Anxiolytic-Like Effects of Lupinus angustifolious Protein Hydrolysates in Alzheimer Model Mice †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. LPHs Preparation
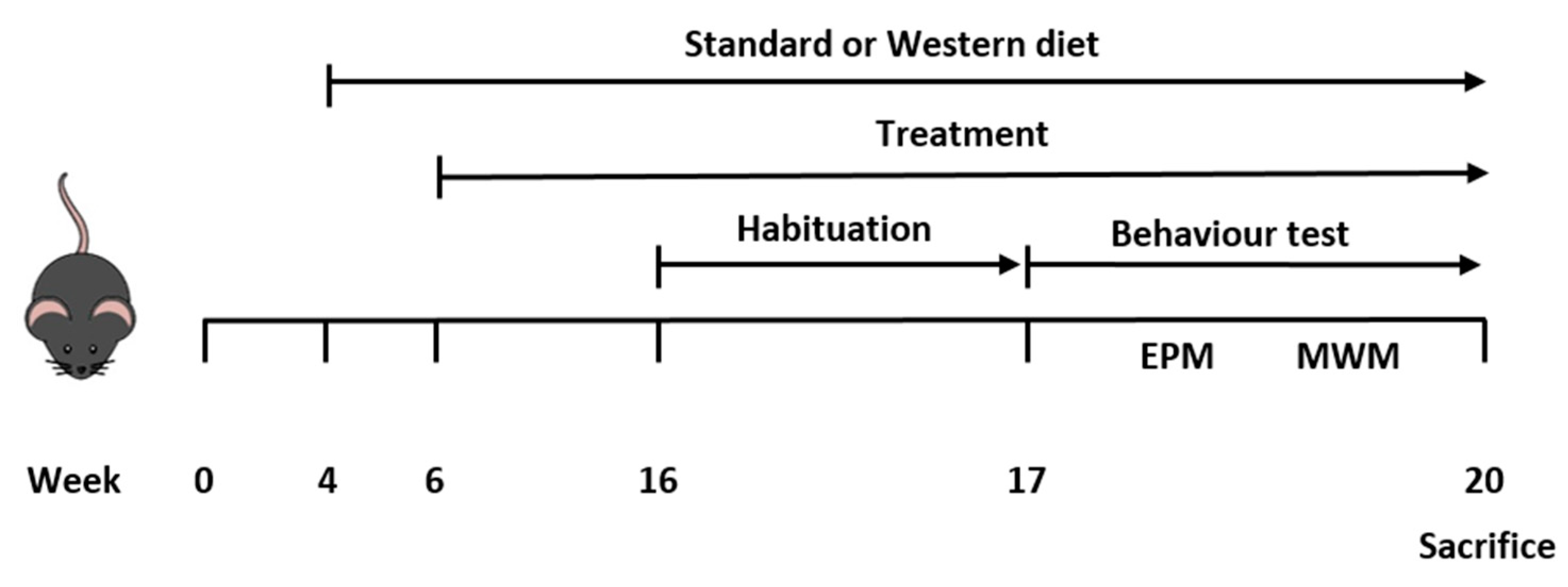
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Behavioral Test
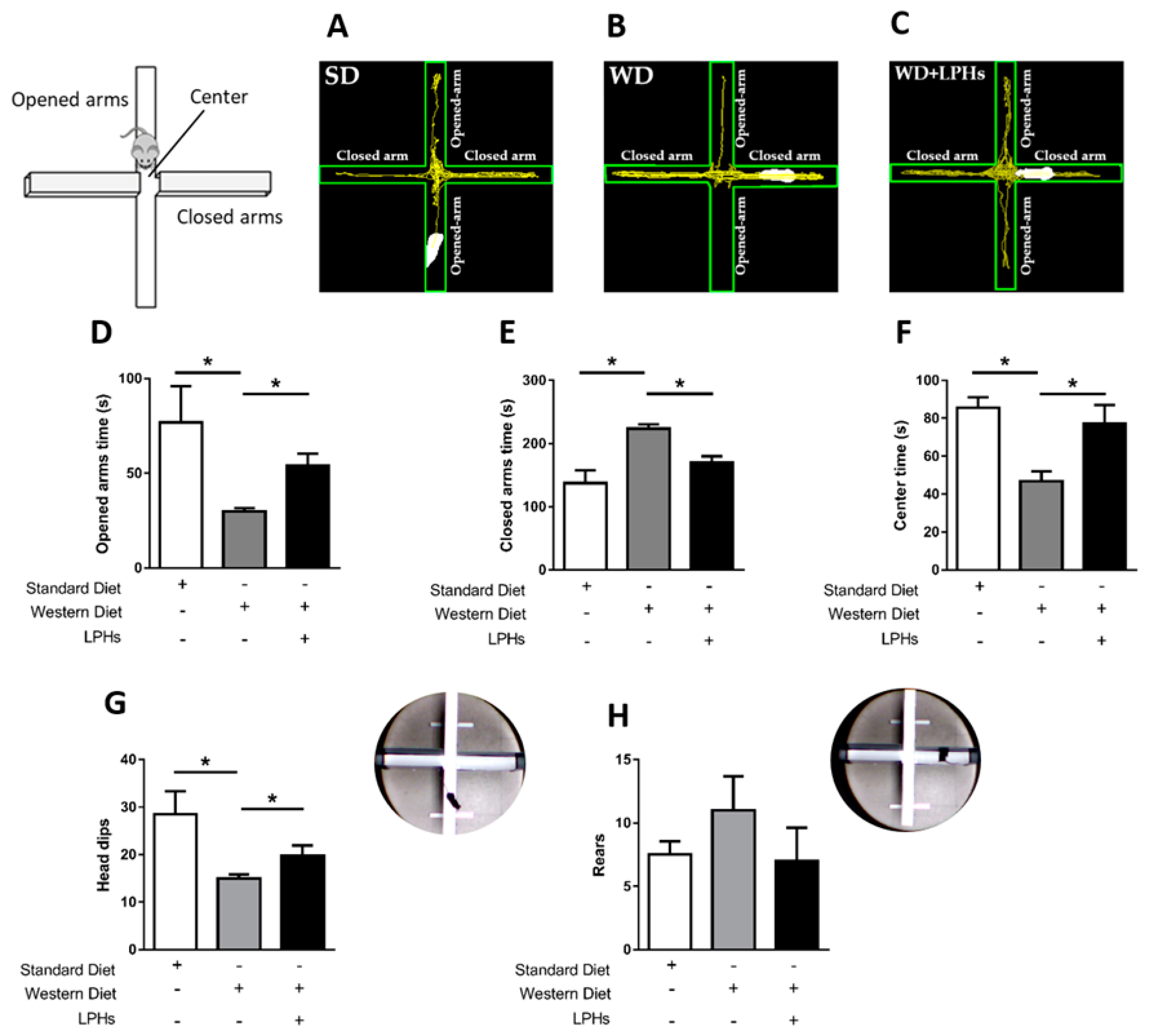
2.3.1. Elevated Plus Maze
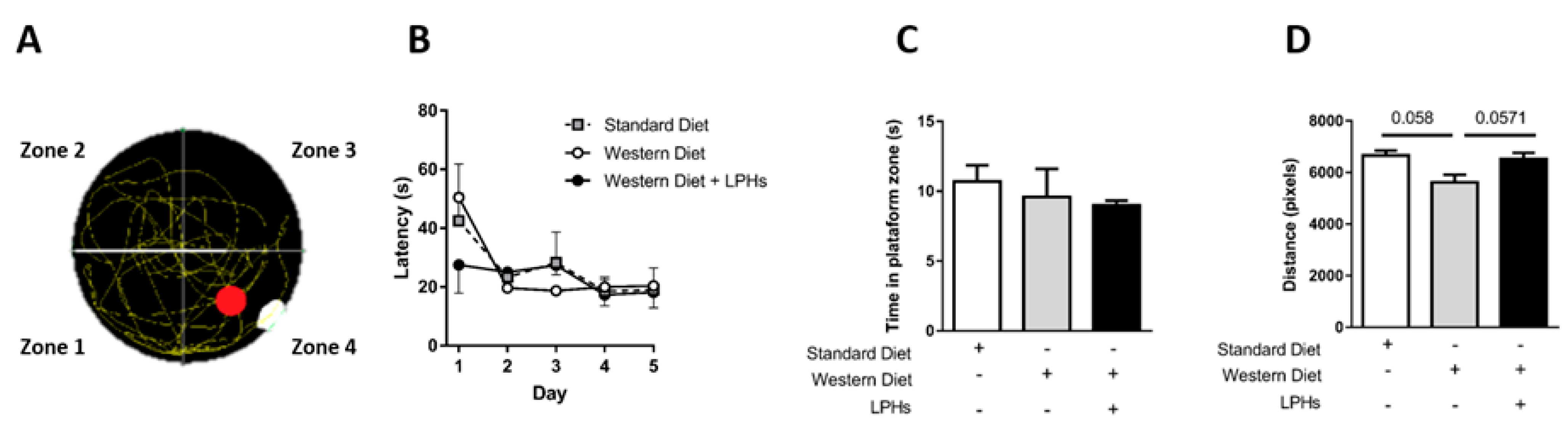
2.3.2. Morris Water Maze
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. LPHs Treatment Does Not Change Body Weight
3.2. LPHs Exert an Anxiolytic-Like Effect
3.3. LPHs Do Not Alter Spatial Memory
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer‘s Association. Alzheimer‘s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 2010, 6, 158–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, P.B.; Mielke, M.M.; Appleby, B.; Oh, E.; Leoutsakos, J.M.; Lyketsos, C.G. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in MCI subtypes: The importance of executive dysfunction. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2011, 26, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.V.F.; Loures, C.d.M.G.; Alves, L.C.V.; de Souza, L.C.; Borges, K.B.G.; das Graças Carvalho, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Risk factors and potentially protective measures. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, W. How western diet and lifestyle drive the pandemic of obesity and civilization diseases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Chu, C.; Shi, R.; Cui, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Hui, Y.; Pan, J.; Qian, R. ApoE-Dependent Protective Effects of Sesamol on High-Fat Diet-Induced Behavioral Disorders: Regulation of the Microbiome-Gut–Brain Axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6190–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohinata, K.; Agui, S.; Yoshikawa, M. Soymorphins, novel μ opioid peptides derived from soy β-conglycinin β-subunit, have anxiolytic activities. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 2618–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; del Carmen Millán-Linares, M.; del Mar Yust, M.; Pedroche, J.; Millán, F.; Lardone, P.J.; Carrera-Sánchez, C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Carrillo-Vico, A. Lupine protein hydrolysates decrease the inflammatory response and improve the oxidative status in human peripheral lymphocytes. Food Res. Int. 2019, 126, 108585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, A.; Kaneko, K.; Mizushige, T.; Lazarus, M.; Urade, Y.; Ohinata, K. Characterization of ovolin, an orally active tryptic peptide released from ovalbumin with anxiolytic-like activity. J. Neurochem. 2012, 122, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, C.I.; Jansen, D.; Mutsaers, M.P.; Dederen, P.J.; Geenen, B.; Mulder, M.T.; Kiliaan, A.J. The effect of a high-fat diet on brain plasticity, inflammation and cognition in female ApoE4-knockin and ApoE-knockout mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puder, J.; Munsch, S. Psychological correlates of childhood obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, S37–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutheil, S.; Ota, K.T.; Wohleb, E.S.; Rasmussen, K.; Duman, R.S. High-fat diet induced anxiety and anhedonia: Impact on brain homeostasis and inflammation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1874–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liang, R.; Li, D.; Jiang, C.; Lin, S. Evaluation of sea cucumber peptides-assisted memory activity and acetylation modification in hippocampus of test mice based on scopolamine-induced experimental animal model of memory disorder. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | SD | Ctrl | LPHs |
