1. Introduction
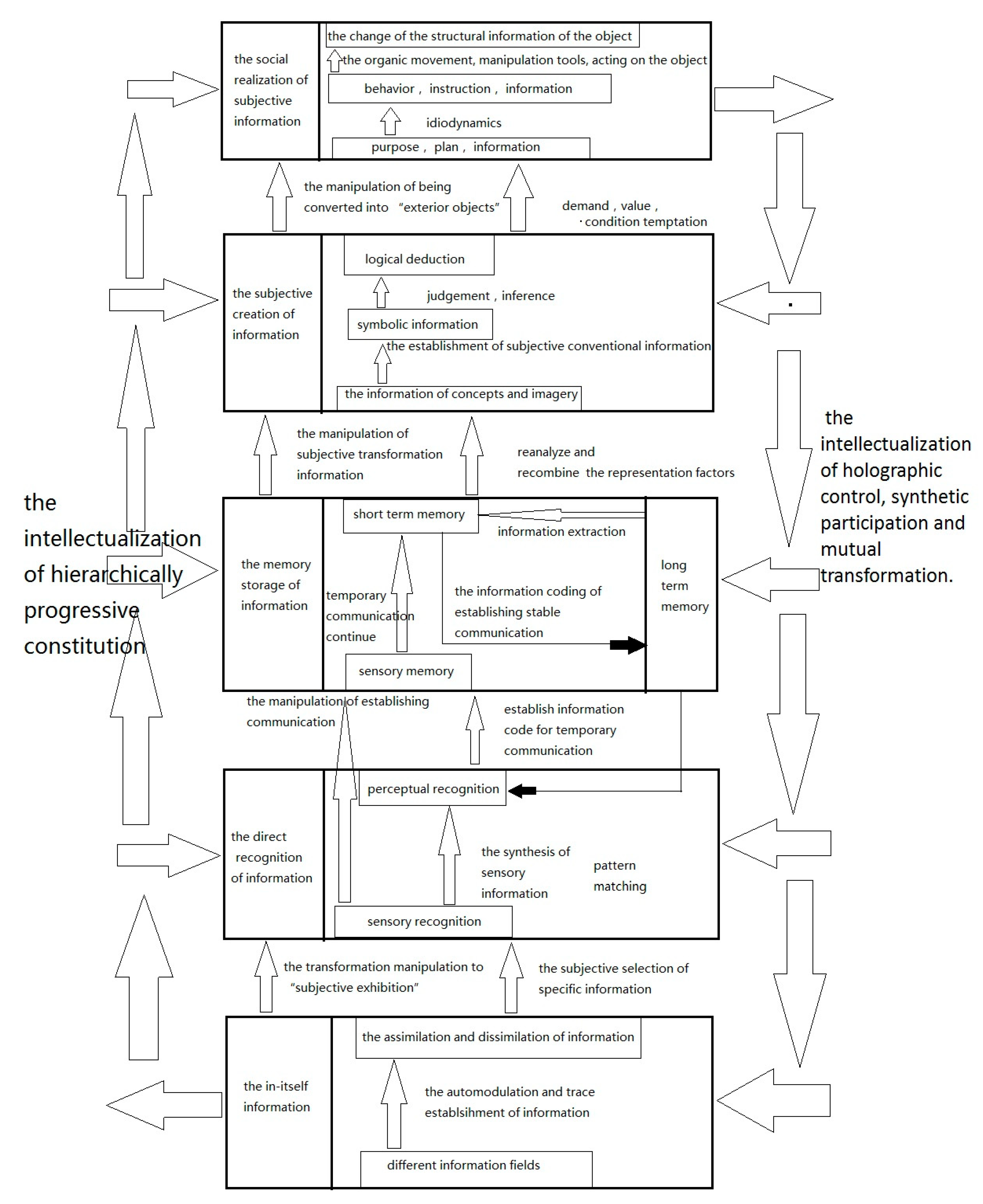
In the human activities, information, knowledge, intelligence and practice have a property of holographic unification. In-itself activity of information, intuitive identification of information, memory storage of information, subject creation of information and social realization of subject information have constituted five basic grades of subject information activity hierarchy from bottom to top. The intellectualization development of human information activities has two directions: one is bottom-up direction of intellectualization constitution and hierarchical progression and the other one is top-down direction of holographic control, comprehensive participation and mutual transformation of hierarchical intellectualization. This paper aims at articulate those concepts, and have a significance on the interdisciplinary study between cognitive science and information philosophy.
