Unsupervised Aerial-Ground Re-Identification from Pedestrian to Group for UAV-Based Surveillance
Abstract
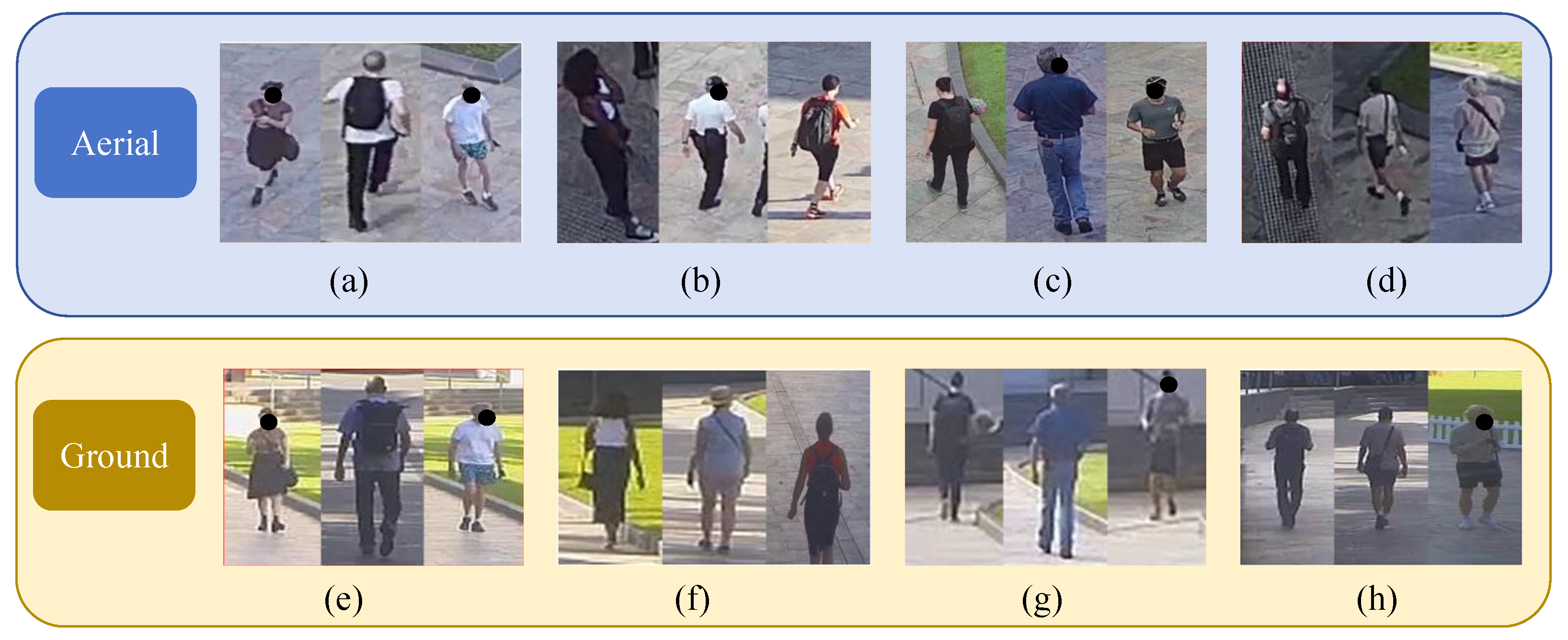
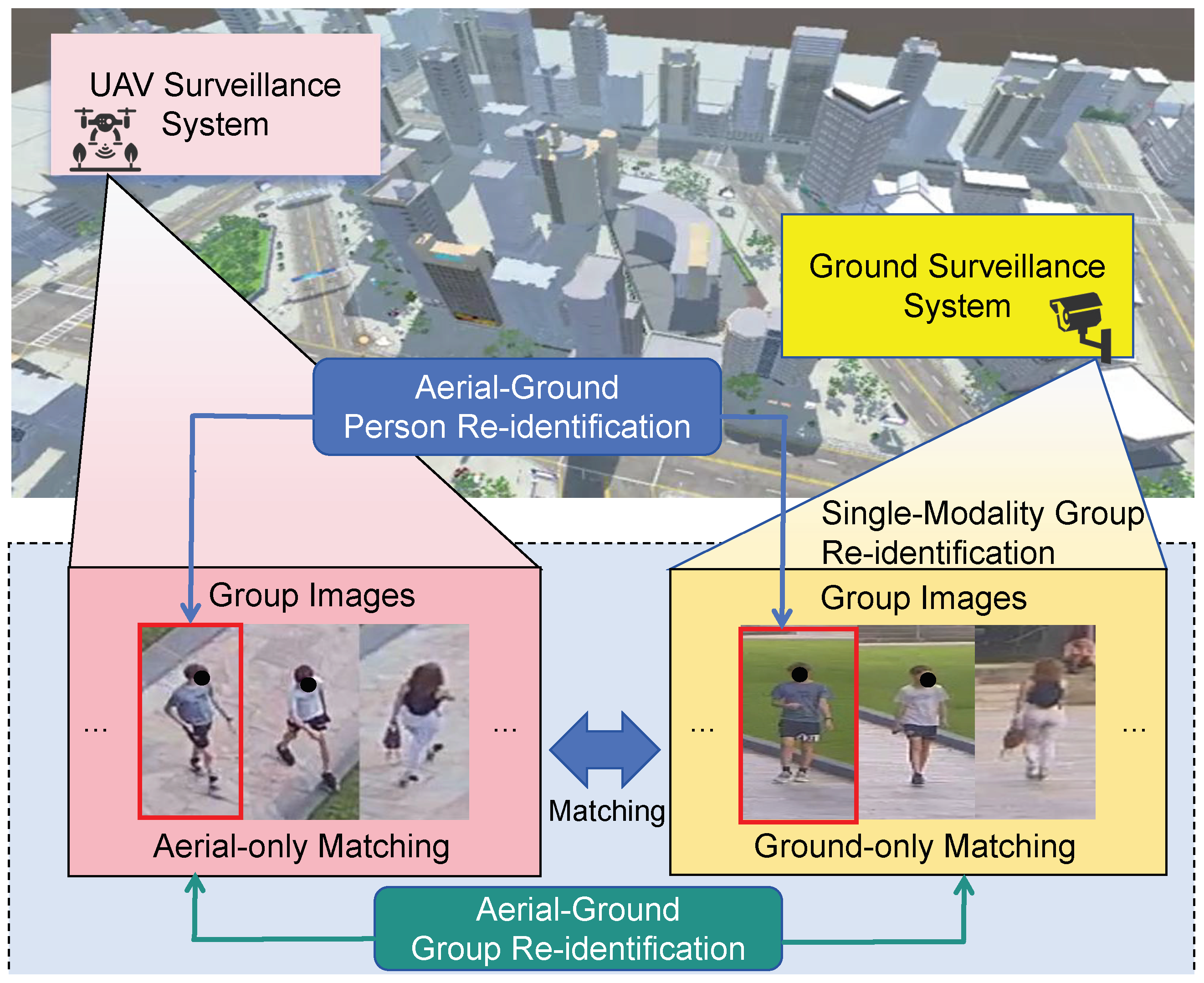
1. Introduction
- •
- We propose the Gradual Graph Correspondence (GGC) method to realize unsupervised group re-identification, which uses neighbor-aware collaborative learning (NCL) to mine the correspondence in the group and find reliable correlations of modalities by matching graphs progressively.
- •
- We propose a novel unsupervised group re-identification framework to effectively mine intra-group correspondences and establish reliable cross-modality correlations through progressive graph matching.
- •
- We introduce a novel minimum pedestrian distance transformation strategy to enhance the accuracy of similarity measurement for group images across aerial and ground domains. Additionally, we present a new aerial-ground group re-identification dataset. Extensive experiments on both person and group re-identification tasks validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating its superior performance and substantial improvements in unsupervised aerial-ground pedestrian retrieval scenarios.
