1. Introduction
The capital market is one of the facilities available to channel funds from parties who have excess funds who need funds. Shares are one of the assets traded by companies in the capital market. The share price is the value of a share that reflects the wealth of the company that issued the shares, but changes and fluctuations in price are largely determined by the supply and demand forces for the shares themselves that appear on the stock exchange (secondary market) [
1]. The more the demand, the more the stock price will increase.
Stock prices in the capital market are influenced by several factors, including a company’s performance. Financial statements are the final result of the accounting process carried out to provide information about the financial condition of a company. Investors or managers use reports to make investment decisions [
2].
To measure the performance of a company, investors usually look at the financial performance as reflected in various ratios. One indicator of financial performance measurement that is often used is a company’s profitability. The company profitability measurement tools that are most often used are Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE) [
3].
The amount of negative sentiment that emerged from the spread of the COVID-19 outbreak both in the world and in Indonesia affected capital market conditions in both stock markets and in bond markets. The uncertainty over the end of the COVID-19 pandemic has prompted investors to make adjustments to their financial portfolios by shifting liquidity to safe haven assets, including developing countries such as Indonesia. These conditions put pressure on the domestic capital market, although in general capital market stability can still be maintained. Stock market conditions experienced a significant weakening, as reflected in the Composite Stock Price Index (JCI), which experienced a contraction. The JCI closed at 4538 in the first quarter of 2020, weakened by 29.8 percent (YoY). This condition is considered the lowest position of the JCI since December 2016.
The financial sector (finance) has the largest weight on the JCI, so the movement of this index also influences the direction of the JCI. Within these conditions, the financial sector also shows a fair amount of sensitivity to market conditions. Referring to the daily report of the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX), the financial sector experienced a decline of 6.69 percent. As to conditions for short-term investors, current conditions can be a yellow light for the regulation of their risk management. However, on the other hand, for long-term investors, depressed index conditions are the best momentum to get stocks at low prices. However, in a panicked market, shares of issuers with good fundamentals will also be depressed.
As for discussion about the company’s reputation, this is very important because it can affect the company’s stock price. For example, the share price of PT Garuda Indonesia experienced a decline in 2019. Pressure on Garuda’s share price came from local investors who began to sell their shares of this stock. Then in May 2021 the share price of PT Garuda Indonesia also experienced a decline. The stock plunged 6.7 percent and then fell 6.8 percent again. This is allegedly because PT Garuda Indonesia has faced problems in paying the company’s debts.
One of the investments made in the capital market today is investment in stocks. The motive of investors in investing in the stock market is to obtain returns in the form of dividends or capital gains as well as company ownership. Before investing, investors will consider the return on shares they will receive and the value of the company. The share price represents the value of a publicly traded company [
4].
Return on Assets (ROA) has a positive and significant effect on a firm’s value. The results of this study confirm the conclusion that ROA has a significant effect on a firm’s value. Subsequent research [
5] states that the Debt to Equity Ratio has a negative and insignificant effect on a firm’s value. The existence of a negative relationship from the leverage variable (DER) to the firm’s value shows that the higher the leverage (DER), the lower the firm’s value and that it does not have a significant effect. This is because no matter how much debt is used, it will not affect the stock price and the firm’s value because the use of debt will cause the cost of ordinary equity to rise by the same level [
6].
A company’s reputation has a positive influence on its market value. The reputation of the company, a metric that is driven by the perception of the effectiveness of the company, is believed to increase investor reactions that the risk of investing in company shares is low. Favorable investor reactions will result in rising stock prices and company stock returns [
5].
Corporate reputation can be defined as a general attribute of an organization that reflects the extent to which internal and external stakeholders see the company as a good company rather than a bad company. A good corporate reputation has a beneficial impact on various stakeholder groups. The formation of a good and positive corporate reputation can benefit the company in many ways, such as by influencing customers in choosing products, limiting the potential for competition by competitors, and securing social status in an industry [
7].