2. The Internal Integration of Philosophy and Science in the Unified Information Science
The division of science and philosophy is a basic way or path of development of modern human knowledge. The reason is that the traditional scientific paradigm and philosophical paradigm have lost their contents, processes, methods and mechanism of mutual engagement¸ integration and unification. The world view of absolute division between matter and spirit of human basic knowledge paradigm directly gives rise to the gradual departure with each other of philosophy and science. Thus, philosophy rejecting science and science rejecting philosophy have become natural things. This universal trait decides that a unified Information Science must runs through all human knowledge hierarchies and fields in nature, from philosophy to science to technology to engineering. Just based on this fundamental cognition, I advocate that “the Unified Information Science is an all-inclusive disciplinary system” [
1]. The inspiring thing is that, during a period of more than thirty years, the development of Information Science and Information Philosophy in China gradually presents a favorable state of mutual fusion, interpenetration, interweaving, reciprocal dependence and unification.
3. Several Basic Concepts and Their Relationship
Information: From the ontological perspective of philosophy, the information is an existence realm that is distinguished with matter realm. According to my definition, “the information is a philosophical category symbolizing the indirect existence, and it is the self-manifestation of the existing way and state of the matter (direct existence)” [
2]. The information has two major realms: objective information and subjective information. The Subjective information, also called the spirit, is just a portion (the advanced pattern of information activities) of information activities. Because the commonly referred phenomena, such as human knowledge, perception, memory, thinking, emotion, volition, wisdom(intelligence) and so on, all belong to spiritual phenomena, the extension of the concept of information ought to include all kinds of such phenomena, all the relevant concepts describing such phenomena are just sub-concepts of the concept of information.
Knowledge: The knowledge is obtained by cognizing and processing the information, which is a systematic information assemblage formed through information processing and creation of perception and thinking performed by cognitive subjects’ brains. Not only the origin of knowledge derives from subject perception, process and creation of information, but also the knowledge itself exists as information and belongs to a portion of information [
3].
Intelligence: Intelligence is a concept of mixing wisdom and ability of cognitive and practical subject. It not only includes commonly referred subject perceptual ability, memory capacity, cognitive ability and creativity of subject thought, but also covers practical ability of cognitive subject, in that the cognitive subject’s practical activities are intelligent behaviors with purpose and plan rather than general things’ unconscious and natural movements or relatively elementary organisms’ instinctive activities. From the most general meaning, the intelligence is the active modes and methods to grasp, manage, create, exploit, utilize and realize information (including knowledge) of subject possessing cognitive and practical abilities.
Practice: Practice has a nature of subject information activities, and practice is a behavioral process of advanced information activities under the control of subject intelligence. Information Philosophy has made a brand-new explanation to human practice and human production activities, believing that human practice is not pure material activities and it is a process of realizing the subject teleonomy information in object through implementing planning information. Information Philosophy not only concerns the practical activities of human material production, but also concerns many other production and practice forms, like human spiritual production, the production of human per se, the production of human interaction relationship and the virtualized production and so on, and treats those kinds of production and practice forms as a unified process of interweaving, internal integration and mutual dependence [
4]. According to matter (mass-energy) conservation principle and information non-conservation theory provided by science, Information Philosophy concludes that human production is not material production (because the matter cannot be created or eliminated, and here the matter is a general abstract concept in philosophy and science, which is different from “material things”), and can only be informational production (because the information could be created and also dissipate), and human productivity cannot be material productivity, but can only be informational productivity [
5].
4. The Holographic Unification of Information, Knowledge, Intelligence, Practice in Human Activities
Information Philosophy study in China regards human cognition and human practical activities as an information activity process of advanced information reflection, grasp, creation and realization. The in-itself activities of information, the direct recognition of information, the memory storage of information, the subject creation of information and the social realization of subject information have constitute five basic levels of subject information activity hierarchy from bottom to top. There exist specific modes and methods of information process and manipulation in and among those information activity levels, which is the function and embodiment of human intelligence. Under the guidance of human intelligence control, complex interaction exists among different human information activity levels. There are four basic principles presented in this unified process of interaction: the relation of progressive construction from bottom to top of human hierarchical information activities; the relation of holographic control from top to bottom of human hierarchical information activities; the relation of comprehensive participation of human hierarchical information activities; the relation of mutual transformation of human hierarchical information activities. The intellectualization development of human information activities has two directions: one is the bottom-up direction of intellectualization constitution and the other one is the top-down intellectualization direction of holographic control, synthetic participation and mutual transformation. The “
Figure 1” concisely indicates such holographic unification relationship of information, knowledge, intelligence and practice in human activities.