Abstract
Lower-limb prostheses have an important function to partially recover the leg movement after amputation. In order to improve the mechanical joint behavior towards a healthy human knee, compliant elements have been introduced to the active prostheses, comprised of the well-known Series Elastic Actuators (SEAs). SEAs are used in lower-limb assistive devices due to their ability to tolerate impacts and passive store mechanical energy during ground-walking. Based on the healthy human knee in the stance phase of walking, this paper brings the design, prototyping, and analysis of a customized planar torsional spring. To enhance the compliance of a rigid active knee prosthesis, the proposed spring will substitute a torque flange between the transmission and the output of the actuator, and this carries a series of constraints to the design. The finite element method (FEM) is applied to the development and exploration of the three initially proposed geometries and the material selection along with its heat treatment is based on the maximum stress obtained in the simulations. The proposed geometry, chosen by comparison of the three, is made of austempered AISI 4340 steel and using two springs in parallel and it has a torsional stiffness of 250 N.m/rad with maximum angular displacement of ± 2.5° and 0.153 kg. In future work, we intend to compare the results of the rigid actuator against the SEA one during walking over the ground.
1. Introduction
The loss of the leg severely affects the gait and daily activities of transfemoral amputees. Only in Brazil, according to DATASUS from the health department [1], the total number of hospitalizations due to lower limb amputations, between 1992 and 2019, is 590.426. Transfemoral amputees’ locomotion tends to expend more metabolic energy walking over the ground. Besides that, the continuous overcompensation on their intact lower members to avoid their prostheses to collide and keep the movement, or to stand up or sit down safely, can harm the healthy members in the long term [2,3].
Lower-limb prostheses have an important function to partially recover the leg movement of the transfemoral amputees and guarantee their mobility, independence, and safety. However, passive and semiactive prostheses cannot provide mechanical power to the user and assist him in such daily activities as stair or ramp ascent and sit-to-stand. Therefore, hence active prostheses are capable of providing positive power; their assistance and ability to replicate the joint kinetics and kinematics in the whole activity can reduce the metabolic energy dispended by the user [3]. Those intelligent prostheses give the user greater mobility, acceptance, autonomy, and a sense of possession over them [4,5].
In order to improve the safety, adaptability, and interaction with the environment of mechanical joints, compliant elements have been introduced to lower-limb assistive devices, composing the Series Elastic Actuators (SEAs). SEAs have the ability to tolerate impacts where the external forces are filtered and attenuated by the elastic component [6], and to passively store mechanical energy during ground-walking and other greater dissipative activities, thereby reducing damages and energy consumption of the prosthesis if it is wisely designed [3,7,8,9].
The healthy human knee has a moment-angle relationship approximately linear during the stance phase of the gait, which is called the quasi-stiffness of the stance phase. Based on the average quasi-stiffness of flexion and extension stages at different gait speeds, Shamaei et al. [10] proposes a stature-based model to estimate this variable, which can be a target to a torsional spring trying to replicate the knee behavior at the preferred gait speed.
Compliant elements have been the focus of several research works, where each one of them was designed to achieve specific requirements. A common material selected for the spring is the maraging steel 300 [9,11,12,13] due to its high tensile yield strength and modulus of resilience [13], but other materials are also employed due to cost and availability.
The geometry described in Reference [14], a tangential corrugated structure illustrated in Figure 1a, is used in a knee orthosis for the rehabilitation of neurological patients. The torsional spring is design to resist to a maximum torque of 15 N.m, with a target value to the spring constant of 200 N.m/rad, but the real one had a stiffness of 105 N.m/rad. The selected material was AISI 6150 due to its cost and its ease of finding in the market, and it was manufactured by the Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (WEDM) process. Wang et al. [11] used a radial corrugated structure exhibited in Figure 1b, which shows a larger deformation than straight units do. The spring provides a stiffness of 288.5 N.m/rad and it was capable of supporting 30 N.m of torque with a deflection of ± 0.105 rad but with a safety factor close to 1.0. The material used in the simulation was Maraging Steel 300 and its manufacturing process was not discussed. Tsagarakis et al. [8] proposed a design using six linear compression springs (Figure 1c) and describes the method to achieve the desired stiffness based on commercial linear spring’s properties. Each spring is initially pre-deformed in half of its maximum allowable contraction, which is not extrapolated by means of mechanical stops. The geometry is capable of deflecting ± 0.18 rad and peak torques of 40 N.m, with a mean stiffness of about 150N.m/rad.

