Bridging the Gaps: Investigating the Complex Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Records in Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Area
2.2. Study Population and Data Source
2.3. Study Steps
2.3.1. Phase 1—Pre-Pandemic Time Series Analysis
2.3.2. Phase 2—Spatial Dynamics of Tuberculosis before (2015–2019) and during the COVID-19 Pandemic (2020 and 2021)
2.3.3. Phase 3—Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Time Trend of Tuberculosis Incidence in Pernambuco in the Pre-Pandemic Period, 2001–2019
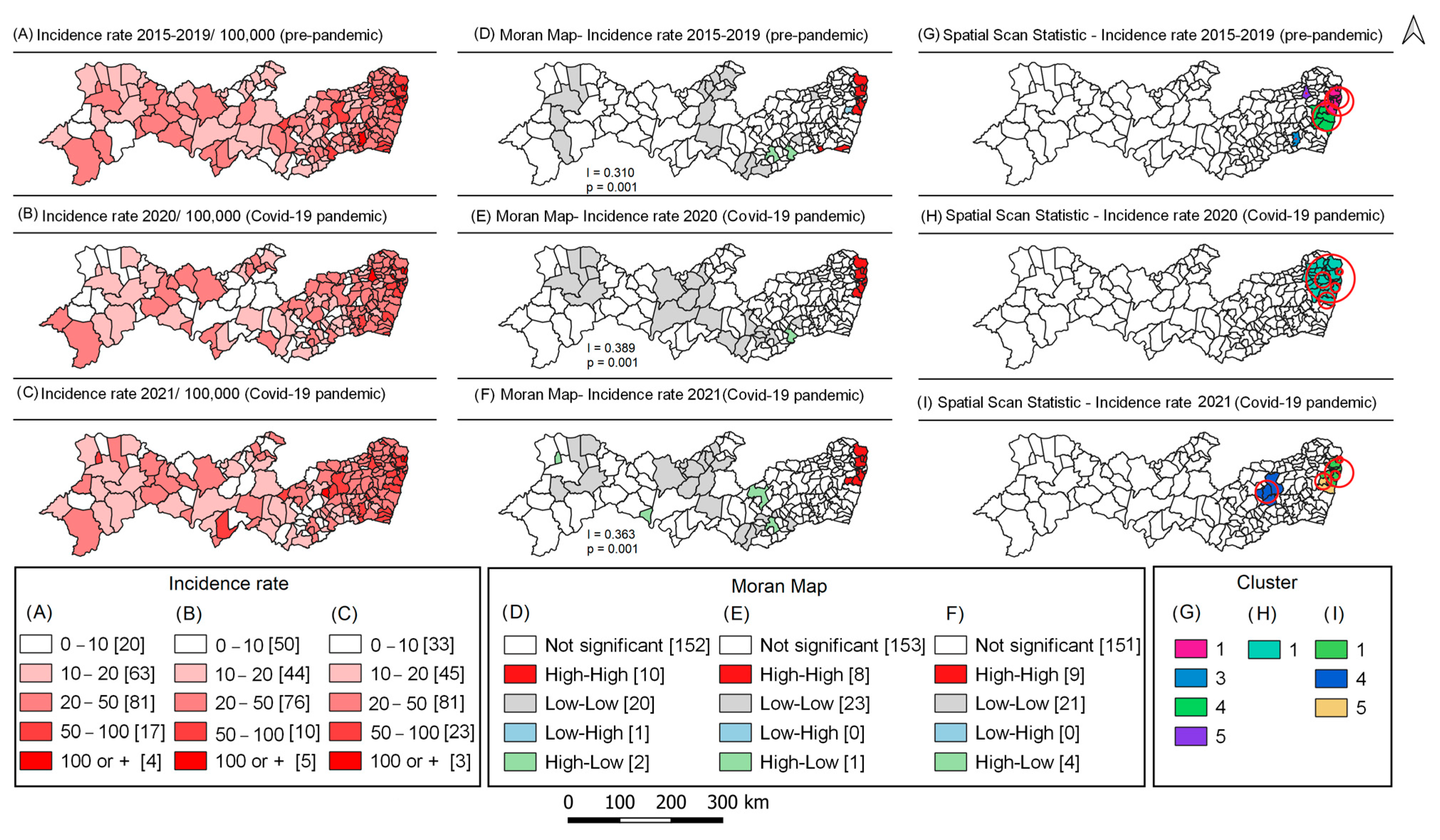
3.2. Spatial Analysis of Tuberculosis before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic
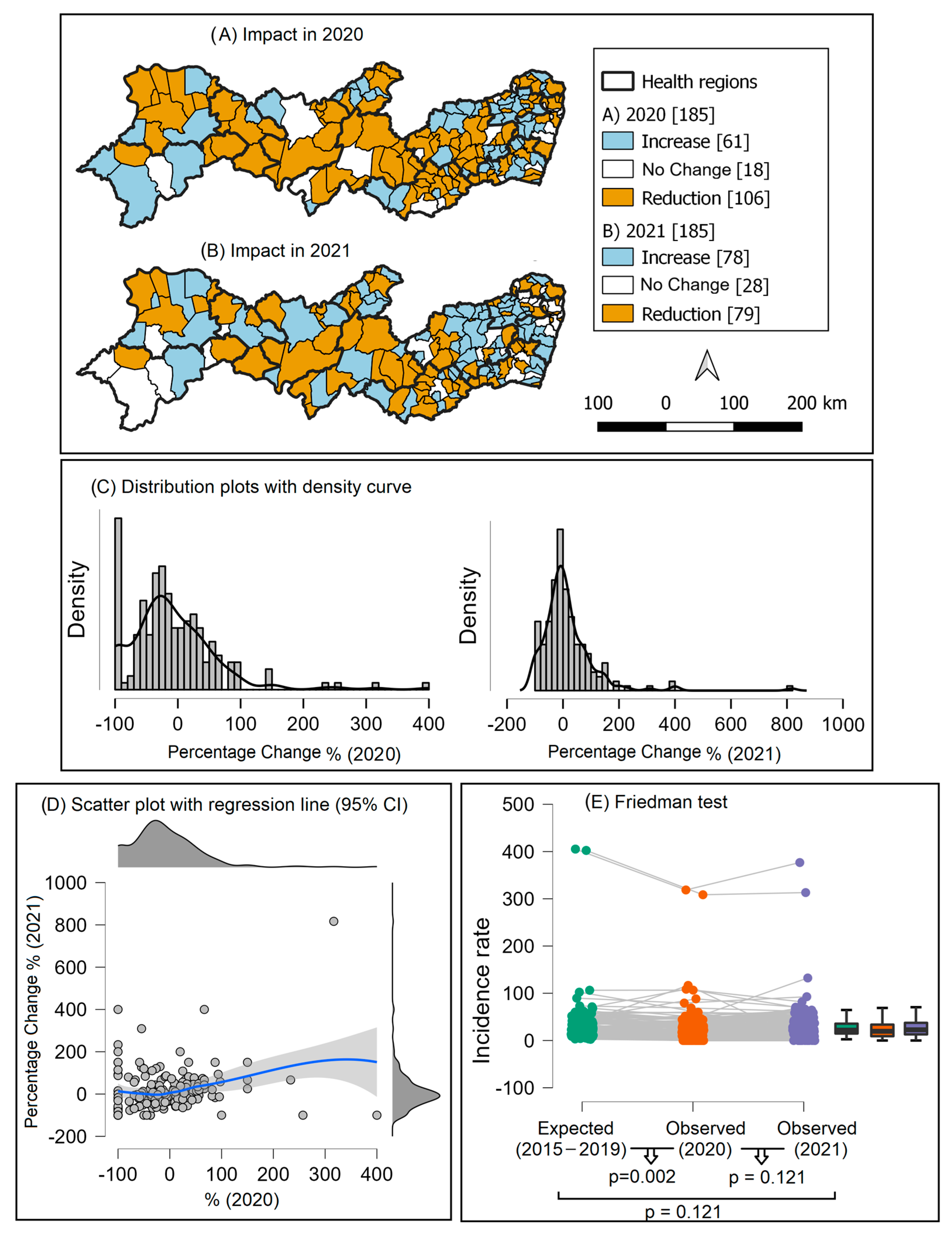
3.3. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on TB Diagnoses in the Years 2020 and 2021
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde. Manual de Recomendações Controle Tuberculose. Brasil; 2019. Available online: http://antigo.aids.gov.br/pt-br/pub/2019/manual-de-recomendacoes-para-o-controle-da-tuberculose-no-brasil (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Penna, G. Manual de Recomendações para o Controle da Tuberculose no Brasil. 2011. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/manual_recomendacoes_controle_tuberculose_brasil.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Migliori, G.B.; Ong, C.W.; Petrone, L.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Centis, R.; Goletti, D. The definition of tuberculosis infection based on the spectrum of tuberculosis disease. Breathe 2021, 17, 210079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Tuberculosis Report 2019; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/world/global-tuberculosis-report-2019?gclid=CjwKCAjwov6hBhBsEiwAvrvN6Coaz6YZmXKmZcf1vKng2ywwpUfvncUYxCQ2j_81CSOkkeE2PZ084RoCNSAQAvD_BwE (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Freitas, A.A.; Guimarães, A.R.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Centis, R.; Muñoz-Torrico, M.; Migliori, G.B. Sequelas pulmonares da tuberculose: Comparação de coortes do Brasil, Itália e México. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2022, 22, 1806–3756. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Tuberculosis Report 2021; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1379788/retrieve (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Ministério, O. Brasil Livre da Tuberculose. Plano Nacional Pelo Fim da Tuberculose Como Problema de Saúde Pública, 1st ed.; Ministério da Saúd: Brasília, Brasil, 2017; p. 40. Available online: http://portalarquivos.saude.gov.br/images/pdf/2017/fevereiro/24/Plano-Nacional-Tuberculose.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Xie, C.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Z.; Song, L. Epidemiological characteristics and spatial-temporal clustering analysis on pulmonary tuberculosis in Changsha from 2013 to 2016. Med. Sci. 2018, 43, 898–903. [Google Scholar]
- Kiani, B.; Raouf Rahmati, A.; Bergquist, R.; Hashtarkhani, S.; Firouraghi, N.; Bagheri, N.; Mohammadi, A. Spatio-temporal epidemiology of the tuberculosis incidence rate in Iran 2008 to 2018. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organização Pan-Americana da Saúde (OPAS). Histórico da pandemia de covid-19. 2022. Available online: https://www.paho.org/pt/covid19/historico-da-pandemia-covid-19 (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Tuberculosis Report 2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/world/global-tuberculosis-report-2020?gclid=CjwKCAjwov6hBhBsEiwAvrvN6KimD9xFoObFXl0B4qs_ZxPOjG2rp4korAR8UpENjCCDwFoAatWllhoCcVMQAvD_BwE (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Brasil, Ministério da Saúde. Brasil Confirma Primeiro Caso do novo Coronavírus. 2020. Available online: https://www.gov.br/pt-br/noticias/saude-e-vigilancia-sanitaria/2020/02/brasil-confirma-primeiro-caso-do-novo-coronavirus (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Barral-Netto, M.; Barreto, M.L.; Pinto Junior, E.P.; Aragão, E. Impactos Sociais e Econômicos da COVID-19. In Construção de Conhecimento no Curso da Pandemia de COVID-19: Aspectos Biomédicos, Clínico-Assistenciais, Epidemiológicos e Sociais; Barreto, M.L., Pinto Junior, E.P., Eds.; Edufba: Salvador, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Global Economic Prospects, January 2021; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chahad, J.P.Z. Os Impactos Globais da COVID-19 Sobre a Pobreza. Finanças Públicas: Gov. Fed. E O Dilema Entre A Saúde Fisc. E A Saúde Da Econ. 2021, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.; Oliveira, A.M. Poverty and food insecurity may increase as the threat of COVID-19 spreads. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 17, 3236–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Paz, W.S.; do Rosario Souza, M.; dos Santos Tavares, D.; de Jesus, A.R.; Dos Santos, A.D.; do Carmo, R.F.; Bezerra-Santos, M. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the diagnosis of leprosy in Brazil: An ecological and population-based study. Lancet Reg. Health-Am. 2022, 9, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Carmo, R.F.; De Souza, C.D.F. Impacto da pandemia de COVID-19 no diagnóstico de hepatite C no Brasil: A estratégia global de eliminação da hepatite C está em risco? J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.D.R.; Paz, W.S.D.; Sales, V.B.D.S.; Jesus GF, H.D.; Tavares DD, S.; Lima SV, A.; Bezerra-Santos, M. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the diagnosis of tuberculosis in Brazil: Is the WHO end TB strategy at risk. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 891711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBGE. In População Pernambuco; 2021. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/pe/panorama (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- IDH–IVS. IPEA. Available online: http://ivs.ipea.gov.br/index.php/pt/planilha (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- Secretaria de Saúde de, Pernambuco. Gerências Regionais de Saúde. 2022. Available online: http://portal.saude.pe.gov.br/secretaria-executiva-de-coordenacao-geral/gerencias-regionais-de-saude (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- Rocha, M.S.; Bartholomay, P.; Cavalcante, M.V.; Medeiros, F.C.D.; Codenotti, S.B.; Pelissari, D.M.; Pinheiro, R.S. Sistema de Informação de Agravos de Notificação (Sinan): Principais características da notificação e da análise de dados relacionada à tuberculose. Epidemiol. E Serviços Saúde 2020, 29, e2019017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laguardia, J.; Domingues, C.M.A.; Carvalho, C.; Lauerman, C.R.; Macário, E.; Glatt, R. Sistema de informação de agravos de notificação em saúde (Sinan): Desafios no desenvolvimento de um sistema de informação em saúde. Epidemiol. E Serviços De Saúde 2004, 13, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ministério da Saúde, B.R. Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Departamento de Vigilância Epidemiológica. In Sistema de Informação de Agravos de Notificação-Sinan: Normas e Rotinas, 2nd ed; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2007; (Série A. Normas e Manuais Técnicos). Available online: http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/07_0098_M.