An Overview on the Formation and Processing of Nitrogen-Vacancy Photonic Centers in Diamond by Ion Implantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
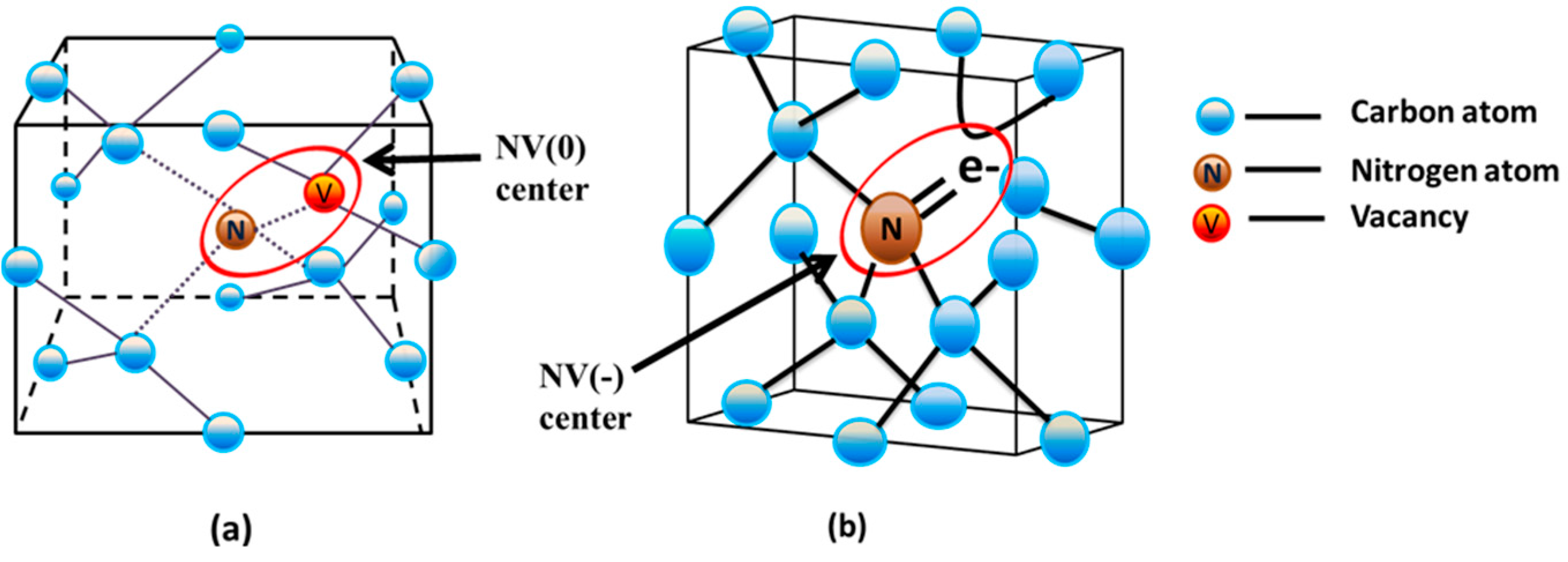
2. General Overview of the NV Center
3. The Formation of NV Centers
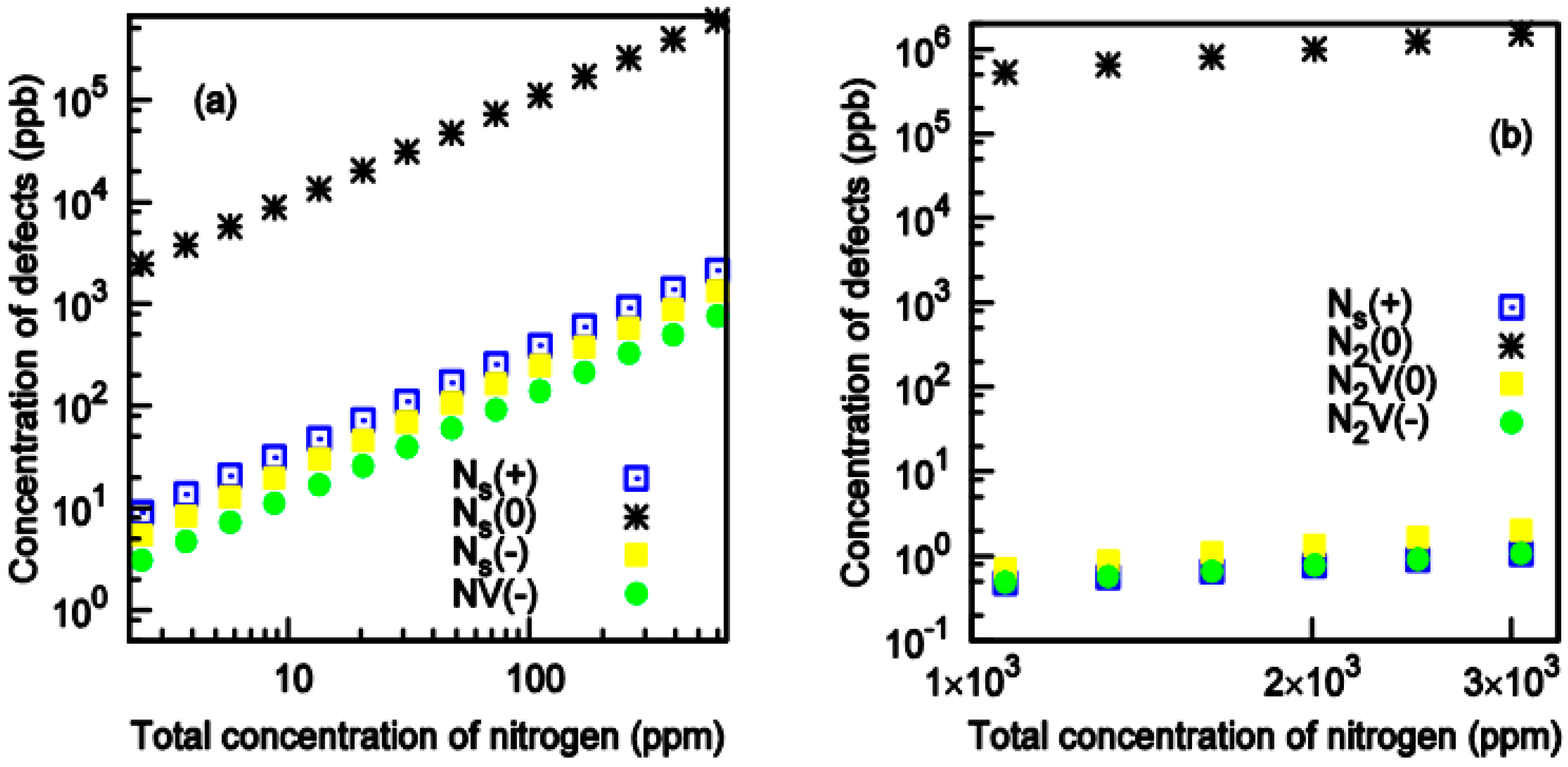