Figure 1.
Literature review: (a) Reference [14] and (b) Reference [11] showing an enhancement in zone A, both torsionally flexible component designs; (c) Reference [8], a design based on linear springs.
In this work, we present the design of a lightweight and planar torsional spring for an active knee actuator, whose stiffness is based on the average Brazilian human knee and on the stature-based model proposed by Reference [10]. Three geometries for the planar spring are proposed based on the literature review. The first two designs are analyzed by the Finite Element Method (FEM) and the third one by Tsagarakis’ et al. method [8] to fit their geometric, mechanical and material properties. The selected geometry is made of austempered AISI 4340 steel and use two springs in parallel to reach a torsional stiffness of 250 N.m/rad with maximum angular displacement of ± 2.5°, and weighing just 0.153 kg.
2. Mechanical Design
The planar torsional spring is a torque flange placed between the transmission, a harmonic drive linked to the foot, and the output of an active knee prosthesis, attached to the thigh. This prosthesis was mechanically designed to be lightweight, compact, to keep the moving parts encapsulated, and to compete assist an average subject of 1.71 m height and 71.6 kg [15], in all daily activities. Therefore, the prosthesis assembly (Figure 2a) consists of a high-torque motor, the EC60 Flat 200W (Maxon Motor, Sachseln, Switzerland), coupled to a CSG 17-50-2A-R harmonic drive (Harmonic Drive AG, Limburg an der Lahn, Germany), with just 51:1 ratio to improve the system transparency and backdrivability [16]. With this configuration, it can provide an active continuous torque up to 27 N.m at 64 rpm, peak torques of 80 N.m, and capable of resisting peaks of 90 N.m. The machined parts are made of 7075 T6 aluminum. The knee prosthesis mass as a rigid actuator is 1.53 kg and its dimensions are also shown in Figure 2a. Figure 2b illustrates the radial geometric design limitations to the flange and consequently to the spring due to the other components. Just the highlighted region is available to accommodate the compliance element, while the axial width is restricted to 18 mm.
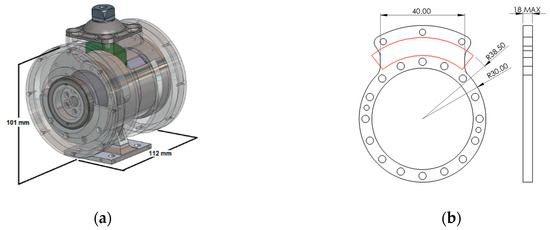
Figure 2.
(a) Knee Prosthesis as a rigid actuator dimensions; (b) Geometric limitations to the torsional spring and space available to accommodate the compliant structure.
Spring Design
According to the structure-based model for optimal gait velocity [10] and the intended user size characteristics, the spring stiffness is supposed to be about 246 N.m/rad with a maximum desired weight of 0.200 kg. Five initial kinds of geometries to give compliance to the flange were tested, but two of them were rapidly discarded because of their high stiffness, stress, and easy self-contact. The three remaining design concepts are shown in Figure 3. Figure 3a shows the first design that is somewhat based on Reference [14]; Figure 3b exhibits the second design adapted from the concept developed in Reference [11]; and Figure 3c illustrates an altered version of Reference [8].

Figure 3.
The three geometries analyzed in this work: (a) First design; (b) Second design; (c) Third design concepts.
Note that all three designs have the inner ring connection between the two compliant elements and the outer ring on the side extremities. That configuration allows the inner ring to have a mechanical end stop that limits both compliance and knee flexion.
