Abstract
Improving the sensitivity of the competitive lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) is important, given the increasing demands for the monitoring of chemical contaminants in food. The choice of nanosized marker is an essential task for improving the LFIA sensitivity. In this study, a CdSe/ZnS quantum dot (QD)-based LFIA combined with a portable reader was developed for rapid and quantitative detection of an antibiotic lincomycin (LIN). The performance of the proposed fluorescence LFIA was compared to the conventional gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-based LFIA realized with the same immunoreagents. The visual cutoff values were 10 ng/mL for AuNP-based LFIA and 20 ng/mL for QD-based LFIA. Furthermore, the instrumental limits of detection have been shown to be comparable for both nanosized markers and amounted to 0.4 ng/mL for AuNPs and 0.2 ng/mL for QDs, respectively. According to the results obtained, both LFIAs may be used for rapid, cost-effective, on-site testing of antibiotics, in particular LIN. However, the QD-based LFIA exhibits lowest limit of detection with the least immunoreagent consumption, which makes it economically beneficial.
1. Introduction
The lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) is a common analytical platform for the point-of-care testing of medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring because of its rapidity and simplicity. The LFIA provides clear advantages, including the availability of results within a few minutes, the small volume of an analyzed sample, and inexpensive and user-friendly point-of-care testing [1]. The LFIA combines immunochemical reactions with a chromatography principle. It relies on interactions between an analyte and pre-immobilized recognition elements initiated by the addition of a liquid sample. The LFIA result is a signal at the test line generated by a nanodispersed marker used. Despite all the advantages mentioned above, the widespread use of LFIAs has been limited by their insufficient sensitivity. Significant effort has been devoted to improving LFIA sensitivity, including the use of alternative labels and detectors, as well as the addition of amplification stages [2,3].
To improve the sensitivity of the immunoassay, the selection of an appropriate nanosized marker is an essential task. In addition to common AuNPs or latex beads, magnetic and fluorescent particles are used as labels in LFIAs. QDs are used as labels because of their unique optical properties, such as high fluorescence, broad and continuous distributed excitation, photostability, and proven immunoassay effectiveness [4,5]. LFIAs with magnetic and photoluminescent labels showed improved sensitivity for a wide range of analytes [6,7,8,9]. Among other markers applied in LFIA, carbon nanoparticles can be mentioned [10,11]. Compared to other labels, carbon nanoparticles are easily detected visually, which contributes to reducing the detection limit of the analyte.
A survey of the literature shows there have been many works published on new immunoassay markers, but they do not go beyond the description of the effectiveness at detecting a particular analyte or report a comparison of the results with conventional AuNP-based LFIAs. These regularities are poorly transformed into other objects of research. Therefore, the assessment of the test systems with the same reagents that vary according to the kind of marker will provide more information.
In this paper, common AuNPs and QDs were used as nanosized markers to develop competitive LFIAs for detection of antibiotic LIN, and the analytical characteristics of both test systems under the same conditions were compared. The quantitative detection of LIN was performed by registering the colorimetric or fluorescence intensity of AuNPs or QDs, respectively, captured on the test line. To the best of our knowledge, there have been no reports of an LFIA with the use of QDs as a marker for the detection of LIN.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactants
Lincomycin hydrochloride monohydrate (LIN), HAuCl4, bovine serum albumin (BSA), sodium azide, sodium citrate, Tween-20, Triton X-100 were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N’-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and sulfo-N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) were supplied from Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland). Goat antibodies against mouse immunoglobulins (GAMI) were purchased from Arista Biologicals (Allentown, PA, USA). The CdSe/ZnS QDs with an emission peak at 625 nm were obtained from Invitrogen (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). All other reagents were of analytical grade.
Ultrapure water (Millipore Corporation, Burlington, MA, USA) with a resistivity of 418.2 MΩ was used to prepare the AuNPs and their conjugates as well as LIN stock solutions (100 μg/mL). The LFIAs were carried out in 96-well transparent Costar 9018 polystyrene microplates provided by Corning Costar (Tewksbury, MA, USA).
2.2. Preparation of Monoclonal Anti-LIN Antibodies
A synthesis of the LIN–BSA conjugate and a preparation of anti-LIN antibodies were carried out in accordance with the procedure described in the study by Cao et al. [12].
