Using Drones to Reveal the Distribution and Population Abundance of Threatened Dasyatid Rays at a Nursery Site in Seychelles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
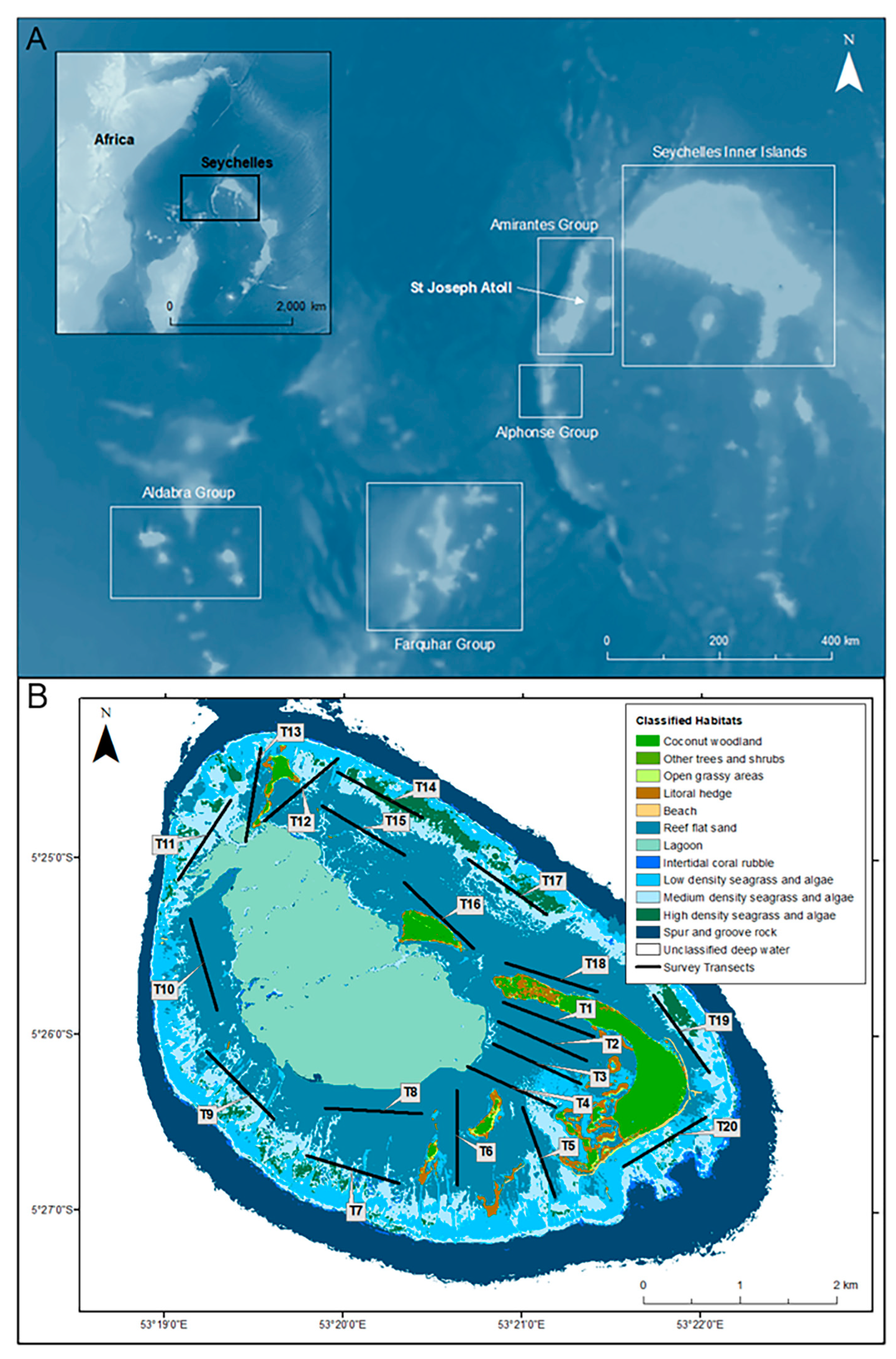
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Drone Surveys
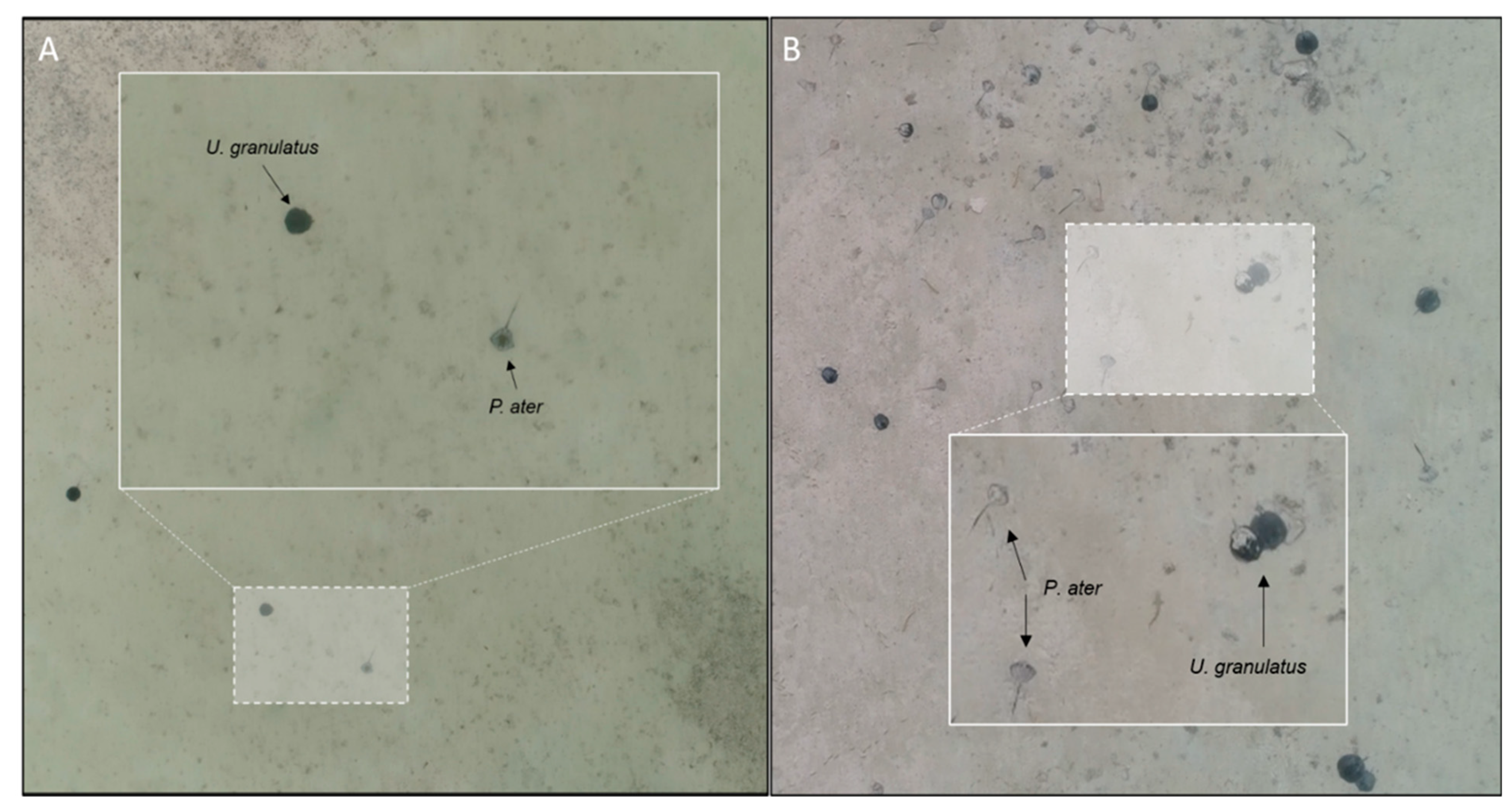
2.3. Video Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
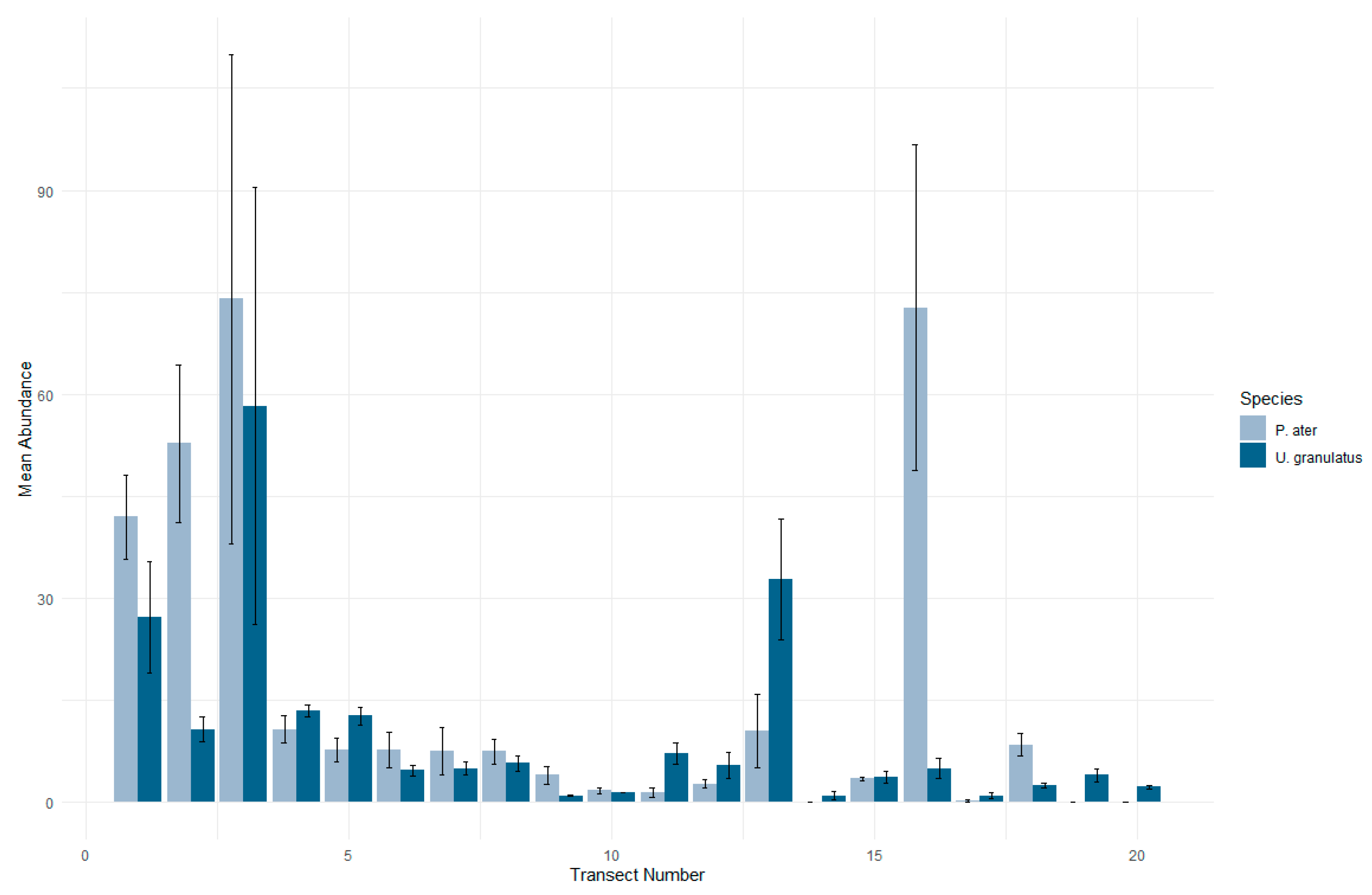
3.1. Patterns in Abundance
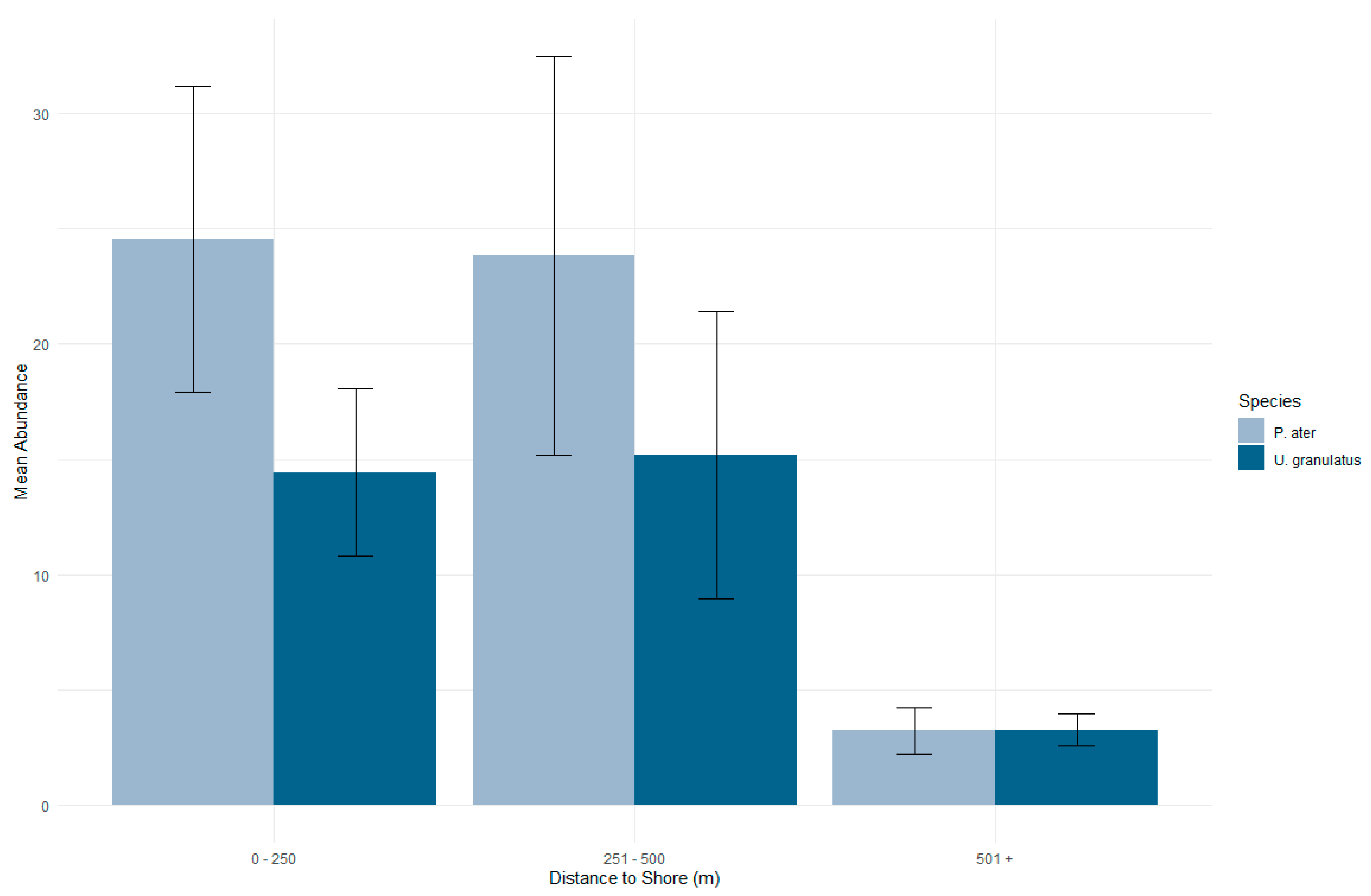
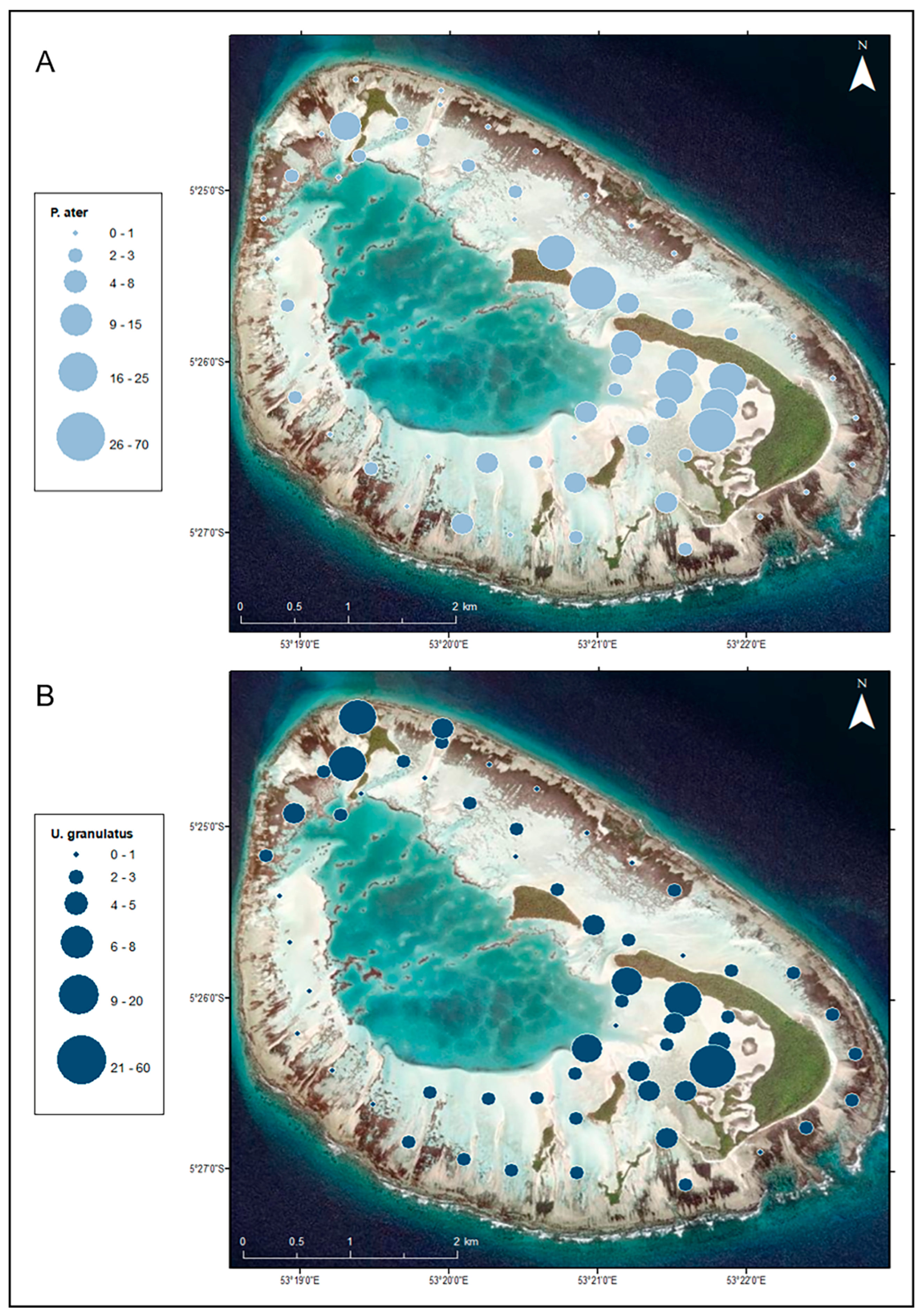
3.2. Distribution in the Habitat
3.3. Population Density and Abundance
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stevens, J.D.; Bonfil, R.; Dulvy, N.K.; Walker, P. The effects of fishing on sharks, rays and chimaeras (Chondrichthyans), and the implications for marine ecosystems. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 476–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.T.; Kyne, P.M. The status of chondrichthyan conservation in the Indo-Australasian region. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 76, 2090–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, A.; Kyne, P.M.; Walker, T.I.; McAuley, R.B. An integrated risk assessment of climate change: Analysing the vulnerability of sharks and rays on Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1936–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Last, P.R.; Naylor, G.J.P.; Seret, B.; White, W.T.; de Carvalho, M.R.; Stehmann, M.F.W. Rays of the World; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dulvy, N.K.; Pacoureau, N.; Rigby, C.L.; Pollom, R.A.; Jabado, R.W.; Ebert, D.A.; Finucci, B.; Pollock, C.M.; Cheok, J.; Derrick, D.H.; et al. Overfishing drives over one-third of all shark and rays towards a global extinction crisis. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 4773–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutti-Pereya, F.; Thums, M.; Austin, C.M.; Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Stevens, J.D.; Babcock, R.C.; Pillans, R.D.; Meekan, M.G. Restricted movements of juvenile rays in the lagoon of Ningaloo Reef, Western Australia—Evidence for the existence of a nursery. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2014, 97, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, K.I.; Heithaus, M.R.; Papastamatiou, Y.P. Buried in the sand: Uncovering the ecological roles and importance of rays. Fish Fish. 2021, 22, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wich, S.A.; Hudson, M.; Andrianandasana, H.; Longmore, S.N. Drones for conservation. In Conservation Technology; Wich, S.A., Piel, A.K., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.P.B.; Heupel, M.R.; Chin, A.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Batoid nurseries: Definition, use and importance. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 595, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.P.B.; Heupel, M.R.; Bierwagen, S.L.; Chin, A.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Diurnal activity patterns and habitat use of juvenile Pastinachus ater in a coral reef flat environment. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksyn, S. The Application of Drones in Ray Research. Master’s Thesis, Macquarie University, Sydney, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Riding, T.A.C.; Dennis, T.E.; Stewart, C.L.; Walker, M.M.; Montgomery, J.C. Tracking fish using ‘buoy-based’ GPS telemetry. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 377, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martins, A.P.B. Refining the Ecological Role of Stingrays in Coral Reef Ecosystems. Ph.D. Thesis, James Cook University, Douglas, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Heupel, M.R.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Using acoustic monitoring to evaluate MPAs for shark nursery areas: The importance of long-term data. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2005, 39, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heupel, M.R.; Ledee, E.J.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Telemetry reveals spatial separation of co-occurring reef sharks. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 589, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, J.S.E.; Humphries, N.E.; Bortoluzzi, J.; Daly, R.; von Brandis, R.G.; Patel, E.; Patel, E.; Clarke, C.R.; Sims, D.W. At the turn of the tide: Space use and habitat partitioning in two sympatric shark species is driven by tidal phase. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elston, C.; Cowley, P.D.; von Brandis, R.G.; Lea, J. Stingray habitat use is dynamically influenced by temperature and tides. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 754404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heupel, M.R.; Semmens, J.M.; Hobday, A.J. Automated acoustic tracking of aquatic animals: Scales, design and deployment of listening station arrays. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2006, 57, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, L.E.; Simpfendorfer, C.A.; Heupel, M.R. Movement patterns and habitat use of juvenile mangrove whiprays (Himantura granulata). Mar. Freshw. Res. 2015, 66, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elston, C.; Cowley, P.D.; von Brandis, R.G.; Lea, J. Residency and habitat use patterns by sympatric stingrays at a remote atoll in the Western Indian Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 662, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagua, E.F.; Berumen, M.L.; Tyler, E.H.M. Topography and biological noise determine acoustic detectability on coral reefs. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, J.A. N-mixture models for estimating population size from spatially replicated counts. Biometrics 2004, 60, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skomal, G.; Bernal, D. Physiological responses to stress in sharks. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 459–490. [Google Scholar]
