Abstract
Recent studies have expanded our understanding of the effects of nanoparticles on hydrogel mechanical properties. However, further studies are needed to validate the generality of these findings, as well as to determine the exact mechanisms behind the enhancements afforded by the incorporation of nanoparticles. In this study, we performed rotational rheological characterizations of chemically crosslinked poly(acrylamide) hydrogels incorporating silica nanoparticles to better understand the role of nanoparticles on the enhanced properties of hydrogel nanocomposites. Our results indicate that incorporating nanoparticles can lead to enhancements in hydrogel elastic moduli greater than the maxima obtainable through purely chemical crosslinking. Moreover, we find that the increases in elastic moduli due to the addition of nanoparticles not only depend on particle concentration, but also on the monomer and chemical crosslinker concentration. Finally, our data indicates a strong role for pseudo-crosslinking mediated by noncovalent interactions between the nanoparticles and hydrogel polymers on the observed reinforcements. Collectively, our results shed further insight into the role of nanoparticles on enhancements of mechanical properties of hydrogels and may thereby facilitate engineering specific mechanical properties in a wide range of hydrogel nanocomposite systems.
1. Introduction
The unique physical and biochemical properties of hydrogels have enabled their emergence as potential candidates for various biomedical and biotechnological applications: cell encapsulation for tissue engineering, release of various chemical and biologicals for drug delivery, and development of stimulus-responsive platforms for use in bioseparations and biosensing [1,2,3,4]. However, their poor mechanical properties have limited their widespread adoption for these and other applications. Leaning on existing research that has demonstrated significant improvements in the mechanical properties of traditional polymers, such as melts and elastomers, upon the addition of nanoparticles [5,6,7], we performed rheological investigations of the role of nanoparticles on the elastic modulus of polyacrylamide hydrogels. Previous studies have indicated that the enhancements mediated by nanoparticles are due in large part to an increase in polymer crosslink density mediated by strong interactions of nanoparticles with the polymer chains [8,9,10,11]. We therefore chose silica nanoparticles because they are known to strongly interact with polyacrylamide chains through hydrophobic interactions and facilitate increases in the hydrogel modulus through an increase in the polymer crosslinking density [12,13,14]. Therefore, our model system enables us to investigate the effects of nanoparticle-mediated physical crosslinking and compare the effects to the enhancements achieved through chemical crosslinking.
2. Results
2.1. Influence of Crosslinker Concentration on Hydrogel Elastic Modulus
We first studied the impact of crosslinker concentration on the modulus of polyacrylamide (pAAm) hydrogels prepared using the bifunctional crosslinking agent N, N′-methylenebisacrylamide (Bis), as shown in Table 1. When hydrogel elastic modulus is plotted against the concentration of Bis, we observe an initial increase in modulus with crosslinker concentration followed by a plateau value above a threshold crosslinker concentration (Table 1).

Table 1.
Elastic modulus for polyacrylamide hydrogels for various monomer and crosslinker ratios.
Next, we show hydrogel elastic modulus as a function of %CBis, relative concentration of the crosslinker Bis (Table 2), which is defined by Equation (1):

Table 2.
Elastic modulus for polyacrylamide hydrogels for various relative crosslinker ratios.
We observe that the threshold point for the different hydrogels occurs at the same relative crosslinker concentration (%CBis = 4.76), irrespective of the initial monomer concentration. The saturation of elastic modulus for hydrogels, prepared using different monomer concentrations, at similar values of relative chemical crosslinker concentration has been demonstrated previously [15], and has been attributed to the formation of highly crosslinked “microgels” connected by a percolating network of linear polymer chains.
2.2. Influence of Nanoparticles on the Elastic Modulus of Chemically Crosslinked Hydrogels
We next proceeded to study the influence of silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) on the chemically crosslinked hydrogels. These experiments revealed an increase in the elastic modulus of pAAm-SiNP composites relative to the neat hydrogels (Figure 1a). Moreover, we observed increases in the elastic modulus that surpassed the maximum modulus observed for the neat hydrogels due to the addition of nanoparticles (Figure 1b). These results are not entirely surprising, given that previous studies have indicated that hydrogen bonding between pAAm chains and SiNP surface enables nanoparticles to serve as pseudo-crosslinkers and thereby increase the extent of crosslinking in the hydrogel network and facilitate reinforcements in their mechanical properties [13,14].
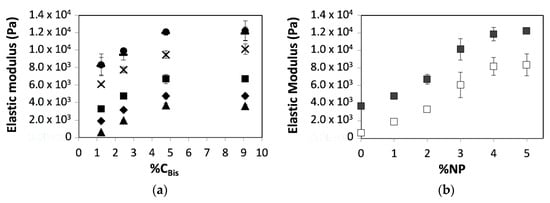
Figure 1.
