Evaluation and Determinants of Secondary Metabolites and its Antioxidant Activities of Various Fractions from Albizia myriophylla Bark †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Plant Material
2.2. Preparation of Dried Barks of Albizia myriophylla
2.3. Preparation of Methanolic Extract of Albizia myriophylla Bark
2.4. Preparation of Hexane, Chloroform, Ethyl Acetate, and Butanol Albizia myriophylla Bark Extract
2.5. Determination of Total Phenolic Contents of Albizia myriophylla Bark Extracts
2.6. Determination of Total Flavonoid Contents of Albizia myriophylla Bark Extracts
2.7. Determination of Total Saponin Contents of Albizia myriophylla Bark Extracts
2.8. Antioxidants Activity Determinations
2.8.1. Total Antioxidants Assay Using ABTS Method
2.8.2. DPPH Scavenging Activity
2.8.3. FRAP Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Total Quantity of Aqueous, Methanol, Hexane, Ethyl Acetate, Chloroform, and Butanol Bark Extracts of ABZ
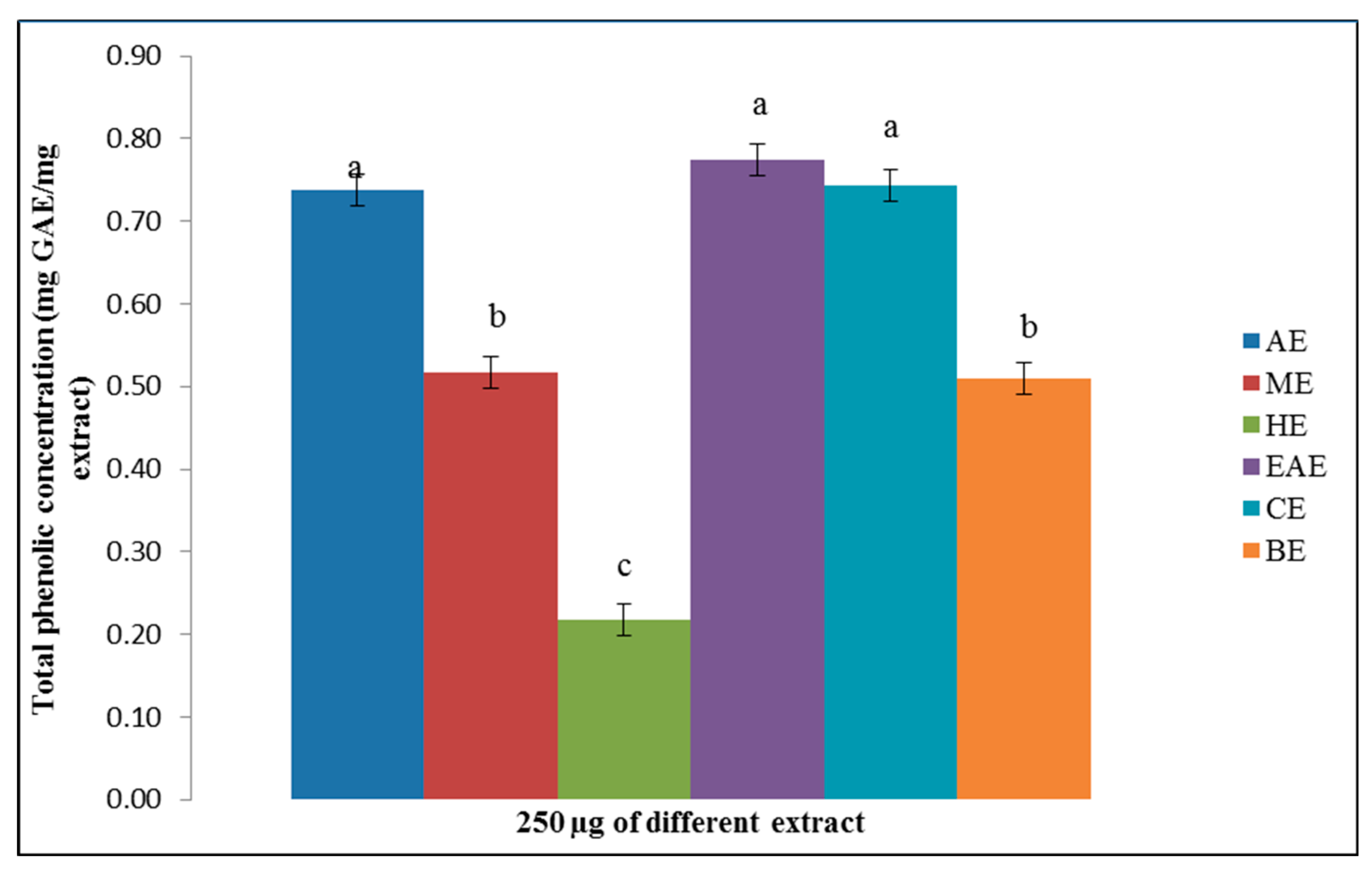
3.2. The Total Phenolic Content of ABZ Bark Extracts
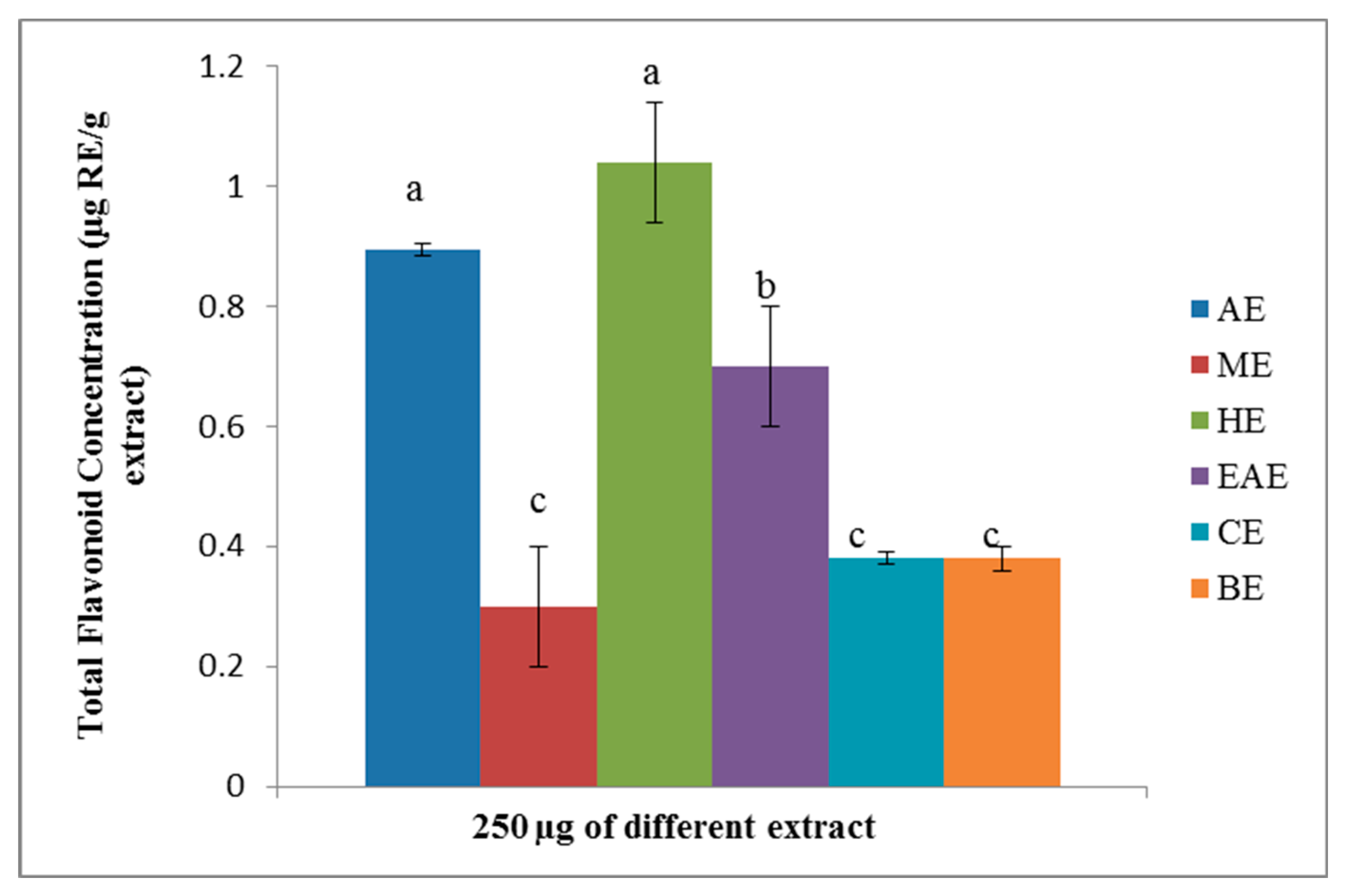
3.3. The Flavonoid Concentrations of ABZ Bark Extracts
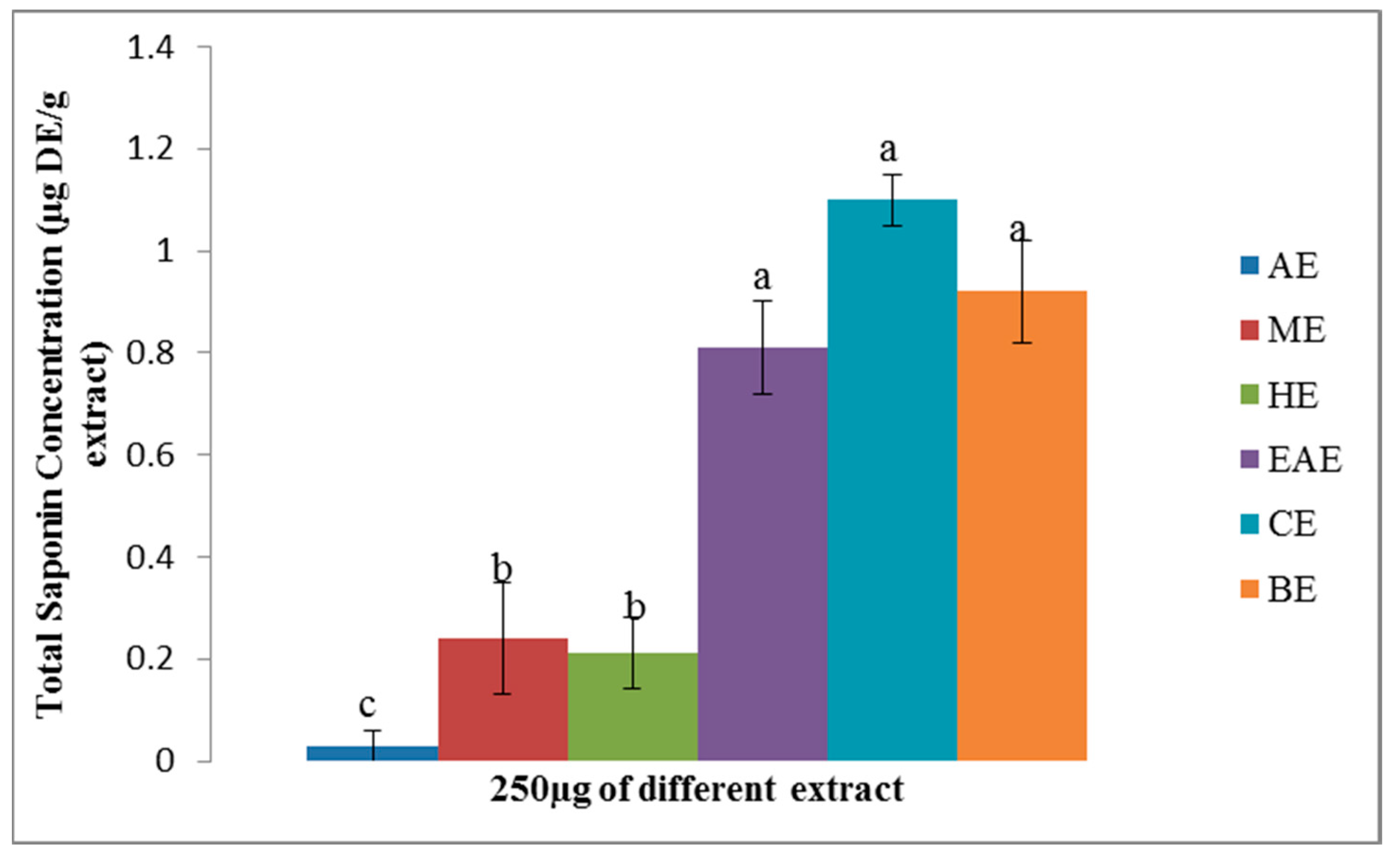
3.4. The Saponin Concentrations of ABZ Bark Extracts
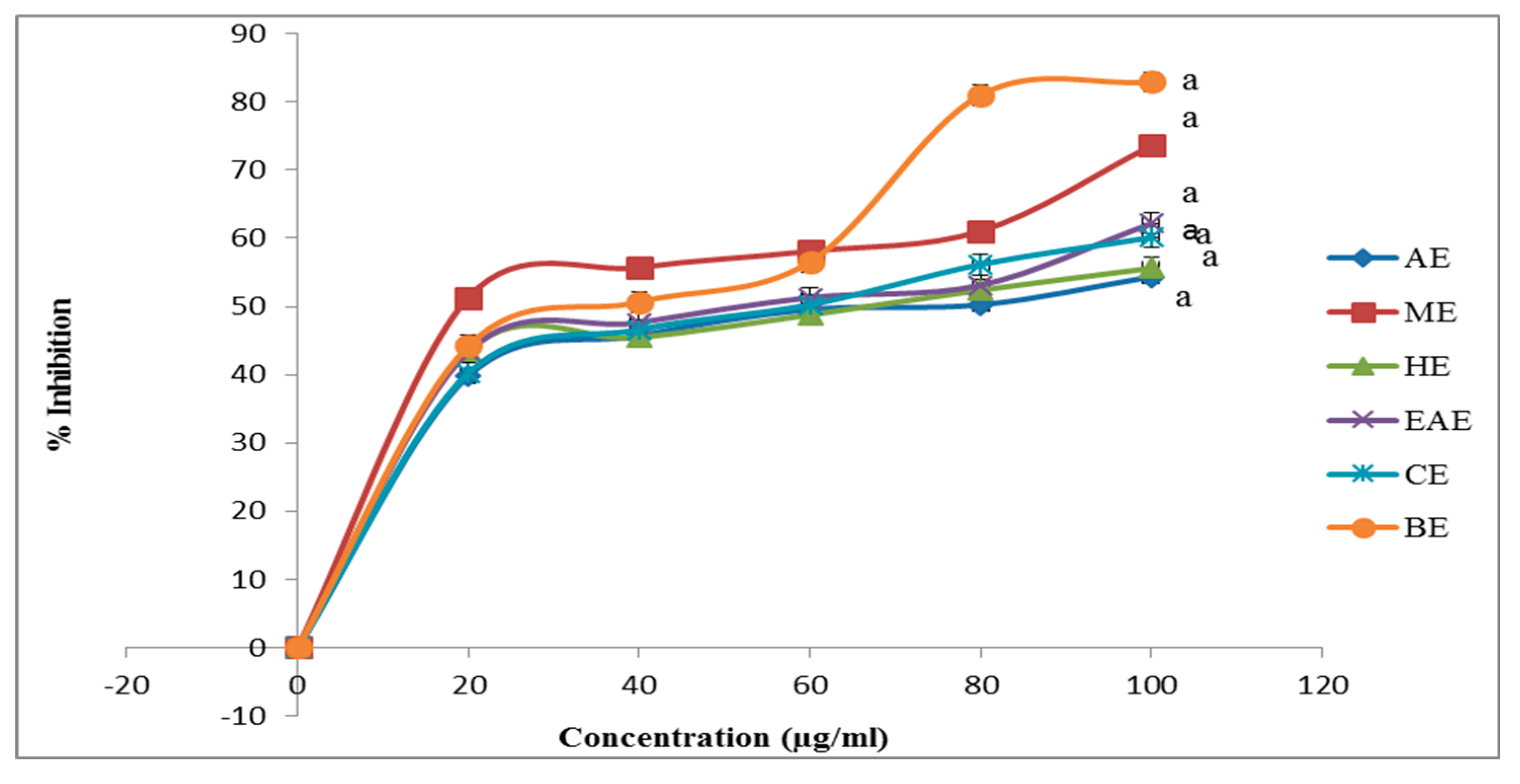
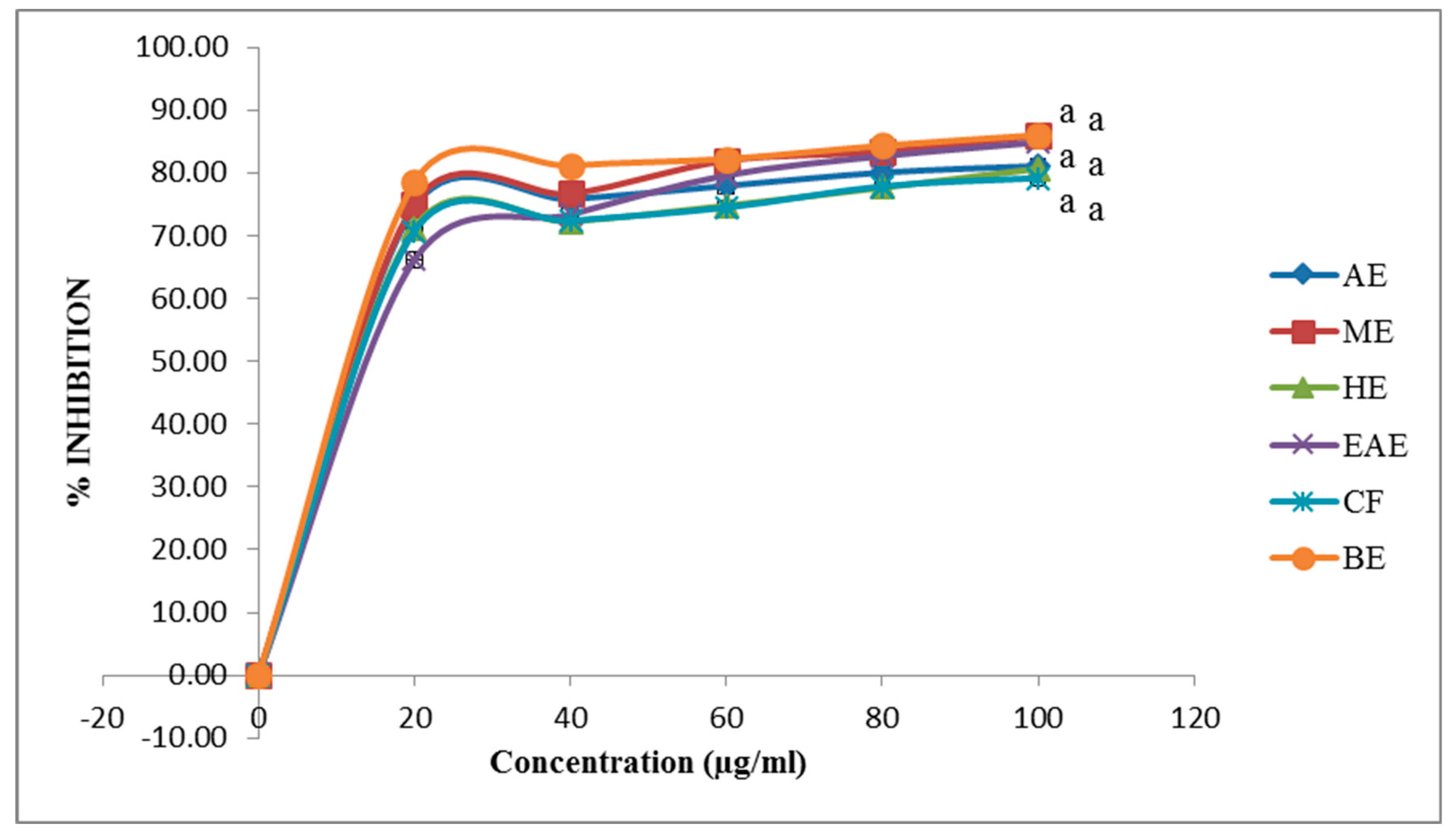
3.5. ABTS Assay of ABZ Bark Extracts
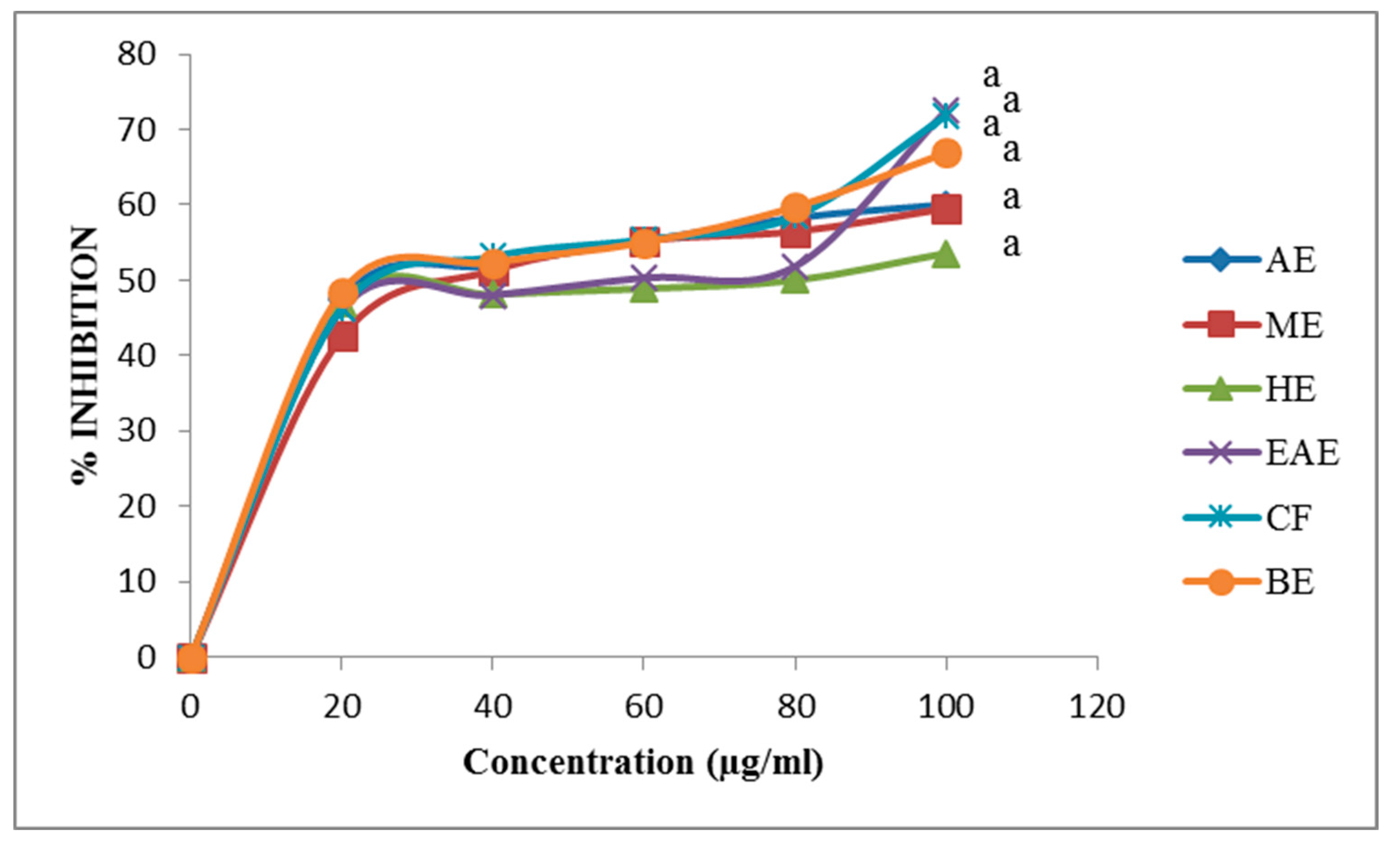
3.6. DPPH Assay of ABZ Bark Extracts
3.7. FRAP Assay of ABZ Bark Extracts
4. Discussion
4.1. The Phenolic Acid, Flavonoids, and Saponin in Various Extracts of ABZ.
4.2. The Antioxidant Activity of Various Extracts of ABZ Bark.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saat:, A.; Syakroni, N.; Rosli, R. Potential hypoglycemic property of Albizia myriophylla in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 427–43l. [Google Scholar]