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Kim, H.J.; Fay, M.P.; Feuer, E.J.; Midthune, D.N. Permutation tests for joinpoint regression with applications to cancer rates. Stat. Med. 2000, 19, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druck, S.; Carvalho, M.S.; Câmara, G.; Monteiro, A.V.M. Análise Espacial de Dados Geográficos; EMBRAPA: Brasília, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kulldorff, M.A. Spatial Scan statistic. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 1997, 26, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakaya, J.; Petersen, E.; Nantanda, R.; Mungai, B.N.; Migliori, G.B.; Amanullah, F.; Zumla, A. The WHO Global Tuberculosis 2021 Report–not so good news and turning the tide back to End TB. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 124, S26–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.G.O.D.; Sá, L.D.D.; Palha, P.F.; Oliveira, R.D.C.C.D.; Nogueira, J.D.A.; Villa, T.C.S. Pontos de estrangulamento sobre o controle da tuberculose na atenção primária. Rev. Bras. De Enferm. 2017, 70, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyazewal, T.; Woldeamanuel, Y.; Blumberg, H.M.; Fekadu, A.; Marconi, V.C. The fight to end tuberculosis must not be forgotten in the COVID-19 outbreak. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 811–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirae, K.; Hoshina, T.; Koga, H. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the epidemiology of other communicable diseases in Japan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 128, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, P.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Martinez, L. Collateral impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on tuberculosis control in Jiangsu Province, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 3, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soko, R.N.; Burke, R.M.; Feasey, H.R.; Sibande, W.; Nliwasa, M.; Henrion, M.Y.; MacPherson, P. Effects of coronavirus disease pandemic on tuberculosis notifications, Malawi. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Boletim Epidemiológico Especial. Tuberculose. 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/epidemiologicos/especiais/2021/boletim-tuberculose-2021_24.03 (accessed on 24 May 2023).