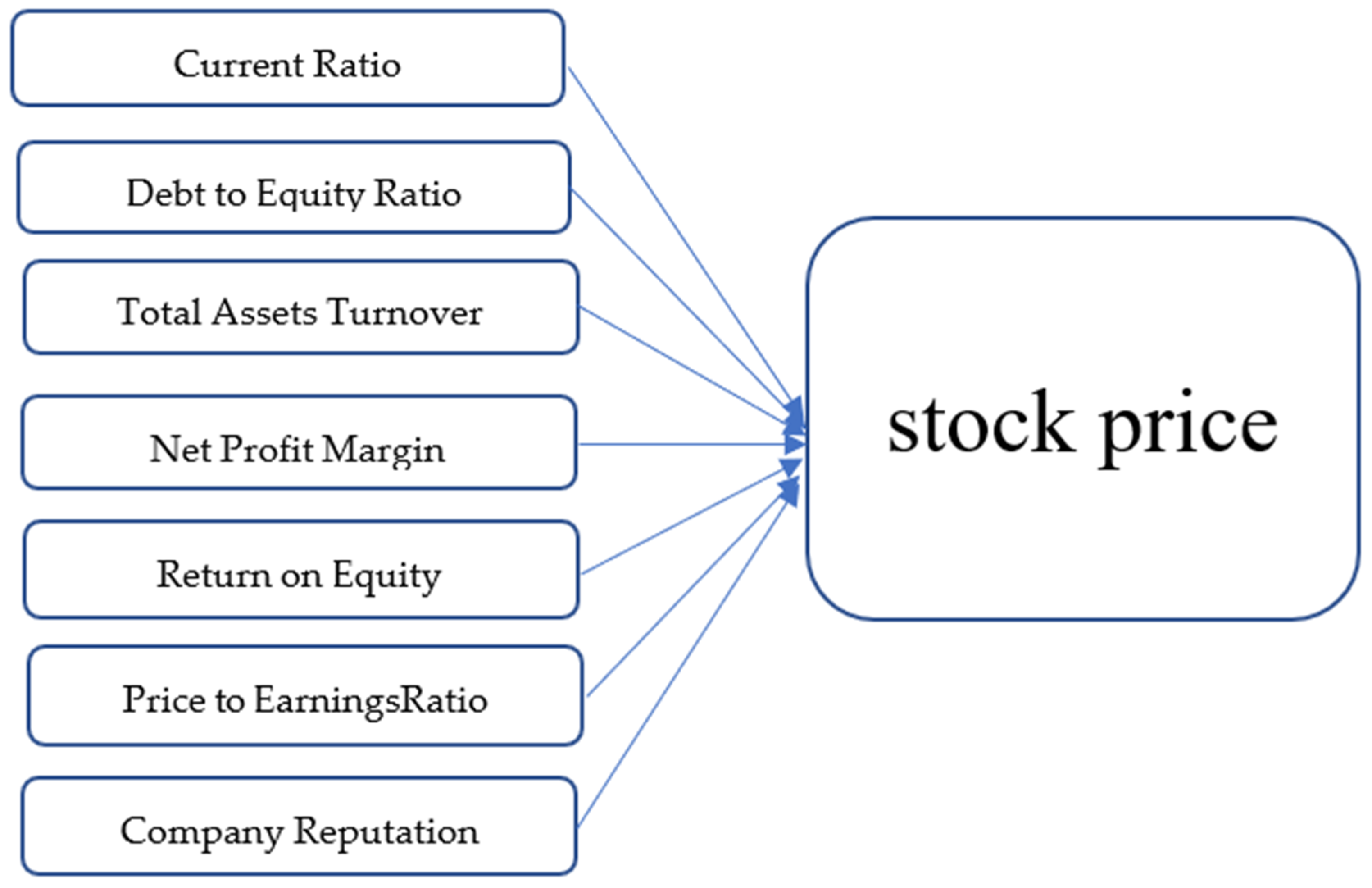
Based on this explanation, the researcher endeavors to see the influence of financial ratios and non-ratio variables on stock prices in financial sector companies in companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange from 2016 to 2020. Researchers want to know more deeply how these ratios affect stock prices so that they can influence investors’ decisions. Therefore, the researcher took the title “The Influence of Current Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio, Total Assets Turnover, Net Profit Margin, Return on Equity, Price to Earnings Ratio, and Company Reputation on Stock Prices of Financial Sector Companies”.
