Pore Morphology of Heavily Doped P-Type Porous Silicon †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- PS oxidation and HF dissolution. When PS is thermally oxidized, a SiO2 layer is formed on its surface. Dissolution of this oxide in HF can increase the pore diameter up to half the SiO2 layer thickness [12]. This process can be repeated but doing so will reduce the pore walls and jeopardize the structural stability.
- Post-treatment with alkaline mixtures. KOH and NaOH solutions anisotropically etch Si and can be used to expand the pores after fabrication [13], although this method has the same limitations as the previous one. They have also been used for partially dissolving the PS film and obtaining a pattern that—if used afterwards in a new electrochemical etching—can yield macropores [6].
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Pacholski, C. Photonic crystal sensors based on porous silicon. Sensors 2013, 13, 4697–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Föll, H.; Christophersen, M.; Carstensen, J.; Hasse, G. Formation and application of porous silicon. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 2002, 39, 93–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X. Porous silicon: Morphology and formation mechanisms. In Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry; Vayenas, C., Gamboa-Adelco, M.E., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 39, pp. 65–133. ISBN 0076-9924. [Google Scholar]
- Caroselli, R.; Ponce-Alcántara, S.; Prats-Quílez, F.; Martín-Sánchez, D.; Torrijos-Morán, L.; Griol-Barres, A.; Bellieres, L.; Bandarenka, H.; Girel, K.; Bondarenko, V.; et al. Experimental study of the sensitivity of a porous silicon ring resonator sensor using continuous in-flow measurements. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 31651–31659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutter, T.; Horesh, M.; Ruschin, S. Method for increasing reliability in gas detection based on indicator gradient in a sensor array. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 152, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, S.; Strambini, L.M.; Barillaro, G. Femtomole detection of proteins using a label-free nanostructured porous silicon interferometer for perspective ultrasensitive biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8502–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canham, L.T. Tunable properties of porous silicon. In Handbook of Porous Silicon; Canham, L.T., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 201–206. ISBN 978-3-319-05744-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lehman, V.; Föll, H. Formation mechanism and properties of electrochemically etched trenches in n-type silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, V.; Rönnebeck, S. The physics of macropore formation in low-doped p-type silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 2968–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, V.; Stengl, R.; Luigart, A. On the morphology and the electrochemical formation mechanism of mesoporous silicon. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2000, 69–70, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, S.; Pino, L.; Strambini, L.M.; Tedeschi, L.; Barillaro, G. 10000-fold improvement in protein detection using nanostructured porous silicon interferometric aptasensors. