Numerical Modelling of the 3D Unsteady Flow of an Inlet Particle Separator for Turboshaft Engines †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
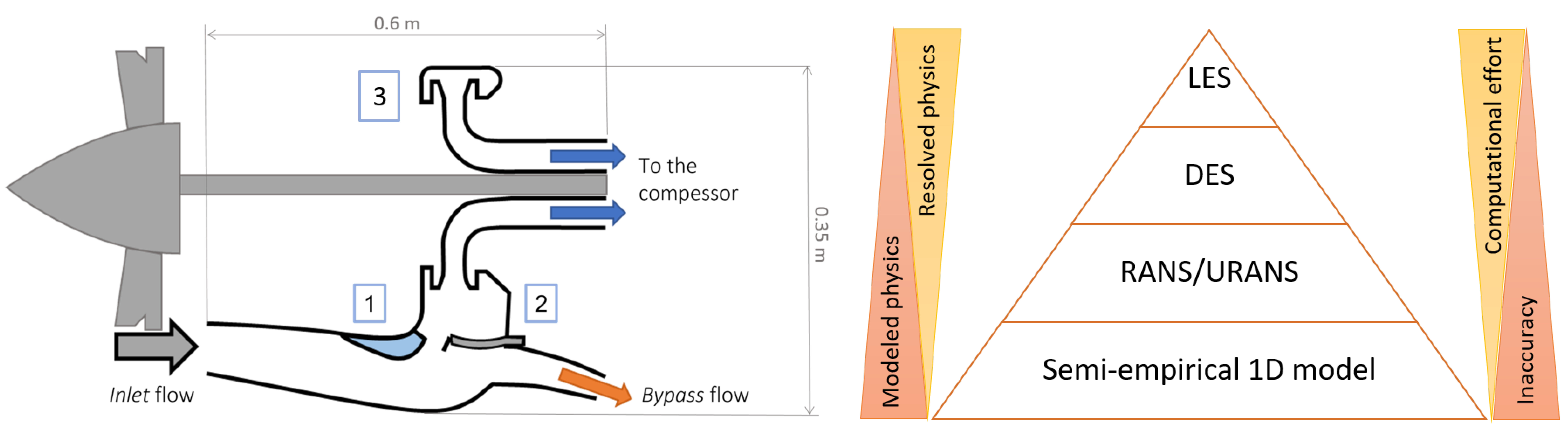
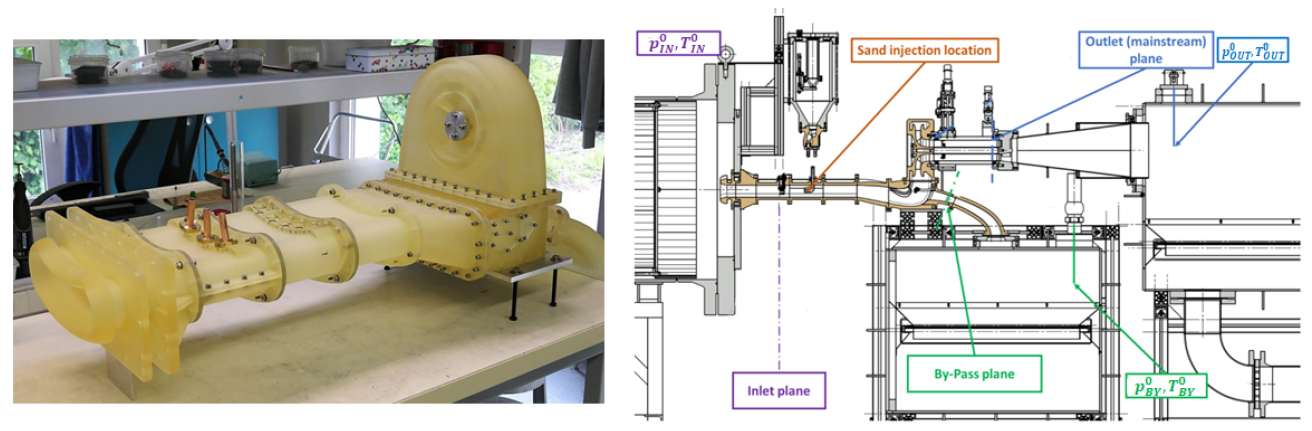
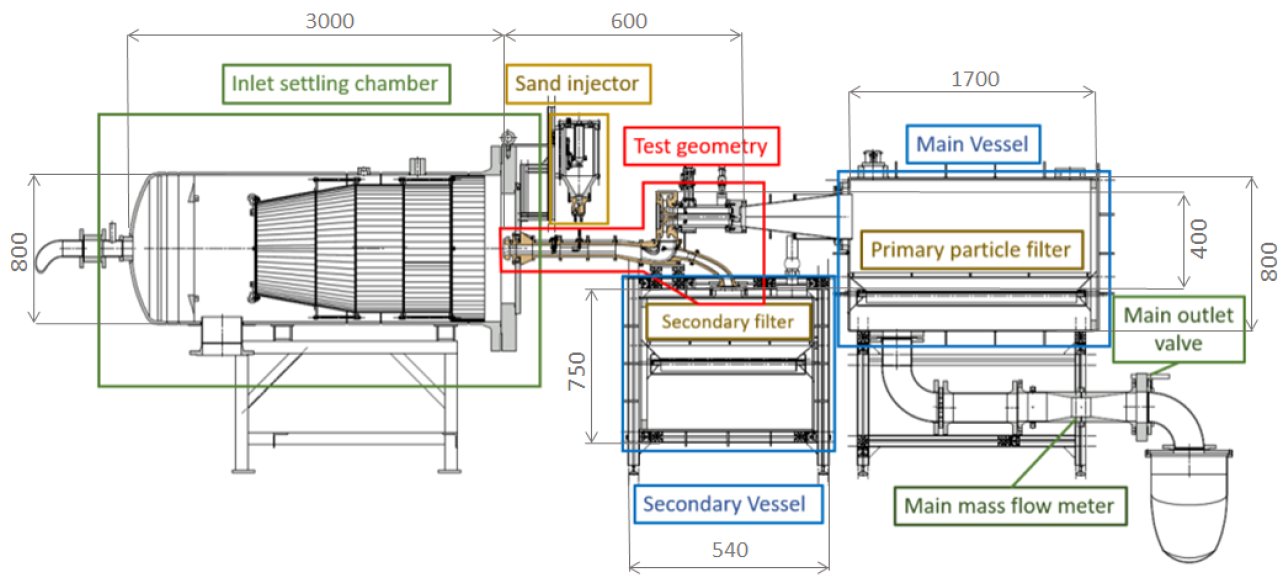
2. Experimental Layout
3. Numerical Setup
3.1. CFD Models
3.2. Semi-Empirical 1D Model
4. Results
4.1. Validation of the Numerical Models
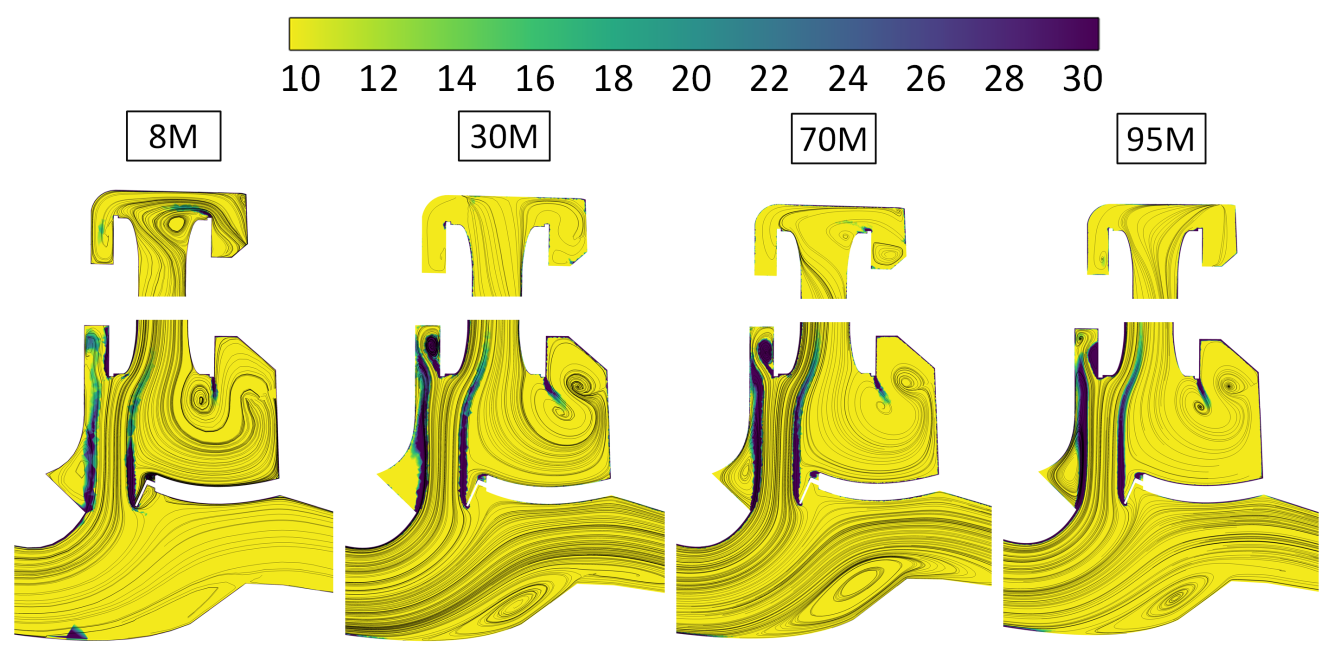
4.2. Unsteady Flow Characterization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Nomenclature
Abbreviations
| IPS | Inlet Particle Separator |
| DES | Detached Eddy Simulation |
| VKI | von Karman Institute |
| Bypass Ratio | |
| RANS | Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes |
| LES | Large Eddy Simulation |
| M | Million (cells) |
| TKE | Turbulent Kinetic Energy |
Nomenclature
| p | pressure |
| Reynolds number | |
| G | reduced mass flow rate |
| m | mass |
| dynamic viscosity | |
| P | wetted perimeter |
| T | temperature |
| pressure loss | |
| density | |
| v | velocity magnitude |
| relative total pressure difference | |
