Splenic Embolism in Infective Endocarditis: A Systematic Review of the Literature with an Emphasis on Radiological and Histopathological Diagnoses
Abstract
1. Introduction
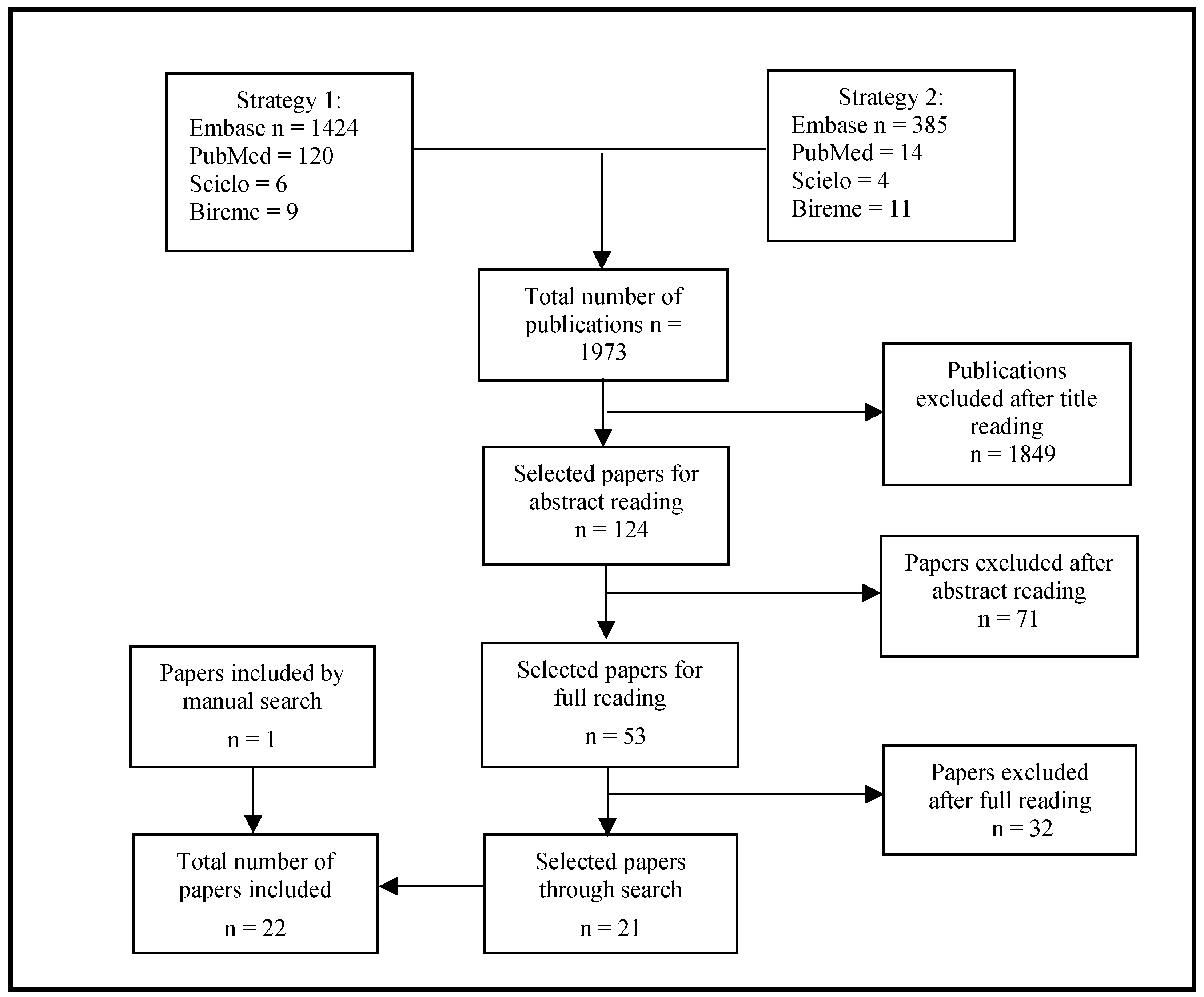
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Habib, G.; Hoen, B.; Tornos, P.; Thuny, F.; Prendergast, B.; Vilacosta, I.; Moreillon, P.; Antunes, M.d.J.; Thilen, U.; Lekakis, J.; et al. Guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of infective endocarditis (new version 2009): The Task Force on the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2009, 30, 2369–2413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baddour, L.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Bayer, A.S.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Tleyjeh, I.M.; Rybak, M.J.; Barsic, B.; Lockhart, P.B.; Gewitz, M.H.; Levison, M.E.; et al. Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications: A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 132, 1435–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, T.L.; Baddour, L.M.; Bayer, A.S.; Hoen, B.; Miro, J.M.; Fowler, V.G. Infective endocarditis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, V.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; de Waha, S.; Bonaros, N.; Brida, M.; Burri, H.; Caselli, S.; Doenst, T.; Ederhy, S.; Erba, P.A.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, G.; Lancellotti, P.; Antunes, M.J.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Casalta, J.-P.; Del Zotti, F.; Dulgheru, R.; El Khoury, G.; Erba, P.A.; Iung, B.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: The Task Force for the Management of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 3075–3128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gould, F.K.; Denning, D.W.; Elliott, T.S.J.; Foweraker, J.; Perry, J.D.; Prendergast, B.D.; Sandoe, J.A.T.; Spry, M.J.; Watkin, R.W. Guidelines for the diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of endocarditis in adults: A report of the Working Party of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilacosta, I.; Graupner, C.; San Román, J.A.; Sarriá, C.; Ronderos, R.; Fernández, C.; Mancini, L.; Sanz, O.; Sanmartín, J.V.; Stoermann, W. Risk of embolization after institution of antibiotic therapy for infective endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, M.W. Ultrasound of the Spleen. World J. Surg. 2000, 24, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancauwenberghe, T.; Snoeckx, A.; Vanbeckevoort, D.; Dymarkowski, S.; Vanhoenacker, F.M. Imaging of the spleen: What the clinician needs to know. Singap. Med. J. 2015, 56, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieciecki, M.; Kożuch, M.; Czarniecki, M.; Mlosek, R.K.; Michno, A.; Olszewski, W.; Danowska, A.; Królicki, L. How to diagnose splenic abscesses? Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2019, 82, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luaces Méndez, M.; Vilacosta, I.; Sarriá, C.; Fernández, C.; San Román, J.A.; Sanmartín, J.V.; López, J.; Rodríguez, E. Endocarditis infecciosa y embolias del eje hepatoesplenorrenal [Hepatosplenic and renal embolisms in infective endocarditis]. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2004, 57, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iung, B.; Klein, I.; Mourvillier, B.; Olivot, J.-M.; Détaint, D.; Longuet, P.; Ruimy, R.; Fourchy, D.; Laurichesse, J.-J.; Laissy, J.-P.; et al. Respective effects of early cerebral and abdominal magnetic resonance imaging on clinical decisions in infective endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 13, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Lu, Q.; Xu, J.; Huang, J.; Gao, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Du, L.; Yan, F. Value of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in the Differential Diagnosis of Focal Splenic Lesions. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 2947–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, L.Z.; Shrestha, N.K.; Dang, V.; Unai, S.; Pettersson, G.; El-Hayek, K.; Coppa, C.; Gordon, S.M. Surgical infective endocarditis and concurrent splenic abscess requiring splenectomy: A case series and review of the literature. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 97, 115082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peddu, P.; Shah, M.; Sidhu, P.S. Splenic abnormalities: A comparative review of ultrasound, microbubble-enhanced ultrasound and computed tomography. Clin. Radiol. 2004, 59, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colen, T.W.; Gunn, M.; Cook, E.; Dubinsky, T. Radiologic manifestations of extra-cardiac complications of infective endocarditis. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 2433–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaya, A.; Weinstein, S.; Desser, T.S. Multiple Lesions of the Spleen: Differential Diagnosis of Cystic and Solid Lesions. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2006, 27, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonolini, M.; Bianco, R. Nontraumatic splenic emergencies: Cross-sectional imaging findings and triage. Emerg. Radiol. 2013, 20, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprinz, C.; Altmayer, S.; Zanon, M.; Watte, G.; Irion, K.; Marchiori, E.; Hochhegger, B. Effects of blood glucose level on 18F-FDG uptake for 18F FDG PET/CT in normal organs: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursier, C.; Duval, X.; Mahida, B.; Hoen, B.; Goehringer, F.; Selton-Suty, C.; Chevalier, E.; Roch, V.; Lamiral, Z.; Bourdon, A.; et al. Hypermetabolism of the spleen or bone marrow is an additional albeit indirect sign of infective endocarditis at FDG-PET. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2020, 28, 2533–2542. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s12350-020-02050-2 (accessed on 3 June 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, J.A.; Hernández, L.; Muñoz, P.; Blanco, G.