A Trend Analysis of Research on the Flipped Classroom in L2 Learning before and after COVID-19 †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Distance Education and Flipped Classroom
2.1. Online Education vs. Distance Education
2.2. Research Questions
- RQ1
- What are the frequent types of research used to investigate the effects of the flipped classroom on EFL learners?
- RQ2
- What are the frequent topics investigated in the reviewed studies?
- RQ3
- What is the trend of the flipped classroom approach used before and during the COVID-19 pandemic?
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Research Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, L.; Ritzhaupt, A.D.; Antonenko, P. Effects of the flipped classroom instructional strategy on students’ learning outcomes: A meta-analysis. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2019, 67, 793–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güvenç, G. The flipped classroom approach in teaching writing: An action research. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Educ. Res. 2018, 4, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mubarok, A.F.; Cahyono, B.; Astuti, U. Effect of Flipped Classroom Model on Indonesian EFL Students’ Writing Achievement across Cognitive Styles. Din. Ilmu 2019, 19, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanpour, F.; Valizadeh, M. A Flipped Writing Classroom: Effects on EFL Learners’ Argumentative Essays. Adv. Lang. Lit. Stud. 2017, 9, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrilyasanti, R.; Cahyono, B.Y.; Astuti, U.P. Indonesian EFL Students’ Perceptions on the Implementation of Flipped Classroom Model. J. Lang. Teach. Res. 2017, 8, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohammadi, J.; Barati, H.; Youhanaee, M. The Effectiveness of Using Flipped Classroom Model on Iranian EFL Learners’ English Achievements and Their Willingness to Communicate. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2019, 12, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-C.V.; Yang, J.C.; Hsieh, J.S.C.; Yamamoto, T. Free from demotivation in EFL writing: The use of online flipped writing instruction. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2020, 33, 353–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-C.V.; Chen Hsieh, J.S.; Yang, J.C. Creating an Online Learning Community in a Flipped Classroom to Enhance EFL Learners’ Oral Proficiency. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2017, 20, 142–157. [Google Scholar]
- Çil, O. An Educator’s Response to COVID-19: Preservice Teachers’ Perspectives on Flipped Distance Education. Int. Acad. Forum 2021, 9, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhanty, S.; Puspitaloka, N. EFL Students’ Experiences in a Flipped Reading Comprehension Classroom. Ethical Ling. 2020, 7, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerantzi, C. The Use of Peer Instruction and Flipped Learning to Support Flexible Blended Learning During and After the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Manag. Appl. Res. 2019, 7, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harida, E.S.; Jufrizal; Syarif, H.; Ratmanida. A Study of Students’ Perceptions of Online Learning in Blended Learning and Flipped Classroom. Adv. Soc. Sci. Educ. Humanit. Res. 2020, 504, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Guessabi, F. Flipped classrooms in higher education in Algeria during period of COVID-19: Challenges and Difficulties. Int. J. Linguist. Lit. Transl. 2021, 4, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Sumardi, S.; Nugrahani, D. Adaptation to emergency remote teaching: Pedagogical strategy for pre-service language teachers amid COVID-19 pandemic. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2021, 22, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarani, A.; Zarei, M.J.; Navidia, H. Effect of Online Flipped Classroom on Students’ Writing Development at Senior High School. J. Engl. Lang. Teach. Learn. 2020, 12, 495–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yağız, O.; Aydın, B.; Akdemir, A.S. ELT research in Turkey: A content analysis of selected features of published articles. J. Lang. Linguist. Stud. 2016, 12, 117–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ekmekci, E. The flipped writing classroom in Turkish EFL context: A comparative study on a new model. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2017, 18, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyraz, S.; Ocak, G. Implementation of flipped education into Turkish EFL teaching context. J. Lang. Linguist. Stud. 2017, 13, 426–439. [Google Scholar]