Elastic moduli of 5% polyacrylamide hydrogel nanocomposites as a function of (a) relative crosslinker concentration (%CBis) prepared using different concentrations of 4 nm silica nanoparticles (SiNPs): 0% SiNPs (triangles), 1% SiNPs (diamonds), 2% SiNPs (squares), 3% SiNPs (Xs), 4% SiNPs (dashes), and 5% SiNPs (circles) and (b) nanoparticle concentration prepared using different concentrations of the chemical crosslinker: 0.0625% Bis (open squares) and 0.5% Bis (closed squares). Data shown are the mean of triplicate measurements ± standard deviation.
2.3. Influence of Chemical Crosslinking on Nanoparticle-Mediated Enhancements of Hydrogel Elastic Modulus
We also explored the combined effects of chemical and nanoparticle-mediated physical crosslinking on the hydrogel elastic modulus. We compared the ratio of elastic modulus of hydrogels that incorporated SiNPs and the neat hydrogels (G’NP/G’0), over a range of crosslinker and monomer conditions, and observed a diminishing impact of nanoparticles on the elastic modulus at higher chemical crosslinker concentrations (Figure 2a). These results indicate a saturation point in the overall crosslinking density achieved by either chemical or physical crosslinking and a combination thereof and therefore enhancements in mechanical properties afforded by increases in crosslinking density.
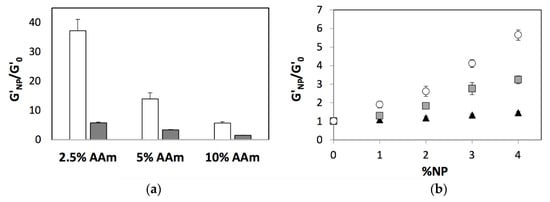
Figure 2.
Relative elastic moduli of polyacrylamide hydrogel nanocomposites as a function of (a) monomer concentration prepared using 5% 4 nm SiNPs and different concentrations of the chemical crosslinker: 0.0625% Bis (white bars) and 0.5% Bis (grey bars) and (b) nanoparticle concentration for 2.5% pAAm (white circles), 5% pAAm (grey squares), and 10% pAAm (black squares) hydrogels. Data shown are the mean of triplicate measurements ± standard deviation.
Interestingly, we also observed decreasing role of nanoparticles with increasing monomer concentrations. To better understand this observation, we defined a new variable (%CNP) that refers to the concentration of SiNPs relative to the monomer concentration in a manner similar to %CBis (Equation (2)).
When the enhancements in elastic modulus due to the addition of nanoparticles were re-plotted against the relative nanoparticle concentration (%CNP) that accounts for the relative reinforcement due to nanoparticles, we observe a collapse in the curves that capture nanoparticle-mediated enhancements for different monomer concentrations into a single master curve (Figure 3). Therefore, we may conclude that enhancements in hydrogel modulus due to the addition of nanoparticles scale with the nanoparticle concentration relative to the monomer concentration, similar to enhancements mediated by chemical crosslinking.
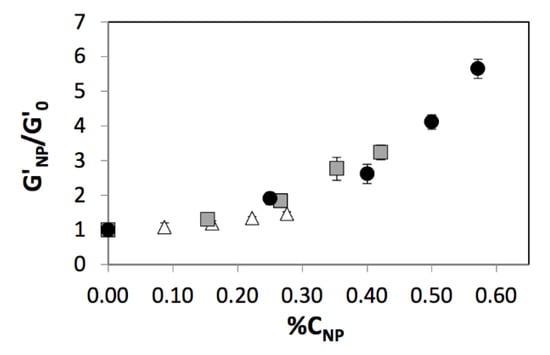
Figure 3.
Relative elastic moduli of polyacrylamide hydrogel nanocomposites prepared using 0.5% AAm (white circles), 5% AAm (grey squares), or 10% AAm (black squares) as a function of relative nanoparticle concentration. Data shown are the mean of triplicate measurements ± standard deviation.
3. Discussion
This work investigates the relative contributions of nanoparticle-mediated physical crosslinking and chemical crosslinking to hydrogel modulus, using pAAm-SiNP composites as the model system. Rheological characterization demonstrated the positive effect of both Bis and SiNP concentration on the hydrogel elastic modulus. Additionally, consistent with previous studies, a combination of chemical crosslinking and addition of nanoparticles led to enhancements in hydrogel modulus compared to either alone [14,16,17]. However, there is an upper limit to the gains in elastic modulus due to a combination of chemical and nanoparticle-mediated physical crosslinking, thereby suggesting a saturation point for the achievable overall crosslinking density. In addition to providing a fundamental insight into the role of nanoparticles in reinforcing hydrogel elastic modulus, this study also positively impacts upon the development of applications such as tissue engineering, drug delivery, and biosensing that may directly benefit from these improvements; examples include [18,19]. These applications may also benefit from enhancements in the chemical and biological properties of the hydrogel, which may be achieved by functionalizing nanoparticles prior to their incorporation into the hydrogel network. Hydrogel nanocomposites may also find further applicability by introducing additional properties, such as thermal, electrical, and magnetic characteristics.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
All of the materials for the polymerization reaction, acrylamide (AAm, monomer), initiator, ammonium persulfate (APS, initiator), N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED, catalyst), and N,N′-methylenebis(acrylamide) (Bis, crosslinker), were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and used as received. Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.2) was obtained from Life Technologies (Carlsbad, CA, USA) and binzil silica nanoparticle colloid solution with a mean particle size of 4 nm was obtained as a gift from AkzoNobel Pulp and Performance Chemicals Inc. (Marietta, GA, USA).