Figure 4 shows the parameters evaluated for the first two planar spring designs: the axial width (W1) of the spring and the elongated corrugation mean radius (R1), length (L1), and thickness (t1). Those parameters can be limited by self-contact, maximum stress at the maximum angular displacement, overall stiffness, and manufacturing limitations, by using a CAD program with FEM analysis. The axial width of a unique spring is limited in 10 mm to ensure better manufacturing results. After reaching an intermediate result to those parameters, the thickness of the regions with the highest stress is manually enhanced to achieve better results in stiffness and angular displacement under loading, thereby improving the fatigue life of the spring. In the static analysis (Figure 5), the outer ring is fixed, while the inner ring is rotated by at least 2.5°, depending on the equivalent stress result, but the input rotation stops when the mechanical end stop is reached. The stiffness is then calculated as the ratio between the reaction torque for the rotation and the angular displacement measured in radians. To make sure the mechanical end stop can endure the maximum torque of the prosthesis, we performed an additional static analysis considering the inner ring rotating until the moment reaction reaches 90 N.m.
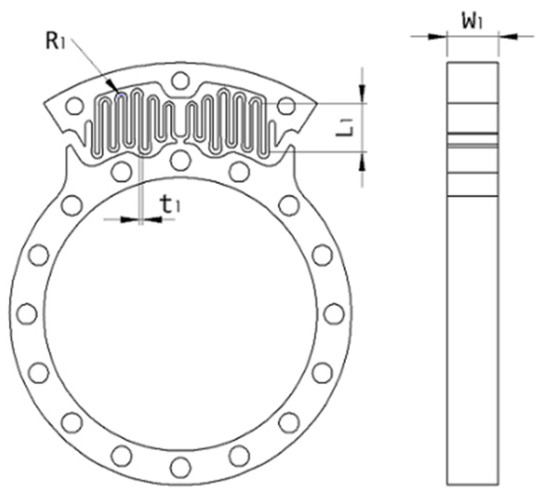
Figure 4.
Parameters of the elongated corrugation structure and spring represented with the first design. The same parameters are valid for the second design.

Figure 5.
Boundary conditions for all geometries analysis but represented with the second design.
The spring material is crucial, as the resulting stiffness is dependent on its elasticity modulus and safety factor. The fatigue life depends on the material yield strength and ultimate tensile strength, heat treatment, and hardness [17,18]. For the carried analysis, the steel alloy AISI 4340 and AISI 6150 were compared since they are commonly commercially available and their mechanical properties, Table 1, after heat treatment of quenching and tempering (Q&T) are available from Reference [19]. For the AISI 4340, both austempered and quenched and tempered fatigue properties are available in Reference [18]. Further, both heat treatments provide identical mechanical properties and mean fatigue limits of 689 MPa for 5 × 106 cycles, which is not sufficient for higher angular displacements. However, for greater stresses, austempering treatment achieves longer fatigue life.

Table 1.
Mechanical properties of the two alloy steels from References [15,16].
The fatigue life was overestimated using the regression for cyclic strain-life for fully reversed tests with elastic strain of an austempered spring [18], a 1000 steps/day rate for ground walking tests of the prosthesis, and the stress at the maximum compliant displacement. In ground walking, each knee is responsible for one step. Observing the knee moment pattern, the torque required to rotate the spring to the mechanical stop, and the number of steps/day it is possible to approximate the number of fatigue cycles per day. However, to do so, the knee moment pattern was simplified considering a sinusoidal waveform with the same frequency and amplitude inside the gait cycles and for all strides.
In the third design (Figure 3c), the desired torsional spring (ks) depends on the angular displacement (θs), the distance from the center of rotation where the springs are placed in the prosthesis (R), the linear springs’ stiffnesses (ka), and their external radius (rs) [8].
An initial overestimation of the linear springs’ stiffnesses was done by ignoring rs and solving the Equation (1) for ka. Once knowing ka, we looked for commercially available springs with similar stiffness that fit in the space requirements, thereby avoiding the need for fatigue and stress analysis on the spring.
The comparison of the three geometries takes into account the difference between their torsional stiffness and the knee quasi-stiffness, the total mass, the maximum angular displacement, safety factor and fatigue life, to choose the final geometry for the planar torsional spring that best fits our design requirements.