- Amiryousefi, M. The incorporation of flipped learning into conventional classes to enhance EFL learners’ L2 speaking, L2 listening, and engagement. Innov. Lang. Learn. Teach. 2019, 13, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santikarn, B.; Wichadee, S. Flipping the Classroom for English Language Learners: A Study of Learning Performance and Perceptions. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2017, 13, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Hamzavi, R. The Effect of Flipped Model of Instruction on EFL Learners’ Reading Comprehension: Learners’ Attitudes in Focus. Adv. Lang. Lit. Stud. 2017, 8, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, G. Implementing the Flipped Classroom in Teacher Education: Evidence from Turkey. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2017, 20, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zainuddin, Z.; Perera, C.J. Exploring students’ competence, autonomy and relatedness in the flipped classroom pedagogical model. J. Furth. High. Educ. 2019, 43, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinabadi, N.; Ebrahimi, A. Increasing peer collaborative dialogue using a flipped classroom strategy. Innov. Lang. Learn. Teach. 2019, 13, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Xie, H. Flipping an English writing class with technology enhanced just-in-time teaching and peer instruction. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2019, 27, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qader, R.; Arslan, F. The effects of the flipped classroom instruction in writing: A case study with Iraqi EFL learners. Teach. Engl. Technol. 2019, 19, 36–55. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.Y.; Hussin, S.; Ismail, K. Investigating the effects of the flipped classroom model on Omani EFL learners’ motivation level in English speaking performance. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 24, 2975–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.R.; Chen, Y. Implementing the flipped classroom approach in primary English classrooms in China. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 25, 1217–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.R. Promotion of learner autonomy within the framework of a flipped EFL instructional model: Perception and perspectives. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2019, 34, 979–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilçınar, S. Using the Flipped Classroom to Enhance Adult EFL Learners’ Speaking Skills. PASAA 2019, 58, 206–234. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi, H.; Jafarigohar, M.; Khoshsima, H.; Vahdany, F. Impact of flipped classroom on EFL learners’ appropriate use of refusal: Achievement, participation, perception. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2019, 32, 261–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altas, E.A.; Mede, E. The impact of flipped classroom approach on the writing achievement and self-regulated learning of pre-service English teachers. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2021, 22, 66–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, R.; Verezub, E.; Badiozaman, I.; Chen, W.S. Tracing EFL students’ flipped classroom journey in a writing class: Lessons from Malaysia. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2020, 57, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, J.; Rahimi, M. Examining the impact of flipped classroom on writing complexity, accuracy, and fluency: A case of EFL students. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2020, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanpour, F.; Valizadeh, M. The Flipped Pedagogy: Effects on the Grammatical Competence and Writing Skill of Basic Users of English. Int. J. Instr. 2020, 13, 761–776. [Google Scholar]
- Arifani, Y.; Khoirul Anwar, S.A.; Budianto, L. Individual or collaborative Whatsapp learning? A flipped classroom model of EFL writing instruction. Teach. Engl. Technol. 2020, 20, 122–139. [Google Scholar]