1.1. Research Questions
Does the Current Ratio (CR), Debt to Equity Ratio (DER), Total Assets Turnover (TATO), Net Profit Margin (NPM), Return on Equity (ROE), Price to Earnings Ratio (PER), and company reputation affect the share prices of Financial Sector companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange from 2016 to 2020?
What is the ratio that has the most influence on stock prices in Financial Sector companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange from 2016 to 2020?
1.2. Research Purposes
- (1)
This study aims to see the effect of several financial ratios such as Current Ratio (CR), Debt to Equity Ratio (DER), Total Assets Turnover (TATO), Net Profit Margin (NPM), Return on Equity (ROE), Price to Earnings Ratio (PER), and also the influence of the company’s reputation on the share price of financial sector companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange from 2016 to 2020.
- (2)
This study aims to determine which ratio has the most influence on the share price of financial sector companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange and the reasons why.
3. Research Methods
3.1. Research Method
The type of research conducted in this study is a quantitative approach. A quantitative approach is used to examine a particular population or sample. In this study, financial performance is used as a benchmark in determining its effect on stock prices using the calculation of the effect of the Current Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio, Total Assets Turnover, Net Profit Margin, Return on Equity, Price to Earnings Ratio, and the company’s reputation.
The population of this study was taken from a sample of 30 banks listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange from 2016 to 2020. In this study, the companies used as samples were selected by purposive sampling from all banks listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange. With this method, the sample is selected based on certain criteria, namely: (1) banks listed on the IDX during the analysis period; (2) issuing financial statements as of 31 December 2016–2020; and (3) having data and financial reports related to the measurement of research variables.
3.2. Operational Variables
In this study the variables to be studied are Current Ratio (CR), Debt to Equity Ratio (DER), Total Assets Turnover (TATO), Net Profit Margin (NPM), Return on Equity (ROE), Price to Earnings Ratio (PER), and the Company’s Reputation on the share price. The objects of the research are the financial statements for the 2016–2020 period in banking sector companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX). Then, operationalization of variables is needed to determine the types and indicators of the variables involved in the research and aims to determine the measurement scale of each variable.
3.3. Sample Selection
In this study, the sample is companies that meet certain criteria. The criteria used as research samples are:
Banking sector companies listed on the IDX during the period 2016–2020;
Financial sector companies that have consecutive financial statements during the 2016–2020 period;
Financial sector companies listed on the IDX, companies with a search based on the main board on stock prices;
The company has all data needed in the study in accordance with the variables studied, namely Current Ratio (CR), Debt to Equity Ratio (DER), Total Assets Turnover (TATO), Net Profit Margin (NPM), Return on Equity (ROE), Price to Earnings Ratio (PER) and the reputation of companies in the financial sector on the IDX.
Based on predetermined criteria, from the number of companies in the finance sector, 53 companies are listed on the main board and 52 companies are on the development board, with a total of 105 companies. So, companies that meet these criteria are 30 companies in the financial sector.
3.4. Data Collection
The source of data used in this research is secondary data. According to (Yulianto, 2018) “Secondary data is data that has been collected by data collection institutions and published to the public using services”. The data used in this study are annual financial reports and stock prices, where the data are taken from the Indonesia Stock Exchange website
www.idx.co.id and id.investing.com for the financial sector 2016–2020. The data collection method is data collection; the data that will be used for this research and the method used in this research is to use the annual financial report documents obtained from the IDX website.
