0.91 | 0.41 | 0.001 | 7.24 | 0 |
| 2 | “My headaches are always strictly unilateral.” | 0.93 | 0.32 | 0.008 | 6.47 | 2 |
| 3 | “My headaches always appear in one eye or close to it.” | 0.93 | 0.31 | 0.009 | 6.30 | 0 |
| 4 | “During the headache attack, the eye on the side of the pain reddens.” | 0.73 | 0.680 | 0.001 | 5.81 | 1 |
| 5 | “During the headache attack, the space between the margins of the eyelids (palpebral fissure) narrows.” | 0.82 | 0.46 | 0.016 | 3.90 | 2 |
| 6 | “During the headache attacks, my eye tears on the side of the pain.” | 0.84 | 0.55 | 0.001 | 6.51 | 1 |
| 7 | “My nose is already blocked at the beginning of a headache attack.” | 0.61 | 0.75 | 0.004 | 4.77 | 2 |
| 8 | “My nose already runs at the beginning of a headache attack.” | 0.46 | 0.72 | 0.146 | 2.19 | 1 |
| 9 | “During the headache attacks, I cannot lie or sit still.” | 0.84 | 0.63 | <0.001 | 9.23 | 2 |
| 10 | “During the headache attacks, I am always restless.” | 0.93 | 0.38 | 0.002 | 8.15 | 2 |
| 11 | “If I do not take medication, my headache attacks last less than three hours.” | 0.71 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 6.91 | 6 |
| 12 | “One headache attack rarely comes alone. When I have one headache attack, the next one often occurs on the same day or at the latest on the next day.” | 0.96 | 0.14 | 0.202 | 3.44 | 0 |
| 13 | “My headache attacks usually occur around the same time of the day.” | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.004 | 4.43 | 1 |
| 14 | “Very often do I get headache attacks during the night.” | 0.64 | 0.78 | 0.001 | 6.13 | 3 |
| 15 | “Headache attacks wake me up if I am asleep at their onset.” | 0.93 | 0.39 | 0.001 | 9.06 | 1 |
| 16 | “I have already wished to die during a headache attack.” | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.052 | 2.80 | 2 |
| 17 | “I am afraid of getting further headache attacks.” | 0.93 | 0.39 | 0.002 | 8.63 | 3 |
| 18 | “At night, I hesitate to go to bed because I do not want to be woken up by a headache attack.” | 0.48 | 0.71 | 0.141 | 2.28 | 2 |
| 19 | “When my headache attacks appear, I avoid drinking alcohol because it could trigger attacks.” | 0.71 | 0.46 | 0.193 | 2.14 | 6 |
| 20 | “When my headache attacks appear, I usually do not leave home without painkillers so that I can treat myself quickly.” | 0.91 | 0.18 | 0.304 | 2.12 | 3 |
| 21 | “During the attacks, I lie down in a darkened room.” | 0.64 | 0.35 | >0.999 | 1.09 | 1 |
| 22 | “I am or used to be a smoker.” | 0.80 | 0.64 | <0.001 | 7.00 | 2 |
| No. | Item | p Value | Coefficient | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | “During the headache attacks, my eye tears on the side of the pain.” | 0.013 | 19.1 | 1.7–195.8 |
| 9 | “During the headache attacks, I cannot lie or sit still.” | 0.034 | 8.9 | 1.2–65.5 |
| 11 | “If I do not take medication, my headache attacks last less than three hours.” | 0.028 | 9.4 | 1.3–69.0 |
| 15 | “Headache attacks wake me up if I am asleep at their onset.” | 0.006 | 56.6 | 3.1–1028.0 |
| 22 | “I am or used to be a smoker.” | 0.046 | 10.5 | 1.0–105.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pohl, H.; Joos, M.; Neumeier, M.S.; Stattmann, M.; Gantenbein, A.R.; Wegener, S. Screening for Cluster Headache—Introduction of the SMARTED Scale. Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2023, 7, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7010001
Pohl H, Joos M, Neumeier MS, Stattmann M, Gantenbein AR, Wegener S. Screening for Cluster Headache—Introduction of the SMARTED Scale. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience. 2023; 7(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7010001
Chicago/Turabian StylePohl, Heiko, Marco Joos, Maria S. Neumeier, Miranda Stattmann, Andreas R. Gantenbein, and Susanne Wegener. 2023. "Screening for Cluster Headache—Introduction of the SMARTED Scale" Clinical and Translational Neuroscience 7, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7010001
APA StylePohl, H., Joos, M., Neumeier, M. S., Stattmann, M., Gantenbein, A. R., & Wegener, S. (2023). Screening for Cluster Headache—Introduction of the SMARTED Scale. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, 7(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7010001







