Electrochemical Analysis of Rationally Designed ZnO Nanostructures for Biodegradable Cellular Scaffolds †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
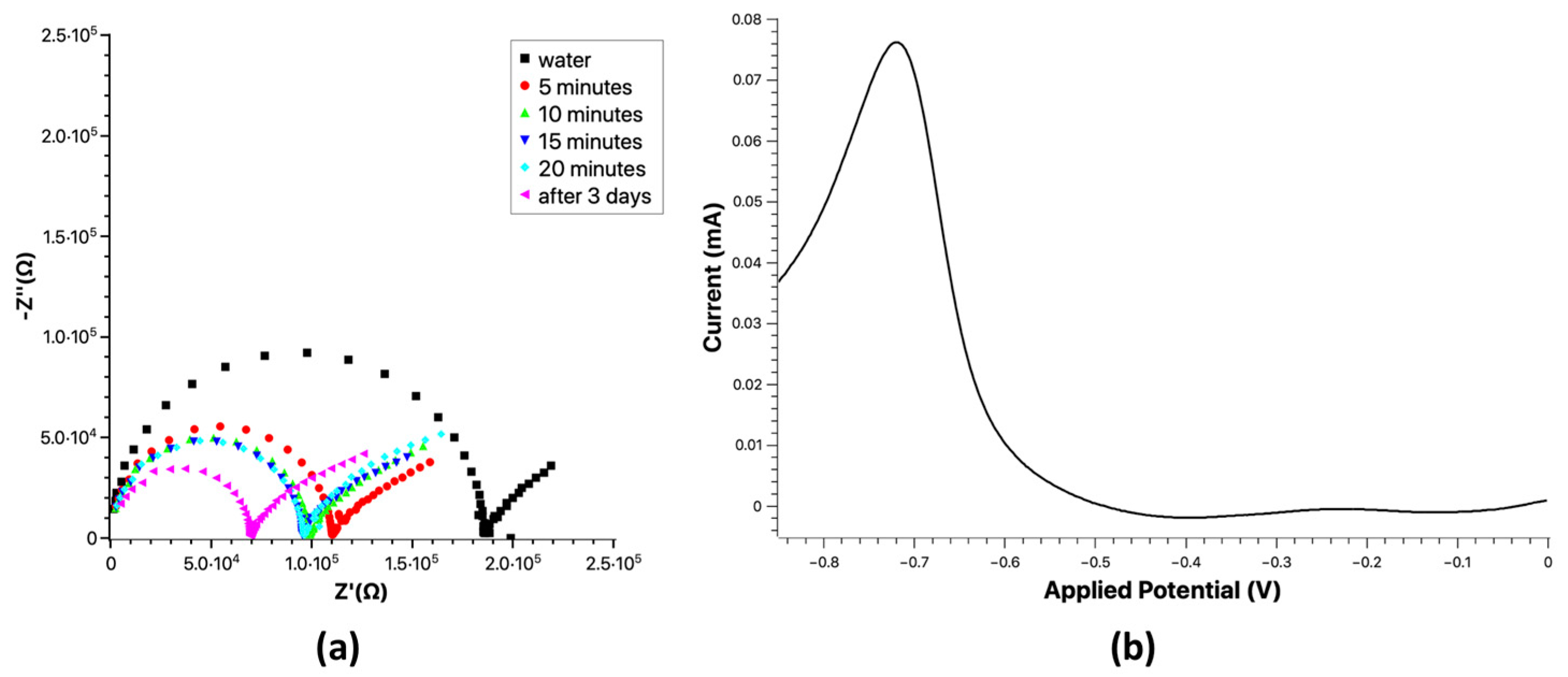
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arrabito, G.; Errico, V.; Zhang, Z.; Han, W.; Falconi, C. Nanotransducers on printed circuit boards by rational design of high-density, long, thin and untapered ZnO nanowires. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errico, V.; Arrabito, G.; Fornetti, E.; Fuoco, C.; Testa, S.; Saggio, G.; Rufini, S.; Cannata, S.; Desideri, A.; Falconi, C.; et al. High-Density ZnO Nanowires as a Reversible Myogenic–Differentiation Switch. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14097–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.S.; Qurashi, A.; Khanday, F.A. ZnO nanostructures based biosensors for cancer and infectious disease applications: Perspectives, prospects and promises. TrAC 2017, 86, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, N.S.; Wang, Z.L. Dissolving behavior and stability of ZnO wires in biofluids: A study on biodegradability and biocompatibility of ZnO nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2432–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, S.; Kazimirsky, G.; Gedanken, A.; Brodie, C. Selective cytotoxic effect of ZnO nanoparticles on glioma cells. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, S.M.; Squissato, A.L.; Rocha, D.P.; Vasconcellos, M.L.; de QFerreira, R.; Richter, E.M.; Munoz, R.A. Improved anodic stripping voltammetric detection of zinc on a disposable screen-printed gold electrode. Ionics 2020, 26, 2611–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arrabito, G.; Ferrara, V.; Prestopino, G.; Medaglia, P.G.; Scopelliti, M.; Pignataro, B. Electrochemical Analysis of Rationally Designed ZnO Nanostructures for Biodegradable Cellular Scaffolds. Proceedings 2024, 97, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097212
Arrabito G, Ferrara V, Prestopino G, Medaglia PG, Scopelliti M, Pignataro B. Electrochemical Analysis of Rationally Designed ZnO Nanostructures for Biodegradable Cellular Scaffolds. Proceedings. 2024; 97(1):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097212
Chicago/Turabian StyleArrabito, Giuseppe, Vittorio Ferrara, Giuseppe Prestopino, Pier Gianni Medaglia, Michelangelo Scopelliti, and Bruno Pignataro. 2024. "Electrochemical Analysis of Rationally Designed ZnO Nanostructures for Biodegradable Cellular Scaffolds" Proceedings 97, no. 1: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097212
APA StyleArrabito, G., Ferrara, V., Prestopino, G., Medaglia, P. G., Scopelliti, M., & Pignataro, B. (2024). Electrochemical Analysis of Rationally Designed ZnO Nanostructures for Biodegradable Cellular Scaffolds. Proceedings, 97(1), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097212