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, R.; Vilar, D.R.; de Alarcón, A.; Goenaga, M.A.; Moreno, M.; Fariñas, M.C. Detection of spleen, kidney and liver infarcts by abdominal computed tomography does not affect the outcome in patients with left-side infective endocarditis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, X.; Iung, B. Extracardiac Imaging of Infective Endocarditis. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2017, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhyari, P.; Mehrabi, A.; Adhiwana, A.; Kamiya, H.; Nimptsch, K.; Minol, J.-P.; Tochtermann, U.; Godehardt, E.; Weitz, J.; Lichtenberg, A.; et al. Is simultaneous splenectomy an additive risk factor in surgical treatment for active endocarditis? Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2012, 397, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, W.; Silverman, N.A.; Arzouman, D.A.; Levitsky, S. Splenic Septic Emboli in Endocarditis. Circulation 1990, 82, IV105–IV109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, T.S.; Correia, M.G.; Golebiovski, W.F.; Barbosa, G.I.F.; Weksler, C.; Lamas, C.C. Asymptomatic and symptomatic embolic events in infective endocarditis: Associated factors and clinical impact. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 21, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanos, L.; Dailiana, T.; Papaioannou, G.; Nikita, A.; Koutrouvelis, H.; Kelekis, D.A. Percutaneous CT-Guided Drainage of Splenic Abscess. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 179, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davido, B.; Dinh, A.; Rouveix, E.; Crenn, P.; Hanslik, T.; Salomon, J. Abcès de la rate: Du diagnostic au traitement. Rev. Méd. Intern. 2017, 38, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, S.; Libson, E.; Sella, T.; Lebensart, P.; Sosna, J. Percutaneous Image-Guided Splenic Procedures: Update on Indications, Technique, Complications, and Outcomes. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2007, 28, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, G.; Erba, P.A.; Iung, B.; Donal, E.; Cosyns, B.; Laroche, C.; Popescu, B.A.; Prendergast, B.; Tornos, P.; Sadeghpour, A.; et al. Clinical presentation, aetiology and outcome of infective endocarditis. Results of the ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO (European infective endocarditis) registry: A prospective cohort study. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3222–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalaei-Andabili, S.H.; Martin, T.; Hess, P.; Hoh, B.; Anderson, M.; Klodell, C.T.; Beaver, T.M. Management of Septic emboli in patients with infectious endocarditis. J. Card. Surg. 2017, 32, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Salvo, G.; Habib, G.; Pergola, V.; Avierinos, J.-F.; Philip, E.; Casalta, J.-P.; Vailloud, J.