3. Results
3.1. First Design
For the initial analysis and to select the spring material, we fixed the axial width (W1), the elongated corrugation mean radius (R1), and thickness (t1) as 10 mm, 0.7 mm, 0.5 mm, respectively, based on previous heuristic analysis. As depicted in Figure 3a, each straight line of the elongated corrugation (L1) changes along the horizontal axis, but it is fixed for the different materials. Considering the safety factor adopted, the AISI 4340 would be able to rotate 2.5°, which is about 0.3° more than the AISI 6150. Moreover, the stiffness of the AISI 4340 spring would be 74 N.m/rad against 72 N.m/rad of the AISI 6150. These results can be explained by the greater tensile yield strength of the AISI 4340, which is more susceptible to heat treatments, but a similar elasticity modulus. In this way, we selected the AISI 4340 steel, since it has better properties for our purposes and easier market disponibility. Furthermore, the austempering heat treatment will be used to provide superior fatigue life than Q&T.
Once the design goal of the springs is to find a geometry with improved displacement and stiffness around 246 N.m/rad [10], with the lowest stress, in the next analysis R1 varies from 0.5 mm to 1.1 mm with steps of 0.2 mm, but W1 and t1 are kept fixed at 10 mm and 0.5 mm, respectively. Here, L1 changes to accommodate the elongated corrugation variations due to R1 in the space available, being as much as possible. The results shown in Figure 6a consider rotation of 2.5° and indicates that the stiffness increases with R1, but the safety factor and maximum angular displacement decreases. Besides that, it was observed that a corrugation with more curves could deflect more due to the better distribution of deflection in each curve. We choose R1 as 0.7 mm to achieve a medium rotation while ensuring the safety factor as 1.8 with an intermediate stiffness. Then, t1 varies from 0.4 to 0.6 mm with a step of 0.05 mm, while W1 is 10 mm, R1 is 0.7 mm from the previous analysis, and L1 does not change. Figure 6b shows that the effect of t1 on stiffness is also directly proportional, and again the safety factor and the allowable angular displacement drops as t1 rises. Besides that, one can see that t1 has a higher sensibility than R1 on those parameters. Due to that, the selected value for t1 is 0.5 mm, which is the intermediary value. Evaluating W1, the spring constant rises as W1 increases, which can be seen as an association of parallel springs.
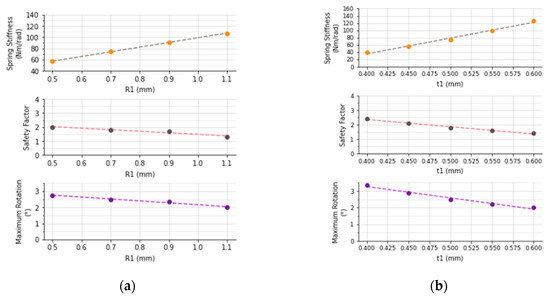
Figure 6.
Parameter results for the first design. Spring stiffness, safety factor and maximum rotation interpolated data for (a) the mean radius R1 and (b) the elongated corrugation thickness t1.
Figure 7 shows that the manual enhancements done in the curves of the corrugation where the stresses were higher before the improvement (Figure 7a) diminished almost 150 MPa in the enhanced spring (Figure 7b). Considering W1 as 10 mm, this allowed an increase in the stiffness from 74 to 106 N.m/rad and in the maximum angular displacement from 2.5 to 3.20° while achieving 649 MPa and the overestimated fatigue life of 2300 days. The final spring weight per width is 0.00927 kg/mm, and to increase the stiffness for near to the knee quasi-stiffness and respect the width restriction, we utilized two springs with W1 = 9 mm in parallel, reaching 191 N.m/rad.
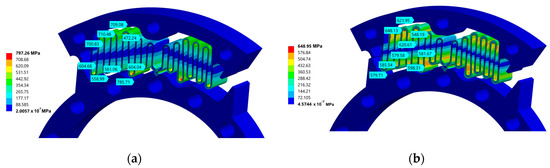
Figure 7.
Equivalent stress results for a rotation of 2.5°. The regions with probe were manually enhanced. (a) First design without the improvements; (b) first design with the proposed improvements.