- Alghasab, M.B. Flipping the Writing Classroom: Focusing on the Pedagogical Benefits and EFL Learners’ Perceptions. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2020, 13, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.M.; Ejtehadi, A.; Hosseini, M.M. Flipping Microlearning-based EFL Classroom to Enhance Learners’ Self-Regulation. Lang. Teach. Res. Q. 2020, 20, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namaziandost, E.; Çakmak, F. An account of EFL learners’ self-efficacy and gender in the Flipped Classroom Model. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 4041–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadfar, P.; Soozandehfar, S.M.A.; Namaziandost, E. An account of EFL learners’ listening comprehension and critical thinking in the flipped classroom model. Cogent Educ. 2020, 7, 1835150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamàa, S. Lecture in the Living Room, Homework in the Classroom: The Effects of Flipped Instruction on Graduate EFL Students’ Exam Performance. Comput. Sch. 2020, 37, 141–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naabi, I.S. Is it Worth Flipping? The Impact of Flipped Classroom on EFL Students’ Grammar. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2020, 13, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, Z.; Cimen, B.A. Flipped classroom in English language teaching: A systematic review. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2020, 33, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, M.; Çakıroğlu, Ü. Flipped learning design in EFL classrooms: Implementing self-regulated learning strategies to develop language skills. Smart Learn. Environ. 2021, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiei, F.; Ebadi, S. Exploring EFL learners’ inferential reading comprehension skills through a flipped classroom. Res. Pract. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2021, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Carballo, V. Prospective primary school EFL teachers’ beliefs about “flipping”. Teach. Engl. Technol. 2021, 21, 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Afzali, Z.; Izadpanah, S. The effect of the flipped classroom model on Iranian English foreign language learners: Engagement and motivation in English language grammar. Cogent Educ. 2021, 8, 1870801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoiriyah, K. Flipping the classroom to enhance EFL students’ listening skill. J. Engl. Foreign Lang. 2021, 11, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRuisseau, L.R. The flipped classroom allows for more class time devoted to critical thinking. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2016, 40, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
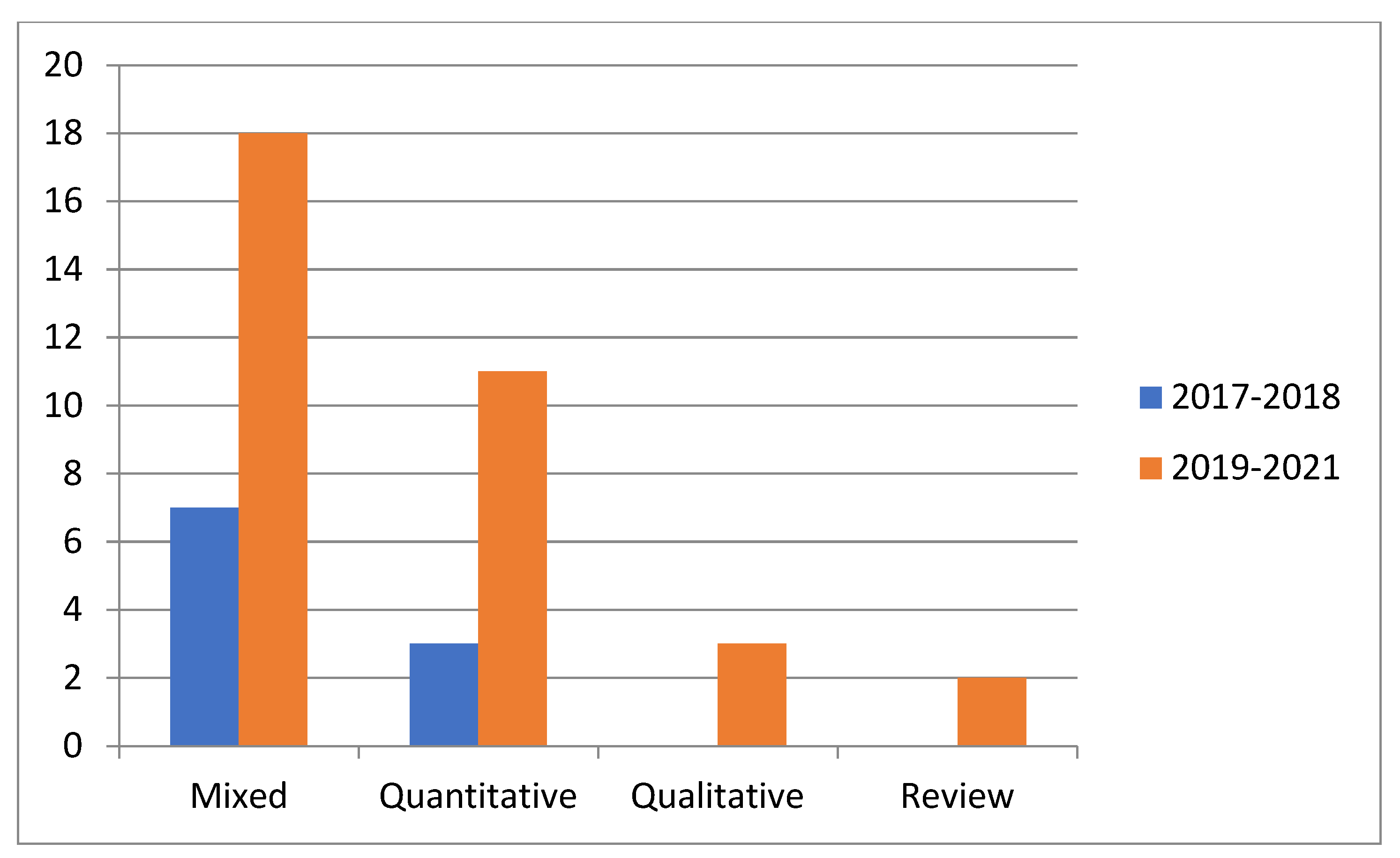


| Author, Year | Purpose | Study Design | Sample Target Population | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ekmekci, E. (2017) [17] | Investigating the impact of flipped instruction on students’ foreign language writing skill. | Mixed Method | 23 | Students in the experimental group outperformed the students in the control group. |
| Boyraz, S., and Ocak, G. (2017) [18] | Examining the effects of FC on academic success and retention of knowledge as well as learners’ opinions on this approach. | Mixed (Quasi-experimental) | 42 | The FC approach had a positive effect on learning compared to the traditional approach. |
| Amiryousefi, M. (2019) [19] | Investigating the effects of flipped learning on EFL learners’ L2 speaking, listening, and out-of-class participation and engagement with course materials and activities. | Mixed Method | 67 | Flipped learning can help EFL learners improve their L2 speaking and listening. |
| Köroğlu, Z.Ç., and Çakır. A (2017) | The effects of flipped instruction on preservice English language teachers’ speaking skills development. | Quantitative data | 48 | The experimental group outperformed the control group. In addition, the FC positively affected the learners’ fluency, pronunciation, grammar, and coherence skills. |
| Santikarn, B., and Wichadee, S. (2017) [20] | Investigating the effects of the flipped classroom on learners’ learning performance and perceptions. | Quantitative | 40 | After implementing the flipped classroom, the learners’ English scores were higher, they were satisfied with the approach, and they also became autonomous learners. |
| Karimi, M., and Hamzavi, R. (2017) [21] | Investigating flipped model instruction‘s effect on EFL learners’ reading comprehension ability. | Mixed Method | 60 | The FC model of instruction positively affected the learners’ reading comprehension skills. In addition, the learners also developed a positive attitude toward this approach. |