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization of AuNPs
AuNPs with an average diameter of 30 nm were prepared according to the citrate-reduction method [13]. Briefly, 1 mL of 1% HAuCl4 was added to 97.5 mL of ultrapure water and heated to boiling. After that, 1.5 mL of 1% sodium citrate was added immediately to the boiling solution during vigorous stirring. The mixture was left to boil for 25 min and then cooled. The colloidal AuNPs were stored at 4 °C.
The transmission electron microscopic (TEM) images were recorded with a JEM-100C electron microscope (JEOL, Japan) operating at 80 kV. The AuNP preparations were applied to 300-mesh grids (Pelco International, Redding, CA, USA) coated with formvar film. The images obtained were analyzed using Image Tool software (University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX, USA). UV-vis absorption spectra were obtained through spectrophotometer UV-2450 (Shimadzu, Japan).
2.4. Conjugation of Antibodies to AuNPs
Antibody–AuNPs conjugates were prepared according to the previously described technique [14]. Anti-LIN antibodies were dialyzed against a Tris-HCl buffer (10 mM, pH 8.5), and added to AuNPs at a concentration of 10 μg/mL (OD520 = 1). The mixture was incubated for 45 min while stirring at room temperature. BSA in the final concentration of 0.25% was further added to this preparation, followed by stirring for 15 min. The excess reagents were removed by centrifugation at 9500 g for 15 min, followed by resuspension of the antibody–AuNPs pellet in Tris buffer (10 mM, pH 8.5) with 1% BSA, 1% sucrose, and 0.1% sodium azide (TBSA).
2.5. Conjugation of Antibodies with QDs
Anti-LIN antibodies were dialyzed against a borate buffer (50 mM, pH 8.7). The molar ratio of QDs to anti-LIN antibodies during synthesis was 1:2. Antibodies (300 μL, 0.2 mg/mL), QDs (25 μL, 8 μM), and freshly prepared EDC and NHS solutions (50 μL, 0.8 mM each) were mixed. After incubation for 90 min in a dark place at room temperature, the resulting mixture was purified by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 15 min using Amicon Ultra 100 kDa tubes. The centrifugation was repeated four times, and, finally, 14 μL of QDs with a concentration of 4.26 mg/mL was obtained.
2.6. Preparation of Test Strips
The schemes of two LFIA formats are shown in Figure 1. Test strips were assembled using MdiEasypack membrane sets (Advanced Microdevices, India) comprising the following elements: A plastic support, a CNPC nitrocellulose working membrane with a pore size of 15 μm, a PT–R7 conjugate fiberglass pad (in case of conventional AuNP- and QD-based LFIAs), a GFB-R4 sample pad, and an AP045 absorbent pad. The control line was formed by applying 0.5 mg/mL GAMI in a K-phosphate buffer (PBS, 50 mM, pH 7.4, with 0.1 M NaCl) by an Iso-Flow automatic dispenser (Imagene Technology, Hanover, NH, USA). To form a test line, LIN–BSA conjugate (0.5 mg/mL–for AuNPs-based, 0.15 mg/mL–for QD-based, in PBS) was applied. After that, the test strips were dried at 37 °C; for 2 h. For AuNP-based LFIA, the antibody-AuNPs conjugate in TBSA containing 0.05% Tween-20 was applied to the conjugate pad and dried at room temperature overnight. For QD-based LFIA, 1 µL of antibody–QDs conjugate (0.09 µM) in a borate buffer (BB, 0.05 M with 1% BSA, 0.1% sucrose, and 0.1% sodium azide, 0.05% Tween-20) was applied to the interface of the sample pad and nitrocellulose membrane and dried at room temperature overnight. Finally, the assembled multimembrane composites were cut into individual test strips 3 mm wide using an automatic guillotine cutter (Index Cutter-1, A-Point Technologies, Gibbstown, NJ, USA).
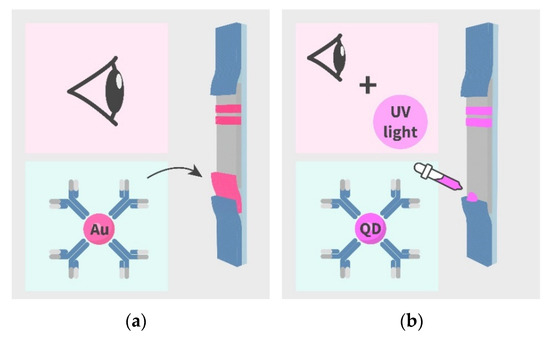
Figure 1.