3.2. Second Design
For the second design, the same parameters are analyzed. We tested different values for R1, ranging from 0.7 to 1.1 mm, with a step of 0.1 mm. Smaller values of R1 were not used because 0.7 and 0.8 mm presented self-contact at approximately 2.45°. Additionally, the maximum R1 used was 1.1 mm as the safety factor was already lower than the desired, at only 1.47. In the results presented in Figure 8a, increased R1 results in an increased spring stiffness and decreased safety factor and maximum rotation, but the results are not monotonic. The value adopted for R1 is 0.9 mm because although it has the second highest safety factor, R1 = 0.7 mm presented self-contact at 2.45°, limiting the rotation and the further enhancements. As depicted in Figure 8b, the t1 variation ranged from 0.4 to 0.6 mm with a step of 0.05 mm, and the same criteria for its maximum value was used. For t1 = 0.45 mm the spring would have the same stiffness of the first design without the improvements, but with more rotation. However, t1 = 0.5 mm results in greater stiffness, although it reduces the spring maximum rotation to 2.40°. Besides, knowing that a thinner t1 requires a more delicate and expensive manufacturing process, t1 as 0.5 mm was selected to ensure greater safety to manufacturing errors and tolerance impacts on stiffness.
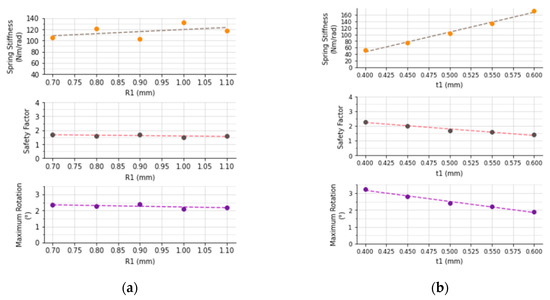
Figure 8.
Parameters results for the second design. Spring stiffness, safety factor and maximum rotation interpolated data for (a) the mean radius R1 and (b) of the elongated corrugation thickness t1.
Figure 9 shows the manual improvements done in the curves of the corrugation. Figure 9a depicts the location where the stresses are higher before the improvement. The corrections reduced only 59 MPa of the maximum stress, as shown in Figure 9b. In addition, considering W1 as 10 mm, the enhancements allowed an increase in the stiffness from 103 to 147 N.m/rad and a maximum angular displacement of 2.5° with 787 MPa. Then, its overestimated fatigue life is 233 days, weighing just 0.00898 kg/mm. The alternative adopted to increase the spring stiffness to be close to the knee quasi-stiffness was to use two springs with W1 = 8.5 mm associated in parallel, reaching a stiffness of 240 N.m/rad.
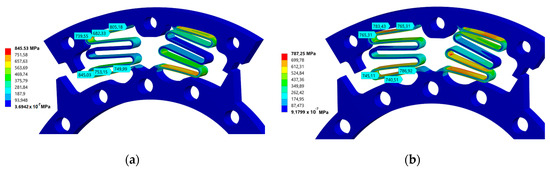
Figure 9.
Equivalent stress results for a rotation of 2.5° and W1 = 10 mm. The regions with probe were manually enhanced. (a) Second design without the improvements; (b) second design with the improvements.
3.3. Third Design
The last design uses the methodology from Reference [8] for one pair of springs (Equation 1) solved for ka and considering R = 34 mm, the desired flexion θs = 10°, and torsional stiffness ks = 246 N.m/rad, so the overvalued stiffness of the linear springs is 113 N/mm. Besides that, for that θs, the spring has to deflect 5.56 mm from its start position, but as the spring is initially pre-deformed half of its capacity, the spring should be able to deflect 11.12 mm. Table 2 presents the data of two commercially available springs that fit in the external diameter and length requirements. The maximum deflection of springs 1 and 2 could make the torsional spring rotate by 6.16° and 3.96°, respectively.

Table 2.
Linear compression spring characteristics.
Once knowing the rs and ka of each spring and by using Equation 1 for the maximum θs, it is possible to calculate the resultant stiffness of the torsional spring. One pair of spring 1 would result in a stiffness of 38.15 N.m/rad, so it would be necessary to use 6.4 springs to achieve the desired ks, while spring 2 provides 60.8 N.m/rad and would require 4.05 springs in parallel. It means that the torsional spring with the second spring could be lighter and less wide than the first one, but with less deflection. In this way, spring 2, which weighs 0.033 kg, would be the chosen one for the third design, but as its stiffness is still significantly lower than the target one, we will not consider this geometry in our analysis.