| Kurt, G. (2017) [22] | Examining the effectiveness of the flipped classroom compared to a traditionally taught class. | Mixed (Quasi-experimental) | 62 pre-service teachers (PTs) | The FC had better learning outcomes and a higher self-efficacy than the control group. The PTs also had a positive attitude toward this approach. |
| Zainuddin, Z., and Perera, C.J. (2019) [23] | Examining the differences in competence, autonomy, and relatedness for EFL students in flipped and nonflipped classrooms. | Mixed Method | 61 | The learners in the flipped classroom fostered autonomous learning and peer interaction. They could control their learning outcomes, were better with online activities, and their intrinsic motivations increased. |
| Zarrinabadi, N., and Ewanbrahimi, A. (2019) [24] | Investigating the effect of the flipped classroom on peer collaborative dialogues. | Mixed Method | 40 | Implementation of the flipped classroom improved peer collaborative dialogue among learners. |
| Soltanpour, F., and Valizadeh, M. (2018) [4] | Investigating the effect of flipped instruction on EFL learners‘quality of argumentative essays. | Quantitative | 55 | FC has a positive effect on learners’ writing quality. |
| Vivian Wu, W.C., Yang, J.C., Hsieh, J.S.C., and Yamamoto, T. (2019) [7] | Examining the effects of the online flipped writing instruction on EFL writing proficiency and demotivation factors in EFL writing. | Mixed Method | 48 | Learners had a positive attitude toward this approach, allowing cross-cultural observation to occur. |
| Zou, D., and Xie, H. (2019) [25] | Examining how flipped classroom promotes active group writing and effective learning from peers. | Mixed Method | 66 | The results of the experimental group were higher than the control group. |
| Qader, R., and Arslan, F. (2019) [26] | Examining the effect of flipped classroom instruction (FCI) on Iraqi EFL learners’ writing skills. | Mixed Method | 66 | The students in the experimental group had higher scores on writing tests than the control groups. In addition, most of the learners had a positive attitude toward this approach. |
| Mohammadi, J., Barati, H., and Youhanaee, M. (2019) [6] | Investigating the effects of the flipped classroom on EFL learners’ willingness to communicate and achievements. | Quantitative (Pre-experimental design) | 95 | The results showed that the experimental group outperformed the control group. There was also a significant difference in learners’ willingness to communicate between the two groups. |
| Abdullah, M.Y., Hussin, S., and Ismail, K. (2019) [27] | Examining the effect of implementing the flipped classroom model (FCM) on the motivation level of Omani EFL learners to speak English. | Mixed Methods (Quasi-experimental) | 27 | Findings showed that implementing the flipped classroom approach helped develop a creative, engaging, and motivating climate in the EFL speaking class. FC also increased learners’ motivation in speaking. |
| Mubarok, A., and Cahyono, B., and Astuti, U. (2019) [3] | Investigating the effect of the flipped classroom model on Indonesian EFL students’ writing achievement across cognitive styles. | Quantitative (factorial quasi-experimental) | 58 | The results showed that the experimental group had a higher score than the control group. |
| Yang, C.C.R., and Chen, Y. (2019) [28] | Investigating the effectiveness of using the FCM in teaching English vowels and perceptions of the learners and the teachers toward the flipped classroom. | Mixed Methods (Quasi-experimental) | 189 | The learners in the flipped classroom had shown a gain in knowledge of the lesson topic taught. In addition, the findings also showed that there was not a significant difference between the two groups’ posttests. |
| Tsai, Y.R. (2019) [29] | Examining the effects of the flipped classroom model on EFL learner autonomy in a content-based instructional context. | Quantitative | 124 | The flipped classroom positively affected learner autonomy, learner behavior, and learner confidence. In addition, learner autonomy was improved in terms of interaction with materials, behavior, and self-management strategy of learning and the use of social resources. |
| Yeşilçınar, S. (2019) [30] | Examining the effects of flipped classroom on speaking skills. | Mixed Method | 22 | FC enhanced speaking skills, and it also increased learners’ motivation. |