Schemes of lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) formats developed in the study: (a) Conventional colorimetric AuNP-based LFIA, (b) fluorescent QD-based LFIA.
2.7. LFIA Procedures
Solutions of LIN (1 µg/mL–1 pg/mL) in PBST (100 μL) were dripped onto the microplate wells. The test strips were vertically placed into the well and left to react for 15 min. The color intensity (in the case of AuNP-based LFIA) of the formed bands was scanned by the CanoScanLiDE 90 (Canon, Tokyo, Japan). The fluorescence intensity (for QD-based LFIA) was recorded under UV light excitation. The obtained images were then digitized using the TotalLab program (Nonlinear Dynamics, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK).
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of AuNPs
AuNPs were used as a marker in conventional LFIA. AuNPs of a diameter close to 30 nm were reported to be optimal for traditional immunochromatography [15]. To prepare AuNPs with diameter of 30 nm, a simple method of sodium citrate-associated reduction of chloroauric acid was applied. The size and shape of AuNPs were estimated by TEM and UV-vis spectroscopy (Figure 2). The as-prepared AuNPs showed localized surface plasmon resonance at 523 nm. The TEM image revealed spherical morphology and homogeneity with a size distribution in the range of 29.5 ± 7.4 nm and a degree of ellipticity of 1.3 (Figure 2b). According to the manufacturer, the size of carboxyl quantum dots varies from 15 to 20 nm.
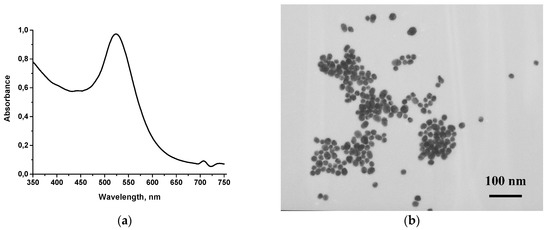
Figure 2.
(a) UV-vis spectrum of AuNPs of 30 nm, (b) microphotograph of 30 nm AuNPs for colorimetric LFIA.
3.2. AuNP-Based LFIA
Given the need to detect a low molecular weight compound in this study, a direct competitive LFIA format was performed. In this assay, free LIN present in the sample competed with the immobilized LIN–BSA conjugate in regard to binding with specific anti-LIN antibodies, which were, in turn, detected by employing different nanosized markers and detection techniques. The preliminary characterization of the immune properties of monoclonal anti-LIN antibodies used by ELISA confirmed their high affinity (data not shown) and allowed for the development of LFIAs.
The scheme of the conventional AuNP-based LFIA is presented in Figure 1a. For the LFIA, LIN–BSA conjugate and GAMI were applied to form test and control lines on the working membrane, respectively. The specific antibody-labeled AuNPs was immobilized on the fiberglass pad. The assay conditions were optimized to achieve the lowest detection limit at a high amplitude of the analytical signal. As a result, the following conditions were found to be optimal for two formats of assay: 0.5 mg/mL–for AuNP-based, 0.15 mg/mL–for QD-based LFIAs (the concentration varies from 0.2 to 1 mg/mL) and 0.5 mg/mL for GAMI (the concentration varies from 0.15 to 0.5 mg/mL). The AuNPs-anti-LIN antibodies solution was then applied to the conjugate pad at the concentration corresponding to OD520 = 1 (we tested OD520 in the range from 0.5 to 2.5). The overall performance of the LFIA was explored by varying the concentration of the analyte (from 1,000 to 0.001 ng/mL). Under optimal experimental conditions, the AuNP-based LFIA exhibits linearity over the range of 0.7–7.2 ng/mL with an instrumental detection limit of 0.4 ng/mL (Figure 3). The cutoff was 10 ng/mL with the assay duration of 15 min.
