Abstract
For transition of a supercritical flow into a subcritical flow in an open channel, a hydraulic jump phenomenon is used. Different shaped channels are used as useful tools in the extra energy dissipation of the hydraulic jump. Accurate prediction of relative energy dissipation is important in designing hydraulic structures. The aim of this paper is to assess the capability of a Kernel extreme Learning Machine (KELM) meta-model approach in predicting the energy dissipation in different shaped channels (i.e., rectangular and trapezoidal channels). Different experimental data series were used to develop the models. The obtained results approved the capability of the KELM model in predicting the energy dissipation. Results showed that the rectangular channel led to better outcomes. Based on the results obtained for the rectangular and trapezoidal channels, the combination of Fr1, (y2-y1)/y1, and W/Z parameters performed more successfully. Also, comparison between KELM and the Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) approach showed that KELM is more successful in the predicting process.
1. Introduction
For transition of a supercritical flow into a subcritical flow in an open channel, a hydraulic jump phenomenon is used. Hydraulic jumps can occur downstream of hydraulic structures, such as normal weirs, gates, and ogee spillways. It is considered as rapidly varying flow, and this type of flow regime transformation is associated with severe turbulence and flow energy dissipation [1]. Based on the energy dissipating action of hydraulic jumps, the stilling basin is one of the possible solutions which may be adopted. In order to design an optimal hydraulic structure, different devices such as sills, baffle blocks, end sills, roughness elements, and roller buckets are used in hydraulic structures. However, modeling hydraulic jump characteristics is of great importance since it plays an important role in designing hydraulic structures. Thus far, various studies have been done to explain the complex phenomenon of the hydraulic jump and to estimate its characteristics. Bhutto et al. developed a semi-empirical equation for calculating the sequent depth and relative energy loss ratio in sloping and horizontal rectangular channels [2]. Finnemore et al. stated that the Froude number has significant impact on the characteristics of the hydraulic jump [3]. The impact of wall friction on the sequent depth ratio was studied by Hager and Bremen [4]. Ayanlar investigated the hydraulic jump properties in channels with corrugated beds [5]. Bilgin collected some experiments in a channel with smooth bed in order to investigate the distribution of shear stress for turbulent flow [6]. However, due to the complexity and uncertainty of the hydraulic jump phenomenon, the results of the classical models are not general and under variable conditions do not present the same results. Therefore, it is essential to use other methods that show more accuracy in predicting the energy dissipation in channels with different shapes and rough elements.
The Meta model approaches such as Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), Neuro-Fuzzy models (NF), Genetic Programming (GP), Kernel extreme Learning Machine (KELM), and Support Vector Machine (SVM), have been applied in investigating the hydraulic and hydrologic complex phenomena in recent decades. Prediction of total bedload [7], urban flash flood forecast [8], precipitation forecasting [9], modeling flow resistance in open channels with dune bedform [10], developing stage-discharge curves [11], and predicting of bedload in sewer pipes [12], are some examples of the applications of Meta model approaches.
The aim of the present study is to assess the capability of KELM as an effective kernel-based approach in modeling energy dissipation in channels with different shapes (i.e., rectangular channel with strip and staggered elements and trapezoidal channel with strip elements). Different inputs combinations were considered, and the impact of hydraulic characteristics and channels geometry was assessed. In addition, the capability of the KELM approach was compared with the ANN meta-model approach.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Used Data Sets
In this study, the experimental data of Simsik (2006) and Evcimen (2012) studies were used for prediction goals [13,14]. Simsik used prismatic roughness elements with different arrangements in a rectangular channel to investigate the impact of these elements on hydraulic jump characteristics. Two types of roughness elements with stripe and staggered arrangements were used during experiments. The experiments of Evcimen were done at the hydraulic laboratory of the Middle East Technical University, which were intended for hydraulic jump in trapezoidal channels, and the impact of prismatic roughness on hydraulic jump was assessed. The used experimental data ranges are given in Table 1. To compare the performance of applied models, the total data were divided into two sets: the training and testing sets. Seventy-five-percent of the whole data were used for training the models and the last 25% of data were used for testing the models. The training set trains the scheme on the basis of a minimization criterion and the testing set is used to evaluate the generated model and assess its generalization capability

Table 1.