-M.; Derumeaux, G.; Gouvernet, J.; Ambrosi, P.; et al. Echocardiography Predicts Embolic Events in Infective Endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deprèle, C.; Berthelot, P.; Lemetayer, F.; Comtet, C.; Fresard, A.; Cazorla, C.; Fascia, P.; Cathébras, P.; Chaumentin, G.; Convert, G.; et al. Risk factors for systemic emboli in infective endocarditis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuny, F.; Di Salvo, G.; Belliard, O.; Avierinos, J.F.; Pergola, V.; Rosenberg, V.; Casalta, J.P.; Gouvernet, J.; Derumeaux, G.; Iarussi, D.; et al. Risk of embolism and death in infective endocarditis: Prognostic value of echocardiography: A prospective multicenter study. Circulation 2005, 112, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Riet, J.; Hill, E.E.; Gheysens, O.; Dymarkowski, S.; Herregods, M.-C.; Herijgers, P.; Peetermans, W.E.; Mortelmans, L. 18F-FDG 18F FDG PET/CT for early detection of embolism and metastatic infection in patients with infective endocarditis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erba, P.A.; Conti, U.; Lazzeri, E.; Sollini, M.; Doria, R.; De Tommasi, S.M.; Bandera, F.; Tascini, C.; Menichetti, F.; Dierckx, R.A.; et al. Added Value of 99m Tc-HMPAO–Labeled Leukocyte SPECT/CT in the Characterization and Management of Patients with Infectious Endocarditis. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menozzi, G.; Maccabruni, V.; Gabbi, E.; Leone, N.; Calzolari, M. Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound Evaluation of Splenic Embolization in Patients with Definite Left-Sided Infective Endocarditis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 2205–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfiglioli, R.; Nanni, C.; Morigi, J.J.; Graziosi, M.; Trapani, F.; Bartoletti, M.; Tumietto, F.; Ambrosini, V.; Ferretti, A.; Rubello, D.; et al. 18F-FDG 18F FDG PET/CT diagnosis of unexpected extracardiac septic embolisms in patients with suspected cardiac endocarditis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kestler, M.; Muñoz, P.; Rodríguez-Créixems, M.; Rotger, A.; Jimenez-Requena, F.; Mari, A.; Orcajo, J.; Hernández, L.; Alonso, J.C.; Bouza, E.; et al. Role of 18 F-FDG PET in Patients with Infectious Endocarditis. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmar, A.; Ozcan, C.; Diederichsen, A.C.P.; Thomassen, A.; Gill, S. Clinical impact of 18F-FDG- PET/CT in the extra cardiac work-up of patients with infective endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 15, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, M.; Ravasio, V.; Carobbio, A.; Mattucci, I.; Crapis, M.; Stellini, R.; Pasticci, M.B.; Chinello, P.; Falcone, M.; Grossi, P.; et al. Predicting the occurrence of embolic events: An analysis of 1456 episodes of infective endocarditis from the Italian Study on Endocarditis (SEI). BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomäki, S.P.; Saraste, A.; Kemppainen, J.; Bax, J.J.; Knuuti, J.; Nuutila, P.; Seppänen, M.; Roivainen, A.; Airaksinen, J.; Pirilä, L.; et al. 18F-FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography in infective endocarditis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2015, 24, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Izumi, C.; Miyake, M.; Imanaka, M.; Kuroda, M.; Nishimura, S.