| separation efficiency | |
| k | turbulent kinetic energy |
| dissipation rate | |
| RANS computational time | |
| S | resolution factor |
| integral length scale | |
| approximate grid size | |
| vorticity magnitude | |
| H | inlet channel height |
| L | IPS longitudinal length |
| d | particle diameter |
| time step | |
| through-flow time | |
| A | cross-section area |
| R | air gas constant |
| specific heat ratio | |
| specific heat at constant pressure | |
| ratio of orifice to pipe diameter | |
| localized pressure difference | |
| compressibility factor | |
| total quantity | |
| outlet section | |
| flow rate | |
| bypass section | |
| inlet section | |
| average | |
| maximum | |
| normalized | |
| throat | |
| collector | |
| orifice | |
| sub-grid scale |
References
- Filippone, A.; Bojdo, N. Turboshaft engine air particle separation. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2010, 46, 224–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.; Tabakoff, W.C.; Wenglarz, R.V. Erosion and deposition in turbomachinery. J. Propuls. Power 2006, 22, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, D.; Loth, E.; Snyder, P.H. Particle Dynamics of a 2-D Inertial Particle Separator. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2014, Düsseldorf, Germany, 16–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Castaldi, M.; Mayo, I.; Demolis, J.; Eulitz, F. Numerical Modelling of the 3D, Unsteady Flow of an Inlet Particle Separator for Turboshaft Engines. In Proceedings of the 15th European Turbomachinery Conference, paper n. ETC2023-358. Budapest, Hungary, 24–28 April 2023; Available online: https://www.euroturbo.eu/publications/conference-proceedings-repository/ (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Barone, D.; Loth, E.; Snyder, P. A 2-d inertial particle separator research facility. In Proceedings of the 28th Aerodynamic Measurement Technology, Ground Testing, and Flight Testing Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–28 June 2012; p. 3290. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, D.; Hawkins, J.; Loth, E.; Snyder, P.H. Inertial particle separator efficiency using spherical particles. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 14–17 July 2013; p. 3666. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, A.; Jun, Y.D.; Yeuan, J.J. Particle dynamics simulations in inlet separator with an experimentally based bounce model. J. Propuls. Power 1995, 11, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, B.J.; Loth, E.; Snyder, P.H.; Smith, C.F. Influence of scavenge leg geometry on inertial particle separator performance. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 2019, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Benner, M.; Bird, J. Assessment of scavenge efficiency for a helicopter particle separation system. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 2012, 57, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J. Introduction to Error Analysis, the Study of Uncertainties in Physical Measurements, 1st ed.; 327 University Science Books: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Seifollahi Moghadam, Z.; Guibault, F.; Garon, A. On the evaluation of mesh resolution for large-eddy simulation of internal flows using OpenFOAM. Fluids 2021, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addad, Y.; Gaitonde, U.; Laurence, D.; Rolfo, S. Optimal unstructured meshing for large eddy simulations. Qual. Reliab. Large Eddy Simulations 2008, 12, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Moin, P. Grid-point requirements for large eddy simulation: Chapman’s estimates revisited. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 011702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoud, F.; Ducros, F. Subgrid-scale stress modelling based on the square of the velocity gradient tensor. Flow Turbul. Combust. 1999, 62, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5167-1:2003; Measurement of Fluid Flow by Means of Pressure Differential Devices Inserted in Circular Cross-Section Conduits Running Full—Part 1: General Principles and Requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/28064.html (accessed on 10 July 2023).


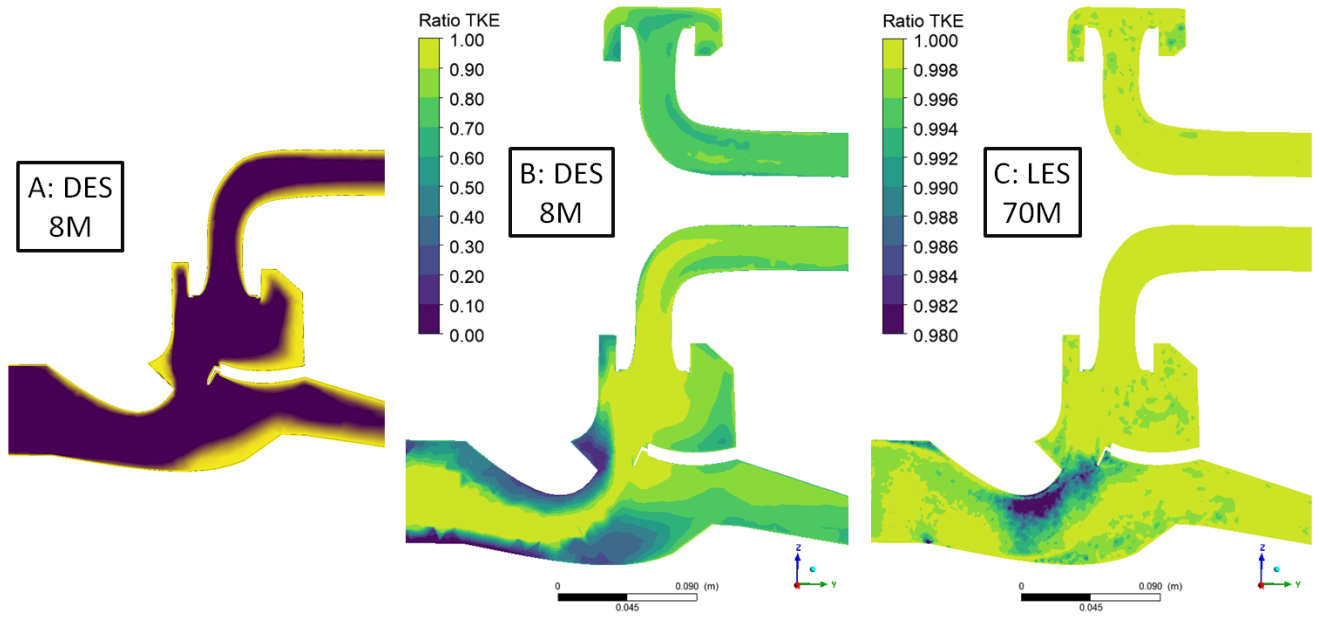
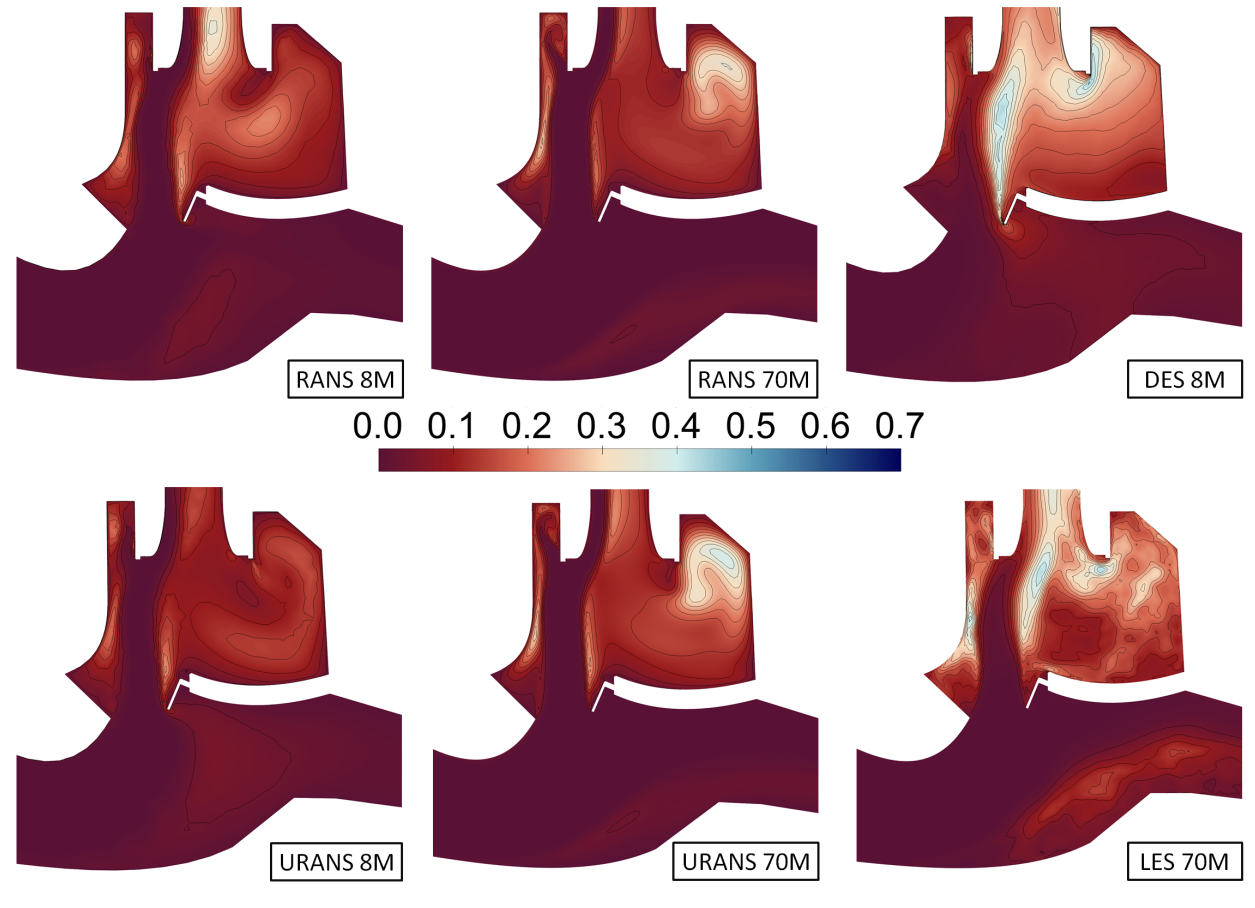
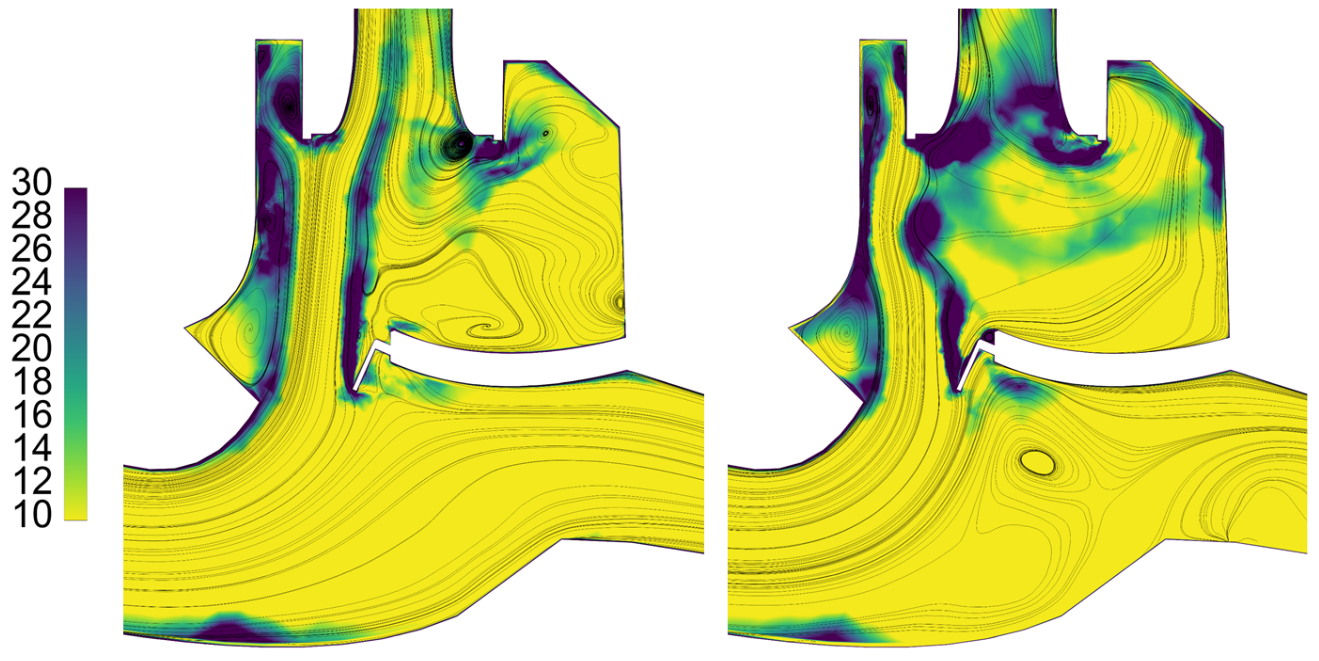
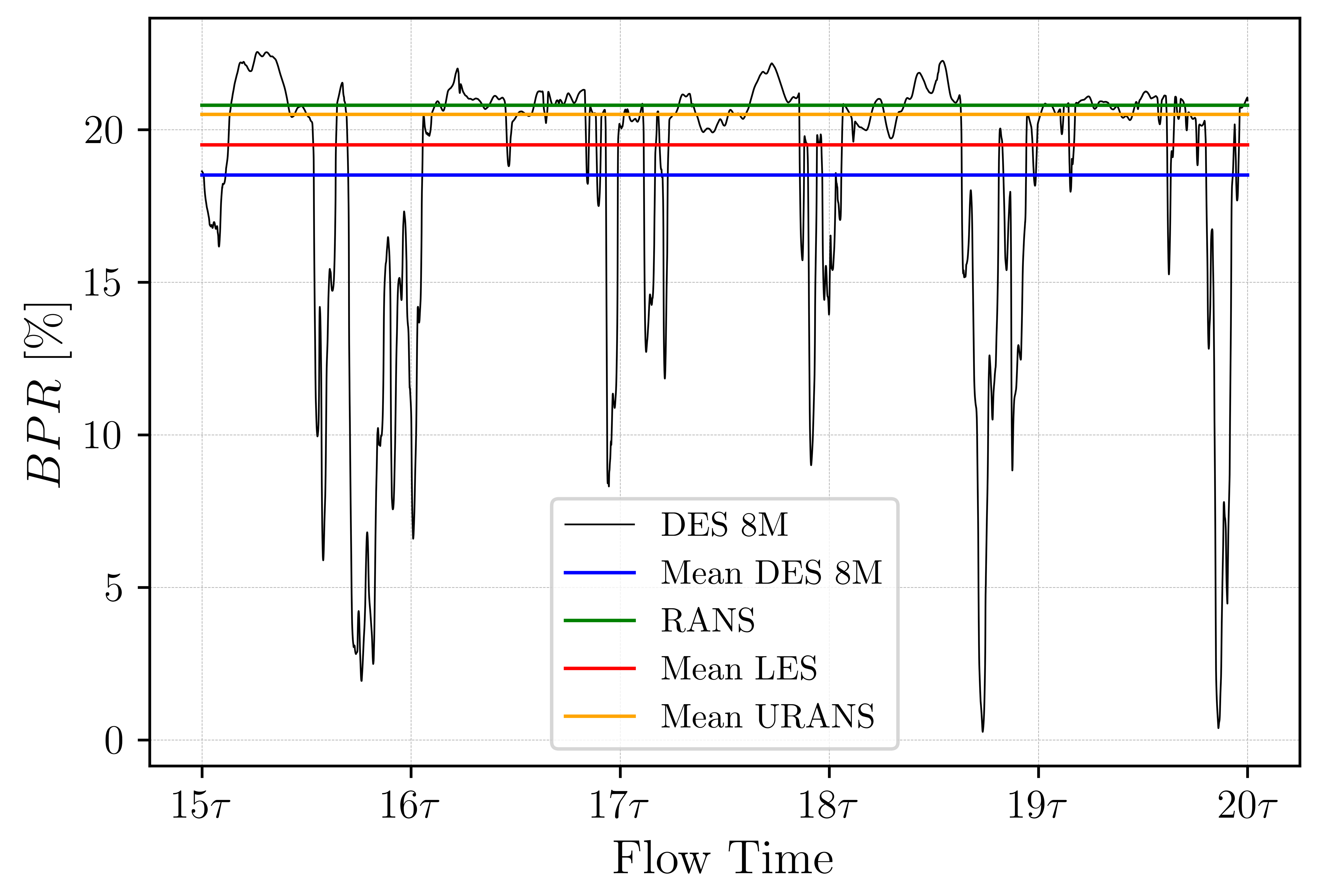