The experimental data used in the study.
2.2. Kernel Extreme Learning Machine (KELM)
ELM is a Single Layer Feed Forward Neural Network (SLFFNN) preparing method initially introduced by Huang et al. [15]. SLFFNN is a straight framework where information weights linked to hidden neurons and hidden layer biases are haphazardly chosen, while the weights among the hidden nodes are resolved logically (see Figure 1). This strategy likewise has preferred execution and adapts progressively over the bygone era learning methods [15]. In light of the fact that, unlike traditional techniques, which involve numerous variables to set up, demonstrating a complex issue utilizing this technique does not need much human intercession to accomplish ideal parameters. The standard single-layer neural system with N random information (xi, yi) (where , ), M hidden neurons, and the active function f(a) is shown as follow:
where is the weight vector that joins the input layer to the hidden layer, is the weight vector that joins hidden layer to the target layer. ci shows the hidden neuron biases. The general SLFFNN network aim is minimizing the difference between the predicted (Oj) and target (tj) values which can be expressed as below:
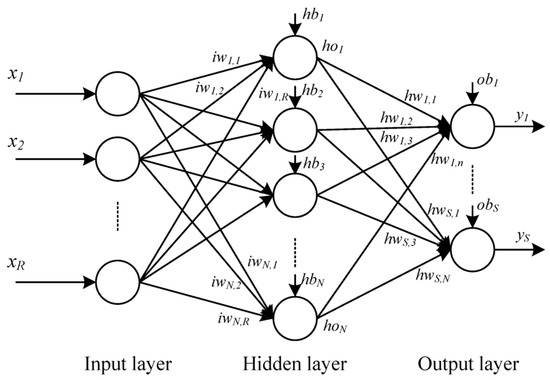
Figure 1.
Single hidden Layer Feedforward Neural network.
The Equation (2) can be summarized as:
where
The matrix T is identified as the target matrix of the hidden layers of the neural network. H is considered as output matrix of neural network. Huang et al. also introduced kernel functions in the design of ELM [16]. Now number of kernel functions is used in the design of ELM such as Linear, radial basis, Normalized polynomial, polynomial kernel functions. Kernel function-based ELM design is named Kernel extreme Learning Machine (KELM). For more detail about KELM, readers and researchers are referred to [16].
2.3. Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is learning systems that have solved a large amount of complex problems related to different areas (classification, clustering, regression, etc.) and is a system loosely modeled on the human brain [17]. The field goes by many names, such as connectionism, parallel distributed processing, neuro-computing, neural intelligent system, machine learning algorithms and Artificial Neural Networks. It is an attempt to simulate within specialized hardware or sophisticated software. This simulation is achieved through multiple layers of simple processing elements called neurons. Each neuron is linked to certain neighbors with varying coefficients of connectivity that represent the strengths of these connections. Learning is accomplished by adjusting these strengths to cause the overall network to output appropriate results. The parameters to be found by training are the weight vectors connecting the different nodes of the input, hidden, and output layers of the network by the so-called error-back propagation method (a specialized version of the gradient-based optimization algorithm). During training, the values of the parameters (weights) are varied so that the ANN output becomes similar to the measured output on a known data set. There are two Artificial Neural Network topologies—Feed Forward and Feedback. In the first type, the information flow is unidirectional. A unit sends information to other unit from which it does not receive any information. There are no feedback loops. They are used in pattern generation/recognition/classification. They have fixed inputs and outputs. In the second type, feedback loops are allowed. They are used in content addressable memories. In this study, feed forward neural networks (FFNNs) are used. FFNNs with one sigmoidal hidden layer and a linear output layer have been proven to be capable of approximating any function with any desired accuracy if the associated conditions are satisfied. In this study, a two-layer feed forward neural network (one hidden layer and one output layer) is used for predicting monthly flows. The number of neurons in the hidden layer, along with the weights and biases, are obtained, based on the errors in the predicted values. Sigmoid and linear activation functions are used for the hidden layer and output layer, respectively.
