Insight into the Toxicological and Pathophysiological Effects of Moroccan Vipers’ Venom: Assessing the Efficacy of Commercial Antivenom for Neutralization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Venoms and Antivenom
2.2. Mice and Ethics Clearance
2.3. Protein Concentration
2.4. SDS-PAGE
2.5. Assessment of the Toxic and Enzymatic Activities of Venoms
2.5.1. Lethality
2.5.2. Hemorrhagic Activity
2.5.3. Edema Forming Activity
2.5.4. Myotoxic Activity
2.5.5. Proteolytic Activity
2.6. Alterations in Skin and Paw
2.7. Neutralizationtoxic Activities
2.7.1. Determination of Median Effective Dose (ED50) Neutralization of Venom Lethality
2.7.2. Determination of MHD (Medium Effective Dose) (MHD-ED50) for the Neutralization of Hemorrhagic Activity
2.7.3. Determination of Medium Effective Dose (MED-ED50) for the Neutralization of Edema-Forming Activity
2.8. Neutralization of Myotoxic Activity
2.9. Histological Study
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Median Lethal Dose (LD50)
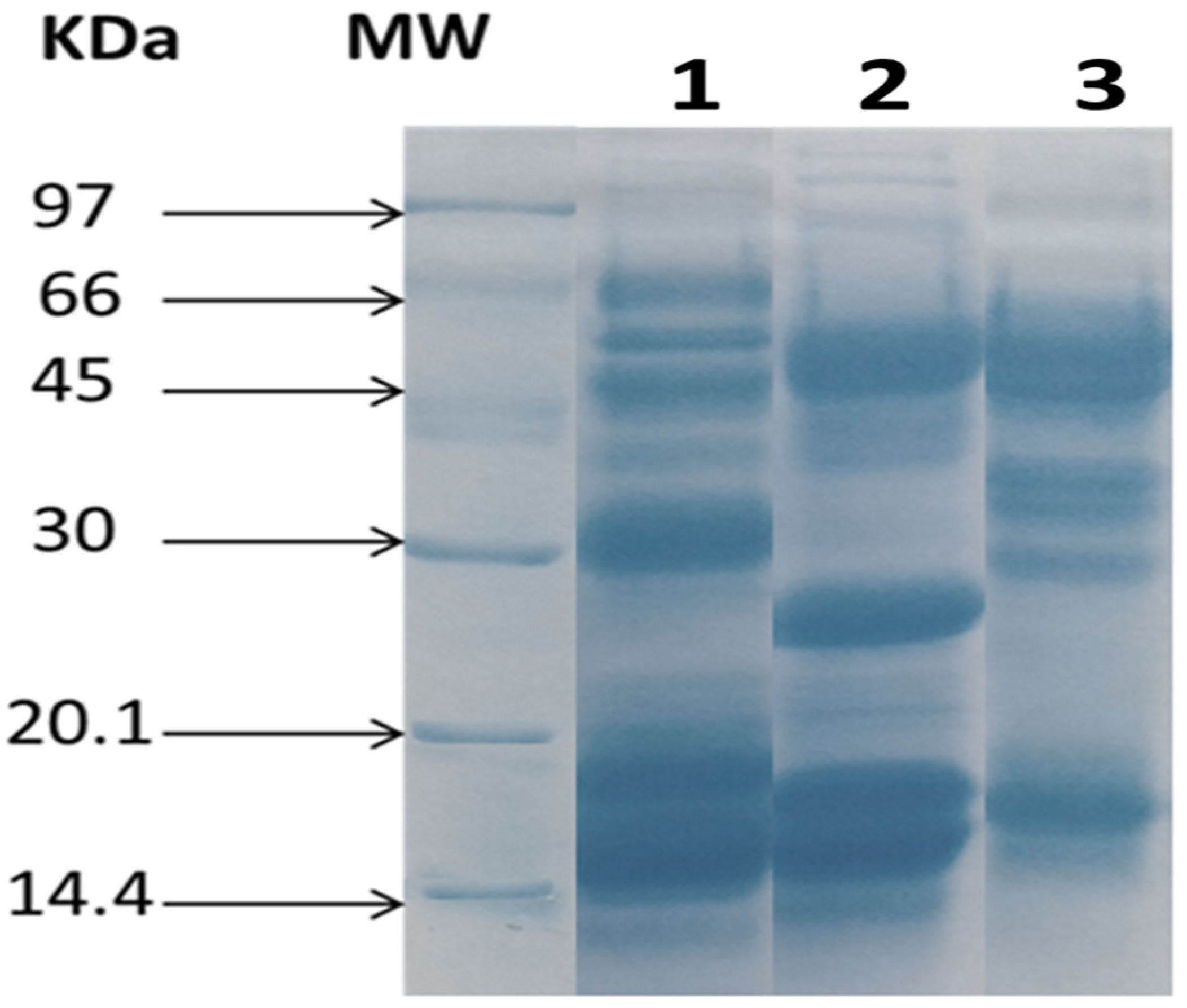
3.2. Electrophoretic Profiling
3.3. Proteolytic Activity
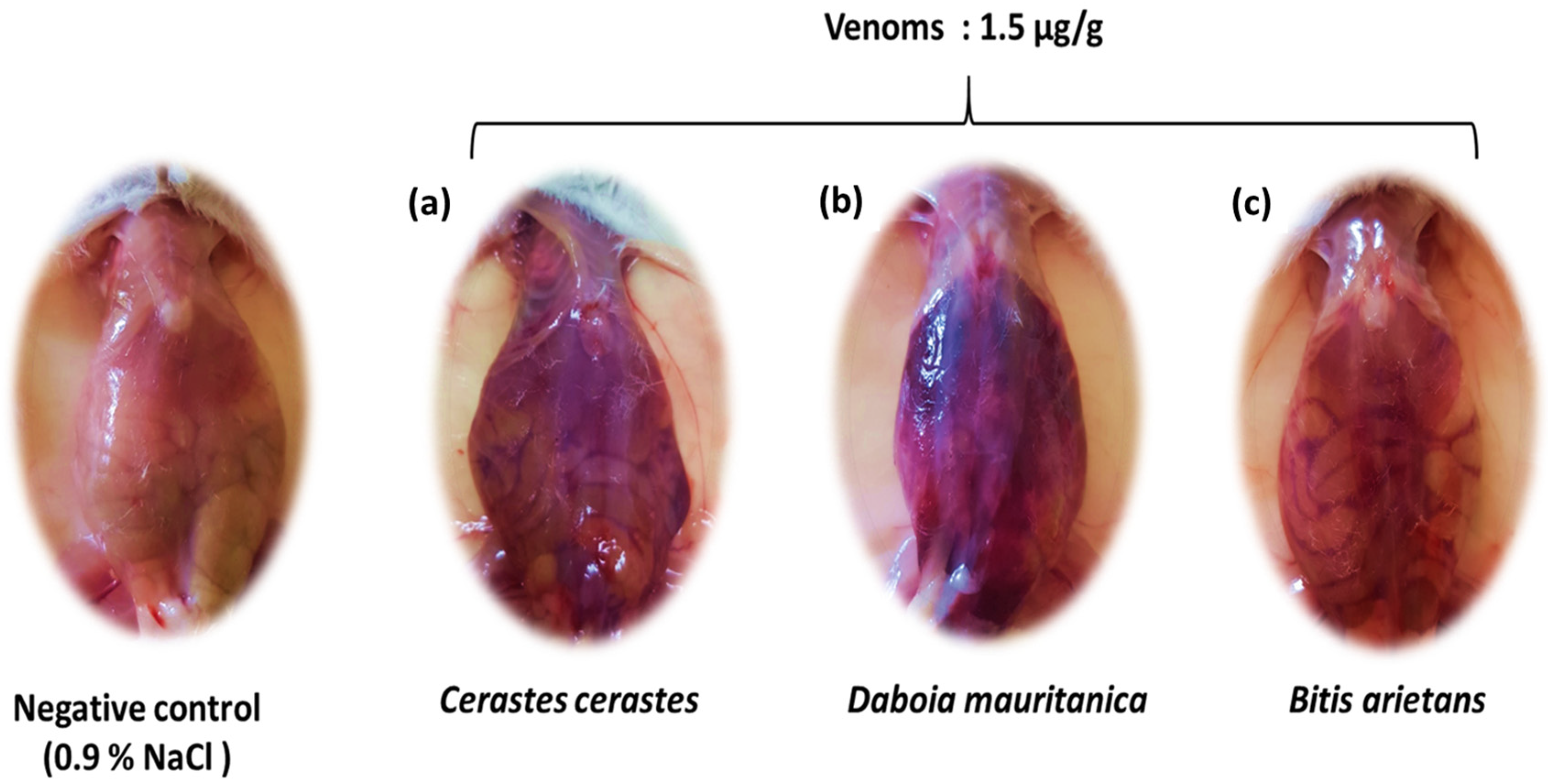
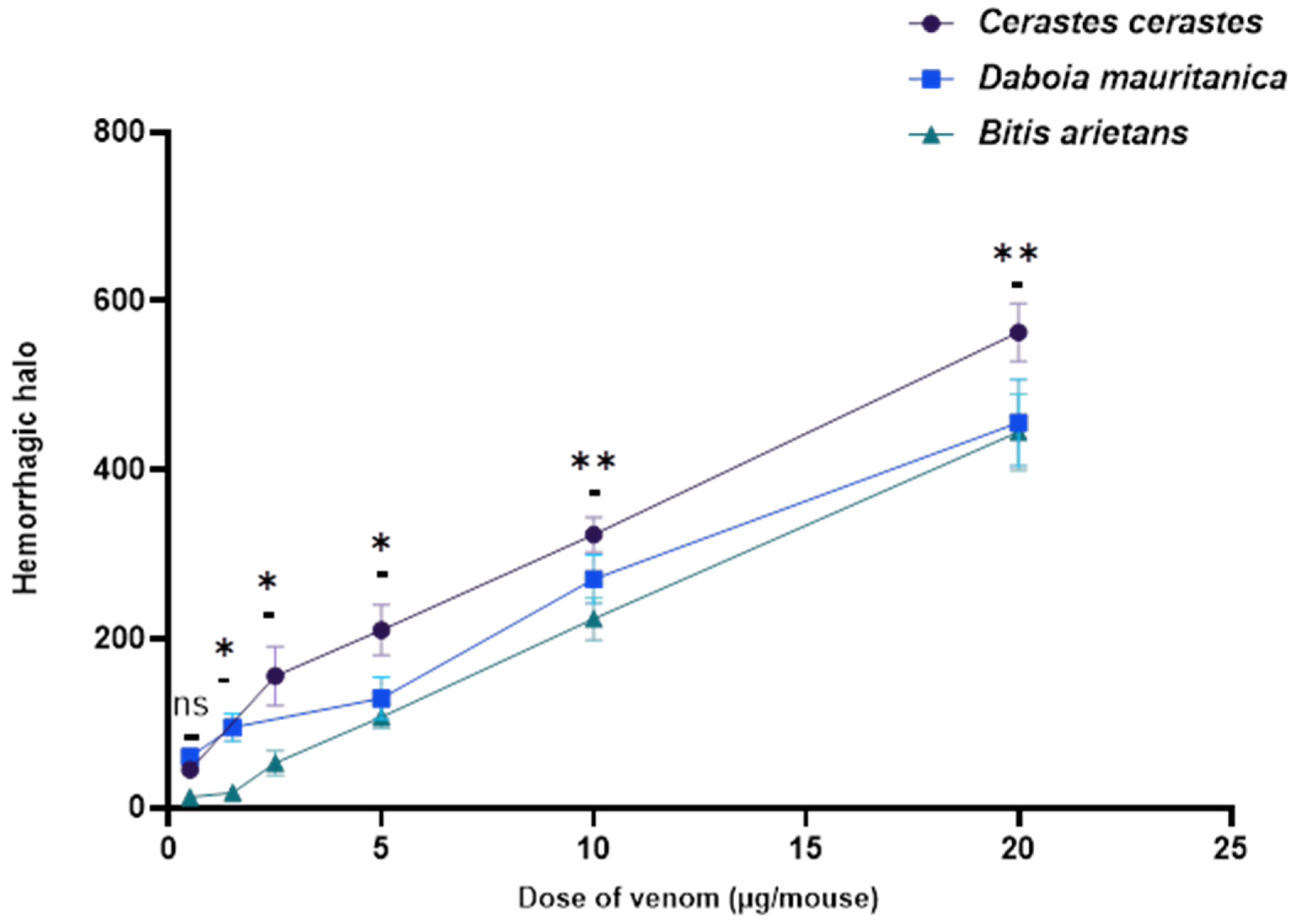
3.4. Hemorrhagic Activity
3.5. Edema-Forming Activity
3.6. Myotoxic Activity
3.7. Histopathological Analysis
3.7.1. Skin Alterations
3.7.2. Paw Alterations
3.8. Neutralization Capacity
3.8.1. Neutralization of Lethality
3.8.2. Neutralization of Hemorrhagic and Edema-Forming Activity
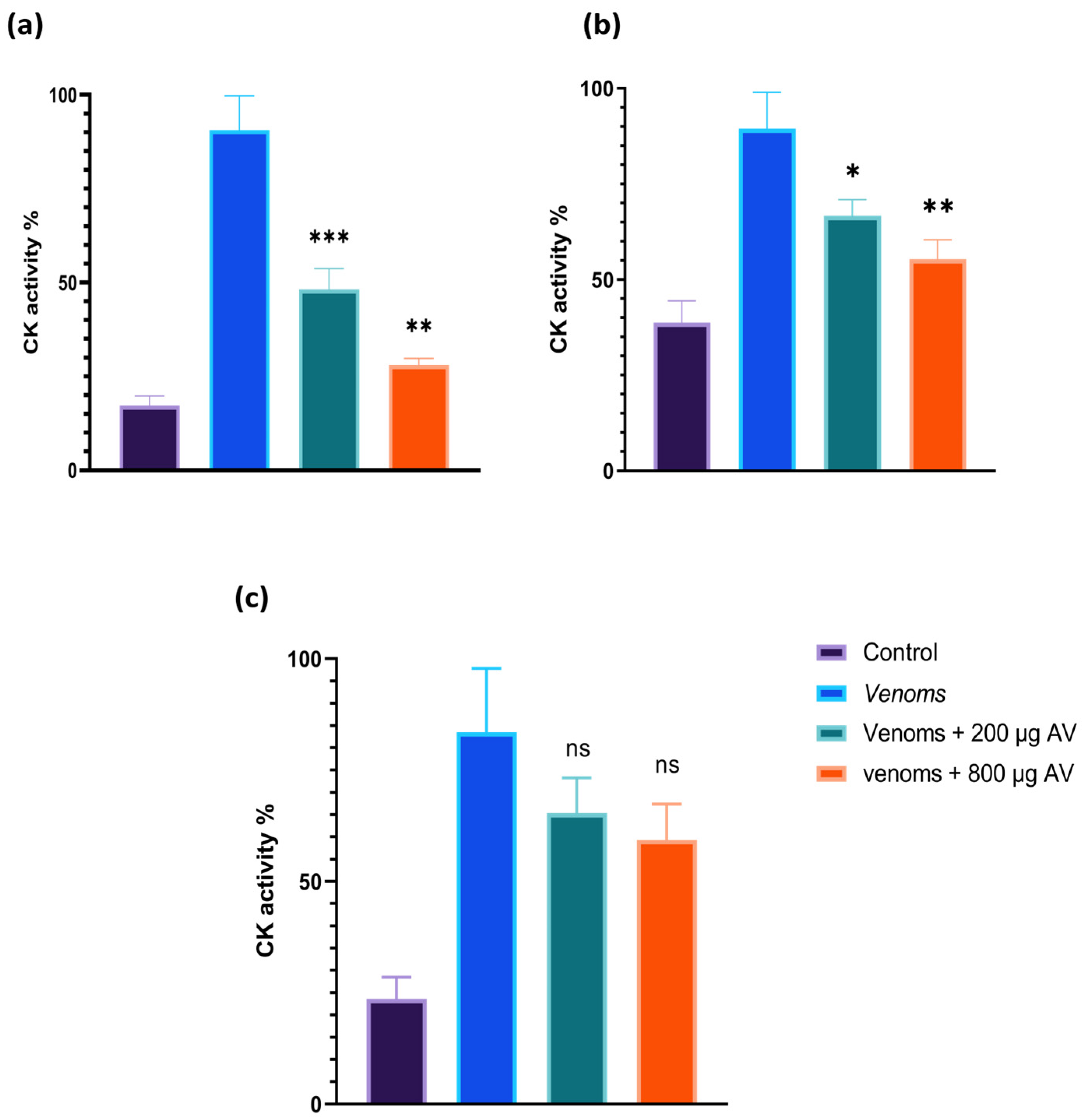
3.8.3. Neutralization In Vitro of Myotoxic Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer. 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P. Estimate of the burden of snakebites in sub-Saharan Africa: A meta-analytic approach. Toxicon 2011, 57, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, J. The Global Burden of Snakebite: A Literature Analysis and Modelling Based on Regional Estimates of Envenoming and Deaths. Winkel, K., Ed. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoual, O.; Rachid, E.; Sebastien, L.; Salma, C.; Chafi, Q.F.; Abdelaziz, H.; Georges, M. Snake bites in morocco: Progress and challenges. Adv. Toxicol. Toxic. Eff. 2019, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafiq, F.; Hmimou, R.; Rhalem, N.; Soulaymani, A.; Mokhtari, A.; Soulaymani Bencheikh, R. Caractéristiques épidémiologiques des morsures de serpent notifiées au centre antipoison et de pharmacovigilance du Maroc. Année 2016. Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 2018, 30, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization. 2016: Geneva S. WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization, Sixty-Seventh Report; WHO Technical Report Series, 1004; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 616. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/255657 (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Longbottom, J.; Shearer, F.M.; Devine, M.; Alcoba, G.; Chappuis, F.; Weiss, D.J.; Ray, S.E.; Ray, N.; Warrell, D.A.; de Castañeda, R.R.; et al. Vulnerability to snakebite envenoming: A global mapping of hotspots. Lancet 2018, 392, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borja, M.; Lazcano, D.; Martínez-Romero, G.; Morlett, J.; Sánchez, E.; Cepeda-Nieto, A.C.; Garza-García, Y.; Zugasti-Cruz, A. Intra-specific Variation in the Protein Composition and Proteolytic Activity of Venom of Crotalus lepidus morulus from the Northeast of Mexico. Copeia 2013, 2013, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaa, A.; Marrakchi, N.; El Ayeb, M.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics: Comparative analysis of the venom proteomes of the Tunisian snakes Cerastes cerastes, Cerastes vipera and Macrovipera lebetina. Proteomic 2005, 5, 4223–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, M.; Hempel, B.F.; Süssmuth, R. Old World Vipers—A Review about Snake Venom Proteomics of Viperinae and Their Variations. Toxins 2021, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yu, H.; Li, P. Highlights of animal venom research on the geographical variations of toxin components, toxicities and envenomation therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2994–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burin, S.M.; Menaldo, D.L.; Sampaio, S.V.; Frantz, F.G.; Castro, F.A. An overview of the immune modulating effects of enzymatic toxins from snake venoms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oukkache, N.; Chgoury, F.; Lalaoui, M.; Cano, A.A.; Ghalim, N. Comparison between two methods of scorpion venom milking in Morocco. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Trop. Dis. 2013, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyugmedzhiev, A.; Andonov, K.; Todorov, V. A possible case of syntopy between Bitis arietans and Daboia mauritanica based on new reptile localities in southwestern Morocco. Herpetol. Notes 2022, 15, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Trevors, J.T. A BASIC Program for Estimating LDso Values Using the IBM-PC|. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1986, 37, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oukkache, N.; Jaoudi, R.E.; Ghalim, N.; Chgoury, F.; Bouhaouala, B.; Mdaghri, N.E.; Sabatier, J.M. Evaluation of the Lethal Potency of Scorpion and Snake Venoms and Comparison between Intraperitoneal and Intravenous Injection Routes. Toxins 2014, 6, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theakston, R.D.; Reid, H.A. Development of simple standard assay procedures for the characterization of snake venom. Bull. World Health Organ. 