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Amano, M.; Imamura, S.; Onishi, N.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the Embolic Risk French Calculator for symptomatic embolism with infective endocarditis among Japanese population. J. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouijzer, I.J.; Berrevoets, M.A.; Aarntzen, E.H.; de Vries, J.; van Dijk, A.P.; Oyen, W.J.; de Geus-Oei, L.-F.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography combined with computed tomography as a diagnostic tool in native valve endocarditis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2018, 39, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selton-Suty, C.; Maigrat, C.-H.; Devignes, J.; Goehringer, F.; Erpelding, M.-L.; Alla, F.; Thivilier, C.; Huttin, O.; Venner, C.; Juilliere, Y.; et al. Possible relationship between antiphospholipid antibodies and embolic events in infective endocarditis. Heart 2018, 104, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecomte, R.; Issa, N.; Gaborit, B.; Le Turnier, P.; Deschanvres, C.; Asseray, N.; Le Tourneau, T.; Michel, M.; Al Habash, O.; Bizouarn, P.; et al. Risk-benefit Assessment of Systematic Thoracoabdominal-pelvic Computed Tomography in Infective Endocarditis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San, S.; Ravis, E.; Tessonier, L.; Philip, M.; Cammilleri, S.; Lavagna, F.; Norscini, G.; Arregle, F.; Martel, H.; Oliver, L.; et al. Prognostic Value of 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Infective Endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holle, S.L.K.; Andersen, M.H.; Klein, C.F.; Bruun, N.E.; Tønder, N.; Haarmark, C.; Loft, A.; Høilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Bundgaard, H.; Iversen, K.K. Clinical usefulness of FDG-FDG PET/CT for identification of abnormal extra-cardiac foci in patients with infective endocarditis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 36, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ruegamer, T.; Brochhausen, C.; Menhart, K.; Hiergeist, A.; Kraemer, L.; Hellwig, D.; Maier, L.S.; Schmid, C.; Jantsch, J.; et al. Infective Endocarditis: Predictive Factors for Diagnosis and Mortality in Surgically Treated Patients. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjabaly Mandjee, A.; Filippetti, L.; Goehringer, F.; Duval, X.; Botelho-Nevers, E.; Tribouilloy, C.; Huguet, R.; Chirouze, C.; Erpelding, M.L.; Hoen, B.; et al. Characteristics of patients with infective endocarditis and no underlying cardiac conditions. Infect. Dis. 2022, 54, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucciferri, C.; Auricchio, A.; Cutone, C.; Di Gasbarro, A.; Vecchiet, J.; Falasca, K. Risk Factors Associated with Poor Outcome in Patients with Infective Endocarditis: An Italian Single-Center Experience. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández Guerrero, M.L.; Álvarez, B.; Manzarbeitia, F.; Renedo, G. Infective endocarditis at autopsy: A review of pathologic manifestations and clinical correlates. Medicine 2012, 91, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlot, G.; Calderan, C.; Fiorenza, C.; Cappelli, D.; Addesa, S.; Bussani, R. Infective and non-infective endocarditis in critically ill patients: A clinical–pathological study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2014, 9, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohananey, D.; Mohadjer, A.; Pettersson, G.; Navia, J.; Gordon, S.; Shrestha, N.; Grimm, R.A.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Griffin, B.P.; Desai, M.Y. Association of Vegetation Size with Embolic Risk in Patients with Infective Endocarditis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, V.G.; Durack, D.T.; Selton-Suty, C.; Athan, E.; Bayer, A.S.; Chamis, A.L.; Dahl, A.; DiBernardo, L.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Duval, X.; et al. The 2023 Duke-International Society for Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases Criteria for Infective Endocarditis: Updating the Modified Duke Criteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 77, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besson, F.L.; Treglia, G.; Bucerius, J.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Buechel, R.R.; Dweck, M.R.; Erba, P.A.; Gaemperli, O.; Gimelli, A.; Gheysens, O.; et al. A systematic review for the evidence of recommendations and guidelines in hybrid nuclear cardiovascular imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
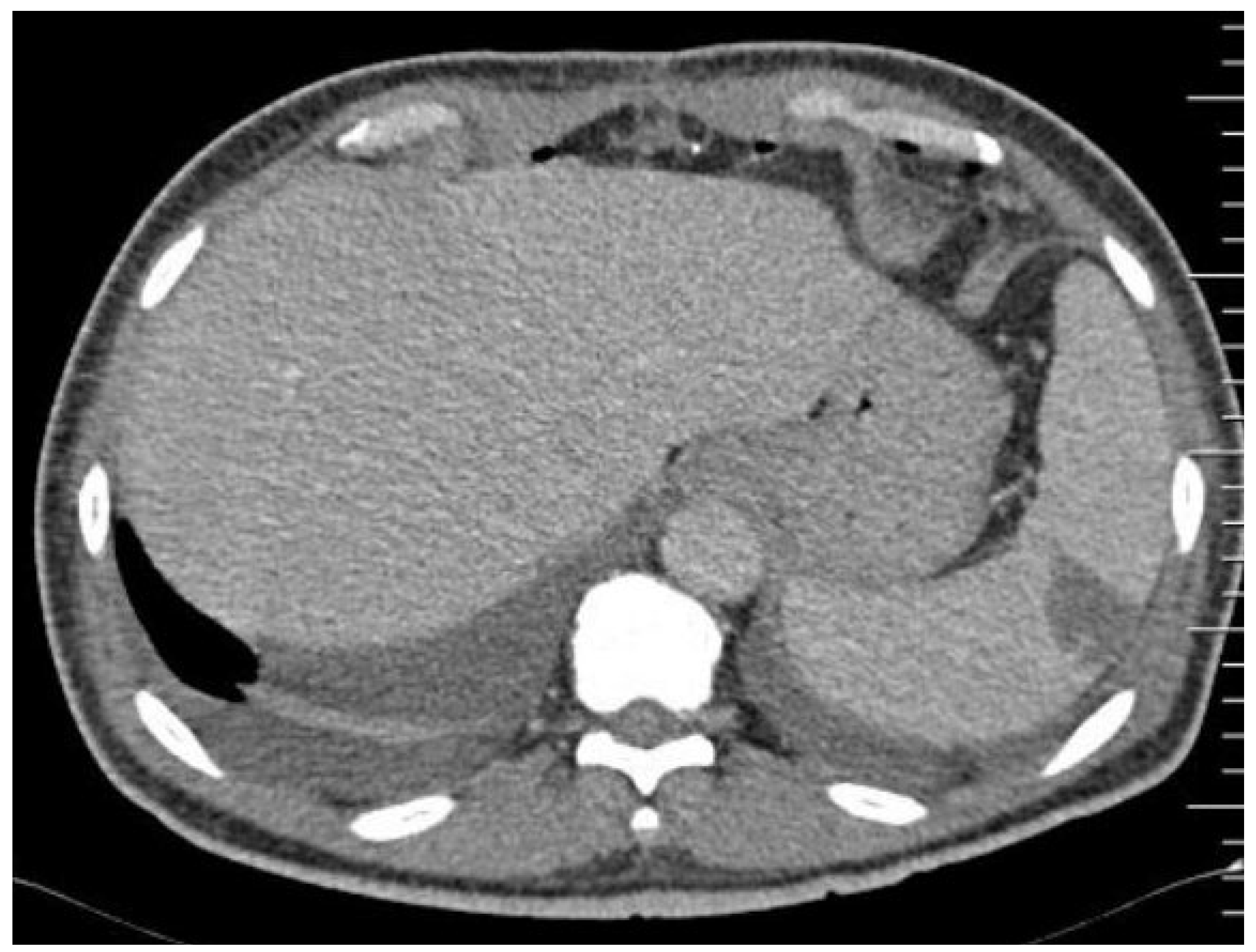
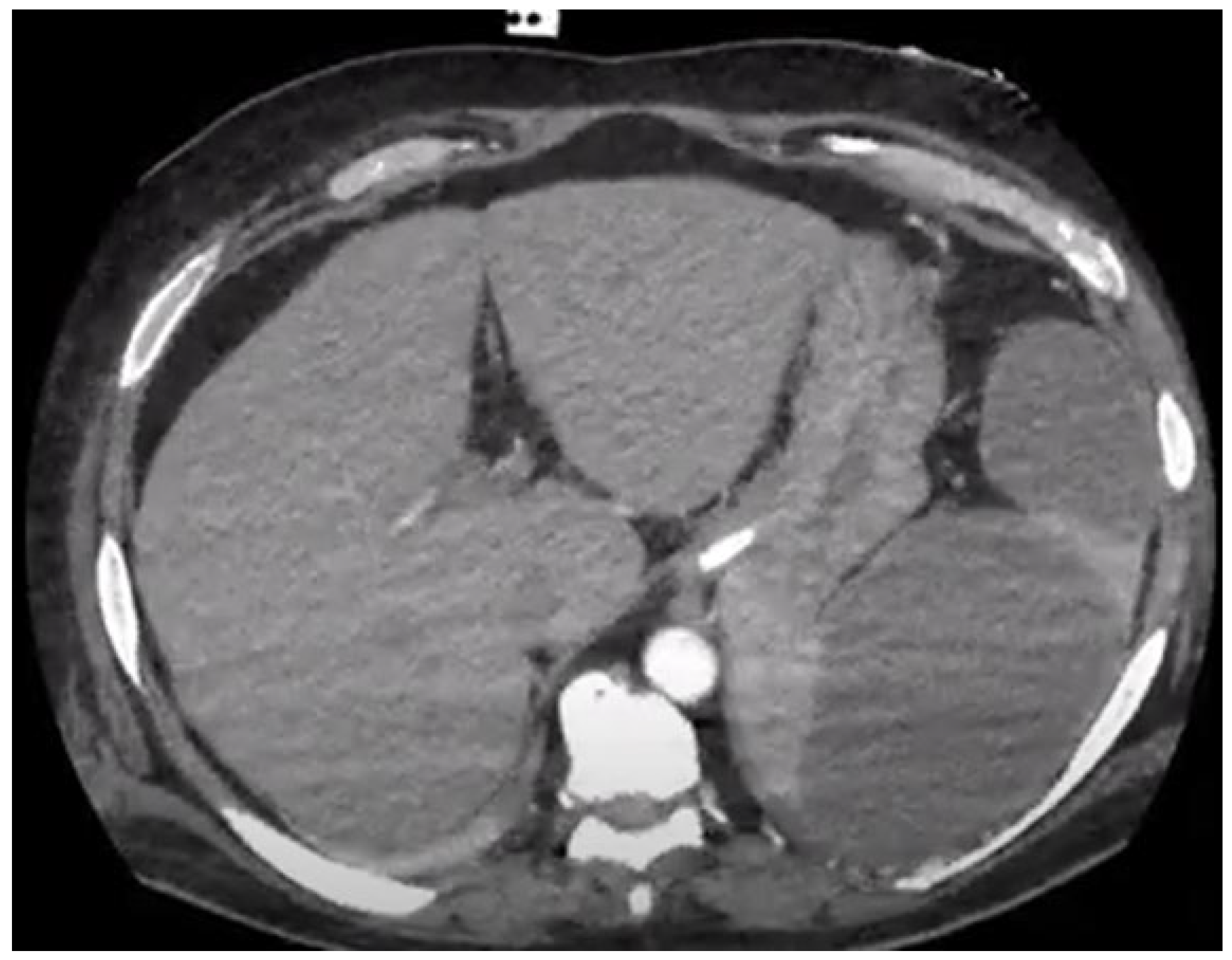

| Author, Year, Country | Number of Episodes of Left-Sided IE | Splenic Emboli n (%) | Radiological Examination Method Used | Emboli to the CNS n (%) | Cardiac Surgery for IE n (%) | In-Hospital or 30-Day Mortality (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Di Salvo et al., 2001, France [32] | 174 | 14/174 (8%) | CT Performed routinely for 167/178 (93.8%) patients | 27/174 (15.5%) | 109/178 (61%) | 19/178 (10.7%) |
| Vilacosta et al., 2002, Argentina and France [7] | 217 91% definite IE | 6/34 (18%) | CT Not routinely performed | 52% | 115/217 (53%) | 42.9% of those with emboli; 30.2% of those without emboli |
| Deprele et al., 2004, France [33] | 80 | 27% | CT Not clear if performed systematically | 34% | 30/80 (37.5%) | 7/80 (8.8%) |
| Thuny et al. 2005, France and Italy [34] | 350 | 49/350 (14%) | CT Systematically performed at study entry | 62/350 (17.7%) | 52.3% | 37/350 (9.6%) |
| Luaces Méndez et al., 2004, Spain [11] | 338 | 34/338 (10%); 4/34 (11.8%) splenic abscess | US 30/34 (88.2%) or CT 26/34 (67.6%) Guided by signs/symptoms | 77/338 (22.7%); 18/34 (52.9%) | 181/338 (53.5%) | 107/338 (31.6%) |