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.W.; Parker, G.J.; Greef, R. High-aspect ratio silicon pillars fabricated by electrochemical etching and oxidation of macroporous silicon. Thin Solid Films 1996, 276, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernienko, A.V.; Astrova, E.V.; Zharova, Y.A. Zigzag structures obtained by anisotropic etching of macroporous silicon. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2013, 39, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, E.A.; Lévy-Clément, C. Macropore formation on p-type silicon. J. Porous Mater. 2000, 7, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, S.; De, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghanta, U. Effect of dimethylformamide, current density and resistivity on pore geometry in p-type macroporous silicon. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
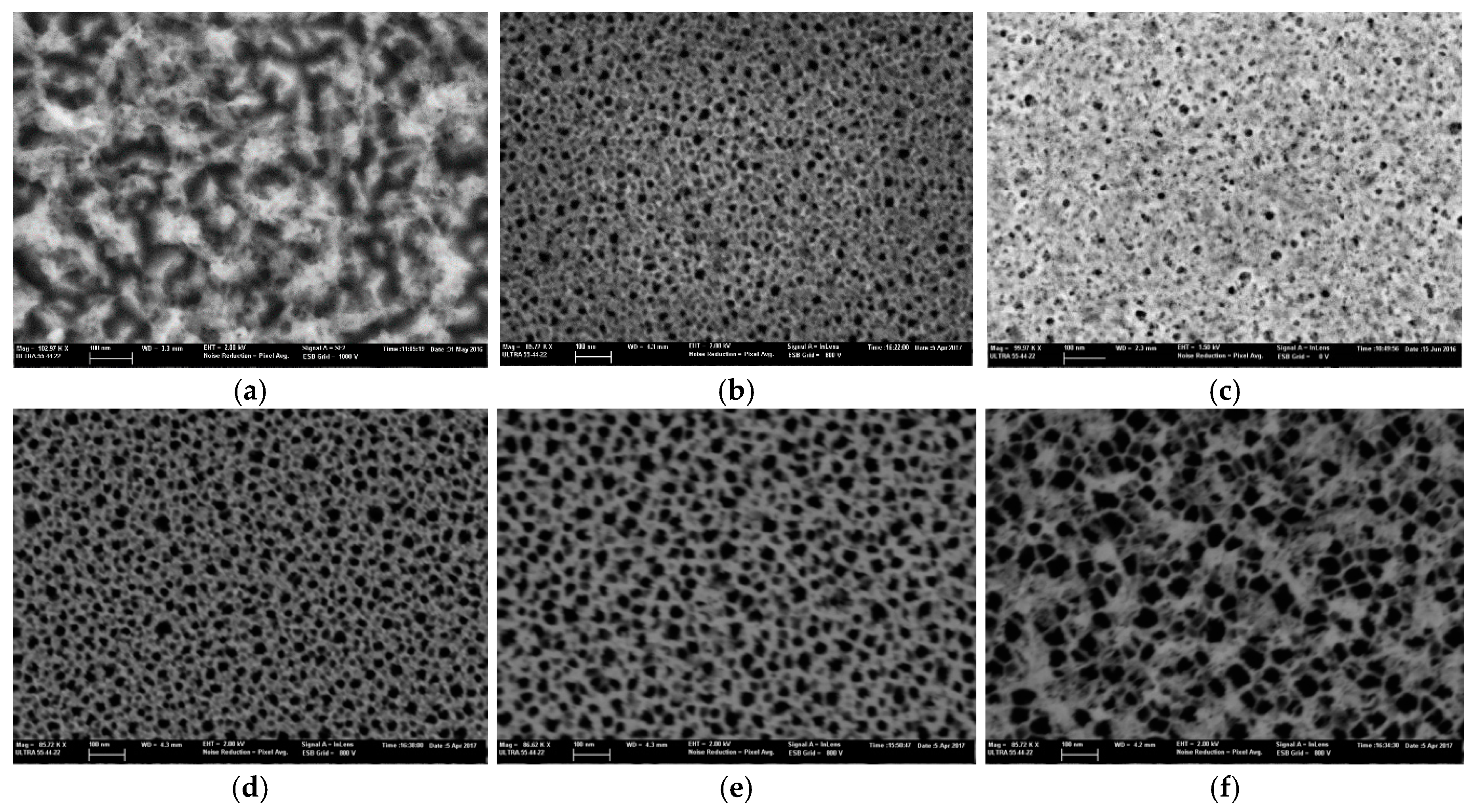

| Electrolyte | HF:EtOH 1:9 | HF:EtOH 1:2 + Oxidation | HF:EtOH 1:2 + KOH | HF:DIW:DMF 1:1:4 | HF:DIW:DMF 1:1:9 | HF:DIW:DMSO 1:1:9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistivity of the electrolyte | 150 Ω∙cm | 100 Ω∙cm | 100 Ω∙cm | 750 Ω∙cm | 1300 Ω∙cm | 1500 Ω∙cm |
| Current range of PS formation | <18 mA/cm2 | <130 mA/cm2 | <130 mA/cm2 | <25 mA/cm2 | <18 mA/cm2 | <18 mA/cm2 |
| Pore surface shape | Pores inter-connected | Holes | Holes | Holes | Holes | Hexagons |
| Pore section shape | Random and short branches | Secondary branches only | Secondary branches only | Secondary branches only | Secondary branches only | Smooth pore wall |
| Pore diameter | ~20 nm | ~25 nm | ~25 nm | ~25 nm | ~30 nm | ~50 nm |
| Etch rate | ~0.5 nm/s, I = 5 mA/cm2, T = 310 s | ~8 nm/s, I = 6 mA/cm2, T = 100 s | ~8 nm/s, I = 6 mA/cm2, T = 120 s | ~20 nm/s, I = 22 mA/cm2, T = 90 s | ~8 nm/s, I = 11 mA/cm2, T = 90 s | ~5 nm/s, I = 11 mA/cm2, T = 90 s |
| Spacing between pores | ~50 nm | ~30 nm | ~60 nm | ~40 nm | ~20 nm | <10 nm |
| Micropore layer on top | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Electrolyte | HF:EtOH 2:1 | HF:EtOH 2:1 + NaOH |
|---|---|---|
| Resistivity of the electrolyte | 10 Ω∙cm | 10 Ω∙cm |
| Current range of PS formation | <750 mA/cm2 | <750 mA/cm2 |
| Pore surface shape | Holes | Holes |
| Pore section shape | Secondary branches only | Secondary branches only |
| Pore diameter | <10 nm | ~100 nm |
| Etch rate | ~400 nm/s, I = 650 mA/cm2, T = 30 s | ~450 nm/s, I = 730 mA/cm2, T = 30 s |
| Spacing between pores | ~20 nm | ~20 nm |
| Micropore layer on top | Yes | No |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martín-Sánchez, D.; Ponce-Alcántara, S.; García-Rupérez, J. Pore Morphology of Heavily Doped P-Type Porous Silicon. Proceedings 2019, 4, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05715
Martín-Sánchez D, Ponce-Alcántara S, García-Rupérez J. Pore Morphology of Heavily Doped P-Type Porous Silicon. Proceedings. 2019; 4(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05715
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartín-Sánchez, David, Salvador Ponce-Alcántara, and Jaime García-Rupérez. 2019. "Pore Morphology of Heavily Doped P-Type Porous Silicon" Proceedings 4, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05715
APA StyleMartín-Sánchez, D., Ponce-Alcántara, S., & García-Rupérez, J. (2019). Pore Morphology of Heavily Doped P-Type Porous Silicon. Proceedings, 4(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05715