2. Related Works
2.1. Supervised View-Homogeneous Person Re-Identification
2.2. Supervised View-Heterogeneous Person Re-Identification
2.3. Unsupervised Person Re-Identification
2.4. Group Re-Identification
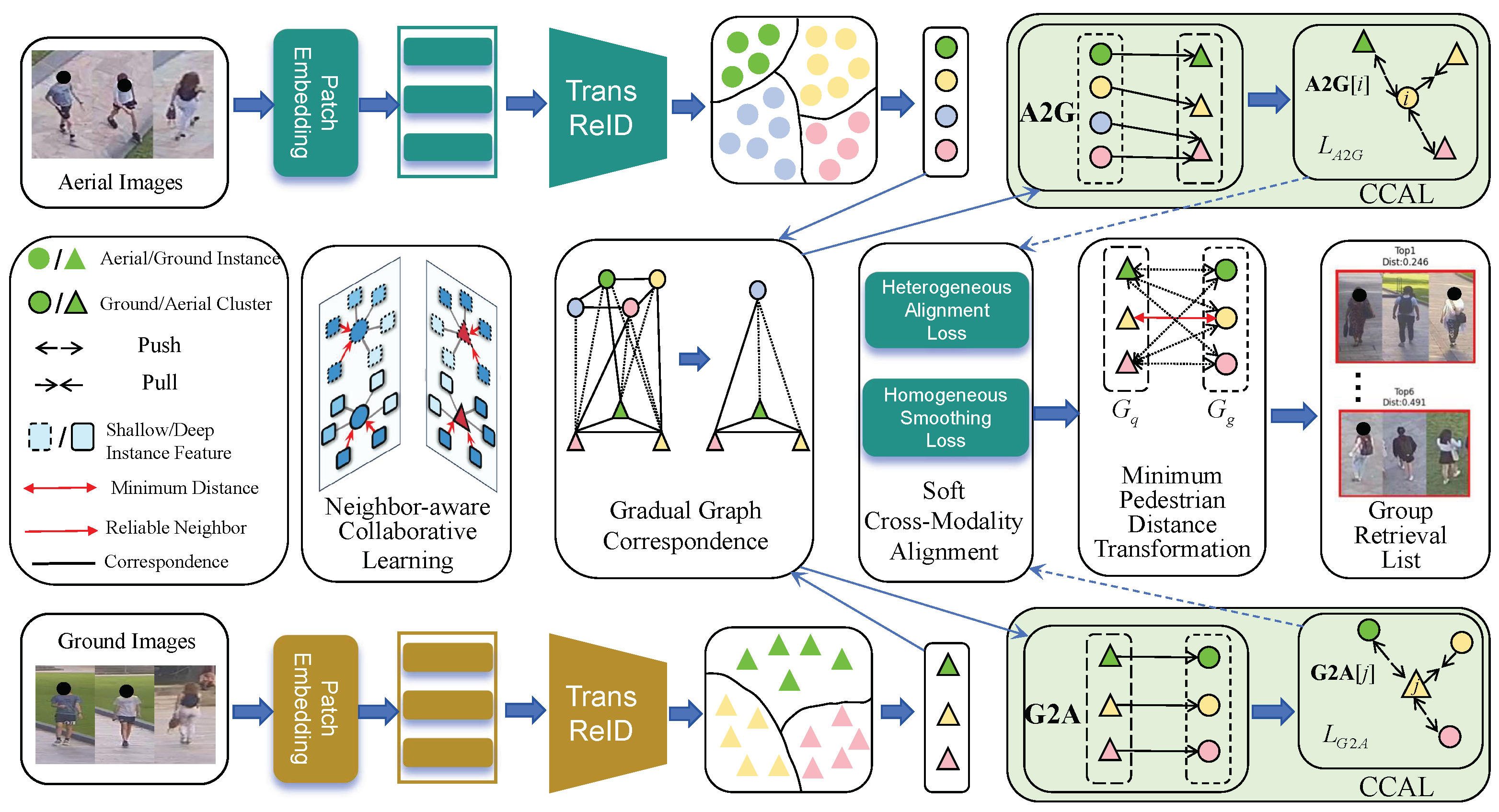
3. The Proposed Methodology
3.1. Neighbor-Aware Collaborative Learning
3.2. Gradual Graph Correspondence (GGC)
3.3. Collaborative Cross-Modality Association Learning (CCAL)
3.4. Soft Cross-Modality Alignment (SCMA)
3.5. Transformation from Pedestrian to Group Distance
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setting
4.1.1. Evaluating Metrics
4.1.2. Dataset Description
4.1.3. Implementation Details
4.2. Evaluation of Person Re-Identification
4.2.1. Aerial-Ground Person Re-Identification
4.2.2. Person Re-Identification of Aerial Scenario
4.3. Evaluation of Cross-Modality Group Re-Identification
4.4. Ablation Study
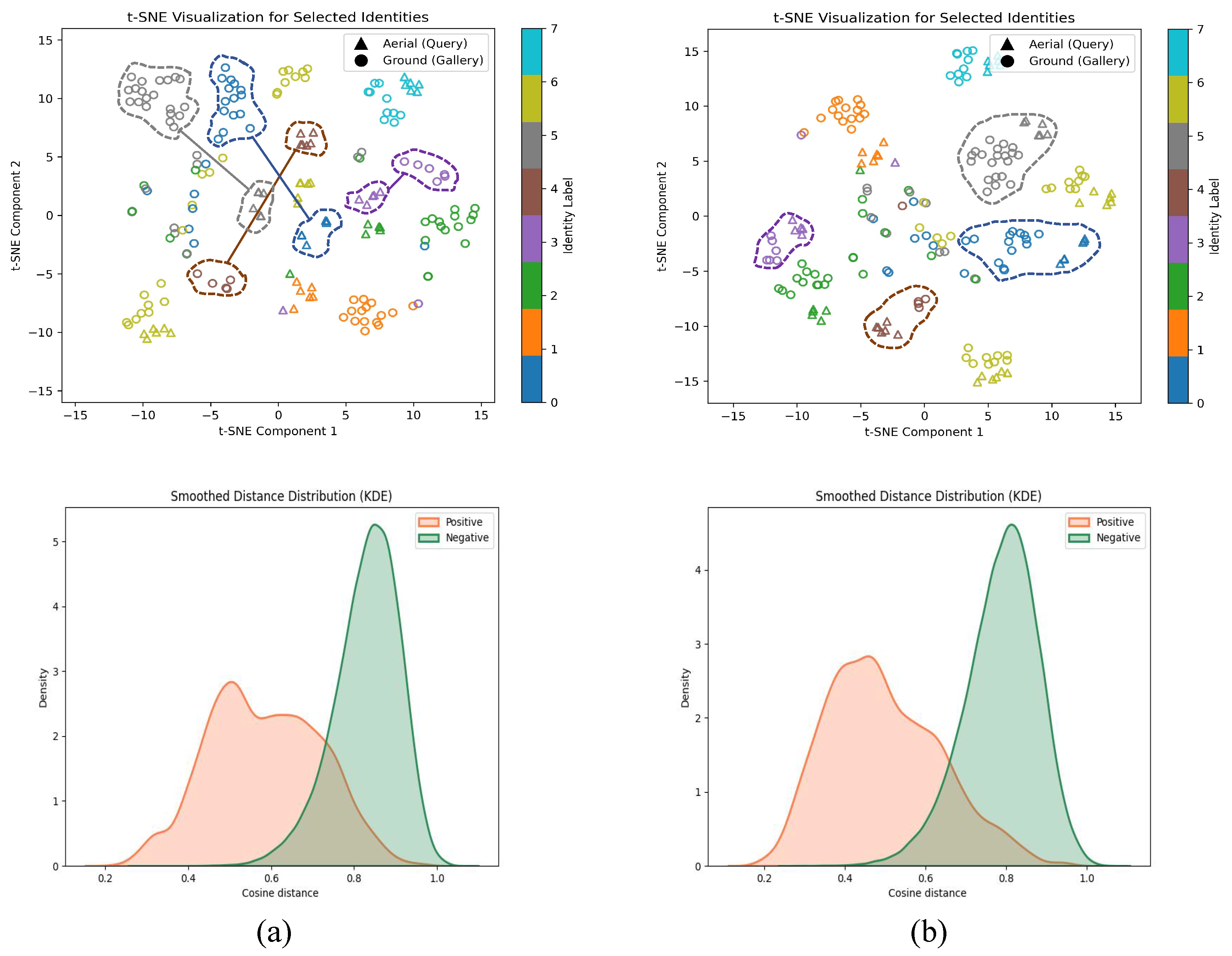
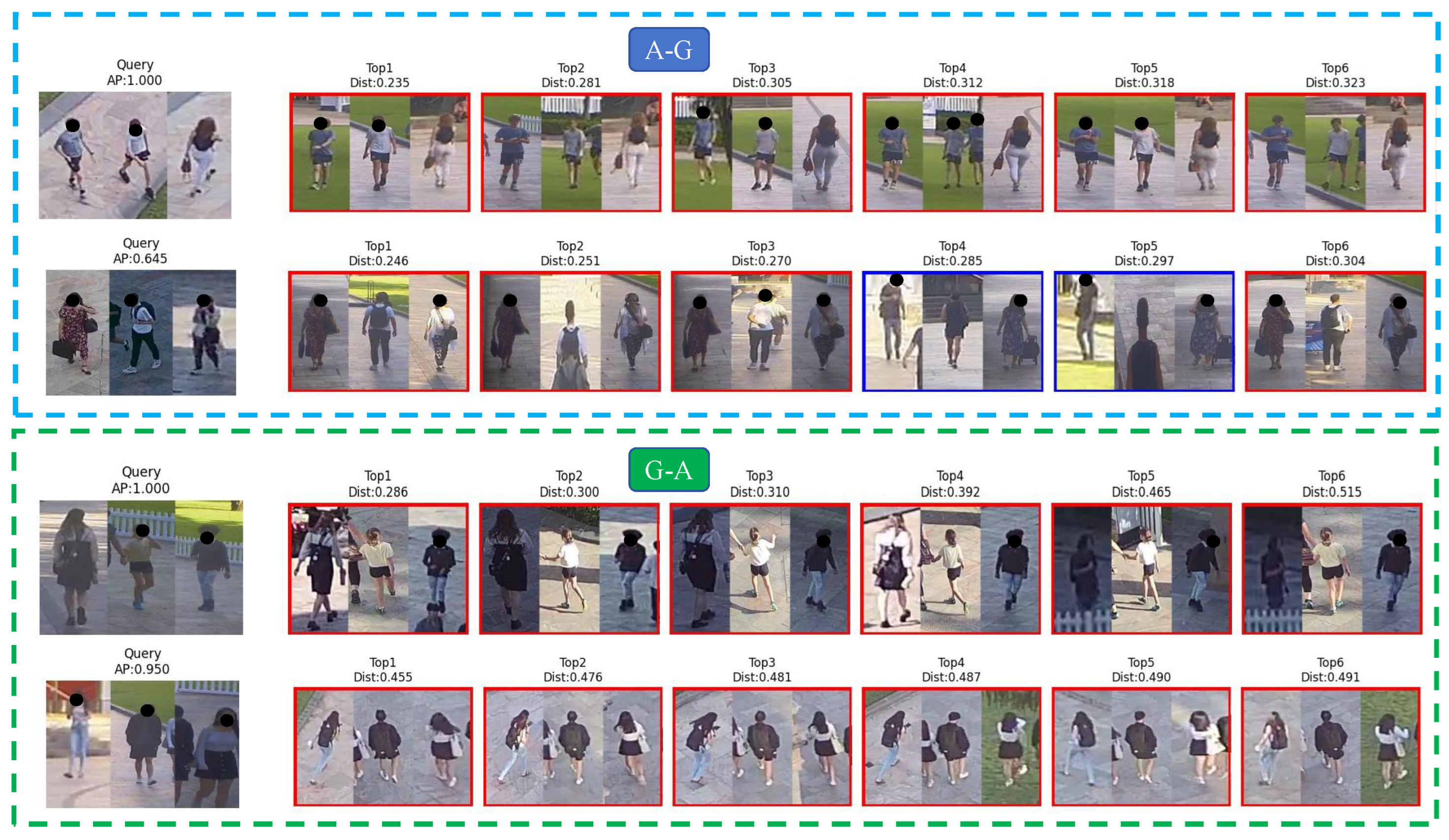
4.5. Visualization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yasmeen, A.; Daescu, O. Recent Research Progress on Ground-to-Air Vision-Based Anti-UAV Detection and Tracking Methodologies: A Review. Drones 2025, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norbelt, M.; Luo, X.; Sun, J.; Claude, U. UAV Localization in Urban Area Mobility Environment Based on Monocular VSLAM with Deep Learning. Drones 2025, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grando, L.; Jaramillo, J.F.G.; Leite, J.R.E.; Ursini, E.L. Systematic Literature Review Methodology for Drone Recharging Processes in Agriculture and Disaster Management. Drones 2025, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wen, G.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J.; Jian, H. An Unsupervised Moving Object Detection Network for UAV Videos. Drones 2025, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, G.; Luo, H. A multi-UAV deployment method for border patrolling based on Stackelberg game. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2023, 34, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Yu, M.; Jia, L.; Fu, M. Crowd Density Estimation via Global Crowd Collectiveness Metric. Drones 2024, 8, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Lai, J.; Chen, Z.; Xie, X. Measuring crowd collectiveness via global motion correlation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1222–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Stöcker, C.; Bennett, R.; Nex, F.; Gerke, M.; Zevenbergen, J. Review of the current state of UAV regulations. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Ni, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Z. Uav-human: A large benchmark for human behavior understanding with unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 16266–16275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Patel, V.M.; Xie, X.; Lai, J. View-decoupled transformer for person re-identification under aerial-ground camera network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–18 June 2024; pp. 22000–22009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, J.; Lai, J. Rotation exploration transformer for aerial person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, K.; Sridharan, S.; Fookes, C. AG-ReID. v2: Bridging aerial and ground views for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 2896–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Lai, J.; Feng, Z.; Xie, X. From pedestrian to group retrieval via siamese network and correlation. Neurocomputing 2020, 412, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Takala, V.; Pietikainen, M. Matching groups of people by covariance descriptor. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 2744–2747. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, T.; Ye, Z. Dynamic Screening Strategy Based on Feature Graphs for UAV Object and Group Re-Identification. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Lai, J.; Feng, Z.; Xie, X. Open-world group retrieval with ambiguity removal: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 584–591. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Qin, J.; Ni, B.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, F.; Zheng, W.S.; Yang, X.; Shao, L. Learning multi-attention context graph for group-based re-identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 45, 7001–7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Lai, J.; Mei, L. Deep representations based on sparse auto-encoder networks for face spoofing detection. In Proceedings of the 11th Chinese Conference on Biometric Recognition (CCBR), Chengdu, China, 14–16 October 2016; pp. 620–627. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Lai, J. Similarity metric learning for RGB-infrared group re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 13662–13671. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Lai, J.; Xie, X.; Jin, X.; Huang, S. Separable Spatial-Temporal Residual Graph for Cloth-Changing Group Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 5791–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lai, J.; Feng, Z.; Xie, X. Uncertainty modeling for group re-identification. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 132, 3046–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Person transfer gan to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, F.; Gou, M.; Camps, O.; Sznaier, M. Person re-identification using kernel-based metric learning methods. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part VII 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Lai, J.; Feng, Z.; Xie, X. Seeing like a human: Asynchronous learning with dynamic progressive refinement for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 31, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, W. Transreid: Transformer-based object re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 15013–15022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Ye, M.; Du, B. Rotation invariant transformer for recognizing object in uavs. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 2565–2574. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, K.; Sridharan, S.; Fookes, C. Aerial-ground person re-id. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Brisbane, Australia, 10–14 July 2023; pp. 2585–2590. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, L. Dissecting person re-identification from the viewpoint of viewpoint. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 608–617. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Xie, L.; Wu, Y.; Yan, C.; Tian, Q. Unsupervised person re-identification via softened similarity learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 3390–3399. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.; Chen, Z.; Cui, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C. Discrepant and multi-instance proxies for unsupervised person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 11058–11068. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, H. Mutual mean-teaching: Pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.01526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Kim, W.J.; Hong, S.; Yoon, S.E. Part-based pseudo label refinement for unsupervised person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7308–7318. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Zhu, F.; Chen, D.; Zhao, R. Self-paced contrastive learning with hybrid memory for domain adaptive object re-id. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 11309–11321. [Google Scholar]
- Layne, R.; Hospedales, T.M.; Gong, S. Investigating open-world person re-identification using a drone. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014 Workshops, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part III 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Albaluchi, Y.; Fu, B.; Damer, N.; Ramachandra, R.; Raja, K. UAV-based person re-identification: A survey of UAV datasets, approaches, and challenges. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2025, 251, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, G.; Lai, J.; Xie, X. Homogeneous-to-heterogeneous: Unsupervised learning for RGB-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 6392–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Ye, M.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z. Augmented dual-contrastive aggregation learning for unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 2843–2851. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.; He, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X. Efficient bilateral cross-modality cluster matching for unsupervised visible-infrared person reid. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 1325–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Ye, M. Unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification via progressive graph matching and alternate learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 9548–9558. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Sheng, B.; Qu, Y.; Xie, Y. Optimal transport for label-efficient visible-infrared person re-identification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Chu, Q.; Yu, N. Consistent matching based on boosted salience channels for group re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 4279–4283. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Li, Y.; Xiao, H.; See, J.; Zou, J.; Xiong, H.; Wang, J.; Mei, T. Group reidentification with multigrained matching and integration. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 1478–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hu, W.; Lin, C.W.; Satoh, S. DoT-GNN: Domain-transferred graph neural network for group re-identification. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1888–1896. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, H.; Lin, W.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Group re-identification with group context graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 2614–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisanti, G.; Martinel, N.; Del Bimbo, A.; Luca Foresti, G. Group re-identification via unsupervised transfer of sparse features encoding. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2449–2458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Dang, K.; Lai, J.H.; Feng, Z.; Xie, X. Modeling 3d layout for group re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7512–7520. [Google Scholar]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mini, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; Volume 96, pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, S.H.; Milan, A.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Q.; Dick, A.; Reid, I. Joint probabilistic data association revisited. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3047–3055. [Google Scholar]
- Bruff, D. The assignment problem and the hungarian method. Notes Math 2005, 20, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, L.; Lai, J.; Xie, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J. Illumination-invariance optical flow estimation using weighted regularization transform. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Lai, J.; Chen, Z. Geodesic-based probability propagation for efficient optical flow. Electron. Lett. 2018, 54, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wan, Z.; Mei, L.; Wu, S. Visual Attention-Guided Weighted Naïve Bayes for Behavior Intention Inference. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Human-Computer Interaction and Robotics (AIHCIR), Tianjin, China, 8–10 December 2023; pp. 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Cheng, D.