Modeling and Simulation of an Array of Dielectric Elestomeric Actuator Membranes †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
- The membrane is initially flat (a);
- An in-plane prestretch is applied to the flat membrane (b);
- An out-of-plane force is supplied via the biasing springs (c);
- The prestretched and biased DEA is finally actuated (d).
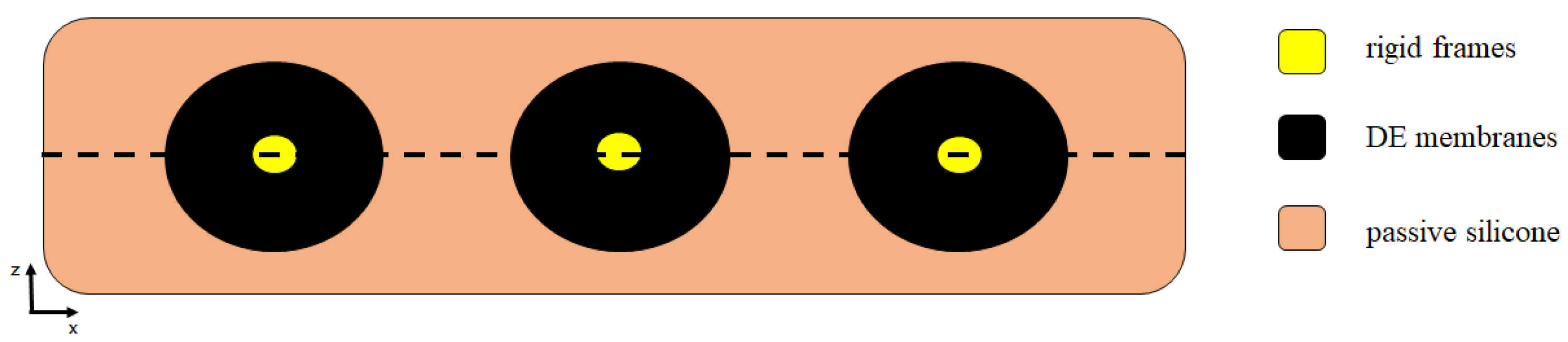
System Modeling
- r1,2,3: DE inner radius of the membrane
- lsi0, i∈ {1, 2, 3}: initial length of the silicone membrane i;
- lDEi0, i∈ {1, 2, 3}: external radius of the DE membrane i;
- d: horizontal prestretch carried out during the first phase;
- O: origin of the fixed reference, with the y-axis oriented orthogonally to the ground;
- w: distance between the point for biasing system attachment and the origin O;
- Gi, i ∈ {1, 2, 3}: coordinates of the center of mass of the rigid spacer i, with respect to the origin O;
- θ: angle of rotation of the rigid frame with respect to its center of mass;
- lDEij, i ∈ {1, 2, 3}, j ∈ {1, 2}: equivalent length of the DE membrane, where i indicates the actuator and j the element.
- di0, i ∈ {1, 2, 3}: undeformed length of the biasing system;
- kBi, i ∈ {1, 2, 3}: rigidity constant of the biasing systems;
- kFi, i ∈ {1, 2}: rigidity constant of the central element, positioned between the actuators.