1983, 61, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Damico, D.C.; da Cruz Höfling, M.A.; Cintra, M.; Leonardo, M.B.; Calgarotto, A.K.; da Silva, S.L.; Marangoni, S. Pharmacological Study of Edema and Myonecrosis in Mice Induced by Venom of the Bushmaster Snake (Lachesis muta muta) and Its Basic Asp49 Phospholipase A2 (LmTX-I). Protein J. 2008, 27, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanath, B.S.; Kini, R.M.; Gowda, T.V. Characterization of three edema-inducing phospholipase A2 enzymes from habu (trimeresurus flavoyiridis) venom and their interaction with the alkaloid aristolochic acid. Toxicon 1987, 25, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Lomonte, B.; Chaves, F.; Moreno, E.; Cerdas, L. Pharmacological activities of a toxic phospholipase a isolated from the venom of the snake Bothrops Asper. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C. Comp. Pharmacol. 1986, 84, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Sanz, L.; Escolano, J.; Fernández, J.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Rucavado, A.; Warrell, D.A.; Calvete, J.J. Snake Venomics of the Lesser Antillean Pit Vipers Bothrops caribbaeus and Bothrops lanceolatus: Correlation with Toxicological Activities and Immunoreactivity of a Heterologous Antivenom. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 4396–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Cerdas, L.; Gené, J.A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Neutralization of local effects of the terciopelo (Bothrops asper) venom by blood serum of the colubrid snake Clelia clelia. Toxicon 1982, 20, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, Y.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Possani, L.D.; Lomonte, B. Isolation and characterization of myotoxin II from Atropoides (Bothrops) nummifer snake venom, a new Lys49 phospholipase A2 homologue. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 32, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Proteolytic activity of snake venoms of Costa Rica on casein. Rev. Biol. Trop. 1983, 31, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Casasola, A.; Ramos-Cerrillo, B.; de Roodt, A.R.; Saucedo, A.C.; Chippaux, J.-P.; Alagón, A.; Stock, R.P. Paraspecific neutralization of the venom of African species of cobra by an equine antiserum against Naja melanoleuca: A comparative study. Toxicon 2009, 53, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chippaux, J.P. Guidelines for the production, control and regulation of snake antivenom immunoglobulins. Biol. Aujourdhui. 2010, 204, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Issues New Recommendation on Antivenom for Snakebites. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/19-08-2018-who-issues-new-recommendation-on-antivenom-for-snakebites (accessed on 21 April 2023).