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. Exploring Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Consistent Label Associations for Unsupervised Visible-Infrared Person ReID. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, L.; et al. Swin transformer v2: Scaling up capacity and resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12009–12019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, X. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Gu, Y.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Jiang, W. Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1487–1495. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Liao, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Cheng, P.; Mei, T. Fastreid: A pytorch toolbox for general instance re-identification. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 9664–9667. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, L.; Lai, J.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xie, X. Person re-identification using group constraint. In Proceedings of the Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering. Visual Data Engineering: 9th International Conference, IScIDE 2019, Nanjing, China, 17–20 October 2019; Proceedings, Part I 9. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 459–471. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, L.; He, Y.; Fishani, F.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Helge, R. Learning Domain-Adaptive Landmark Detection-Based Self-Supervised Video Synchronization for Remote Sensing Panorama. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Fu, M.; Wang, B.; Jia, L.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. LSN-GTDA: Learning Symmetrical Network via Global Thermal Diffusion Analysis for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Scenarios. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Model | Protocol | R1 | R5 | R10 | R20 | mAP | mINP | Publication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USL [40] | A–G | 31.82 | 42.35 | 47.61 | 54.30 | 19.96 | 4.30 | CVPR’2023 |
| MBCCM [39] | 32.31 | 48.27 | 55.37 | 62.28 | 19.49 | 4.05 | MM’2023 | |
| MULT [54] | 28.29 | 45.10 | 51.82 | 57.61 | 13.30 | 2.16 | IJCV’2024 | |
| Ours | 59.20 | 69.28 | 73.48 | 77.68 | 40.94 | 14.88 | - | |
| USL [40] | G–A | 42.62 | 54.57 | 61.95 | 66.84 | 28.72 | 7.85 | CVPR’2023 |
| MBCCM [39] | 42.00 | 53.95 | 59.15 | 65.18 | 28.96 | 7.88 | MM’2023 | |
| MULT [54] | 17.57 | 27.65 | 34.82 | 43.04 | 10.60 | 1.91 | IJCV’2024 | |
| Ours | 50.94 | 62.06 | 66.94 | 72.04 | 36.76 | 12.52 | - |
| Model | mAP | R1 | mINP | Publication | Supervision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swin [55] | 67.37 | 68.23 | - | Arxiv’2021 | S |
| HRNet-18 [56] | 64.52 | 65.48 | - | TPAMI’2021 | S |
| SwinV2 [57] | 69.15 | 70.12 | - | CVPR’2022 | S |
| MGN [58] | 70.40 | 70.38 | - | MM’2018 | S |