3.4. Mechanical End Stop
The mechanical end stop has the function of transmitting the torque in a rigid way after the compliance region had passively absorbed an initial amount of torque at heel-strike subphase. As the prosthesis is capable of resisting peaks of torque of 90 N.m during descent stair activities, the result of the static analysis, which considers the contact of the inner and the outer rings at the mechanical end stop, is taken when the reaction torque reaches 90 N.m. Besides, the first geometry consider W1 as 9 mm and the second geometry consider W1 as 8.5 mm, which would be able to fit two springs in parallel, while respecting the width restriction. Additionally, Figure 10a shows that the maximum equivalent stress is 975 MPa for the first design and Figure 10b shows 824 MPa for the second one. As those results consider just one spring, they are acceptable for short-term use, e.g., in testbench experiments. For long-term use, two springs are recommended in parallel, since the torque is divided between them. The third design was not analyzed due to previous discussion.
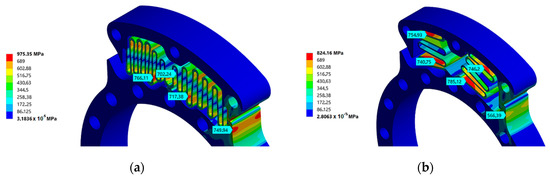
Figure 10.
Equivalent stress for the mechanical end stop analysis. (a) First design results with W1 = 9 mm; (b) second design results with W1 = 8.5 mm.
4. Discussion
As presented in the results section, the proposed springs do not match the healthy knee quasi-stiffness with the maximum W1 of 10 mm, for the first and second design. The third design also cannot meet it with only one torsional spring with one pair of linear compression springs. It means that, to obtain the desired stiffness, and so the user does not feel that difference, two or more springs would have to be associated in parallel. Table 3 brings the used W1, the number of springs in parallel, the maximum rotation, and the total mass of each design to achieve the higher stiffness possible, while respecting the maximum width of 18 mm.

Table 3.
Results comparison and selection of the most suitable design.
The geometry that best fits the stiffness requirement is the second one, and it also accomplishes the mass limit. While the first geometry is the heavier one within the limit, its stiffness and maximum angular displacement are the second best choice. The third geometry has the highest allowable rotation and it is the lighter one; however, its stiffness is approximately half of the required and because of that, it is discarded. Despite that, for other actuators that do not have as many restrictions as this one, it could be a promising design. Between the other two, as the second design concept has a spring constant closer to the knee quasi-stiffness and, then, the user will not feel jerkiness and instabilities in heel strike. Moreover, the second designed spring presents more stability and lower stresses on the mechanical end stop, which can result in more fatigue life. For those reasons, the second design is selected to integrate the knee prosthesis, thereby resulting in a weight of 1.660 kg.
5. Conclusions
This paper presented the design of a planar torsional spring for a specific active knee prosthesis. The spring constant target was defined as 246 N.m/rad, based on the average human knee and the stature-based model proposed by Reference [10]. Two different designs that fitted the geometric limitations were analyzed by the FEM and one by the methodology proposed in Reference [8]. The results comparison of maximum rotation, spring weight, and stiffness already considered two or more springs associated in parallel. The selected geometry is made of austempered AISI 4340 steel and uses two springs, in parallel, to reach a torsional stiffness of 250 N.m/rad with a maximum angular displacement of ± 2.5° and 0.153 kg. The main advantage of the selected geometry towards the others is that the spring constant is close to the knee quasi-stiffness in the stance phase of ground walking and lower stresses at higher torques.
In future works, we intend to test the torsional spring prototype in a testbench to obtain its real stiffness and to check the fatigue life. We also plan to compare the performance of the knee prosthesis integrated with the rigid flange against the SEA one during walking on the ground. If the results are promising, another material with better mechanical properties can be further used to achieve more angular displacement as a compliant element, and thus, absorb more energy in the heel strike.