- Amornchat, C.; Kraivaphan, P.; Dhanabumi, C.; Tandhachoon, K.; Trirattana, T.; Choonharcongdej, S. Effect of cha-em Thai mouthwash on salivary levels of mutans streptococci and total Ig A. Southeast. Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2006, 37, 528–531, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17120974. [Google Scholar]
- Panmei, C.; Singh, P.K.; Gautam, S.; Variyar, P.S.; Shantibala Devi, G.A.; Sharma, A. Phenolic acids in Albizia bark used as a starter for rice fermentation in Zou preparation. JFAE 2007, 5, 147–150. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261675944 (accessed on 22 April 2007).
- Saat, A.; Syakroni, N.; Rosli, R. Potential hypoglycemic activity of Albizia myriophylla and virgin coconut oil in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 199–202. Available online: https://innovareacademics.in/journal/ijpps/Vol4Issue3/4144.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2013).
- Tunsaringkarn, T.; Rungsiyothin, A.; Ruangrungsi, N. α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of Thai Mimosaceous plant extracts. Int. J. Health Res. 2008, 22, 29–33. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242753490 (accessed on 15 November 2007).
- Manickam, M.; Ramanathan, M.; Farboodinay Jahromi, M.A.; Chansouria, J.P.N.; Ray, A.B. Antihyperglycemic activity of phenolics from Pterocarpus marsupium. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 609–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pumthong, G.; Nathason, A.; Tuseewan, M.; Pinthong, P.; Klangprapun, S.; Thepsuriyanon, D.; Kotta, P. Complementary and alternative medicines for diabetes mellitus management in ASEAN countries. Complement. Ther. Med. 