2.4. Performance Criteria
Three statistical criteria named Determination Coefficient (DC), Correlation Coefficient (R), and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) were used for assessing the proposed model’s efficiency. The used criteria equations are as follows:
where , , , , N are the observed values, predicted values, mean observed values, mean predicted values and number of data samples, respectively.
3. Simulation and Models Development
3.1. Input Variables
Appropriate selection of input combination has significant impact on the accuracy of developed models. In Figure 2, the quantities measured for jumps in channels with different shape are shown. Based on [18,19,20], the important variables which affect the energy dissipation are:
where y1 and y2: sequent depth of upstream and downstream, V1: upstream flow velocity, µ: water dynamic viscosity, g: gravity acceleration, Lj: length of jump, ρ: density of water, ΔE (=E1 − E2) in which E1 and E2 are energy per unit weight before and after the jump, Z: rough element height, and W: space between rough elements.
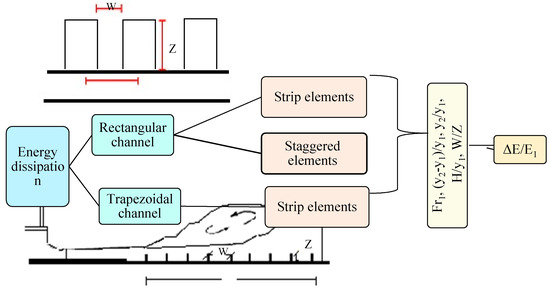
Figure 2.
The schematic view of different types of channels used in this study.
From dimensional analysis and considering y1, g and µ as repeating variables, these parameters of Equation (7) can be expressed as follows:
Equation (8) can be expressed as:
where Fr1 is flow Froude number and Re is flow Reynolds number.
Experimental studies by several researchers (i.e., [21,22]) revealed that hydraulic jump characteristics only depend on Froude number, and the Reynolds number has no effective role in the predicting process. Also, Hager showed that the height of jump can affect the characteristics of the hydraulic jump [1]. Therefore, in this study, based on upstream hydraulic data and geometric data, the models of Table 2 were considered for modeling energy dissipation due to the hydraulic jump in different types of channels with different rough elements. It should be noted that the modeling process was done using developed cods for KELM and ANN approaches in MATLAB software.

Table 2.
Kernel Extreme Learning Machine (KELM)-developed Models.
3.2. KELM Parameters Setting
It should be noted that each artificial intelligence method has its own parameters. To achieve the desired results, the optimized amount of these parameters should be determined. For example, in designing the KELM approach, the selection of the appropriate type of kernel function is needed. There are various kernel functions which can be used based on the nature of the studied phenomenon. In this research, the model M (V) of the rectangular channel with strip elements was predicted using different kernel types. In this regard, the Fr1, (y2-y1)/y1, W/Z parameters were used as inputs for KELM approach and considering different kernel types this model was run. Then, for each kernel the amount of the RMSE was calculated and compared with the others. According to Figure 3a, the RBF kernel function ( in which γ is the kernel parameter) was defined as the best kernel function. Figure 3b shows the RMSE statistic parameter via γ values for comparing the impact of RBF kernel parameter of γ on performance of employed algorithm for testing set of the model M (V) for rectangular channel with strip elements. In this study, optimization of γ was performed by a systematic grid search of the parameter using cross-validation. It could be seen that γ = 5 (the optimum amount) led to the least RMSE value. On the other hand, in ANN modeling the network topology has direct effects on its computational complexity and generalization capability. Therefore, the appropriate structure of ANN should be selected. In this study, various networks were tried for determining the hidden layer node numbers. For this aim, different numbers of neurons (i.e., 2, 3, 5, and 7) in the hidden layer were tested. Also, it was found that the tangent sigmoid and pure linear functions are suitable for the hidden and output node activation functions, respectively. The model training was done using the scheme of back propagation approach.