| Haghighi, H., Jafarigohar, M., Khoshsima, H., and Vahdany, F. (2019) [31] | Investigates the impact of a flipped classroom on enhancing EFL learners’ pragmatic competence. | Quantitative data | 60 | The FC had a positive impact on the learners’ pragmatic competence and the learners enjoyed learning English |
| Author, Year | Purpose | Study Design | Sample Target Population | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altas, E.A., and Mede, E. (2020) [32] | Investigating the impact of the flipped classroom on preservice English teachers’ advanced writing achievements. | Mixed Method | 55 | FC approach had a positive impact on writing skills; however, self-regulated learning showed no difference. |
| Ping, R., Verezub, E., Badiozaman, I., and Wang, S.C. (2020) [33] | Investigating English as a Foreign Language (EFL) low proficiency students’ reflections and experience of learning in a structured flipped writing program. | Qualitative | 18 | The learners had a positive attitude toward the approach. It was also found that the flipped approach supported the learners positively. |
| Fathi, J., and Rahimi, M. (2020) [34] | Investigating the impact of the flipped classroom on EFL students’ writing performance, writing accuracy, complexity, and fluency. | Mixed (Quasi-experimental) | 51 | The flipped classroom outperformed the nonflipped classroom on EFL students’ writing performance and fluency. |
| Soltanpour, F., and Valizadeh, M. (2020) [35] | Exploring the effect of semiflipped instruction on grammatical competence and writing skills. | Quantitative (Experimental study) | 53 | The flipped classroom outperformed the nonflipped classroom in grammatical competence and writing skills. |
| Arifani, Y., Khoirul Anwar, S.A., and Budianto, L. (2020) [36] | Measuring the effect of the individual and collaborative WhatsApp approach using a flipped instruction model on EFL learners’ cohesion. | Mixed (quasi-experimental study) | 50 | Teaching writing using a flipped approach instruction model through the WhatsApp group reveals itself to be more effective than the individual one. |
| Alghasab, M.B. (2020) [37] | Investigating the pedagogical benefits for the development of writing skills of EFL learners. | Qualitative | 30 | Results revealed that the flipped classroom positively affected learners’ writing skills. Next, the learners also had a positive attitude towards this approach. |
| Hosseini, H.M., Ejtehadi, A., and Hosseini, M.M. (2020) [38] | Examining the effect of this flipped learning approach on raising Iranian EFL learners’ self-regulation. | Mixed Method | 26 | Learners taught with the flipped approach were more aware of the learning process and had fun, which allowed them to develop self-regulated learning. |
| Namaziandost, E., and Çakmak, F. (2020) [39] | Investigating the flipped classroom’s difference on students’ self-efficacy and gender. | Quantitative | 58 | The flipped classroom approach increased learners’ self-efficacy. In addition, when gender was considered, it was found that the female learners’ self-confidence increased compared to the males. |
| Etemadfar, P., Soozandehfar, S.M.A, and Namaziandost, E. (2020) [40] | Investigating the effects of flipped classrooms on improving Iranian EFL learners’ listening comprehension. | Mixed Method | 40 | Using the flipped classroom positively affected EFL learners’ listening comprehension and critical thinking skills. |
| Djamàa, S. (2020) [41] | Investigating the effect of flipped instruction on students’ exam performances. | Quantitative | 384 | The learners in the flipped classroom received higher exam scores than the nonflipped students. |
| Al-Naabi, I.S. (2020) [42] | Investigating the impact of flipped learning on Omani EFL learners’ grammar and examining students’ perceptions of the flipped classroom. | Mixed (Quasi-experimental) | 28 | Implementing the flipped classroom had a positive effect on learners’ grammar knowledge. In addition, the learners also developed a positive attitude toward this approach. |
| Turan, Z., and Akdag-Cimen, B. (2020) [43] | Examining the trends and main findings of the studies concerning the flipped classroom method in the field of English Language Teaching (ELT). | Literature review | The findings revealed that the flipped classroom had benefits on EFL learners. Speaking and writing abilities were the most commonly studied language skills. | |
| Abdullah, M.Y., Hussin, S., and Ismail, K. (2019) [27] | Investigating the effectiveness of the FCM on EFL learners’ anxiety in English speaking performance. | Mixed Methods | 27 | The findings showed that speaking anxiety levels of learners decreased. |