3.5. Analysis Method
This study applies an analysis that leads to inferential statistical analysis, namely by examining the effect of financial ratios such as the Current Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio, Total Assets Turnover, Net Profit Margin, Return on Equity, Price to Earnings Ratio, and the reputation of the financial sector companies in companies that listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in 2016–2020.
4. Analysis and Discussion
This study will examine whether there is an effect of Current Ratio (X1), Debt to Equity Ratio (X2), Total Assets Turnover (X3), Net Profit Margin (X4), Return on Equity (X5), Price to Earnings Ratio (X6), and Company Reputation (X7), to Share Price (Y1) in financial sector companies. There are seven independent variables and one dependent variable which will be analyzed causally in this study. The data to be used is annual data from 2016 to 2020 (5 years) with a sample of 30 companies in the financial sector.
The total observations that should be used are 150 units of observation data, but because there are some incomplete data, only 137 units of observation will be analyzed. The data used is available on the attachment page. The stages in this analysis, starting from descriptive analysis to hypothesis testing (
Table 1).
4.1. Statistical Analysis (Regression)
The next step of this analysis is to perform a regression analysis. The results and outputs of the regression analysis are as follows (
Table 2 and
Table 3):
In the ANOVA table, it can be seen that the Sig value obtained is 0.000 which is smaller than 0.05; it was then decided to reject H0 and accept H1, that is to say, that there is at least 1 variable out of 7 X variables that affect Y. To find out which X variable affects Y, the next step is to conduct an analysis using the t test as below.
4.2. Individual Test (t Test)
This test uses the COEFFICIENT table output. The table in question is the following table (
Table 4).
The t-test for the CR variable obtained the regression coefficient value with a negative direction of −0.219. The result of the CR variable is t = −2.758 with a probability of 0.007. The significance value of 0.007 is smaller than 0.05. Based on the explanation above, it can be concluded that the first hypothesis which states “Current Ratio (CR) has a positive effect” is accepted.
Based on the t-test for the Debt to Equity Ratio (DER) variable, the regression coefficient value in the negative direction is −0.034. The result of the DER variable is t = −0.401 with a probability of 0.689. The value is greater than 0.05. So, it can be concluded that the second hypothesis which states “Debt to Equity Ratio (DER) has a negative effect” is accepted.
In the t-test for the Total Assets Turnover (TATO) variable, the regression coefficient value is obtained with a positive direction of 0.015. The result of the TATO variable is t = 0.189 with a probability of 0.850. The value is greater than 0.05. So, it can be concluded that the third hypothesis which states “Total Assets Turnover (TATO) has a positive effect” is rejected.
Based on the t-test for the Net Profit Margin (NPM) variable, the regression coefficient value is obtained with a positive direction of 0.009. The results of the NPM variable are t = 0.117 with a probability of 0.907. The value is greater than 0.05. So, it can be concluded that the fourth hypothesis which states “Net Profit Margin (NPM) has a positive effect” is rejected.
Based on the t-test for the Return on Equity (ROE) variable, the regression coefficient value is obtained with a positive direction of 0.353. The results of the ROE variable are t = 4.289 with a probability of 0.000. The value is smaller than 0.05. So, it can be concluded that the fifth hypothesis which states “Return on Equity (ROE) has a positive effect” is accepted.
Based on the t-test for the Price to Earnings Ratio (PER) variable, the regression coefficient value is obtained with a negative direction of −0.051. The result of the PER variable is t = −0.623 with a probability of 0.534. The value is greater than 0.05. It therefore can be concluded that the sixth hypothesis which states “Price to Earnings Ratio (PER) has a positive effect” is rejected.
In the t-test for Company Reputation, the regression coefficient value is obtained with a negative direction of −0.029. The result of the PER variable is t = −0.355 with a probability of 0.723. The value is greater than 0.05. So, it can be concluded that the seventh hypothesis which states “Company reputation has a positive effect” is rejected.