- Morais, V.; Ifran, S.; Berasain, P.; Massaldi, H. Antivenoms: Potency or median effective dose, which to use? J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Trop Dis. 2010, 16, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Sim, S.M.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, N.H. Geographical venom variations of the Southeast Asian monocled cobra (Naja kaouthia): Venom-induced neuromuscular depression and antivenom neutralization. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 185–186, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Wong, K.Y.; Tan, K.Y.; Sim, S.M.; Tan, N.H. Integrating snake venom proteomics, antivenom pharmacology and immunological innovation: Toward better management of cobra envenomation in the tropics. Proc. Annu. Meet. Jpn. Pharmacol. Soc. 2018, WCP2018, OR32-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Leong, P.K.; Fung, S.Y.; Sim, S.M.; Ponnudurai, G.; Ariaratnam, C.; Khomvilai, S.; Sitprija, V.; Tan, N.H. Cross neutralization of Hypnale hypnale (hump-nosed pit viper) venom by polyvalent and monovalent Malayan pit viper antivenoms in vitro and in a rodent model. Acta Trop. 2011, 117, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, N.H. Venomics, lethality and neutralization of Naja kaouthia (monocled cobra) venoms from three different geographical regions of Southeast Asia. J. Proteomics. 2015, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, J.D. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 742. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, M.H.; Pawlina, W. Histology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; p. 934. [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer, R.T. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. JAMA 1983, 250, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, H.; Mohamed, M. Beneficial effect of low dose gamma irradiation or quercetin on Cerastes cerastes snake venom induced toxicity in male rats. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abib, H.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Effects of 60Co gamma radiation on toxicity and hemorrhagic, myonecrotic, and edema-forming activities of Cerastes cerastes venom. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 81, 1125–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaiza, S.; Oussedik-Oumehdi, H.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Pathophysiological effects of Cerastes cerastes and Vipera lebetina venoms: Immunoneutralization using anti-native and anti-60Co irradiated venoms. Biologicals 2016, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makran, B.; Fahmi, L.; Boussada, L.; Oukkache, N.; Chgoury, F.; Benomar, H.; Ghalim, N.; Lkhider, M. Comparative toxicological characterization of venoms of Cerastes cerastes and Macrovipera mauritanica from Morocco and neutralization by monospecific antivenoms. Toxin Rev. 2020, 39, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennacef-Heffar, N.