Abstract
This paper reports, for the first time, on the use of thin-film platinum microheaters to influence the flow boiling of DI water in microchannels with rapid low power heating pulses. A custom-designed control module allows microheaters to be actuated simultaneously and independently, enabling precise local control of flow regimes along an entire channel. In this study, bubbly flow was converted into a slug and annular flow. This pioneering technique promises a radical improvement in the heat transfer and performance of flow-boiling cooling devices by actively targeting flow conditions with high heat dissipation.
1. Introduction
Two-phase flow boiling in microchannels, i.e., the partial conversion of a fluid into steam, has been one of the most important research topics in the field of heat transfer for the last decades, especially because of its promising application in high heat flux cooling of electronic chips and components [1]. At high steam quality, the slug and annular flow regimes of two-phase flow exhibit the highest heat transfer coefficients. Therefore, it is of great interest to keep the flow-boiling process in these two regimes in order to maximize heat transfer. We do this by influencing the flow regime via local heating, using thin-film platinum heaters located at one microchannel side wall [2]. In comparison to this active flow regime manipulation, two-phase flow boiling is currently only controlled passively by global parameters such as mass flow rate, global heat input, channel dimensions, and restrictions of the channel geometry.
2. Materials and Methods
A Pyrex glass lid with an array of 17 platinum microheaters with a thickness of 200 nm, a width of 300 µm, and lengths from 0.5 mm to 2 mm (Figure 1a) was pressed onto a stainless-steel microchannel such that all heaters were in direct contact with the flowing DI water. All platinum structures had electroplated gold pads at each end that served as electrical contacts for spring probes. An O-ring in a trench surrounding the microchannel provided a hermetic seal between the microchannel and the glass cover. To induce flow boiling, 11 heater cartridges inserted into holes at the microchannel bottom were subjected to a specific heating power. A high-temperature stable 3D-printed reactor enclosure provided mechanical fixation and thermal isolation for all components. Figure 1b shows an exploded view of the experimental apparatus. A high-speed camera was mounted above to study boiling through the transparent glass lid. A micro annular gear pump passed the DI water through the microchannel at a mass flow rate of 1.5 g min−1.
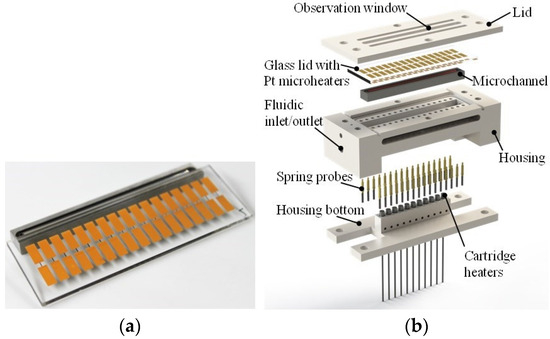
Figure 1.
Pyrex glass lid with 17 platinum microheaters (a); CAD drawing of experimental apparatus consisting of the 3D-printed reactor housing, stainless-steel microchannel, glass lid with microheaters, cartridge heaters, and spring probes for electrical contact formation to the microheaters (b).
3. Discussion
Figure 2a shows a bubbly flow at a fixed location of the microchannel. For this purpose, the 11 heater cartridges were heated with a total power of 14.18 W. Figure 2b illustrates the transition of this bubbly flow into a slug and annular flow with a 0.5 mm long microheater pulsed with a heating power of 870 mW. As seen in Figure 2, a heating pulse length of 110 ms was required to generate a slug flow, and a heating pulse of 205 ms was sufficient to generate an annular flow.
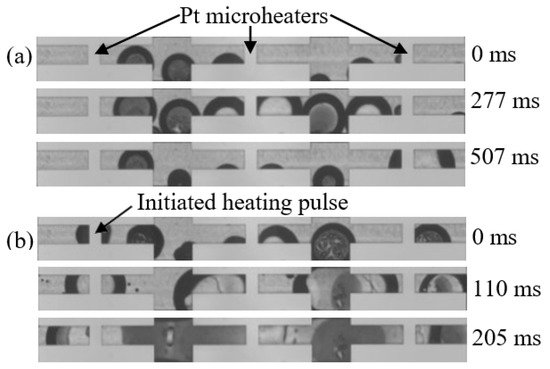
Figure 2.
Time frames of a bubbly flow (a) and time frames of a bubbly flow affected by an 870 mW heating pulse from a 0.5 mm long microheater (b). All frames were acquired with DI water at a mass flow rate of 1.5 g min−1 using a high-speed camera at 2000 frames per second.
Author Contributions
Writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition, project administration, P.W.; software, S.A.; conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, visualization, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) under Grant No. WO 883/24-2.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cheng, L.; Xia, G. Fundamental issues, mechanisms and models of flow boiling heat transfer in microscale channels. Appl. Thermal Eng. 2017, 115, 1372–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepperle, M.; Ghanam, M. Noninvasive platinum thin-film microheater/temperature sensor array for predicting and controlling flow boiling in microchannels. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2022, 345, 113811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).