In the COEFFICIENT table, it can be seen that the Sig value which is less than 0.05 is the Sig value for the CR variable of 0.007 and the ROE of 0.000; it is concluded that only these two variables affect Variable Y or Stock Price.
4.3. Coefficient of Determination (R2)
The value of determination or influence on Variable Y or Stock Price can be seen in the R-Square value in the table below (
Table 5).
The R-Square value obtained is 0.212 or 21.2% in other words, the CR and ROE variables are able to predict stock prices with an accuracy of 21.2%. This accuracy value is included in the Weak category.
4.4. Classical Assumption Test
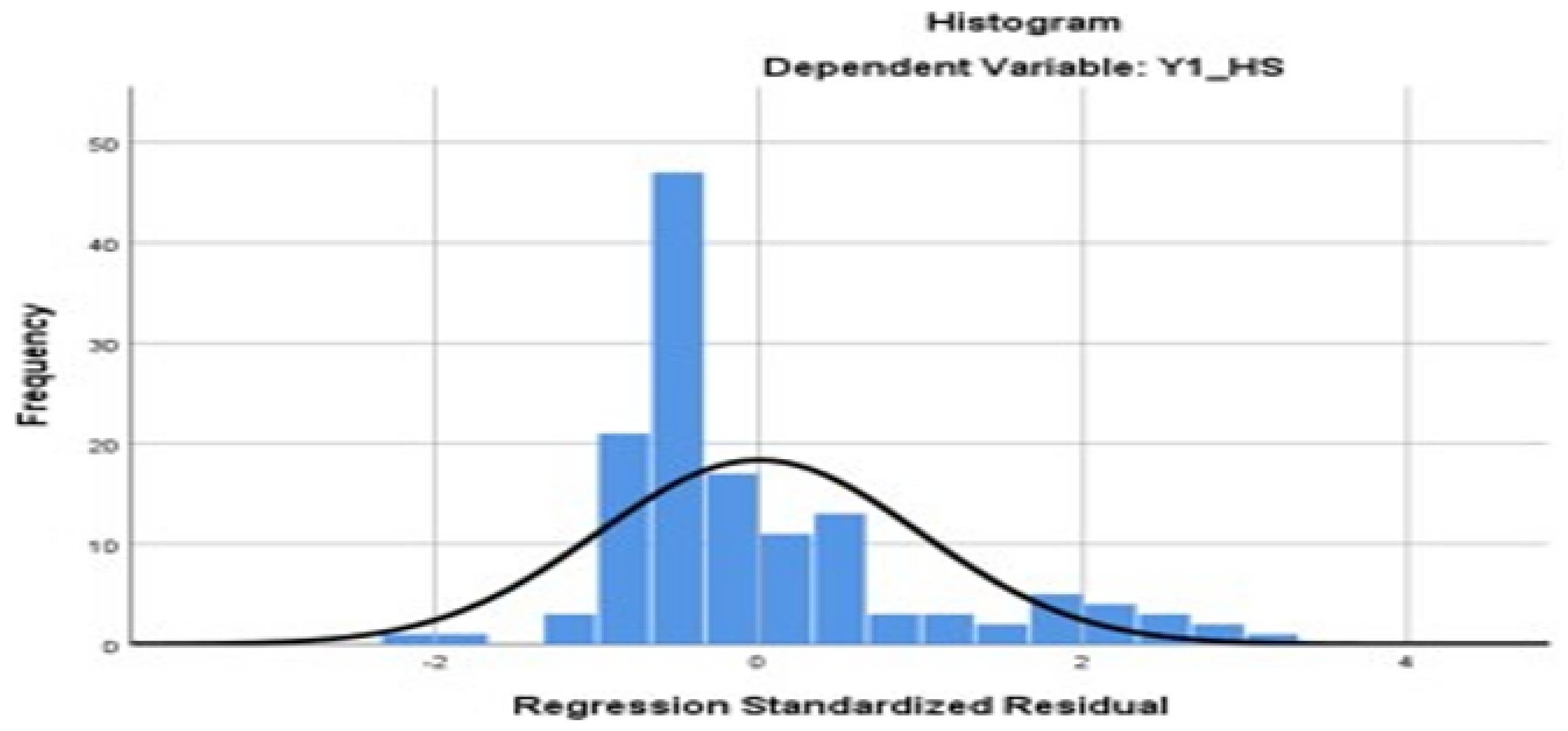
4.4.1. Data Normality Test
The graph below (
Figure 2) shows that the data used in the analysis has met the criteria for Normality, as can be seen from the Histogram that is formed quite closely following the distribution pattern of the Normal Distribution.