|---|---|---|---|
| BBW (g) | 20.35 ± 0.41 | 20.98 ± 0.36 | 20.88 ± 0.49 |
| FBW (g) | 26.20 ± 0.87 | 26.50 ± 0.54 | 27.15 ± 0.69 |
| BWG (g) | 5.85 ± 1.18 | 5.53 ± 0.65 | 6.28 ± 1.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos-Sánchez, G.; Ponce-España, E.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; López, J.C.; Álvarez-López, A.I.; Pedroche, J.; Millán-Linares, M.C.; Millán, F.; Lardone, P.J.; Bejarano, I.; et al. Anxiolytic-Like Effects of Lupinus angustifolious Protein Hydrolysates in Alzheimer Model Mice. Proceedings 2021, 70, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07685
Santos-Sánchez G, Ponce-España E, Cruz-Chamorro I, López JC, Álvarez-López AI, Pedroche J, Millán-Linares MC, Millán F, Lardone PJ, Bejarano I, et al. Anxiolytic-Like Effects of Lupinus angustifolious Protein Hydrolysates in Alzheimer Model Mice. Proceedings. 2021; 70(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07685
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos-Sánchez, Guillermo, Eduardo Ponce-España, Ivan Cruz-Chamorro, Juan Carlos López, Ana Isabel Álvarez-López, Justo Pedroche, María Carmen Millán-Linares, Francisco Millán, Patricia Judith Lardone, Ignacio Bejarano, and et al. 2021. "Anxiolytic-Like Effects of Lupinus angustifolious Protein Hydrolysates in Alzheimer Model Mice" Proceedings 70, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07685
APA StyleSantos-Sánchez, G., Ponce-España, E., Cruz-Chamorro, I., López, J. C., Álvarez-López, A. I., Pedroche, J., Millán-Linares, M. C., Millán, F., Lardone, P. J., Bejarano, I., Guerrero, J. M., & Carrillo-Vico, A. (2021). Anxiolytic-Like Effects of Lupinus angustifolious Protein Hydrolysates in Alzheimer Model Mice. Proceedings, 70(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07685