- Murchie, K.J.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Cooke, S.J.; O’Toole, A.C.; Shultz, A.; Haak, C.; Brooks, E.; Suski, C.D. Considerations for tagging and tracking fish in tropical coastal habitats: Lessons from bonefish, barracuda, and sharks tagged with acoustic transmitters. In Handbook of Fisheries Telemetry; American Fisheries Society Special Publication: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.W. Unoccupied aircraft systems in marine science and conservation. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2019, 11, 439–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, N.J.; Bigelow, W.F.; Cuffley, J.; Gary, M.; Hoefer, S.; Mills, S.; Smith, A.; Miguel Blanco, A. Validating the use of drones for monitoring the abundance and behaviour of juvenile green sea turtles in mangrove creeks in the Bahamas. Testudo 2020, 9, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, H.J.; Mortimer, J.A.; Laloe, J.-O.; Hays, G.C.; Esteban, N. Synergistic use of UAV surveys, satellite tracking data, and mark-recapture to estimate abundance of elusive species. Ecosphere 2023, 14, e4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiszka, J.J.; Mourier, J.; Gastrich, K.; Heithaus, M.R. Using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to investigate shark and ray densities in a shallow coral lagoon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 560, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiszka, J.J.; Heithaus, M.R. Using aerial surveys to investigate the distribution, abundance, and behavior of sharks and rays. In Shark Research: Emerging Technologies and Applications for the Field and Laboratory; Carrier, C., Heithaus, M.R., Simpfendorfer, C.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Pate, J.H.; Marshall, A.D. Urban manta rays: Ptoential manta ray nursery habitat along a highly developed Florida coastline. Endanger. Species Res. 2020, 43, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desgarnier, L.; Mouillot, D.; Vigliola, L.; Chaumont, M.; Mannocci, L. Putting eagle rays on the map by coupling aerial video-surveys and deep learning. Biol. Conserv. 