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Evaluation of the effect of gamma rays on the venom of Vipera lebetina by biochemical study. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 81, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Coto, J.; Segura, Á.; Vargas, M.; Solano, G.; Herrera, M.; Villalta, M.; Estrada, R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; León, G. Effect of geographical variation of Echis ocellatus, Naja nigricollis and Bitis arietans venoms on their neutralization by homologous and heterologous antivenoms. Toxicon 2015, 108, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oukkache, N.; Lalaoui, M.; Ghalim, N. General characterization of venom from the Moroccan snakes Macrovipera mauritanica and Cerastes cerastes. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Trop. Dis. 2012, 18, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
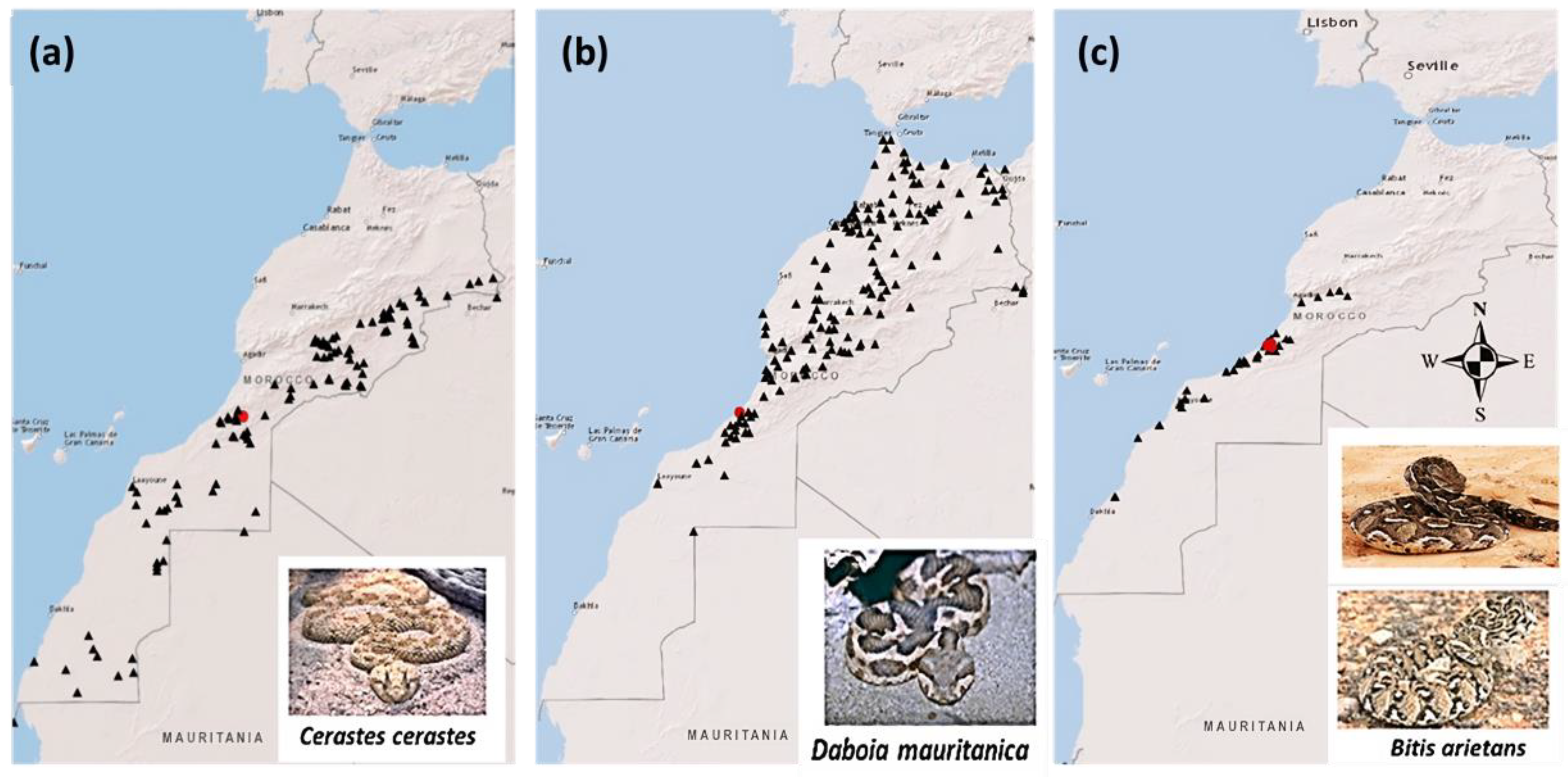
- Brito, J.C.; Fahd, S.; Geniez, P.; Martínez-Freiría, F.; Pleguezuelos, J.M.; Trape, J.F. Biogeography and conservation of viperids from North-West Africa: An application of ecological niche-based models and GIS. J. Arid. Environ. 2011, 75, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Wüster, W.; Cook, D.A.N.; Bolton, F.M.S.; King, S.I.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J.; Harrison, R.A. Medically important differences in snake venom composition are dictated by distinct postgenomic mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9205–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currier, R.B.; Harrison, R.A.; Rowley, P.D.; Laing, G.D.; Wagstaff, S.C. Intra-specific variation in venom of the African Puff Adder (Bitis arietans): Differential expression and activity of snake venom metalloproteinases (SVMPs). Toxicon 2010, 55, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmi, L.; Makran, B.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Oukkache, N.; Lkhider, M.; Harrison, R.A.; Ghalim, N.; Calvete, J.J. Venomics and antivenomics profiles of North African Cerastes cerastes and C. vipera populations reveals a potentially important therapeutic weakness. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2442–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.J.; Escolano, J.; Sanz, L. Snake Venomics of Bitis Species Reveals Large Intragenus Venom Toxin Composition Variation: Application to Taxonomy of Congeneric Taxa. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 2732–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingwoke, E.J.; Adamude, F.A.; Mohamed, G.; Klein, A.; Salihu, A.; Abubakar, M.S.; Sallau, A.B. Venom proteomic analysis of medically important Nigerian viper Echis ocellatus and Bitis arietans snake species. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 28, 101164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán-Padrón, O.; Castro-Guillén, J.L.; García-Arredondo, J.A.; Cruz-Pérez, M.S.; Díaz-Peña, L.F.; Saldaña, C.; Blanco-Labra, A.; García-Gasca, T. Snake Venom Hemotoxic Enzymes: Biochemical Comparison between Crotalus Species from Central Mexico. Molecules 2019, 24, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Flores-Ortiz, R.J.; Alvarenga, V.G.; Eble, J.A. Direct Fibrinolytic Snake Venom Metalloproteinases Affecting Hemostasis: Structural, Biochemical Features and Therapeutic Potential. Toxins 2017, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roodt, A.R.; Litwin, S.; Vidal, J.C. Hemorrhagic activity of Bothrops venoms determined by two different methods and relationship with proteolytic activity on gelatin and lethality. Toxicon 2003, 41, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.E.; Galán, J.A.; Powell, R.L.; Reyes, S.R.; Soto, J.G.; Russell, W.K.; Russell, D.H.; Pérez, J.C. Disintegrin, hemorrhagic, and proteolytic activities of Mohave rattlesnake, Crotalus scutulatus scutulatus venoms lacking Mojave toxin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 141, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, A.; Sánchez, A.; Durán, G.; Cordero, D.; Segura, A.; Vargas, M.; Solano, D.; Herrera, M.; Chaves-Araya, S.; Villalta, M.; et al. Intrageneric cross-reactivity of monospecific rabbit antisera against venoms of the medically most important Bitis spp. and Echis spp. African snakes. Ainsworth SR, éditeur. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, T.P.; Ahmadi, S.; Bittenbinder, M.A.; Stewart, T.K.; Akgun, D.E.; Hale, M.; Nasrabadi, N.N.; Wolff, D.S.; Vonk, F.J.; Kool, J.; et al. Terrestrial venomous animals, the envenomings they cause, and treatment perspectives in the Middle East and North Africa. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Aziz, T.M.; Soares, A.G.; Stockand, J.D. Advances in venomics: Modern separation techniques and mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1160, 122352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhalfa-Abib, H.; Meksem, A.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Purification and biochemical characterization of a novel hemorrhagic metalloproteinase from horned viper (Cerastes cerastes) venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 150, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, N.; Escalante, T.