| Case | Total Pressure [ ] | Reynolds Number | Reduced Mass Flow Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 127,700 | 580,000 | 14.2 | 28% |
| 2 | 126,250 | 580,000 | 14.4 | 13% |
| 3 | 139,804 | 710,000 | 15.9 | 6% |
| 4 | 137,874 | 710,000 | 16.2 | 28% |
| 5 | 138,793 | 710,000 | 16.0 | 13% |
| 6 | 125,500 | 580,000 | 14.4 | 6% |
| Cell Count | (x,y,z) | AR | OQ | CPU Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 M | (500,80,200) | <20 | >0.19 | 58.4 | 774 | 7.84% | |
| 30 M | (875,125,350) | <23 | >0.20 | 45.6 | 189 | 7.90% | |
| 50 M | (925,150,400) | <31 | >0.12 | 41.6 | 159 | 8.05% | |
| 70 M | (1000,175,450) | <37 | >0.15 | 37.0 | 143 | 8.36% | |
| 95 M | (1100,185,475) | < | >0.01 | 34.9 | 125 | 8.21% |
| Case | Mesh | Model | CPU Time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 127,700 | 580,000 | 14.2 | 28% | 8 M | RANS, Steady PT | , |
| 2 | 126,250 | 580,000 | 14.4 | 13% | |||
| 3 | 139,804 | 710,000 | 15.9 | 6% | |||
| 4 | 137,874 | 710,000 | 16.2 | 28% | 8 M | RANS, Steady PT | , |
| 5 | 138,793 | 710,000 | 16.0 | 13% | DES | – | |
| 6 | 125,500 | 580,000 | 14.4 | 6% | URANS, Unsteady PT | , 190–260 | |