| BoT [59] | 63.41 | 62.48 | - | CVPRW’2019 | S |
| SBS [60] | 65.93 | 66.38 | - | MM’2023 | S |
| V2E [12] | 71.47 | 72.75 | - | TIFE’2024 | S |
| USL [40] | 67.76 | 96.83 | 23.48 | CVPR’2023 | U |
| MBCCM [39] | 55.43 | 92.25 | 12.99 | MM’2023 | U |
| MULT [54] | 48.19 | 90.76 | 8.19 | IJCV’2024 | U |
| Ours | 76.02 | 98.13 | 37.66 | - | U |
| Model | Protocol | R1 | R5 | R10 | R20 | mAP | mINP | Publication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USL [40] | A–G | 72.22 | 90.74 | 98.15 | 100.00 | 80.32 | 40.19 | CVPR’2023 |
| MBCCM [39] | 53.70 | 83.33 | 90.74 | 94.44 | 65.35 | 14.55 | MM’2023 | |
| MULT [54] | 40.74 | 70.37 | 81.48 | 87.04 | 55.38 | 11.46 | IJCV’2024 | |
| Ours | 90.74 | 96.30 | 96.30 | 98.15 | 92.25 | 56.88 | - | |
| USL [40] | G–A | 57.41 | 77.78 | 85.19 | 94.44 | 66.36 | 26.44 | CVPR’2023 |
| MBCCM [39] | 51.85 | 74.07 | 88.89 | 96.30 | 63.85 | 6.73 | MM’2023 | |
| MULT [54] | 25.93 | 48.15 | 64.81 | 79.63 | 37.76 | 6.89 | IJCV’2024 | |
| Ours | 74.07 | 94.44 | 98.15 | 100.00 | 81.87 | 42.25 | - |
| Module | A–G | G–A | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCL | GGC | ACCL | SCMA | R1 | mAP | mINP | R1 | mAP | mINP |
| Yes | 46.78 | 29.03 | 7.59 | 35.34 | 23.93 | 6.60 | |||
| Yes | Yes | 53.22 | 34.84 | 10.46 | 39.50 | 27.68 | 7.87 | ||
| Yes | Yes | Yes | 54.72 | 36.09 | 11.75 | 43.76 | 30.80 | 9.44 | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 59.20 | 40.94 | 14.88 | 50.94 | 36.76 | 12.52 |
| Module | A–G | G–A | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCL | GGC | ACCL | SCMA | R1 | mAP | mINP | R1 | mAP | mINP |
| Yes | 74.07 | 80.73 | 49.10 | 57.41 | 66.79 | 31.65 | |||
| Yes | Yes | 75.93 | 83.01 | 50.50 | 61.11 | 68.34 | 31.82 | ||
| Yes | Yes | Yes | 87.04 | 90.38 | 58.24 | 70.37 | 77.70 | 40.22 | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 90.74 | 92.25 | 56.88 | 74.07 | 81.87 | 42.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, L.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Jia, L.; Yu, Y. Unsupervised Aerial-Ground Re-Identification from Pedestrian to Group for UAV-Based Surveillance. Drones 2025, 9, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9040244
Mei L, Cheng Y, Chen H, Jia L, Yu Y. Unsupervised Aerial-Ground Re-Identification from Pedestrian to Group for UAV-Based Surveillance. Drones. 2025; 9(4):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9040244
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Ling, Yiwei Cheng, Hongxu Chen, Lvxiang Jia, and Yaowen Yu. 2025. "Unsupervised Aerial-Ground Re-Identification from Pedestrian to Group for UAV-Based Surveillance" Drones 9, no. 4: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9040244
APA StyleMei, L., Cheng, Y., Chen, H., Jia, L., & Yu, Y. (2025). Unsupervised Aerial-Ground Re-Identification from Pedestrian to Group for UAV-Based Surveillance. Drones, 9(4), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9040244