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forni, C.; Facchiano, F.; Bartoli, M.; Pieretti, S.; Facchiano, A.; D’Arcangelo, D.; Norelli, S.; Valle, G.; Nisini, R.; Beninati, S.; et al. Beneficial Role of Phytochemicals on Oxidative Stress and Age-Related Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 8748253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Arora, S.; Singh, B. Antioxidant activity of the phenol rich fractions of leaves of Chukrasia tabularis A. Juss. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7692–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, A.; Lamien, C.E.; Romito, M.; Millogo, J.; Nacoulma, O.G. Determination of the total phenolic, flavonoid and proline contents in Burkina Fasan honey, as well as their radical scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quettier-Deleu, C.; Gressier, B.; Vasseur, J.; Dine, T.; Brunet, C.; Luyckx, M.; Cazin, M.; Cazin, J.C.; Bailleul, F.; Trotin, F. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) hulls and flour. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 72, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasaribu, T.; Astuti, D.A.; Wina, E.S.; Setiyono, A. Saponin content of Sapindus rarak pericarp affected by particle size and type of solvent, its biological activity on Eimeria tenella oocysts. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2014, 13, 347–352. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275584738 (accessed on 25 January 2014). [CrossRef]
- Fidrianny, I.; Permatasari, L.; Wirasutisna, K.R. Antioxidant activities from various bulbs extracts of three kinds allium using DPPH, ABTS assays and correlation with total phenolic, flavonoid, carotenoid content. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 438–444. Available online: https://pharmascope.org/index.php/ijrps/article/view/682 (accessed on 15 July 2013).