3.1. Formation of Substitutional Nitrogen (Ns)
3.2. The Single Vacancy (V)
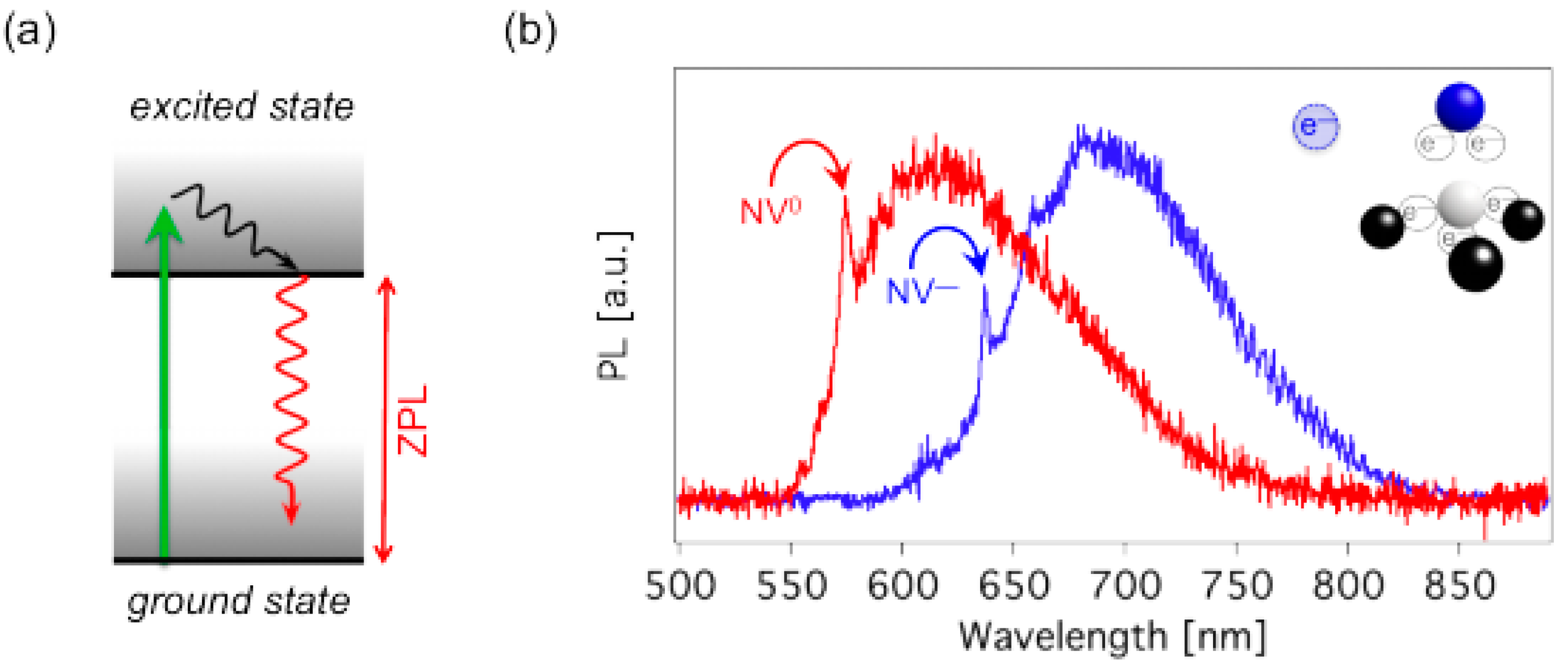
3.3. The Nitrogen-Vacancy (NV) Center
4. Energetics to Produce NV Centers
- (1)
- The XV point defect is stable or bound if the formation energy (enthalpy) of XV center, EXV, is less than that of X (EX) and V (EV). Therefore, EXV < EX + EV.