| Öztürk, M., and Çakıroğlu, Ü. (2021) [44] | Examining the development of students’ language skills in a flipped EFL course designed with self-regulated learning strategies. | Mixed (Quasi-experimental) | 49 | Self-regulated learning had a positive effect on EFL development in a flipped classroom model. |
| Samiei, F., and Ebadi, S. (2021) [45] | Investigating the effects of the WebQuest-based flipped classroom on the EFL learners’ inferential reading comprehension skills. | Mixed Method | 40 | Using a WebQuest-based flipped classroom had a positive effect on learners’ inferential reading comprehension skills. |
| Fernández-Carballo, V. (2021) [46] | Investigating EFL learners’ perspectives towards the flipped classroom approach. | Mixed Method | 40 | The learners preferred the flipped classroom over the traditional one. |
| Afzali, Z., and Izadpanah, S. (2021) [47] | Examining the effect of the flipped classroom model on learners’ engagement and motivation in learning English grammar. | Mixed (Quasi-experimental) | 360 | Learners in the experimental group showed an increase in their performance on grammar tests. They also developed a positive attitude toward grammar and were more motivated. |
| Khoiriyah (2021) [48] | Investigating the effect of the flipped classroom on EFL learners’ listening skills. It also explored the learners perceptions toward the flipped classroom approach. | Mixed Method | 51 | The results showed that implementing the flipped classroom enhanced learners’ listening skills. In addition, learners had a positive attitude towards the approach. |
| Ghufron, M.A., and Nurdianingsih, F. (2021) | Examining the strengths, weaknesses, and effectiveness of the flipped classroom with CALL in EFL writing class. | Mixed Method | 150 learners and 14 teachers | The results showed that implementing the flipped classroom with CALL has many advantages, and the results also revealed that it had a positive effect on learners’ writing skills. |
| Bataineh, R.F., and Al-Sakal, R.M.I. (2021) | Investigating the effects of the flipped classroom on reading comprehension skills. | Quantitative Method | 67 | The results revealed that the learners taught in the flipped classroom outperformed the learners taught in the traditional classroom. |
| Ramadhanty, S., and Puspitaloka, N. (2020) [10] | Focusing on the challenges of implementing ERT-based instructions to promote students’ engagement during instructional practices. | Mixed (Qualitative and descriptive) | 9 students | The learners had a positive attitude toward this approach; however, students faced some challenges. |
| Harida, E.S., Jufrizal; Syarif, H.; Ratmanida; (2020) [12] | Investigating the students’ perception of online learning, including flipped classroom learning. | Quantitative (Descriptive study) | 32 | Students showed a positive perspective on flipped learning. |
| Çil, O. (2021) [10] | Investigating the perception of preservice elementary school teachers on the flipped classroom approach. | Qualitative study | 53 | The results showed that the flipped classroom approach was efficient during distance education. |
| Sumardi, S., and Nugrahani, D. (2021) [14] | Investigating the use of flipped classroom in higher education. | Case study (qualitative) | 17 pre-service language teachers | ERT has successfully replaced face-to-face education; however, there were also some challenges: low achieving students had problems dealing with the situation by themselves. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Köksal, M.; Han, T. A Trend Analysis of Research on the Flipped Classroom in L2 Learning before and after COVID-19. Proceedings 2022, 80, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022080003
Köksal M, Han T. A Trend Analysis of Research on the Flipped Classroom in L2 Learning before and after COVID-19. Proceedings. 2022; 80(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022080003
Chicago/Turabian StyleKöksal, Merve, and Turgay Han. 2022. "A Trend Analysis of Research on the Flipped Classroom in L2 Learning before and after COVID-19" Proceedings 80, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022080003
APA StyleKöksal, M., & Han, T. (2022). A Trend Analysis of Research on the Flipped Classroom in L2 Learning before and after COVID-19. Proceedings, 80(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022080003