- Thaipong, K.; Boonprakob, U.; Crosby, K.; Zevallos, L.C.; Byrne, D.H. Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2006, 19, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, H. Resources and biological activities of natural polyphenols. Nutrients 2014, 6, 6020–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven, S.; Frenis, K.; Oelze, M.; Kalinovic, S.; Kuntic, M.; Jimenez, M.T.B.; Vujacic-Mirski, K.; Helmstädter, J.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Münzel, T.; et al. Vascular inflammation and oxidative stress: Major triggers for cardiovascular disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 7092151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakrishnan, S.; Kavitha, J.; Muthu, A.K. Antioxidant potential, total phenolic and flavonoids content of aerial parts of ethanolic extract of Albizia procera (Family: Mimosoideae). Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2012, 6, 108–110. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331802940 (accessed on 23 March 2019).
- Boeing, J.S.; Barizão, E.O.; Silva, B.C.; Montanher, P.F.; Almeida, V.C.; Visentainer, J.V. Evaluation of solvent effect on the extraction of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacities from the berries: Application of principal component analysis. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N.; Baharlouei, A.; Watson, D.G.; Lightfoot, D.A. Phytochemicals: Extraction, isolation, and identification of bioactive compounds from plant extracts. Plants 2017, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Kumar, B.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, H. Phytochemical screening and extraction: A review. Inter. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 98–106. Available online: http://docshare01.docshare.tips/files/9403/94036813.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2011).
- Iloki-Assanga, S.B.; Lewis-Luján, L.M.; Lara-Espinoza, C.L.; Gil-Salido, A.A.; Fernandez-Angulo, D.; Rubio-Pino, J.L.; Haines, D.D. Solvent effects on phytochemical constituent profiles and antioxidant activities, using four different extraction formulations for analysis of Bucida buceras L. and Phoradendron californicum. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 1–14. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281376622 (accessed on 28 August 2015). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, L.L.; Carvalho, M.V.; Melo, L. Health promoting and sensory properties of phenolic compounds in food. Rev. Ceres 2014, 61, 764–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Hampsch-Woodill, M.; Flanagan, J.A.; Prior, R.L. Highthroughput assay of oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) using a multichannel liquid handling system coupled with a microplate fluorescence reader in 96-well format. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4437–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.; Nguyen, D.H.; Ta, N.T.A.; Bui, A.V.; Do, T.H.; Nguyen, H.C. Evaluation of the use of different solvents for phytochemical constituents, antioxidants, and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities of Severinia buxifolia. J. Food Qual. 2019, 8178294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungmunnithum, D.; Thongboonyou, A.; Pholboon, A.; Yangsabai, A. Flavonoids and other phenolic compounds from medicinal plants for pharmaceutical and medical aspects: An overview. Medicines 2018, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, C.; Coșarcă, S.; Muntean, D. A critical review of phenolic compounds extracted from the bark of woody vascular plants and their potential biological activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, S.C.; Moldão-Martins, M.; Alves, V.D. Antioxidants of natural plant origins: From sources to food industry applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, M.; Islam, E.; Islam, R.; Rahman, A.A.; Alam, A.H.M.K.; Khondkar, P.; Rashid, M.; Parvin, S. Estimation of total phenol and in vitro antioxidant activity of Albizia procera leaves. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzialo, M.; Mierziak, J.; Korzun, U.; Preisner, M.; Szopa, J.; Kulma, A. The Potential of plant phenolics in prevention and therapy of skin disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xiao, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Xing, B.; Li, X.; Kong, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. An overview of plant phenolic compounds and their importance in human nutrition and management of type 2 diabetes. Molecules 2016, 21, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Bi, K. Bioactive flavonoids in medicinal plants: Structure, activity and biological fate. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Rajkapoor, B.; Perumal, P. Antioxidant activities of Indigofera cassioides Rottl. Ex. DC. Using various in vitro assay models. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gupta, A.; Pandey, A.K. Calotropis procera root extract has capability to combat free radical mediated damage. Pharmacology 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.A.R.; Miller, N.J.; Bolwell, P.G.; Broamley, P.M.; Pridham, J.B. The relative antioxidant activities of plant derived polyphenolic flavonoids. Free Radic. Res. 1995, 22, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.C.; Samman, S. Review: Flavonoids-chemistry, metabolism, cardioprotective effects and dietary sources. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1996, 7, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K. Anti-staphylococcal activity of a pan-tropical aggressive and obnoxious weed Parthenium histerophorus: An in vitro study. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2007, 30, 383–386. [Google Scholar]