| (A) Pre-Pandemic Period (2015–2019) | ||||||
| Cluster | No. Municipalities | Incidence Rate | No. Cases | Radius (km) | RR | p Value |
| 1 | 10 | 80.1 | 14,348 | 27.8 | 2.66 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 8 | 85.9 | 11,916 | 20.4 | 2.54 | <0.001 |
| 3 | 1 | 102.1 | 321 | 0.0 | 2.10 | <0.001 |
| 4 | 7 | 53.5 | 3664 | 27.4 | 1.11 | <0.001 |
| 5 | 1 | 71.2 | 201 | 0.0 | 1.45 | <0.001 |
| (B) First year of the pandemic (2020) | ||||||
| Cluster | No. municipalities | Incidence rate | No. cases | Radius (km) | RR | p value |
| 1 | 30 | 66.4 | 3075 | 47.0 | 2.8 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 3 | 75.9 | 1677 | 9.0 | 2.2 | <0.001 |
| 3 | 2 | 312.9 | 168 | 5.9 | 7.3 | <0.001 |
| 4 | 1 | 108.3 | 61 | 0.0 | 2.5 | <0.001 |
| 5 | 3 | 54.9 | 539 | 15.8 | 1.3 | <0.001 |
| 6 | 7 | 60.9 | 208 | 15.3 | 1.4 | 0.004 |
| (C) Second year of the pandemic (2021) | ||||||
| Cluster | No. municipalities | Incidence rate | No. cases | Radius (km) | RR | p value |
| 1 | 10 | 77.2 | 2827 | 27.8 | 2.5 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 2 | 86.5 | 1782 | 8.9 | 2.3 | <0.001 |
| 3 | 2 | 344.2 | 187 | 6.0 | 7.4 | <0.001 |
| 4 | 4 | 62.7 | 278 | 22.0 | 1.3 | 0.014 |
| 5 | 4 | 56.5 | 623 | 15.8 | 1.2 | 0.030 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, C.D.F.d.; Neto, E.R.D.; Matos, T.S.; Ferreira, A.C.F.; Bezerra-Santos, M.; Silva Junior, A.G.d.; do Carmo, R.F. Bridging the Gaps: Investigating the Complex Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Records in Brazil. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8090454
Souza CDFd, Neto ERD, Matos TS, Ferreira ACF, Bezerra-Santos M, Silva Junior AGd, do Carmo RF. Bridging the Gaps: Investigating the Complex Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Records in Brazil. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(9):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8090454
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Carlos Dornels Freire de, Epaminondas Ribeiro Dias Neto, Thais Silva Matos, Ana Carolina Furtado Ferreira, Márcio Bezerra-Santos, Adeilton Gonçalves da Silva Junior, and Rodrigo Feliciano do Carmo. 2023. "Bridging the Gaps: Investigating the Complex Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Records in Brazil" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 9: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8090454
APA StyleSouza, C. D. F. d., Neto, E. R. D., Matos, T. S., Ferreira, A. C. F., Bezerra-Santos, M., Silva Junior, A. G. d., & do Carmo, R. F. (2023). Bridging the Gaps: Investigating the Complex Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Records in Brazil. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(9), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8090454