| Van Riet et al., 2010, Belgium [35] | 25 | 6/25 (24%) | 18F-FDG PET/CT Performed systematically 2 weeks after IE diagnosis | NA | 17/25 (68%) | 1/25 (4%) |
| Erba et al., 2012, Italy [36] | 51 | 4/51 (7.8%) | SPECT/CT Performed in all patients | NA | NA | NA |
| Menozzi et al., 2013, Italy [37] | 6 | 5/6 (83.3%) | CEUS Performed in all patients within 10 days after IE diagnosis | NA | NA | NA |
| Bonfiglioli et al., 2013, Italy [38] | 29/71 unclear if left-sided or right-sided IE | 1/17 (5.9%) | 18F-FDG PET/CT Performed systematically | NA | NA | NA |
| Kestler et al., 2014, Spain [39] | 38/47 | 3/47 (6.4%) | 18F-FDG PET/CT Performed systematically | 3/47 (6.4%) | 30/47 (63.8%) | NA |
| Asmar et al., 2014, Denmark [40] | 72 (majority left-sided IE) | 1/72 (1.4%) abscess | PET/CT Performed systematically | NA | 44% | 15% |
| Rizzi et al., 2014, Italy [41] | 1456 − (89 + 61) = 1306 (definite and possible) | 113/1306 (8.6%) | CT Not performed systematically | 242/1306 (18.5%) | NA | NA |
| Salomäki et al., 2015, Finland [42] | 11/12 | 1/12 (8.3%) | 18F-FDG PET/CT Performed systematically | NA | 5/12 (41.7%) | 1/12 (8.3%) |
| Aalaei-andalabi et al., 2017, United States of America [31] | 437 surgical IE; 46 studied for emboli | 33/46 (71.7%) | CT Guided by signs/symptoms | 29/46 (63%) | 100% | 8.7% |
| Monteiro et al., 2017, Brazil [25] | 119/136 (87.5%) | 44/136 (32.8%) | CT All patients | 32/136 (23.5%) | 98/136 (72%) | 24% |
| Takahashi et al., 2017, Japan [43] | 166 | 5/166 (3%) “new emboli” | CT or MRI All patients | 28/166 (17%) | 87/166 (52%) | 19% |
| Kouijzer et al., 2018, Netherlands [44] | 10/88 (not specified if left-sided or right-sided) | 7.9% splenic abscesses (definite and possible IE) | 18F-FDG PET/CT All patients | NA | NA | NA |
| Parra et al., 2018, Spain [21] | 147 | 44/147 (29.9%) | CT All included patients; 1/3 due to symptoms | 37/147 (25.1%) | 72/147 (48.9%) | 34/147 (23.1%) |
| Selton-Suty et al., 2018, France [45] | 133 | 46/133 (34.6%) | CT Routinely performed for all patients, but 57 were symptomatic | 52/133 (39%) | 89/186 (48%) | 29/186 (16%) |
| Lecomte et al., 2019, France [46] | 477/522 (91.4%) | 131/522 (25.1%) | CT (thoraco–abdominal–pelvic) All patients | NA | NA | 82/522 (15.8%) overall; 65/316 (20.6%) with emboli |
| Habib et al., 2019, multicentre, predominantly European [30] | 3116 (308 were device-related) | 10.1% overall; 22.3% of embolic events on admission | CT, 18F-FDG PET/ CT SPECT/CT All as per centre | 350/788 (44.4%) | 1596/3116 (51.2%) | 17.1% |
| Boursier et al., 2019, France [20] | 88/129 | 62/88 (71%) diffuse splenic hypermetabolism | 18F-FDG PET/CT Performed systematically | NA | NA | NA |
| San et al., 2019, France [47] | 173 | 24/173 (13.8%) | 18F-FDG PET/CT Systematic | NA | 93/173 (54%) | 14/173 (8%) |
| Holle et al., 2020, Denmark [48] | 169/178 definite left-sided IE | 11/169 (6.5%) | 18F-FDG PET/CT Performed systematically | NA | 71/178 (40%) | 13/178 (7%) |