- Sparg, S.G.; Light, M.E.; van Staden, J. Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 94, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.S.M.; Woo, J. Prevention of overweight and obesity: How effective is the current public health approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musman, M. Toxicity of Barringtonia racemosa (L.) kernel extract on Pomacea canaliculata (Ampullariidae). Trop. Life Sci. Res. 2010, 21, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zubairi, S.I.; Sarmidi, M.R.; Aziz, R.A. The effects of raw material particles size, types of solvents and solvent-to-solid ratio on the yield of rotenone extracted from Derris elliptica roots. Sains Malays. 2014, 43, 707–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.F.; Yang, Z.B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.R.; Jiang, S.Z.; Gai, G.S. Effects of ginger root (Zingiber officinale) processed to different particle sizes on growth performance, antioxidant status and serum metabolites of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; McPherson, K.; Matsh, T.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Brown, M. Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. Lancet 2011, 378, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, A.; Radin, N.S. Lipid extraction of tissues with a low-toxicity solvent. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 90, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinpelu, B.A.; Igbeneghu, O.A.; Awotunde, A.I.; Iwalewa, E.O.; Oyedapo, O.O. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of saponin fractionsof Erythrophyleum suaveolens (Guill and Perri.) stem bark extract. Sci. Res. Essays 2014, 9, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.Y.R.; Adanlawo, I.G. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity of saponin extractd from the root of Garcinia kola (bitter kola) on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 8–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kedare, S.B.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/ISC/abstract/20083133473 (accessed on 18 January 2007). [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Wang, X.Z.; Chen, D.F. Antioxidant activity and mechanism of protochatechuic acid in vitro. J. Func. Food Health Dis. 2011, 1, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siahpoosh, A.; Mehrpeyma, M. Antioxidant effects of Albizia lebbek and Prosopis julifora barks. Inter. J. Biosci. 2014, 5, 273–284. Available online: https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/FullTextPDF/2015/20153063562.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2014).
- Khennouf, S.; Amira, S.; Arrar, L.; and Baghiani, A. Effect of some phenolic compounds and quercus tannins on lipid peroxidation. World Applied Sci. 2010, 8, 1144–1149. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268045543 (accessed on 20 November 2009).

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, G.Y.; Abas, R.; Syakroni, N.; Razak, N.I.A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Asri, S.F.M.; Salihan, S.; Zainal, N.H.M.; Thani, S.M.; Saat, A. Evaluation and Determinants of Secondary Metabolites and its Antioxidant Activities of Various Fractions from Albizia myriophylla Bark. Proceedings 2020, 61, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECN2020-07004
Meng GY, Abas R, Syakroni N, Razak NIA, Nor NHM, Asri SFM, Salihan S, Zainal NHM, Thani SM, Saat A. Evaluation and Determinants of Secondary Metabolites and its Antioxidant Activities of Various Fractions from Albizia myriophylla Bark. Proceedings. 2020; 61(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECN2020-07004
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Goh Yong, Razif Abas, Nurmawati Syakroni, Nur Izah Abdul Razak, Nurul Huda Mohd. Nor, Siti Fadziyah Mohamad Asri, Safuraa Salihan, Nurul Hayati Mohamad Zainal, Suryati Mohd. Thani, and Azmah Saat. 2020. "Evaluation and Determinants of Secondary Metabolites and its Antioxidant Activities of Various Fractions from Albizia myriophylla Bark" Proceedings 61, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECN2020-07004
APA StyleMeng, G. Y., Abas, R., Syakroni, N., Razak, N. I. A., Nor, N. H. M., Asri, S. F. M., Salihan, S., Zainal, N. H. M., Thani, S. M., & Saat, A. (2020). Evaluation and Determinants of Secondary Metabolites and its Antioxidant Activities of Various Fractions from Albizia myriophylla Bark. Proceedings, 61(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECN2020-07004