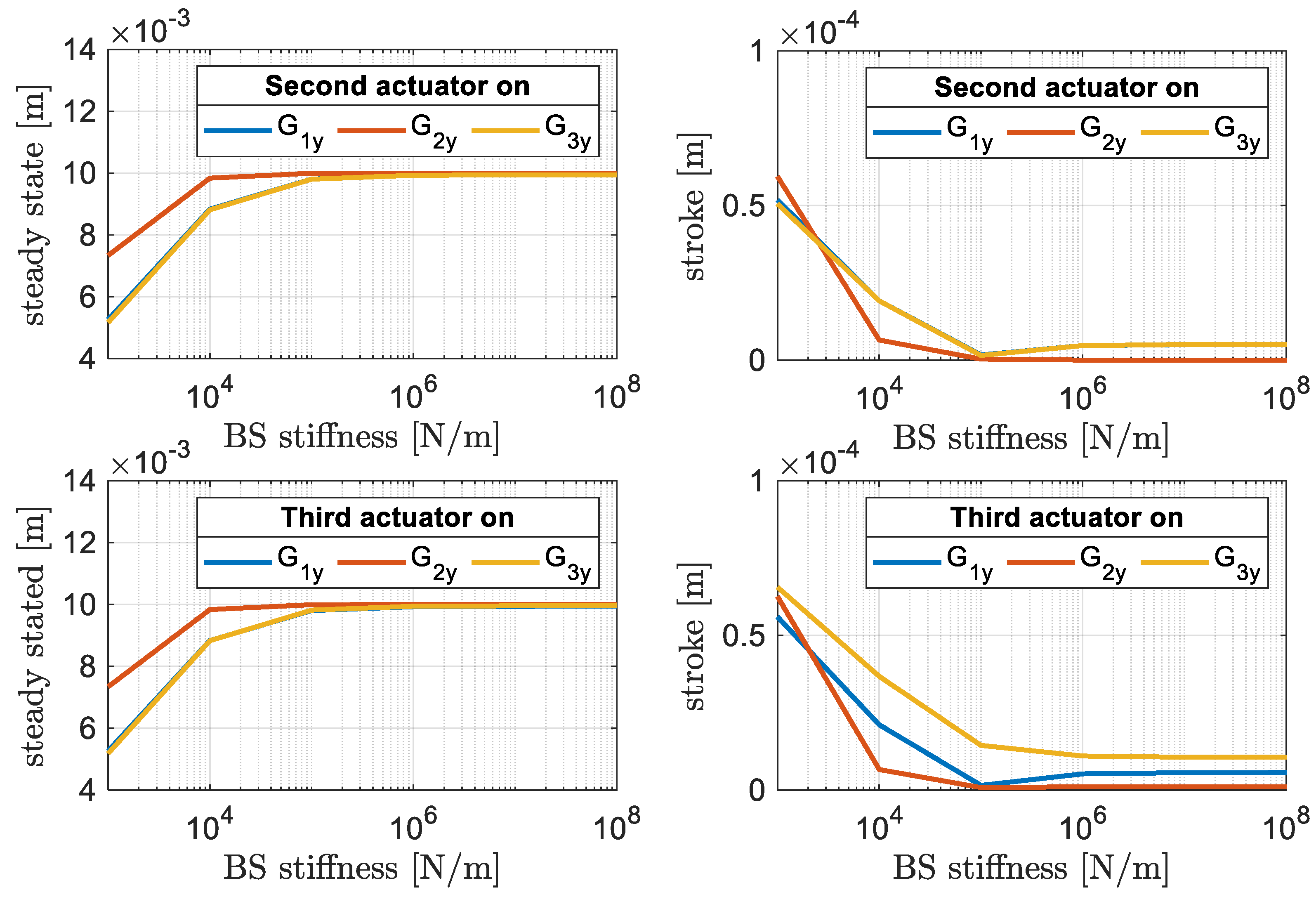
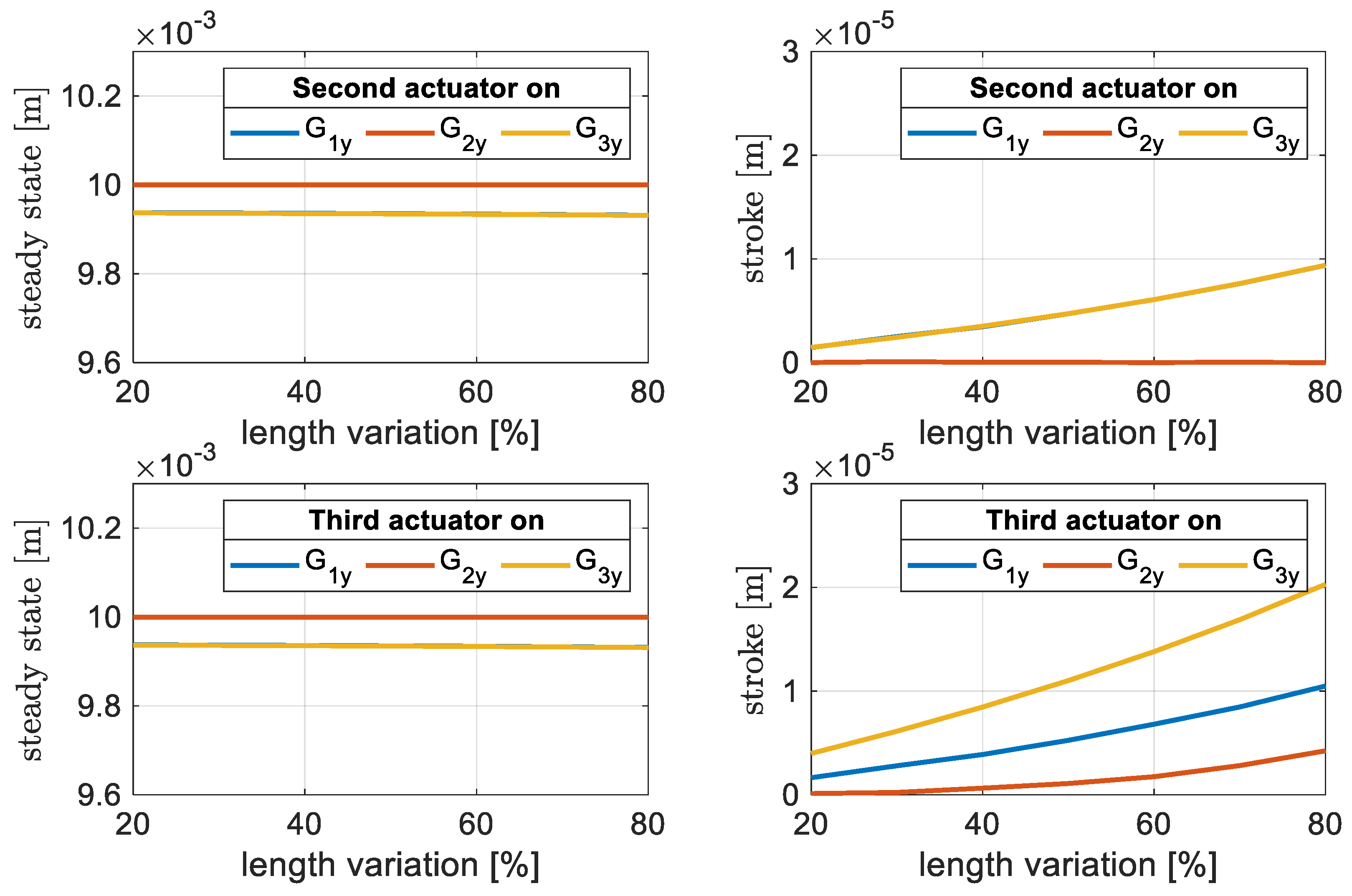
3. Results and Discussion
- d = 0.01 m;
- w = −0.01 m;
- ri, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 0.0025 m;
- lDEi0, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 0.01 m;
- lSi0, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 0.01 m;
- mDEi, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 0.0118 g;
- mSi, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 0.028 g;
- mRFi, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 10 g;
- kDEi, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 19.6 kN/m;
- kSi, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 19.6 kN/m;
- kBi, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 10 MN/m;
- kFi, i ∈ {1, 2} = 0 N/m;
- di0, i ∈ {1, 2, 3} = 0.02 m.
- α = [10−6, …, 106]: ratio between the stiffness of the elastic element placed in the center between two DE membranes (kF) and the silicone stiffness (ks);
- kBi = [103, …, 108]: stiffness of the biasing system;
- µ = [20%, …, 80%]: percentage variation of the DE length (lDEi0) relative to the sum of the DE and silicone lengths (3 lDEi0 + 3 lSi0) (this value will be kept as constant throughout the study).