| 7 | 124,200 | 580,000 | 14.4 | 21% | Table 2 | RANS | Table 2 |
| 8 | 144,200 | 580,000 | 12.2 | 21% | 8 M | RANS DES | |
| 9 | 247,000 | 1,280,000 | 16.5 | 21% | 8 M 70 M | RANS, URANS, DES RANS, URANS, LES | , , , , |
| Case | Separation Efficiency (%) | Pressure Loss (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | BPR | Exp. | Unc. | Steady Tracking | Unsteady Tracking | Exp. | Unc. | 1D | RANS 8 M | URANS 8 M | DES 8 M |
| 1 | 28% | 78 | ±10 | 73 | - | 7.1 | ±1.3 | 7.33 | 7.11 | - | - |
| 2 | 13% | 59 | ±8 | 63 | - | 6.8 | ±1.3 | 6.72 | 7.09 | - | - |
| 3 | 6% | 49 | ±16 | 32 | - | 7.7 | ±1.2 | 8.28 | 8.53 | - | - |
| 4 | 28% | 82 | ±12 | 72 | 89 | 8.5 | ±1.2 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 9.50 | 9.52 |
| 5 | 13% | 64 | ±11 | 58 | 68 | 7.9 | ±1.2 | 8.77 | 9.74 | 9.41 | 7.92 |
| 6 | 6% | 45 | ±10 | 21 | 46 | 6.7 | ±1.3 | 6.56 | 7.01 | 7.40 | 7.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY-NC-ND) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castaldi, M.; Mayo, I.; Demolis, J.; Eulitz, F. Numerical Modelling of the 3D Unsteady Flow of an Inlet Particle Separator for Turboshaft Engines. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2023, 8, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp8040052
Castaldi M, Mayo I, Demolis J, Eulitz F. Numerical Modelling of the 3D Unsteady Flow of an Inlet Particle Separator for Turboshaft Engines. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power. 2023; 8(4):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp8040052
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastaldi, Marco, Ignacio Mayo, Jacques Demolis, and Frank Eulitz. 2023. "Numerical Modelling of the 3D Unsteady Flow of an Inlet Particle Separator for Turboshaft Engines" International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power 8, no. 4: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp8040052
APA StyleCastaldi, M., Mayo, I., Demolis, J., & Eulitz, F. (2023). Numerical Modelling of the 3D Unsteady Flow of an Inlet Particle Separator for Turboshaft Engines. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power, 8(4), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp8040052