- (2)
- If the energy required to displace a carbon from the lattice site in the diamond is EC, then the defect complex XV is likely to form, provided EXV + EC < EX.
- (3)
- If the energy of the displaced interstitial carbon is EI (~12 eV), then the XV complex will not be formed unless EXV + EI < EX.
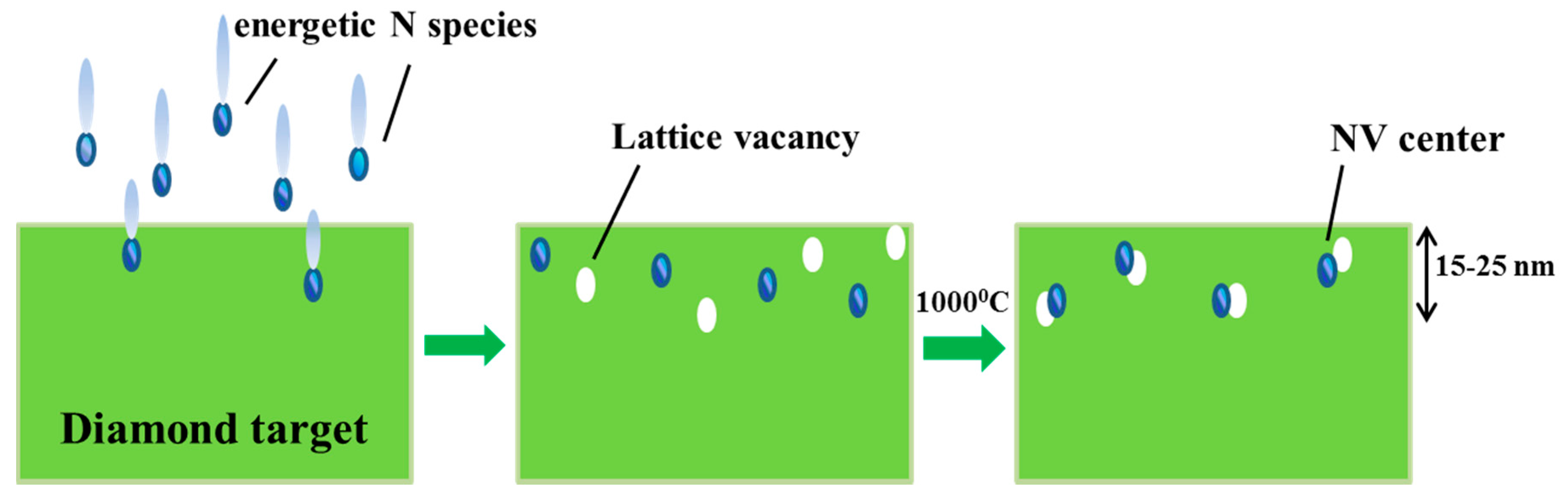
5. NV Centers Produced by Ion Irradiation and Subsequent Annealing
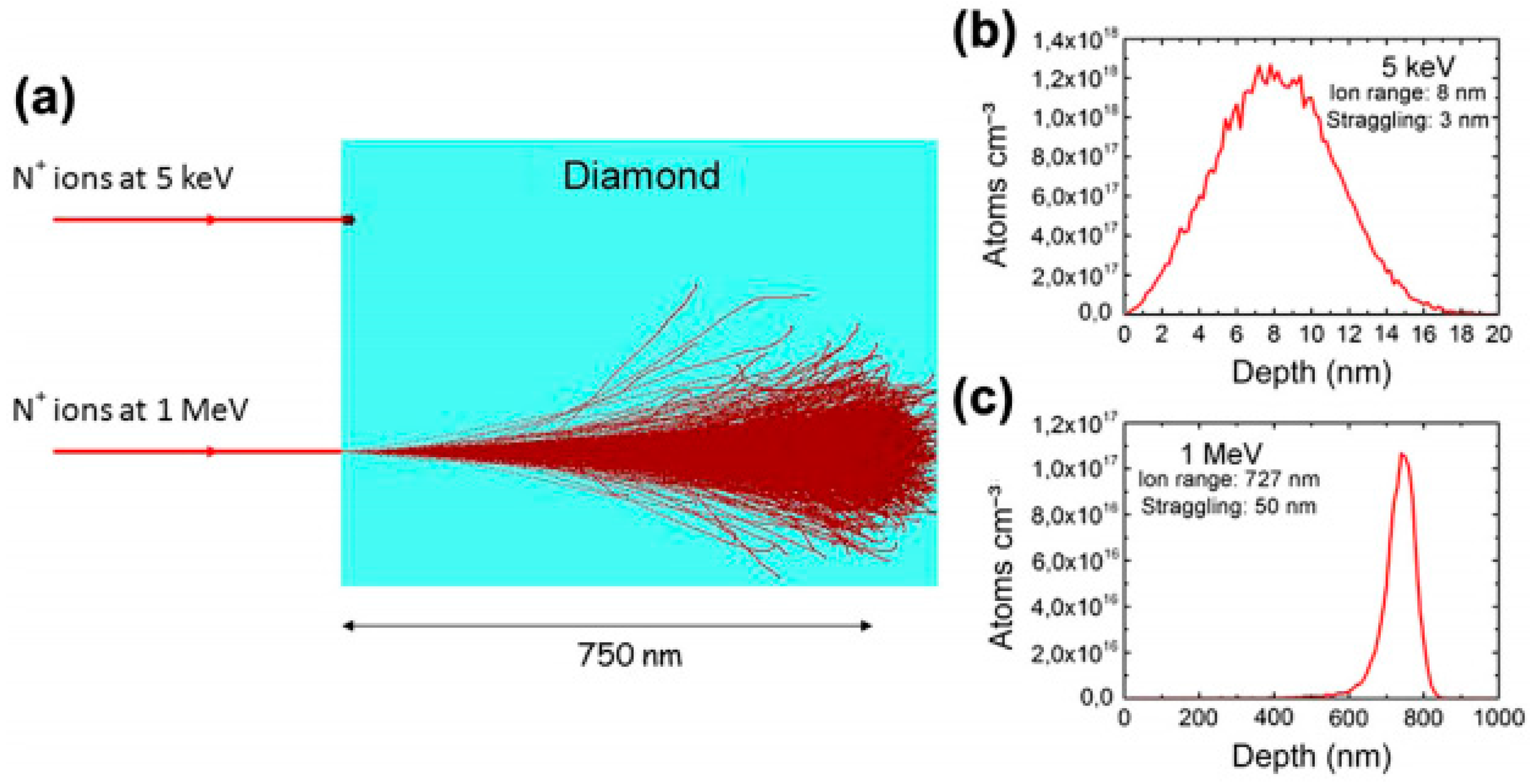
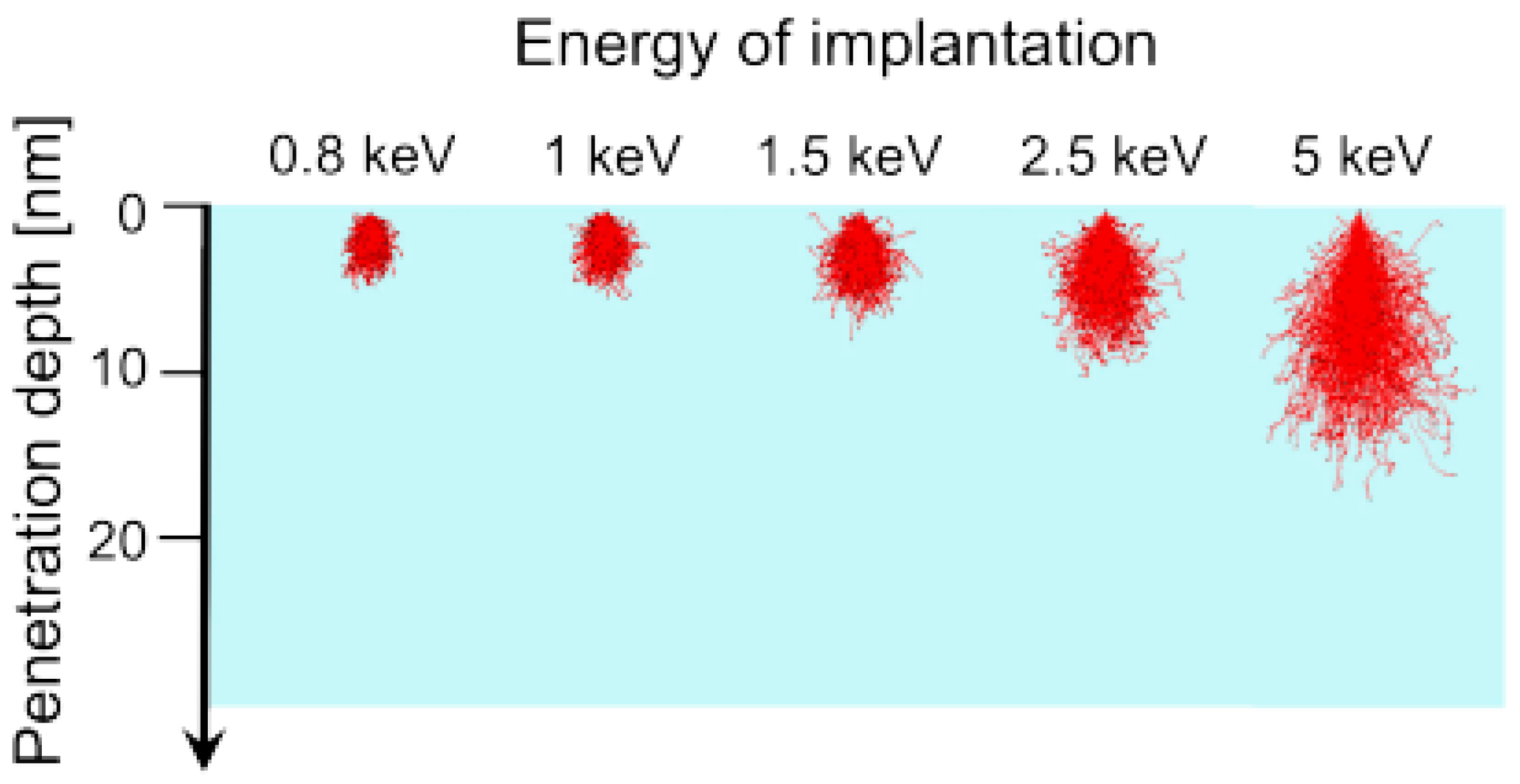
6. Factors to Be considered during the Nitrogen Ion Implantation on Diamond
6.1. Ion Struggling
6.2. Ion Channeling
6.3. Other Factors
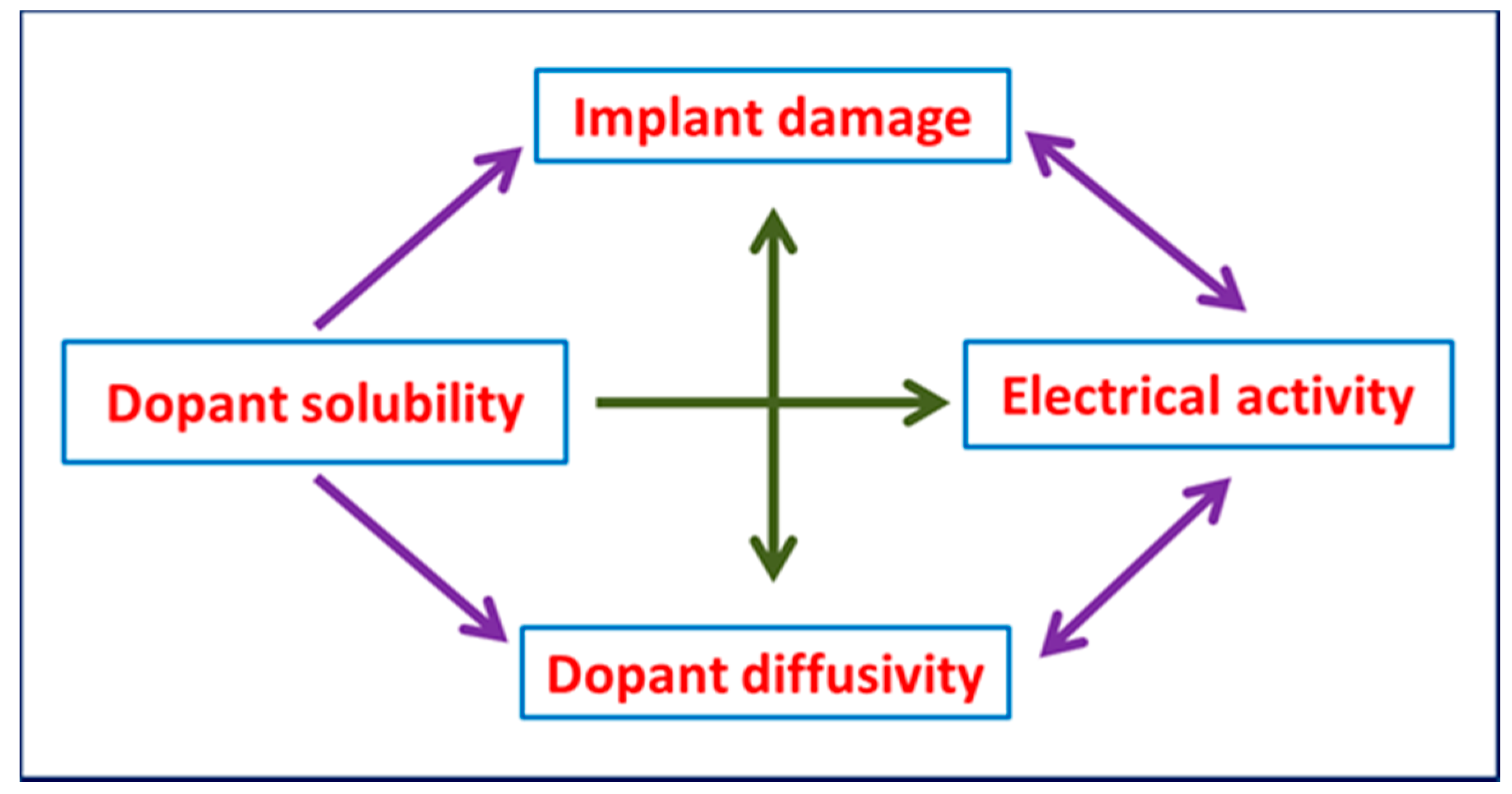
7. Implant Damage and Damage Annealing
- (1)
- Type of the implant species (heavy ion produces more damage)
- (2)
- Energy of the incident ions (more energy, more ion struggling)
- (3)
- Fluence size (at a fluence size of ~1014 cm−2 or above, extended damage sets in)
- (4)
- Implantation current (high current causes for the overlapping collision cascades)
8. Problems with Ion Irradiation on Diamond
- (1)
- There exists a critical dose size above which the implantation damage may form complex amorphous or graphitic regions either spontaneously at the time of irradiation or after annealing. The formation of graphitic entities was observed at low ion dose size, as low as 1014 cm−2, during the implantation of 15 N ions at 100 keV energy [25].
- (2)
- High temperature and sometimes high pressure is required to allow the substitutional species/atoms to migrate, which is not an easy process.
- (3)
- At the time of annealing much residual radiation damage or complexes may form, which tend to compensate the implanted dopants.
- (4)
- As the bond lengths in diamond are short, a large concentration of substitutional N atoms create a substantial amount of strain. For this reason, careful measurements/calculations of ion dose, energy, duration of implantation, etc. have to be performed before starting the process.
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgement
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, C.H.; DiVincenzo, D.P. Quantum information and computation. Nature 2000, 404, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, L.; Salathe, Y.; Oppliger, M.; Kurpiers, P.; Baur, M.; Lang, C.; Eichler, C.; Puebla-Hellmann, G.; Fedorov, A.; Wallraff, A. Deterministic quantum teleportation with feed-forward in a solid state system. Nature 2013, 500, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, R.B. Nature and location of quantum information. Phys. Rev. A 2002, 66, 012311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dräbenstedt, A.; Fleury, L.; Tietz, C.; Jelezko, F.; Kilin, S.; Nizovtzev, A.; Wrachtrup, J. Low-temperature microscopy and spectroscopy on single defect centers in diamond. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 11503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.; Awschalom, D.D. Coherent manipulation of single spins in semiconductors. Nature 2008, 453, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.Y.; Liu, G.Q.; Yang, L.L.; Fan, H. Solid-state optimal phase-covariant quantum cloning machine. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 051113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, G.; Chan, I.Y.; Kolesov, R.; Al-Hmoud, M.; Tisler, J.; Shin, C.; Kim, C.; Wojcik, A.; Hemmer, P.R.; Krueger, A.; et al. Nanoscale imaging magnetometry with diamond spins under ambient conditions. Nature 2008, 455, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babinec, T.M.; Hausmann, B.J.; Khan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Maze, J.R.; Hemmer, P.R.; Lončar, M. A diamond nanowire single-photon source. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaumik, A.; Haque, A.; Karnati, P.; Taufique, M.F.N.; Patel, R.; Ghosh, K. Copper oxide based nanostructures for improved solar cell efficiency. Thin Solid Films 2014, 572, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiVincenzo, D.P. The physical implementation of quantum computation. arXiv, 2000; arXiv:preprint quant-ph/0002077. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzagna, S.; Naydenov, B.; Jelezko, F.; Wrachtrup, J.; Meijer, J. Creation efficiency of nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 065017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dréau, A.; Spinicelli, P.; Maze, J.R.; Roch, J.F.; Jacques, V. Single-shot readout of multiple nuclear spin qubits in diamond under ambient conditions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 060502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maertz, B.J.; Wijnheijmer, A.P.; Fuchs, G.D.; Nowakowski, M.E.; Awschalom, D.D. Vector magnetic field microscopy using nitrogen vacancy centers in diamond. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 092504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelezko, F.; Wrachtrup, J. Single defect centres in diamond: A review. Phys. Status Solidi A 2006, 203, 3207–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, A.M. Optical Properties of Diamond: A Data Handbook; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Childress, L.; Hanson, R. Diamond NV centers for quantum computing and quantum networks. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamarat, P.; Manson, N.B.; Harrison, J.P.; McMurtrie, R.L.; Nizovtsev, A.; Santori, C.; Beausoleil, R.G.; Neumann, P.; Gaebel, T.; Jelezko, F.; et al. Spin-flip and spin-conserving optical transitions of the nitrogen-vacancy centre in diamond. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santori, C.; Tamarat, P.; Neumann, P.; Wrachtrup, J.; Fattal, D.; Beausoleil, R.G.; Rabeau, J.; Olivero, P.; Greentree, A.D.; Prawer, S.; et al. Coherent population trapping of single spins in diamond under optical excitation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 247401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamarat, P.; Gaebel, T.; Rabeau, J.R.; Khan, M.; Greentree, A.D.; Wilson, H.; Hollenberg, L.C.L.; Prawer, S.; Hemmer, P.; Jelezko, F.; et al. Stark shift control of single optical centers in diamond. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 083002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, R.; Gywat, O.; Awschalom, D.D. Room-temperature manipulation and decoherence of a single spin in diamond. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 161203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childress, L.; Dutt, M.G.; Taylor, J.M.; Zibrov, A.S.; Jelezko, F.; Wrachtrup, J.; Hemmer, P.R.; Lukin, M.D. Coherent dynamics of coupled electron and nuclear spin qubits in diamond. Science 2006, 314, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelezko, F.; Gaebel, T.; Popa, I.; Gruber, A.; Wrachtrup, J. Observation of coherent oscillations in a single electron spin. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 076401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesik, M. Engineering of NV Color Centers in Diamond for Their Applications in Quantum Information and Magnetometry. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Cachan, Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, J.; Aloni, S.; Ogletree, D.F.; Schenke, T. Effects of low-energy electron irradiation on formation of nitrogen–vacancy centers in single-crystal diamond. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 043024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapatra, S.; Cheng, J.-Y.; Chakrapani, N.; Trasobares, S.; Cao, A.; Vajtai, R.; Huang, M.B.; Ajayan, P.M. Ion irradiation induced structural modifications in diamond nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.; Qi, Z. The kinetics of the aggregation of nitrogen atoms in diamond. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1982, 381, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainwood, A. Nitrogen and nitrogen-vacancy complexes and their formation in diamond. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, E.B.; Mainwood, A.; Osuch, K.; Reynhardt, E.C. Computational models of the single substitutional nitrogen atom in diamond. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 3135–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.; Lawson, S.C.; Collins, A.T.; Mainwood, A.; Sharp, S.J. Vacancy-related centers in diamond. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, H.; Jones, R.; Palmer, D.W.; Goss, J.P.; Briddon, P.R.; Öberg, S. On the diffusion of NV defects in diamond. Phys. Status Solidi A 2012, 209, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deák, P.; Aradi, B.; Kaviani, M.; Frauenheim, T.; Gali, A. Formation of NV centers in diamond: A theoretical study based on calculated transitions and migration of nitrogen and vacancy related defects. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 075203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Ahsan, Q. Building integrated photovoltaic system: Cost effectiveness. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 7th International Conference on Electrical & Computer Engineering (ICECE), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 20–22 December 2012; pp. 904–907. [Google Scholar]
- Grotz, B.; Hauf, M.V.; Dankerl, M.; Naydenov, B.; Pezzagna, S.; Meijer, J.; Jelezko, F.; Wrachtrup, J.; Stutzmann, M.; Reinhard, F.; et al. Charge state manipulation of qubits in diamond. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, J.P.; Briddon, P.R.; Rayson, M.J.; Sque, S.J.; Jones, R. Vacancy-impurity complexes and limitations for implantation doping of diamond. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 035214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmelnitsky, R.A.; Dravin, V.A.; Tal, A.A.; Zavedeev, E.V.; Khomich, A.A.; Khomich, A.V.; Alekseev, A.A.; Terentiev, S.A. Damage accumulation in diamond during ion implantation. J. Mater. Res. 2015, 30, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Umeda, T.; Watanabe, K.; Onoda, S.; Markham, M.L.; Twitchen, D.J.; Naydenov, B.; McGuinness, L.P.; Teraji, T.; Koizumi, S.; et al. Extending spin coherence times of diamond qubits by high-temperature annealing. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 075206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzagna, S.; Meijer, J. Single-Ion Implantation in Diamond with a High Lateral Resolution-3.13: A Key Technology for the Fabrication of Quantum Devices. In Comprehensive Hard Materials; Sarin, V.K., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 321–336. [Google Scholar]
- Hobler, G. Monte Carlo simulation of two-dimensional implanted dopant distributions at mask edges. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 1995, 96, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saslow, W.; Bergstresser, T.K.; Cohen, M.L. Band Structure and Optical Properties of Diamond. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 354, Erratum 1968, 21, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, M.S.; Khan, M.M.S.; Haque, A. Improvement of load-margin and bus voltage of Bangladesh power system with the penetration of PV based generation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–18 May 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Toyli, D.M.; Weis, C.D.; Fuchs, G.D.; Schenkel, T.; Awschalom, D.D. Chip-scale nanofabrication of single spins and spin arrays in diamond. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3168–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.S.; Allen, E.L.; Robinson, H.G.; Stevenson, D.A.; Deal, M.D.; Plummer, J.D. Extended defects of ion-implanted GaAs. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 70, 6790–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saguy, C.; Reznik, A.; Baskin, E.; Remes, Z.; Kalish, R. Defect-dopant interaction in n-and p-type diamond and its influence on electrical properties. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2004, 13, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigler, J.F.; Biersack, J.P.; Littmark, U. The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter; SRIM-2008; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.-M.; Chen, X.-D.; Fan, L.-L.; Gong, Z.-J.; Zou, C.-W.; Sun, F.-W.; Han, Z.-F.; Guo, G.-C. Generation of nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond with ion implantation. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2012, 29, 036103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenov, B.; Reinhard, F.; Lämmle, A.; Rafi Kalish, V.R.; D’Haenens-Johansson, U.F.S.; Newton, M.; Jelezko, F.; Wrachtrup, J. Increasing the coherence time of single electron spins in diamond by high temperature annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 242511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Feng, F.; Wang, J.; Lou, L.; Zhu, W. Generation of nitrogen-vacancy color center in nanodiamonds by high temperature annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 133109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.D.; Ditchburn, R.W.; Dyer, H.B. The absorption spectra of irradiated diamonds after heat treatment. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1956, 237, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakoubovskii, K.; Stesmans, A. Chemical vapour deposition diamond studied by optical and electron spin resonance techniques. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2002, 14, R467–R499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakoubovskii, K.; Stesmans, A. Dominant paramagnetic centers in 17 O-implanted diamond. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 045406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Haque, A.; Rahman, J. Production of MHD power from municipal waste & Algal biodiesel. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 18–19 May 2012; pp. 1097–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Fahy, S. Molecular-dynamics study of single-atom radiation-damage in diamond. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.D.; Mitchell, E.W.J. Radiation sects in Semiconductors. In IOP Conference Proceedings No. 31; Urli, N.B., Corbett, J.W., Eds.; Institute of Physics and Physical Society: London, UK, 1977; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Prins, J.F.; Derry, T.E.; Sellschop, J.P.F. Volume expansion of diamond during ion implantation. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 34, 8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.A.; Cann, B.L.; Martineau, P.M.; Samartseva, J.; Freeth, J.J.P.; Sibley, S.J.; Hartland, C.B.; Newton, M.E.; Dhillon, H.K.; Twitchen, D.J. Colour-causing defects and their related optoelectronic transitions in single crystal CVD diamond. J. Phys Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 275801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, D.N.; Yang, C.; Hopf, T.; Hearne, S.M.; Pakes, C.I.; Prawer, S. Controlled shallow single-ion implantation in silicon using an active substrate for sub-20-keV ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 202101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, J.; Vogel, T.; Burchard, B.; Rangelow, I.W.; Bischoff, L.; Wrachtrup, J.; Domhan, M.; Jelezko, F.; Schnitzler, W.; Schulz, S.A. Concept of deterministic single ion doping with sub-nm spatial resolution. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Proc. 2006, 83, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzler, W.; Jacob, G.; Fickler, R.; Schmidt-Kaler, F.; Singer, K. Focusing a deterministic single-ion beam. New J. Phys. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haque, A.; Sumaiya, S. An Overview on the Formation and Processing of Nitrogen-Vacancy Photonic Centers in Diamond by Ion Implantation. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2017, 1, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp1010006
Haque A, Sumaiya S. An Overview on the Formation and Processing of Nitrogen-Vacancy Photonic Centers in Diamond by Ion Implantation. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2017; 1(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaque, Ariful, and Sharaf Sumaiya. 2017. "An Overview on the Formation and Processing of Nitrogen-Vacancy Photonic Centers in Diamond by Ion Implantation" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 1, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp1010006
APA StyleHaque, A., & Sumaiya, S. (2017). An Overview on the Formation and Processing of Nitrogen-Vacancy Photonic Centers in Diamond by Ion Implantation. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 1(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp1010006