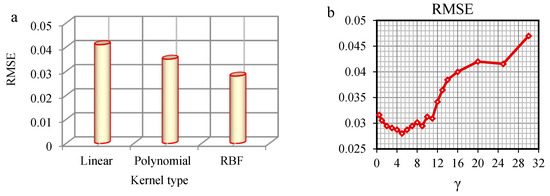
Figure 3.
Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) statistics parameter via (a) KELM kernels function types and (b) γ values to find KELM optimums of testing set for the model M (V).
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Results Obtained for Rectangular Shape Channels
For rectangular shape channel, two states were considered. In the first state the efficiencies of the developed models were investigated in the channel with strip rough elements and in the second state channel with staggered rough elements. In developing models, the flow condition and geometry of the applied rough elements were considered. The developed models were analyzed with KELM model to carry out the energy dissipation ratio prediction in these channels. Table 3 and Figure 4 show the results of the KELM models. Based on the results of the RMSE, R, and DC statistical parameters, it was observed that, between two types of channels, the developed models for the case of the channel with strip elements in modeling the energy dissipation performed more successfully. For both cases, the model M (V) with input parameters of Fr1, (y2-y1)/y1, W/Z led to more accurate outcome than the other models. A comparison between the results of the models showed that, for prediction the relative energy dissipation in rough bed channels, using parameter Z/y1 and W/Z as the input parameters caused an increment in the models’ efficiency and the Z/y1 parameter is more efficient.

Table 3.
Statistical parameters of the KELM models for the rectangular shape channels.
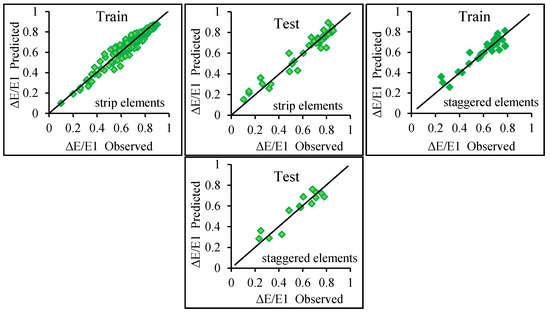
Figure 4.
Comparison of observed and predicted energy dissipation for the rectangular shape channels superior models.
4.2. Results Obtained for Trapezoidal Shape Channel
The obtained results for trapezoidal shape channel are listed in Table 4 and shown in Figure 5. In this case, the model M (V) with input parameters of Fr1, (y2-y1)/y1, W/Z was the superior model. According to the results, it could be seen that adding parameters (y2-y1)/y1, Z/y1, and W/Z as an input parameter caused an increment in the models’ efficiency. However, for this state, the variable W/Z was more effective than variables (y2-y1)/y1 and Z/y1 in improving the model accuracy. This issue shows the impact of the rough elements’ geometry on predicting the relative energy dissipation. From the comparison between the results of Table 3 and Table 4, it could be stated that the model developed for a rectangular channel with rough elements performed more successfully in predicting the energy dissipation than that of a trapezoidal channel with rough elements.

Table 4.
Statistical parameters of the KELM models for the trapezoidal shape channels.
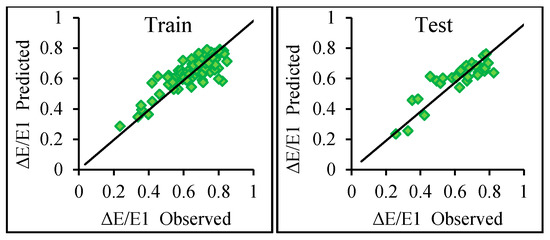
Figure 5.
Comparison of observed and predicted relative energy dissipation for the trapezoidal shape channel superior model.
4.3. Validation of Proposed Best KELM Models Using ANN Method
The experimental data of both applied channels were used to evaluate the performance of the best-KELM model compared with the other data driven model. In this regard, for each channel the superior model was run using ANN method and the results were compared with the KELM. Table 5 shows the results of this comparison. As it can be seen from Table 5, ANN led to the desired accuracy, and the efficiency of this model was good at energy dissipation modeling. However, the KELM model yielded slightly better results in comparison with the ANN method.

Table 5.