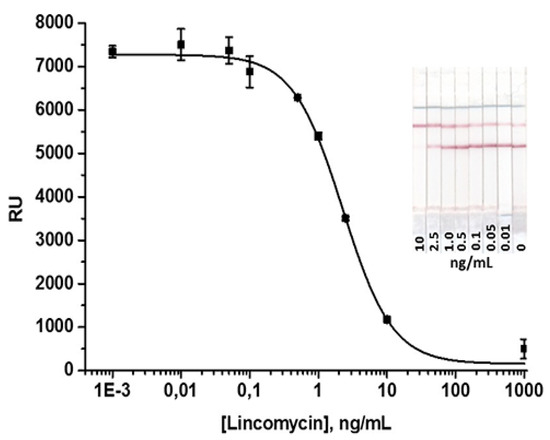
Figure 3.
Calibration curve of lincomycin (LIN) in the AuNPs-based LFIA.
3.3. QD-Based LFIA
The scheme of QD-based LFIA is demonstrated in Figure 1b. For QD-based LFIA, the selection of working membranes aimed to decrease background fluorescence was carried out together with the optimization of specific reagent concentrations described above. For this purpose, CNPC SS12 12/15µ (Advanced Microdevices), HF120, and HF180 (Millipore) membranes differing in pore size and flow rates were tested. Figure 4 indicates that the use of CNPC SS12 (of a 12 and 15 µm pore size, respectively) leads to the formation of background coloration over its entire surface. Testing of Millipore membranes with different pore sizes and flow rates demonstrated that the application of the Millipore HF180 membrane facilitated achieving the maximum analytical signal intensity (as opposed to a 20% reduction in intensity when using a HF120 membrane), eliminating nonspecific binding, and ensuring uniform movement of samples.
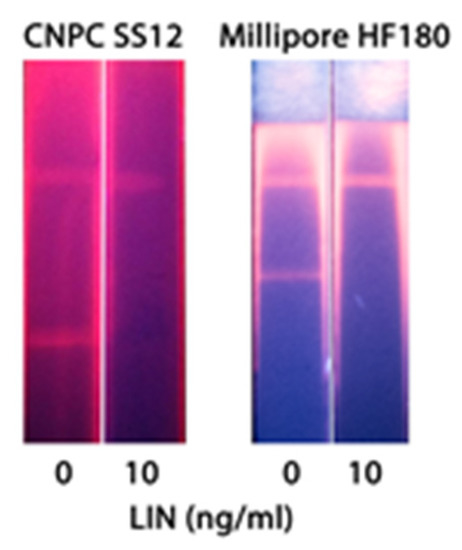
Figure 4.
Images of the test zones after the LFIA performed using CNPC SS12 and Millipore HF180 membranes.
The next stage of assay optimization was to select the optimal reaction medium that would decrease nonspecific binding and provide a higher signal intensity. The use of PBST as a buffer solution for QD-based LFIA led to nonspecific binding of the antibody–QDs conjugate and background staining of the working membrane. For LIN detection, significantly higher signal intensities were obtained with BB. It is acknowledged that for the effective elution of the antibody–QDs conjugate and its movement along the membrane, detergents must be added to the buffer [13]. It was shown that the addition of Tween-20 (0.05%), BSA (1%), and sucrose (0.1%) to BB eliminated the nonspecific sorption of QD-labeled antibodies in the test zone and increased the intensity of the analytical signal by 15%. BSA and sucrose were added to the buffer to reduce the flow rate (due to a viscosity increase) and, hence, to maximize the contact time of the sample with the labeled antibodies. Furthermore, the use of BSA allows blocking the sites of nonspecific sorption of the conjugate [16].
An antibody–QDs conjugate solution was applied to the interface of the sample pad and working membrane at a volume of 1 µL and a concentration range of 0.09 to 0.28 µM. The 0.09 µM conjugate concentration was shown to give the optimal fluorescence intensity. A further decrease in the concentration of the antibody–QDs conjugate led to a drop in the signal amplitude and a decrease in the reproducibility of the test results.
Figure 5 shows the calibration curve for LIN detection in the optimized LFIA. The instrumental LOD was 0.2 ng/mL and the dynamic linear range was 0.6–10.4 ng/mL. The visual LOD was 20 ng/mL. QD-based LFIA can provide results in 15 min.