4.2. Polymerization Reaction
Chemically crosslinked pAAm hydrogels were prepared as previously reported [14,20]. Briefly, the monomer (AAm) and crosslinker (Bis) stocks were diluted to their desired concentrations in pH 7.2, 250 mM Tris-HCl buffer, followed by the addition of TEMED (0.1% of the final reaction volume) and 10% w/v APS solution (1% of the final reaction volume). For nanocomposite hydrogels, various amounts of silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) were added to the reaction mixture prior to the addition of APS and TEMED. Polymerization reactions were performed at 25 °C between parallel plates of the rheometer cell to minimize exposure to air as oxygen inhibits the free radical polymerization reaction.
4.3. Measurment of Hydrogel Elastic Modulus
Rheological measurements of the hydrogels were carried out, as previously described, using the MCR302 rotational rheometer (Antor Paar, Austria). Briefly, 500 μL of a well-mixed reaction mixture was pipetted onto the lower plate of the rheometer and the upper plate was lowered until the desired gap distance (1 mm) was achieved. Amplitude sweeps at a constant frequency of 1 Hz were then carried out to ensure measurements were carried out in the linear viscoelastic regime of the hydrogels. Next, dynamic sweep tests over frequencies ranging from 0.1 to 100 Hz were carried out in the linear viscoelastic regimes (strain amplitude = 0.01) to determine the shear storage modulus. Final hydrogel parameters were determined by following the gelation for 90 min at 1 Hz and 1% strain for all samples. Relative elastic moduli were calculated by normalizing the values for pAAm-SiNP hydrogels (G’NP) to the corresponding values for control pAAm gels (G’0).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the School of Engineering at Santa Clara University. Silica nanoparticles were a kind gift from AkzoNobel Pulp and Performance Chemicals Inc.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Liaw, C.Y.; Ji, S.; Guvendiren, M. Engineering 3D hydrogels for personalized in vitro human tissue models. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, N.A.; Huang, Y.; Torres-Lugo, M.; Ward, J.H.; Zhang, J. Physicochemical foundations and structural design of hydrogels in medicine and biology. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, T.; Goyal, A.K. Biomaterial-based scaffolds—Current status and future directions. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 767–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.; Gutowska, A. Lessons from nature: Stimuli-responsive polymers and their biomedical applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, J.; Jacob, K.I.; Tannenbaum, R.; Sharaf, M.A.; Jasiuk, I. Experimental trends in polymer nanocomposites—A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 393, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C. Structural and mechanical properties of polymer nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2006, 53, 73–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münstedt, H.; Triebel, C. Elastic properties of polymer melts filled with nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 2011, 1375, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopanos, P.; Schneider, G.A.; Dreyer, A.; Handge, U.A.; Filiz, V.; Feld, A.; Yilmaz, E.D.; Krekeler, T.; Ritter, M.; Weller, H.; et al. Exceptionally strong, stiff and hard hybrid material based on an elastomer and isotropically shaped ceramic nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangal, R.; Srivastava, S.; Archer, L.A. Phase stability and dynamics of entangled polymer-nanoparticle composites. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.H.; Yu, A.B.; Lu, G.Q. Multiscale modeling and simulation of polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 191–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Thomin, J.D.; Kumar, S.K.; Keblinski, P. Molecular underpinnings of the mechanical reinforcement in polymer nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 4059–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Mi, Y. Characterization of the interfacial interaction between polyacrylamide and silicon substrate by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zeng, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C. Effects of silica sol content on the properties of poly(acrylamide)/silica composite hydrogel. Polym. Bull. 2012, 68, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza, J.; Babhadiashar, N.; O’Brien, V.; Chang, A.; Blanco, M.; Zabalegui, A.; Lee, H.; Asuri, P. Experimental investigation of mechanical and thermal properties of silica nanoparticle-reinforced poly(acrylamide) nanocomposite hydrogels. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvet, D.; Wong, J.Y.; Giasson, S. Rheological monitoring of polyacrylamide gelation: Importance of cross-link density and temperature. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 7762–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibnia, V.; Taghavi, S.M.; Hill, R.J. Roles of chemical and physical crosslinking on the rheological properties of silica-doped polyacrylamide hydrogels. Rheol. Acta 2017, 56, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Gaharwar, A.K.; Chan, B.K.; Schmidt, G. Mechanically tough Pluronic F127/Laponite nanocomposite hydrogels from covalently and physically cross-linked networks. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 8215–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Peppas, N.A.; Khademhosseini, A. Nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical applications of hydrogels: A review of patents and commercial products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza, J.; Chang, A.; Asuri, P. Effect of crosslinker length on the elastic and compression modulus of poly(acrylamide) nanocomposite hydrogels. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 790, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).