| Li et al., 2022, Germany [49] | 201 | 21/215 (9.8%); 21/62 (33.8%) of those who had 18F-FDG PET/CT | 18F-FDG PET/CT Performed preferably in PVE | 77/215 (35.8%) | 201/201 (100%) | 32/215 (14.9%) |
| Radjabaly Mandjee et al., 2022, France [50] | 1502 − 80 = 1422 | 325/1502 (21.63%) | MSCT in 1319 patients 18F-FDG PET/CT in 217 patients | 552/1502 (36.8%) | 53.5% and 36.3% | 550/1488 (37%) |
| Ucciferri et al., 2022, Italy [51] | 68 | 12/68 (17.6%) | MRI-18F-FDG PET/CT Not systematically performed | 7/68 (10.3%) | NA | 20.6% |
| Author, Year, Country | Number of Patients Studied, Type of Valve | Method of Analysis | Mean Age (Years) | Splenic Embolism n (%) | Splenic Findings n (%) | Emboli to the CNS n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fernández Guerrero et al., 2019, Spain [52] | 68 40P1 28P2 60 left-sided IE | Autopsy | 46.6—Period 1 57.6—Period 2 | 27/60 (45%) | Infarct: 22/27 (81.5%) Abscess: 5/27 (18.5%) | 20/68 (29.4%) |
| Berlot et al., 2014, Italy [53] | 12 | Autopsy | 66 | 4/12 (33.3%) | NA | 5/12 (41.6%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, G.S.; Feijóo, N.d.A.P.; Tinoco-da-Silva, I.B.; Aguiar, C.M.; da Conceição, F.O.; de Castro, G.C.M.; de Carvalho, M.G.B.; de Almeida, T.V.d.P.A.; Garrido, R.Q.; Lamas, C.d.C. Splenic Embolism in Infective Endocarditis: A Systematic Review of the Literature with an Emphasis on Radiological and Histopathological Diagnoses. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9040083
Moreira GS, Feijóo NdAP, Tinoco-da-Silva IB, Aguiar CM, da Conceição FO, de Castro GCM, de Carvalho MGB, de Almeida TVdPA, Garrido RQ, Lamas CdC. Splenic Embolism in Infective Endocarditis: A Systematic Review of the Literature with an Emphasis on Radiological and Histopathological Diagnoses. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2024; 9(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9040083
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Gabriel Santiago, Nícolas de Albuquerque Pereira Feijóo, Isabella Braga Tinoco-da-Silva, Cyntia Mendes Aguiar, Francijane Oliveira da Conceição, Gustavo Campos Monteiro de Castro, Mariana Giorgi Barroso de Carvalho, Thatyane Veloso de Paula Amaral de Almeida, Rafael Quaresma Garrido, and Cristiane da Cruz Lamas. 2024. "Splenic Embolism in Infective Endocarditis: A Systematic Review of the Literature with an Emphasis on Radiological and Histopathological Diagnoses" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 9, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9040083
APA StyleMoreira, G. S., Feijóo, N. d. A. P., Tinoco-da-Silva, I. B., Aguiar, C. M., da Conceição, F. O., de Castro, G. C. M., de Carvalho, M. G. B., de Almeida, T. V. d. P. A., Garrido, R. Q., & Lamas, C. d. C. (2024). Splenic Embolism in Infective Endocarditis: A Systematic Review of the Literature with an Emphasis on Radiological and Histopathological Diagnoses. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 9(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9040083