Statistical parameters of the KELM and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) methods for the superior models.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the KELM method was used to predict the relative energy dissipation in two rectangular and trapezoidal channels with different rough elements. The KELM was applied for different models based on flow conditions and geometry of channels and rough elements. The obtained results showed that, in predicting the energy dissipation in rectangular and trapezoidal channels, the model M (V) with input parameters of Fr1, (y2-y1)/y1, and W/Z performed more successfully than the other models. It was observed that Z/y1 and W/Z parameters increased the models’ efficiency; therefore, it could be stated that the height and space of applied elements were important factors in the energy dissipation prediction. Between two types of rectangular channels, the developed models for the case of channel with strip elements were more accurate than the staggered elements. Comparison between the results of two channels revealed that the models developed in the case of the rectangular channel led to more accurate outcomes. A comparison was also done between the KELM results and ANN method and the results verified the superior performance of the KELM method.
Author Contributions
S.M.S.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Review & Editing; D.D.-S.: Investigation, Resources, Data Curation; R.G.: Project administration, Methodology, Writing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hager, W.H. Energy Dissipators & Hydraulic Jumps; Kluwer Academic Publication: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 151–173. [Google Scholar]
- Bhutto, H.; Mirani, S.; Chandio, S. Characteristics of free hydraulic jump in rectangular channel. Mehran Univ. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 1989, 8, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Finnemore, J.E.; Franzini, B.J. Fluid Mechanics with Engineering Applications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 790. [Google Scholar]
- Hager, W.H.; Bremen, R. 1989 Classical Hydraulic Jump: Sequent Depths. J. Hydraul. Res. 1989, 7, 565–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanlar, K. Hydraulic Jump on Corrugated Beds. Master’s Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Department of Civil Engineering, Ankara, Turkey, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin, A. Correlation and Distribution of Shear Stress for Turbulent Flow in a Smooth Rectangular Open Channel. J. Hydraul. Res. 2005, 43, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.K.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Zakaria, N.A.; Ghani, A.A. Appraisal of soft computing techniques in prediction of total bed material load in tropical rivers. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 121, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Jin, J.; Chen, F.; Yu, G.; Yin, H.; Wang, W. Urban flash flood forecast using support vector machine and numerical simulation. J. Hydroinform. 2018, 20, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Shiri, J. Precipitation forecasting using wavelet-genetic programming and wavelet-neuro-fuzzy conjunction models. J. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 3135–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushangar, K.; Alami, M.T.; Saghebian, S.M. Modeling open channel flow resistance with dune bedform via heuristic and nonlinear approaches. J. Hydroinform. 2018, 20, 356–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Ghani, A.A.; Leow, C.S.; Chang, C.K.; Zakaria, N.A. Gene-expression programming for the development of a stage-discharge curve of the Pahang River. J. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 2901–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushangar, K.; Ghasempour, R. Estimation of bedload discharge in sewer pipes with different boundary conditions using an evolutionary algorithm. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 32, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, C. Forced Hydraulic Jump on Artificially Roughned Beds. Master’s Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Department of Civil Engineering, Ankara, Turkey, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Evcimen, T.U. Effect of Prismatic Roughness on Hydraulic Jump in Trapezoidal Channels. Ph.D. Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Department of Civil Engineering, Ankara, Turkey, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhou, H.; Ding, X.; Zhang, R. Extreme Learning Machine for Regression and Multiclass Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 2012, 42, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haykin, S.; Cybenko, G. Approximation by Superposition of a Sigmoidal Function Neural Networks, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaratnam, N.; Subramanya, K. Hydraulic Jump below Abrupt Symmetrical Expansions. J. Hydraul. Div. ASCE 1968, 94, 481–503. [Google Scholar]
- Hager, W.H. Hydraulic Jumps in Non-Prismatic Rectangular Channels. J. Hydraul. Res. 1985, 23, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S. Characteristics of Hydraulic Jump. Int. J. Math. Comput. Phys. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2014, 8, 692–697. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Rajaratnam, N. Transition from hydraulic jump to open channel flow. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1996, 122, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elevatorski, E.A. Hydraulic Energy Dissipators; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).