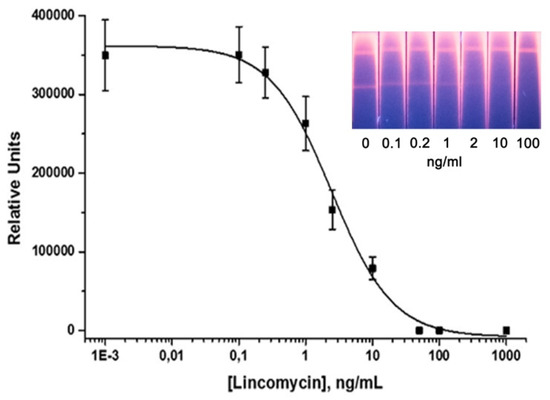
Figure 5.
Calibration curve of LIN in the QD-based LFIA and images of the corresponding test strips.
4. Discussion
In this study, we developed QD-based fluorescence LFIA for detection of LIN, followed by a comparison of analytical performance to conventional AuNP-based colorimetric LFIA using the same immunoreagents. The analyses were carried out in the direct competitive format with the use of anti-LIN antibodies labeled with AuNPs or QDs. The AuNP-based LFIA was characterized by a detection limit of 0.4 ng/mL. The replacement of the colorimetric marker with a fluorescent one resulted in a two-fold enhancement in sensitivity (the detection limit was 0.2 ng/mL) and less immunoreagent consumption. In addition, QD-based LFIA combined with a portable fluorescence reader fulfills all the requirements of quantitative point-of-care testing and can be used to detect other contaminants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.V.Z.; methodology, O.D.H.; investigation, E.A.Z., D.S.P., K.V.S., O.D.H.; formal analysis, E.A.Z., D.S.P.; writing—original draft preparation, K.V.S.; writing—review and editing, A.V.Z.; resources, C.X.; project administration, B.B.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Project 19-14-00370).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to S.M. Pridvorova (Research Center of Biotechnology of the Russian Academy of Sciences) for obtaining electronic microphotographs of the AuNPs.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Quesada-González, D.; Merkoçi, A. Nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensors. Biosensors Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urusov, A.E.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Towards Lateral flow quantitative assays: Detection approaches. Biosensors 2019, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Wang, K.; Alfranca, G.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Cui, D. A plasmonic thermal sensing based portable device for lateral flow assay detection and quantification. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlina, A.N.; Taranova, N.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Vengerov, Y.Y.; Dzantiev, B.B. Quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay for detection of chloramphenicol in milk. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4997–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, P.; Upadhyay, N.; Nara, S. Recent advancements in lateral flow immunoassays: A journey for toxin detection in food. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1715–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangheri, M.; Di Nardo, F.; Anfossi, L.; Giovannoli, C.; Baggiani, C.; Roda, A.; Mirasoli, M. Multiplex chemiluminescent biosensor for type B-fumonisins and aflatoxin B1 quantitative detection in maize flour. Analyst 2014, 140, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Narváez, E.; Naghdi, T.; Zor, E.; Merkoçi, A. Photoluminescent lateral-flow immunoassay revealed by graphene oxide: Highly sensitive paper-based pathogen detection. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8573–8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.R.; Kim, M.G. Highly Sensitive chemiluminescence-based lateral flow immunoassay for cardiac troponin i detection in human serum. Sensors 2020, 20, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Dou, L.; Bu, T. Highly sensitive furazolidone monitoring in milk by a signal amplified lateral flow assay based on magnetite nanoparticles labeled dual-probe. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguera, P.; Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; van Tuil, M.; van der Wal, F.J.; de Boer, A.; Moers, A.P.H.A.; Amerongen, A. Carbon nanoparticles in lateral flow methods to detect genes encoding virulence factors of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiriyachaiporn, N.; Sirikett, H.; Maneeprakorn, W.; Dharakul, T. Carbon nanotag based visual detection of influenza A virus by a lateral flow immunoassay. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1827–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Song, S.; Liu, L.; Kong, N.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Comparison of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with an immunochromatographic assay for detection of lincomycin in milk and honey. Immunol. Investig. 2015, 44, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, O.D.; Zvereva, E.A.; Shanin, I.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Tarannum, N.; Dzantiev, B.B. Highly sensitive immunochromatographic detection of antibiotic ciprofloxacin in milk. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2018, 54, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasel, M.; Keusgen, M. Two protein modified gold nanoparticles for one step serological diagnosis. Phys. Status Solidi A 2018, 215, 1700700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, B. Evolution in lateral flow–based immunoassay systems. Chapter 1. In Lateral Flow Immunoassay; Wong, R.C., Tse, H.Y., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).