Optimization of Hydrocolloid Levels in Medium-Chain Triglyceride-Enriched Soymilk by Response Surface Methodology †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preliminary Study for the Development of MCT-Enriched Soymilk
2.3. Experimental Design for the Determination of Optimal Concentrations of Glycerine, Κ-Carrageenan, and Locust Bean Gum (LBG) in MCT-Enriched Soymilk
2.4. Overall Acceptability Evaluation
2.5. Emulsion Stability Determination
2.6. Product Cost Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fitting of Models for the Determination of Optimal Concentrations of Glycerine, Κ-Carrageenan, and Locust Bean Gum (LBG) in MCT-Enriched Soymilk
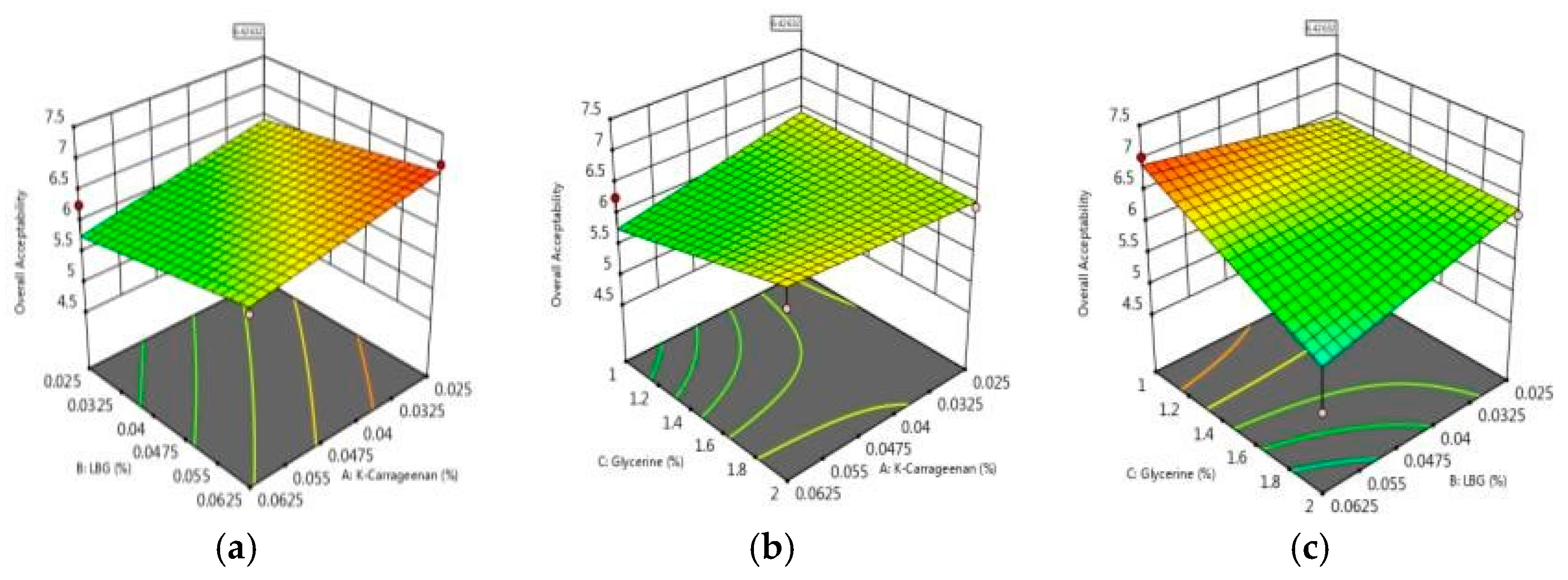
3.1.1. Effect of Hydrocolloid Concentrations on Overall Acceptability
3.1.2. Effect of Hydrocolloid Concentrations on Emulsion Stability
3.1.3. Effect of Hydrocolloid Concentrations on Product Costs
3.2. Validation of the Models with the Optimal Concentrations of Glycerine, Κ-Carrageenan, and Locust Bean Gum (LBG) in MCT-Enriched Soymilk
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lester, J. Nomenclature of Fatty Acids and their Classification; Presentation; Institute of Food Science and Nutrition, University of Sargodha: Sargodha, Pakistan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Iowa State University. Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases. Master’s Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, M.K.; Osborne, B.; Brown, S.H.J.; Small, L.; Mitchell, T.W.; Cooney, G.J.; Turner, N. Contrasting metabolic effects of medium- vs. long-chain fatty acids in skeletal muscle. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 59, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, A.C.; Ingenbleek, Y.; Frey, A. The usefulness of dietary medium-chain triglycerides in body weight control: Fact or fancy? J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 708–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marten, B.; Pfeuffer, M.; Schrezenmeir, J. Medium-chain triglycerides. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayan, V.K. Medium-chain triglycerides—Their composition, preparation, and application. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 45, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.D.; Limketkai, B.N. The use of medium-chain triglycerides in gastrointestinal disorders. Pract. Gastroenterol. 2017, 160, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Abiodun, P. Use of soya-beans for the dietary prevention and management of malnutrition in Nigeria. Acta Paediatr. Scand. Suppl. 2008, 374, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Preparation of Fluid Soymilk. Proceedings of the World Congress on Vegetable Protein Utilization in Human Foods and Animal Feedstuffs; Applewhite, T.H., Ed.; American Oil Chemists’ Society: Champaign, IL, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Cai, W.; Xu, B. Food quality improvement of soymilk made from short-time germinated soybeans. Foods 2013, 2, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muredzi, P. Soybean, Nature, Processing, and Utilisation; Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2013; p. 229. [Google Scholar]
- Fabe, J.; Goldstein, R.; Blondheim, O.; Stankiewicz, H.; Darwashi, A.; Bar-Maor, J.A.; Gorenstein, A.; Eidelman, A.I.; Freier, S. Absorption of MCT in infant stomach. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1968, 7, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkins, R.W.; Sarett, H.P. Medium-chain triglycerides. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1968, 203, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids as emulsifiers and emulsion stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonen, H.; Bas, H. Mono-and diglycerides. In Emulsifiers in Food Technology; Whitehurst, R.J., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkonen, K.S.; Tenkanen, M.; Cooke, P.; Xu, C.; Rita, H.; Willfor, S.; Holmbom, B.; Hicks, K.B.; Yadav, M.P. Mannans as stabilizers in oil-in-water beverage emulsions. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids acting as emulsifying agents–how do they do it? Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 78, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; McClements, D.J. Progress in natural emulsifiers for utilization in food emulsions. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, R. Special formula preparations that can be prepared in the home. Dis. Mon. 2006, 17, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J. Critical reviews of techniques and methodologies for characterization of emulsion stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 611–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbion. Available online: https://www.corbion.com/food/emulsifiers (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/tempref/codex/Meetings/CCNFSDU/ccnfsdu36/CRDS/CRD_33.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Spagnuolo, P.A.; Dagleish, D.G.; Goff, H.D.; Morris, E.R. Kappa-carrageenan interactions in systems containing casein micelles and polysaccharide stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.N.D.; O’Connor, C.; Eyres, L. Application of emulsifiers/stabilizers in dairy products of high rheology. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 123–126, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, N.; Nussinovitch, A. Rheological characterization of k-carrageenan soy milk gels. Food Hydrocoll. 1997, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, C.; Dalgleish, D.G.; Goff, H.D. Effect of k-carrageenan addition to dairy emulsions containing sodium caseinate and locust bean gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 19, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D. Locust bean gum: processing properties and food applications—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 66, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, M.M.; Martinez-Navarrete, N.; Chiralt, A. Rheological characterization of experimental dairy cream formulated with locust bean gum (LBG) and l-carrageenan combinations. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 15, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Won, J.W.; Park, K.M.; Chang, P.S. A new method for determining the emulsion stability index by backscattering light detection. J. Food Process Eng. 2014, 37, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Choi, K.K. Reliability-based design optimization using response surface method with prediction interval estimation. J. Mech. Des. 2008, 130, 12401-1–12401-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Response | Optimal | Confidence Interval | Prediction Interval | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted | Actual | Low | High | Low | High | |
| Overall Acceptability | 6.39 | 7.35 | 5.17 | 7.68 | 4.75 | 8.10 |
| Emulsion Stability (mL) | 9.80 | 9.90 | 6.58 | 13.06 | 5.54 | 14.10 |
| Product Cost (Php) | 292.00 | 292.00 | 292.00 | 292.00 | 292.00 | 292.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villones, I.T.Y.; Dumelod, B.D. Optimization of Hydrocolloid Levels in Medium-Chain Triglyceride-Enriched Soymilk by Response Surface Methodology. Proceedings 2021, 70, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07815
Villones ITY, Dumelod BD. Optimization of Hydrocolloid Levels in Medium-Chain Triglyceride-Enriched Soymilk by Response Surface Methodology. Proceedings. 2021; 70(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07815
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillones, Irene Tonette Y., and Benelyn D. Dumelod. 2021. "Optimization of Hydrocolloid Levels in Medium-Chain Triglyceride-Enriched Soymilk by Response Surface Methodology" Proceedings 70, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07815
APA StyleVillones, I. T. Y., & Dumelod, B. D. (2021). Optimization of Hydrocolloid Levels in Medium-Chain Triglyceride-Enriched Soymilk by Response Surface Methodology. Proceedings, 70(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07815