2022, 267, 109494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIvor, A.J.; Spaet, J.L.Y.; Williams, C.T.; Berumen, M.L. Unoccupied aerial video (UAV) surveys as alternatives to BRUV surveys for monitoring elasmobranch species in coastal waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 79, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, R.W.; Grimmel, H.M.V.; Moulinie, E.E.; Pouponeau, D.P.; Lea, J.S.E. Using global Red List data to inform localized research and conservation priorities—A case study in the Republic of Seychelles. Diversity 2022, 14, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weideli, O.C.; Papastamatiou, Y.P.; Planes, S. Size frequency, dispersal distances and variable growth rates of young sharks in a muliti-species aggregation. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elston, C.; Cowley, P.D.; von Brandis, R.G.; Fisk, A. Dietary niche differentiation in a mesopredatory dasyatid assemblage. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Getting started with PRIMER v7; Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 2015; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods. Primer-E Limited; 2008. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1370572092711312918 (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Kappes, M.A.; Coustaut, K.; Le Corre, M. Census of wedge-tailed shearwaters Puffinus pacificus breeding at D’Arros Island and St Joseph Atoll, Seychelles. Mar. Ornithol. 2013, 41, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, P.S.; Francis, T.B.; Heinemann, D.; Long, K.J.; Moore, J.E.; Punt, A.E.; Reeves, R.R.; Sepulveda, M.; Mar Sigurosson, G.; Siple, M.C.; et al. Estimating the Abundance of Marine Mammal Populations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 735770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, T.M.; Wildhaber, M.L.; Green, N.S.; Albers, J.L.; Debenedetto, G.P. Enumerating white-tailed deer using unmanned aerial vehicles. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2021, 45, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, O.; Thums, M.; van Keulen, M.; Meekan, M.G. Bioturbation by stingrays at Ningaloo reef, Western Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 63, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Tamaki, A. Assessment of benthic disturbance associated with stingray foraging for ghost shrimp by aerial survey over an intertidal sandflat. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 84, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filmalter, J.D.; Dagorn, L.; Cowley, P.D. Spatial behaviour and site fidelity of the sicklefin lemon shark Negaprion acutidens in a remote Indian Ocean atoll. Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 2425–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.P.B.; Heupel, M.R.; Bierwagen, S.L.; Chin, A.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Tidal-diel patterns of movement, activity and habitat use by juvenile mangrove whiprays using towed-float GPS telemetry. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 72, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpfendorfer, C.A.; Milward, N.E. Utilisation of a tropical bay as a nursery area by sharks of the families Carcharhinidae and Sphyrnidae. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1993, 37, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPeek, M.A. Limiting factors, competitive exclusion, and a more expansive view of species coexistence. Am. Nat. 2014, 183, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.P.B.; Matley, J.K.; Heupel, M.R.; Fis, A.T.; Chin, A.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Trophic ecology of sympatric juvenile stingrays within a nursery area. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2022, 73, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk, C.A.D.; Dill, L.M. Anti-predator benefits of mixed-species groups of cowtail rays (Pastinachus sephen) and whiprays (Himantura uarnak) at rest. Ethology 2006, 112, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, E.; Wenclawski, S.; Layman, C.A. Using a small, consumer-grade drone to identify and count marine megafauna in shallow habitats. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 46, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelaher, B.P.; Colefax, A.P.; Tagliafico, A.; Bishop, M.J.; Giles, A.; Butcher, P.A. Assessing variation in assemblages of large marine fauna off ocean beaches using drones. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 71, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliafico, A.; Butcher, P.A.; Colefax, A.P.; Clark, G.F.; Kelaher, B.P. Variation in cownose ray Rhinptera neglecta abundance and group size on the central east coast of Australia. J. Fish Biol. 2020, 96, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornatowski, H.; Braga, R.R.; Abilhoa, V.; Correa, M.F.M. Feeding ecology and trophic comparisons of six shark species in a coastal ecosystem off southern Brazil. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 85, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, S.A.; Burgess, K.B.; Teixeira, D.; Bennett, M.B. Local-scale resource partitioning by stingrays on an intertidal flat. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 533, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, I.V.; Kindel, A.; de Oliveira, L.F.B.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J. Optimally designing drone-based surveys for wildlife abundance estimation with N-mixture models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2023, 14, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieaucau, G.; Kiszka, J.J.; Castillo, J.C.; Mourier, J.; Boswell, K.M.; Heithaus, M.R. Using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) surveys and image analysis in the study of large surface-associated marine species: A case study on the reef sharks Carcharhinus melanopterus shoaling behaviour. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 93, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colefax, A.P.; Butcher, P.A.; Pagendam, D.E.; Kelaher, B.P. Reliability of marine faunal detections in drone-based monitoring. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 174, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, S.T.; Burt, M.L.; Rexstad, E.A.; Mellor, M.; Williams, A.E.; Wooward, R. Aerial surveys of seabirds: The advent of digital methods. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisk, M.G.; Martell, S.J.D.; Miller, T.J.; Sosebee, K. Exploring the population dynamics of winter skate (Leucoraja ocellata) in the Georges Bank region using a statistical catch-at-age model incorporating length, migration, and recruitment process errors. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 67, 774–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, K.J.; Cailliet, G.M.; Andrews, A.H.; Natanson, L.J. Assessing the age and growth of chondrichthyan fishes. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 423–451. [Google Scholar]
- Kuempel, C.D.; Jones, K.R.; Watson, J.E.M.; Possingham, H.P. Quantifying biases in marine protected area placement relative to abatable threats. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bullock, R.; Fermor, D.; Pouponeau, D.; Moulinie, E.; Grimmel, H. Using Drones to Reveal the Distribution and Population Abundance of Threatened Dasyatid Rays at a Nursery Site in Seychelles. Drones 2024, 8, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8020048
Bullock R, Fermor D, Pouponeau D, Moulinie E, Grimmel H. Using Drones to Reveal the Distribution and Population Abundance of Threatened Dasyatid Rays at a Nursery Site in Seychelles. Drones. 2024; 8(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleBullock, Robert, Daisy Fermor, Dillys Pouponeau, Ellie Moulinie, and Henriette Grimmel. 2024. "Using Drones to Reveal the Distribution and Population Abundance of Threatened Dasyatid Rays at a Nursery Site in Seychelles" Drones 8, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8020048
APA StyleBullock, R., Fermor, D., Pouponeau, D., Moulinie, E., & Grimmel, H. (2024). Using Drones to Reveal the Distribution and Population Abundance of Threatened Dasyatid Rays at a Nursery Site in Seychelles. Drones, 8(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8020048