Author Contributions
G.G.F. and R.M.d.A. conceived ideas to the springs; G.G.F. and J.d.S.d.M. performed the analysis and analyzed the data; P.H.F.U. edited figures and graphs; G.G.F. wrote the paper; P.H.F.U. and R.M.d.A. revised the paper; R.M.d.A. selected the design. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This study was financed by FAPES (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Espírito Santo, TO 207/2018, Project No. 83276262).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CAD | Computer Aided Design |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| SEA | Series Elastic Actuator |
References
- DATASUS. Informações de Saúde. Procedimentos Hospitalares do SUS. Available online: http://tabnet.datasus.gov.br/cgi/deftohtm.exe?sih/cnv/piuf.def (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Andrade, R.M. Joelho Magneto-Reológico Para Próteses Transfemurais: Prototipagem Digital, Fabricação e Identificação Experimental. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rouse, E.J.; Mooney, L.M.; Herr, H.M. Clutchable series-elastic actuator: Implications for prosthetic knee design. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanciullacci, C.; McKinney, Z.; Monaco, V.; Milandri, G.; Davalli, A.; Sacchetti, R.; Paternò, L. Evaluation of Human Factors for the User-centered Design of Powered Robotic Transfemoral Prostheses: A Survey of Transfemoral Amputee Experience and Priorities. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-68433/v1 (accessed on 10 July 2020). [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.M.; Filho, A.B.; Vimieiro, C.B.S.; Pinotti, M. Optimal design and torque control of an active magnetorheological prosthetic knee. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal junior, A.G.; Andrade, R.M.; Filho, A.B. Series Elastic Actuator: Design, Analysis and Comparison. Recent Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 1, 203–234. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/recent-advances-in-robotic-systems/series-elastic-actuator-design-analysis-and-comparison (accessed on 13 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.M.; Filho, A.B.; Vimieiro, C.B.S.; Pinotti, M. Evaluating Energy Consumption of an Active Magnetorheological Knee Prosthesis. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2–6 December 2019; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, N.G.; Laffranchi, M.; Vanderborght, B.; Caldwell, D.G. A compact soft actuator unit for small scale human friendly robots. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. 2009, 4356–4362. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5152496 (accessed on 4 October 2020). [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Accoto, D.; Sergi, F.; Tagliamonte, N.; Guglielmelli, E. A Novel Compact Torsional Spring for Series Elastic Actuators for Assistive Wearable Robots. J. Mech. Des. 2012, 134, 1–10. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234154327_A_Novel_Compact_Torsional_Spring_for_Series_Elastic_Actuators_for_Assistive_Wearable_Robots (accessed on 7 September 2020). [CrossRef]
- Shamaei, K.; Sawicki, G.S.; Dollar, A.M. Estimation of quasi-stiffness of the human knee in the stance phase of walking. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59993. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236085195_Estimation_of_Quasi-Stiffness_of_the_Human_Hip_in_the_Stance_Phase_of_Walking (accessed on 1 July 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y. A flat torsional spring with corrugated flexible units for series elastic actuators. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), Hefei, China, 27–31 August 2017; pp. 138–143. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8273149 (accessed on 27 June 2020). [CrossRef]
- Irhke, C.A.; Parsons, A.H.; Mehling, J.S.; Griffith, B.K. Planar Torsion Spring. United States Patent Application Publication No. US 2010/0145510 A1, 10 June 2010. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20100145510A1/en (accessed on 7 October 2020).
- Doan, T.D. A Novel Torsional Spring Design for Knee Prostheses and Exoskeletons. Bachelor’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, W.M.; Caurin, G.A.P.; Siqueira, A.A.G. Design and control of an active knee orthosis driven by a rotary Series Elastic Actuator. Control Eng. Pract. 2015. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2015.09.008 (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- IBGE. Pesquisa de Orçamentos Familiares: Tabela 2645—Estimativas Populacionais das Medianas de Altura e Peso de Crianças, Adolescentes e Adultos, por Sexo, Situação do Domicílio e Idade—Brasil e Grandes Regiões. 2010. Available online: https://sidra.ibge.gov.br/tabela/2645 (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Andrade, R.M.; Sapienza, S.; Bonato, P. Development of a ‘transparent operation mode’ for a lower-limb exoskeleton designed for children with cerebral palsy. In Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24 June 2019; pp. 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, B. Fatigue Resistance of Steels. In Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys; ASM International: Almere, The Netherland, 1990; Volume 1, pp. 673–688. [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia, J.M.; Hayrynen, K.L. A Comparison of Fatigue Properties of Austempered Versus Quenched and Tempered 4340 Steel. J. Mater. Eng Perform 2012, 21, 1008–1024. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-011-9951-y (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- MATWEB. Material Property Data. Available online: http://www.matweb.com/ (accessed on 6 October 2020).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).