4.4.2. Multicollinearity Test Non-Multicollinearity Assumption
Multicollinearity Testing uses the VIF value (
Table 6). If the VIF value is greater than 10, it is stated that there is multicollinearity. In the table above, it can be seen that the VIF value for all variables is less than 10, so it is stated that there is no problem with Multicollinearity.
Non-Autocorrelation Assumption
The obtained DW value is greater than 2000. It can therefore be stated that there is no autocorrelation problem (
Table 7).
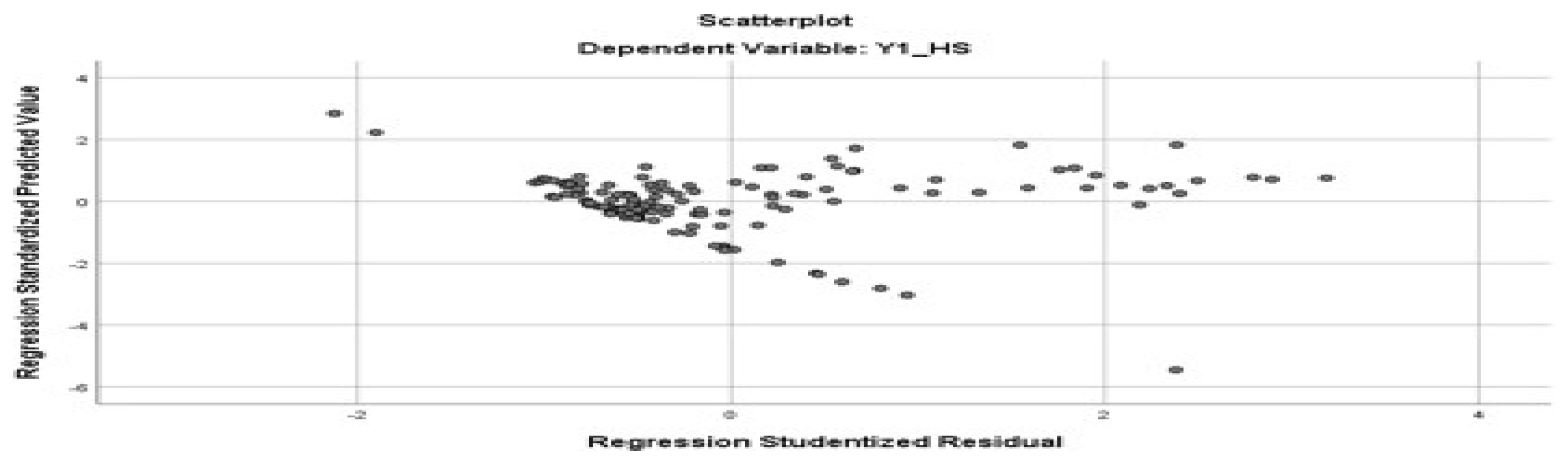
4.4.3. Heteroscedasticity Test; Homoscedasticity Assumption
The graph below (
Figure 3) shows the distribution pattern of residuals that do not follow a certain distribution pattern, or do not have a pattern. Because it has no pattern, it is concluded that this regression model meets the assumption of homoscedasticity.