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DE | Dielectric Elastomer |
| DEA | Dielectric Elastomer Actuators |
References
- Carpi, F.; Rossi, D.D.; Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R.E.; Sommer-Larsen, P. Dielectric Elastomers as Electromechanical Transducers: Fundamentals, Materials, Devices, Models and Applications of an Emerging Electroactive Polymer Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.; Rizzello, G.; Seelecke, S. Development and experimental characterization of a pneumatic valve actuated by a dielectric elastomer membrane. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 085023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giousouf, M.; Kovacs, G. Dielectric elastomer actuators used for pneumatic valve technology. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, F.A.M.; Mah, C.K.; AbuZaiter, A.; Chee, P.S.; Ali, M.S.M. Soft dielectric elastomer actuator micropump. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 263, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loverich, J.J.; Kanno, I.; Kotera, H. Concepts for a new class of all-polymer micropumps. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydt, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Eckerle, J.; Pelrine, R. Sound radiation properties of dielectric elastomer electroactive polymer loudspeakers. In Proceedings of the Smart Structures and Materials 2006: Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD), San Diego, CA, USA, 22 March 2006; Volume 6168, p. 61681M. [Google Scholar]
- Heydt, R.; Pelrine, R.; Joseph, J.; Eckerle, J.; Kornbluh, R. Acoustical performance of an electrostrictive polymer film loudspeaker. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, A.T.; Hinitt, A.D.; Wang, P. Soft segmented inchworm robot with dielectric elastomer muscles. In Proceedings of the Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD), San Diego, CA, USA, 8 March 2014; p. 90562L. [Google Scholar]
- Shintake, J.; Rosset, S.; Schubert, B.; Floreano, D.; Shea, H.R. Versatile Soft Grippers with Intrinsic Electroadhesion Based on Multifunctional Polymer Actuators. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechtl, J.; Kunze, J.; Nalbach, S.; Seelecke, S.; Rizzello, G. Soft robotic module actuated by silicone-based rolled dielectric elastomer actuators: Modeling and simulation. In Proceedings of the Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD), online only, 22 April 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffli, L.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H.R. Mm-size bistable zipping dielectric elastomer actuators for integrated microfluidics. In Proceedings of the Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD), San Diego, CA, USA, 9 April 2013; p. 86872M. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, P.; Toprakci, H.A.K.; Yang, P.; Di Spigna, N.; Franzon, P.; Ghosh, T. A compact dielectric elastomer tubular actuator for refreshable Braille displays. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 179, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Frediani, G.; De Rossi, D. Electroactive elastomeric haptic displays of organ motility and tissue compliance for medical training and surgical force feedback. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 2327–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G. Arm Wrestling Robot Driven by Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. In Proceedings of the First IEEE/RAS-EMBS nternational Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Pisa, Italy, 20–22 February 2006; pp. 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy, B.; Shea, H. Reconfigurable and Latchable Shape-Morphing Dielectric Elastomers Based on Local Stiffness Modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 200159710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Croce, S.; Neu, J.; Hubertus, J.; Seelecke, S.; Schultes, G.; Rizzello, G. Modeling and Simulation of an Array of Dielectric Elestomeric Actuator Membranes. Proceedings 2020, 64, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08489
Croce S, Neu J, Hubertus J, Seelecke S, Schultes G, Rizzello G. Modeling and Simulation of an Array of Dielectric Elestomeric Actuator Membranes. Proceedings. 2020; 64(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08489
Chicago/Turabian StyleCroce, Sipontina, Julian Neu, Jonas Hubertus, Stefan Seelecke, Günter Schultes, and Gianluca Rizzello. 2020. "Modeling and Simulation of an Array of Dielectric Elestomeric Actuator Membranes" Proceedings 64, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08489
APA StyleCroce, S., Neu, J., Hubertus, J., Seelecke, S., Schultes, G., & Rizzello, G. (2020). Modeling and Simulation of an Array of Dielectric Elestomeric Actuator Membranes. Proceedings, 64(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08489