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A. Skin Pathology Induced by Snake Venom Metalloproteinase: Acute Damage, Revascularization, and Re-epithelization in a Mouse Ear Model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabaan, A.M.; El Feky, A.A.; Abdel Latif, A.K.M.; Moghib, H.K. In vitro antibacterial and bio-histological effects of cerastes cerastes venom on albino mice. Biochem. Lett. 2018, 14, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topyildiz, H.; Hayretdağ, S. Histopathological effects of Montivipera xanthina venom on rats. Turk. J. Zool. 2012, 36, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A. Experimental pathophysiology of systemic alterations induced by Bothrops asper snake venom. Toxicon 2009, 54, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T.; Díaz, C. Hemorrhage induced by snake venom metalloproteinases: Biochemical and biophysical mechanisms involved in microvessel damage. Toxicon 2005, 45, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.; Escalante, T.; Voisin, M.-B.; Rucavado, A.; Morazán, D.; Macêdo, J.; Calvete, J.; Sanz, L.; Nourshargh, S.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Tissue Localization and Extracellular Matrix Degradation by PI, PII and PIII Snake Venom Metalloproteinases: Clues on the Mechanisms of Venom-Induced Hemorrhage. Moura, A., Ed. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamede, C.C.N.; de Sousa Simamoto, B.B.; da Cunha Pereira, D.F.; de Oliveira Costa, J.; Ribeiro, M.S.M.; de Oliveira, F. Edema, hyperalgesia and myonecrosis induced by Brazilian bothropic venoms: Overview of the last decade. Toxicon 2020, 187, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.W. A brief review of the scientific history of several lesser-known snake venom proteins: L-amino acid oxidases, hyaluronidases and phosphodiesterases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Escalante, T.; Hernández, R.; Gastaldello, S.; Saravia-Otten, P.; Rucavado, A. Why is Skeletal Muscle Regeneration Impaired after Myonecrosis Induced by Viperid Snake Venoms? Toxins 2018, 10, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.; Lewin, M.R.; Carter, R.; Soria, R.; Aldridge, M.; Fry, B.G. Extreme Procoagulant Potency in Human Plasma of Venoms from the African Viperid Genera Atheris, Cerastes, and Proatheris and the Relative Efficacy of Antivenoms and Synthetic Enzyme-Inhibitors. Toxins 2022, 14, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomran, N.; Alsolaiss, J.; Albulescu, L.-O.; Crittenden, E.; Harrison, R.A.; Ainsworth, S.; Casewell, N.R. Pathology-specific experimental antivenoms for haemotoxic snakebite: The impact of immunogen diversity on the in vitro cross-reactivity and in vivo neutralisation of geographically diverse snake venoms. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essafti, M.; Fajri, M.; Rahmani, C.; Abdelaziz, S.; Mouaffak, Y.; Younous, S. Snakebite envenomation in children: An ongoing burden in Morocco. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 77, 103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senji Laxme, R.R.; Khochare, S.; De Souza, H.F.; Ahuja, B.; Suranse, V.; Martin, G.; Whitaker, R.; Sunagar, K. Beyond the ‘big four’: Venom profiling of the medically important yet neglected Indian snakes reveals disturbing antivenom deficiencies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandesha, V.D.; Darshan, B.; Tejas, C.; Girish, K.S.; Kempaiah, K. A comparative cross-reactivity and paraspecific neutralization study on Hypnale hypnale, Echis carinatus, and Daboia russelii monovalent and therapeutic polyvalent anti-venoms. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022, 16, e0010292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
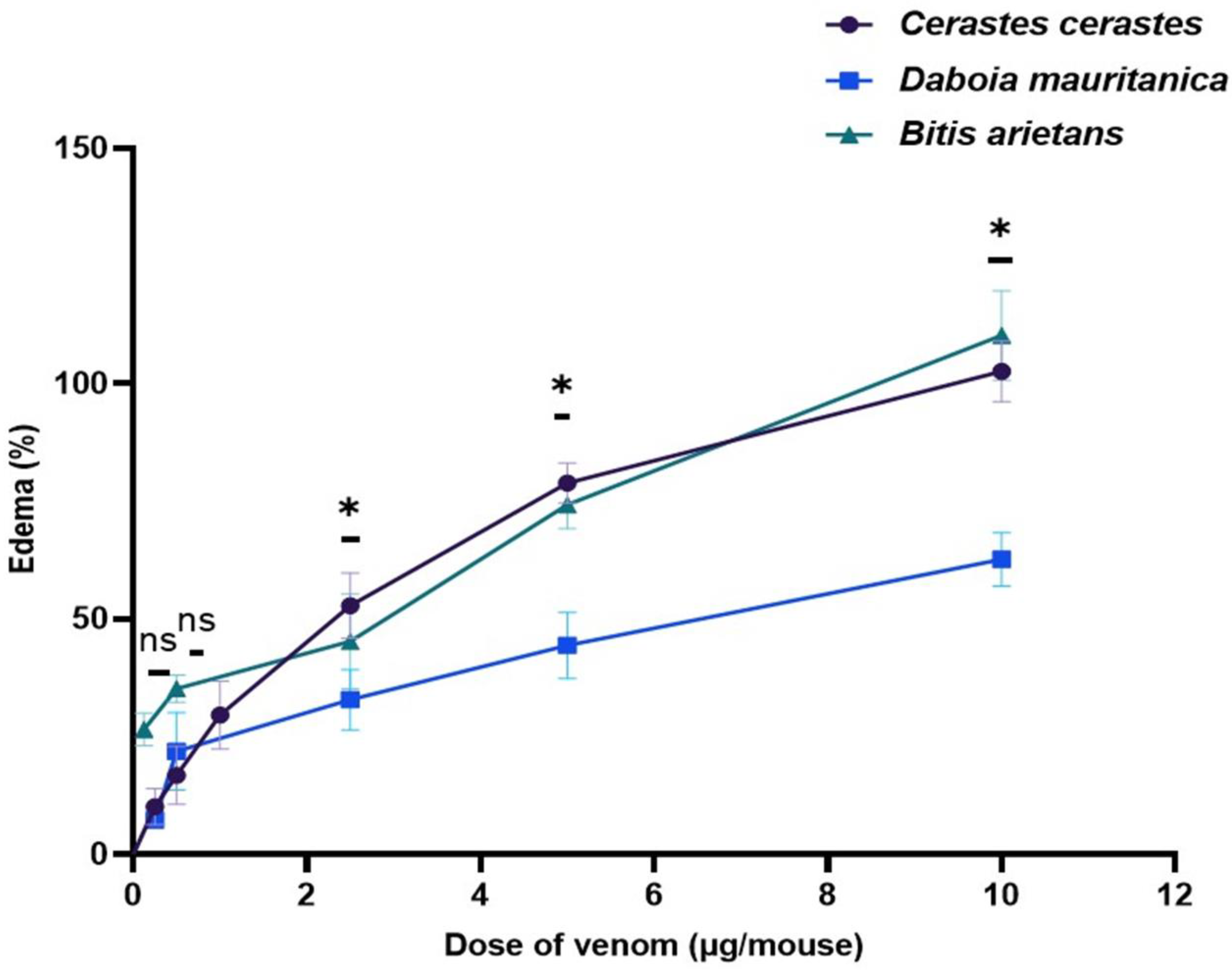
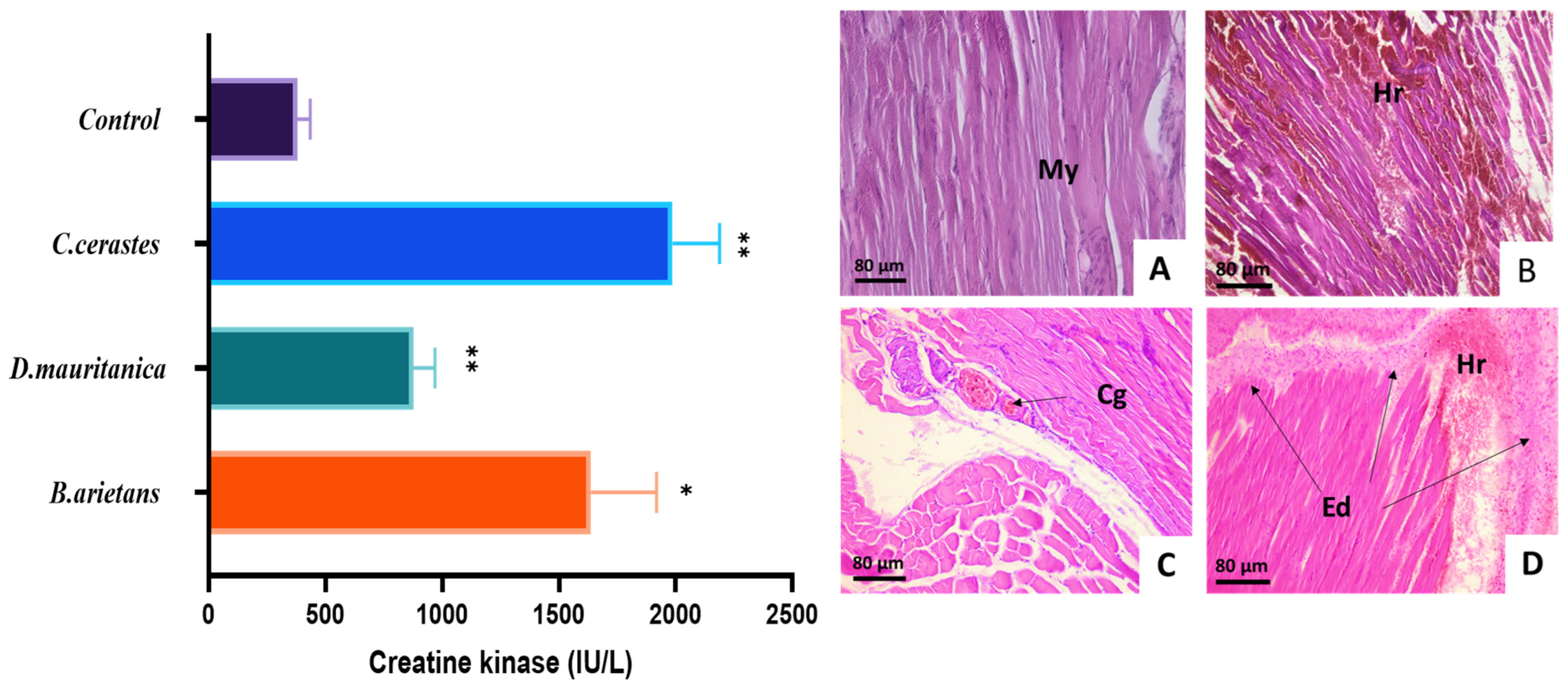
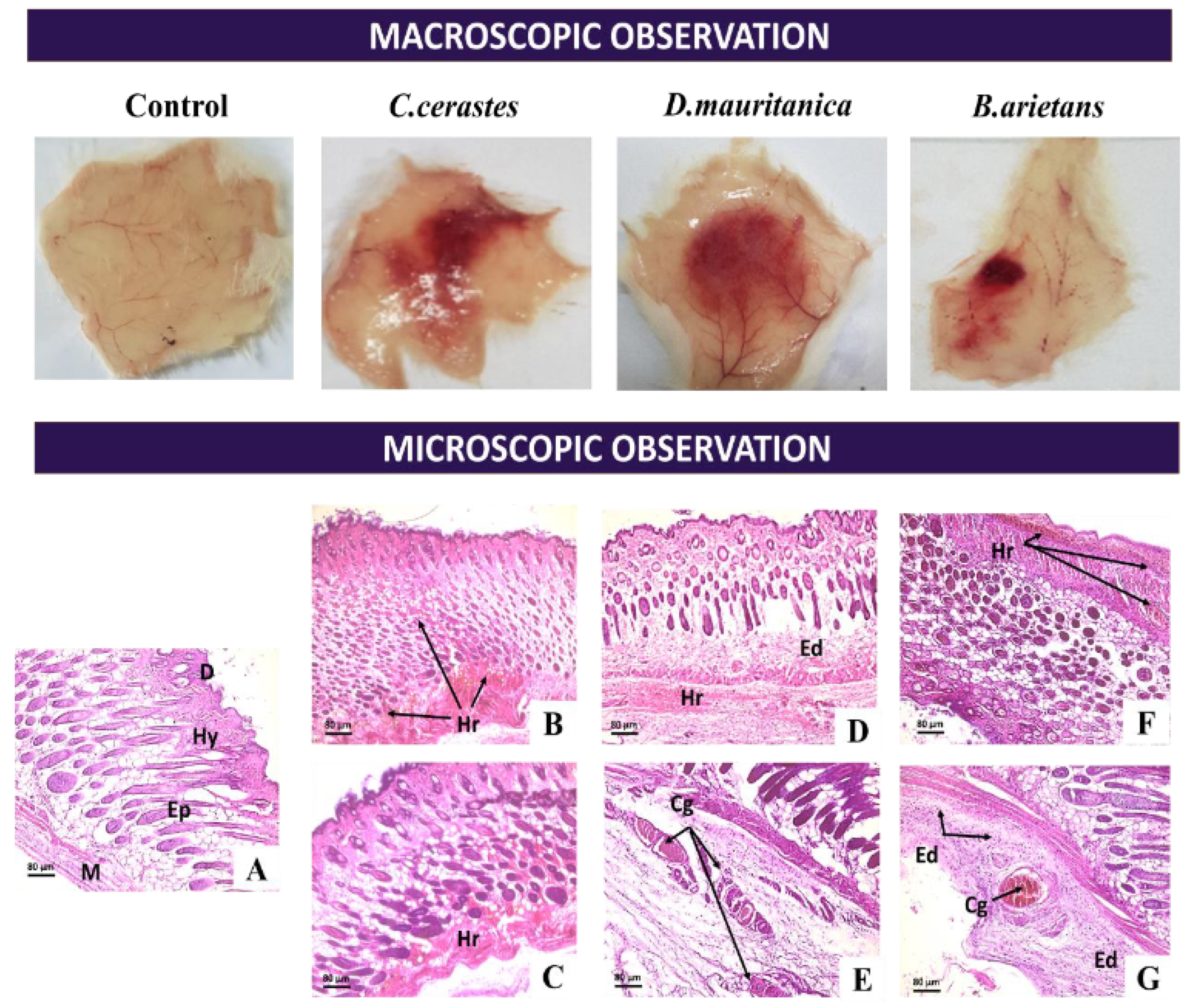
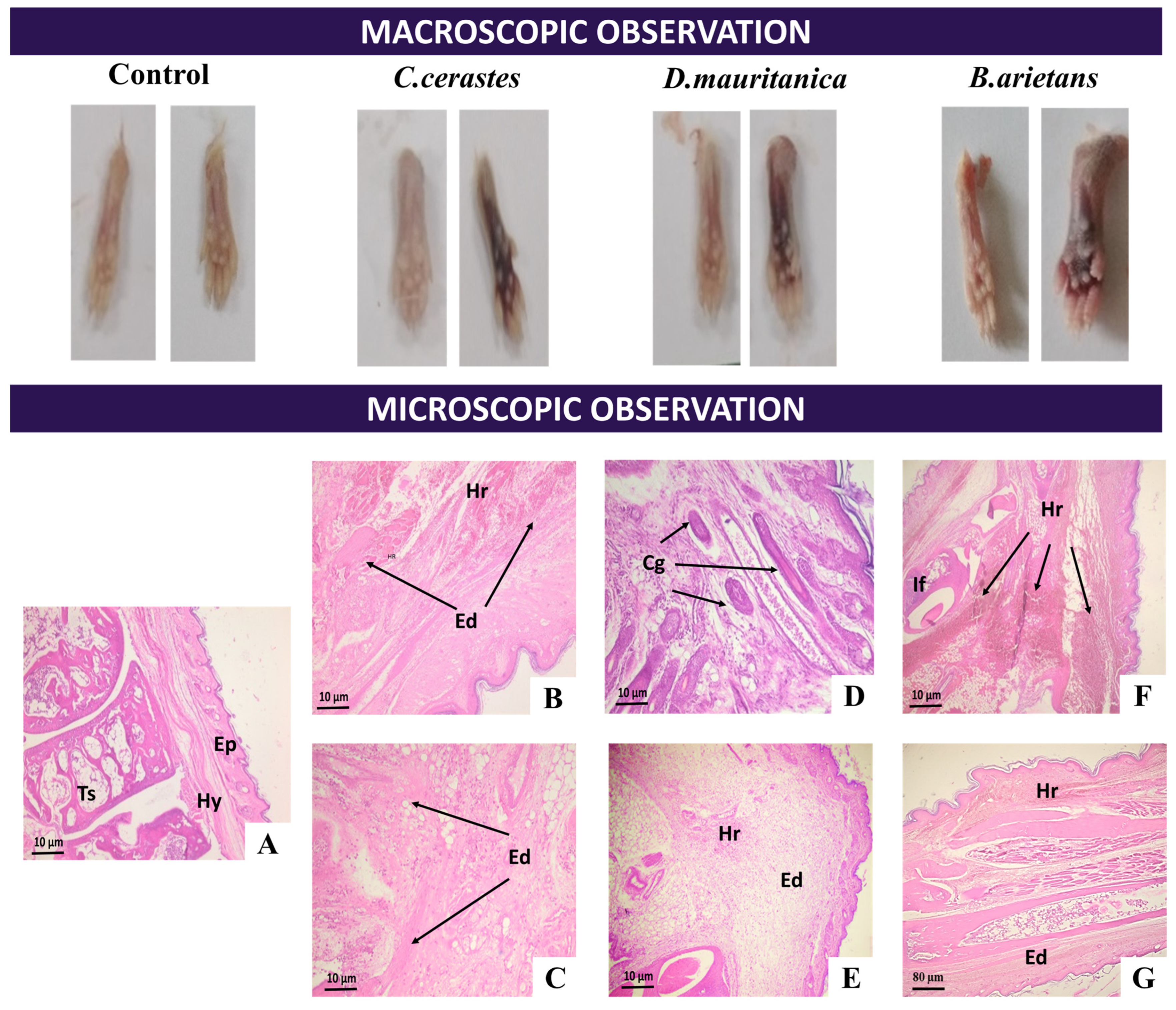
| Venom | Lethality Potency | Hemorrhagic Activity | Edematogenic Activity | Myotoxic Activity | Proteolytic Activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD50 (µg/mouse) a | LD50 (µg/g) | MHD (μg) b | MED (μg) c | (IU/L) | U/mg d | |
| Cerastes cerastes | 36.30 (30.98–40.57) | 1.815 (1.549–2.028) | 0.34 ± 0.11 | 1.74 ± 0.82 | 1986.4 ± 201.18 | 67.43 ± 2.8 |
| Daboia mauritanica | 48.64 (47.12–49.86) | 2.432 (2.356–2.493) | 1.37 ± 0.89 | 3.05 ± 1.30 | 876.6 ± 92.91 | 61.8 ± 3.04 |
| Bitis arietans | 78.06 (70.87–82.89) | 3.903 (3.543–4.145) | 3.70 ± 1.88 | 0.23 ± 0.1 | 1636.67 ± 281.12 | 44 ± 1.23 |
| Venoms | i.p. LD50 (μg/g) | Challenge Dose (μg/g) | ED50 a (μL of Antivenom) | ER50 b (mg/mL) | P (mg/mL) c | Normalized P (mg/g) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerastes cerastes | 1.815 (1.549–2.028) | 3 LD50 | 38.13 (32.74–44.19) | 2.89 | 1.93 | 95.20 |
| Daboia mauritanica | 2.432 (2.356–2.493) | 3 LD50 | 201 (1.8078–214.5) | 0.72 | 0.486 | 24.1 |
| Bitis arietans | 3.903 (3.543–4.145) | 3 LD50 | 400 | - | - | - |
| Neutralization of Hemorrhagic Activity | |||
| ED50 a (μL) | ED50 b (mg/mL ) | n-DE50 c (mg/g) | |
| Cerastes cerastes | 3.644 (3.193–4.179) | 0.18 (0.21–0.16) | 18.66 |
| Daboia mauritanica | 18.90 (16.62–21.52) | 0.14 (0.16–0.12) | 14.50 |
| Bitis arietans | 68.21 (60.81 to 77.11) | 0.10 (0.12–0.09) | 10.84 |
| Neutralization of Edema-Forming Activity | |||
| ED50a (μL) | ED50 b (mg/mL) | n-DE50 c (mg/g) | |
| Cerastes cerastes | 21.98 (18.99–25.42) | 0.16 (0.18–0.13) | 15.83 |
| Daboia mauritanica | 16.67 (14.41–19.28) | 0.35 (0.42–0.311) | 36 |
| Bitis arietans | 18.02 (14.94–21.71) | 0.0255 (0.0307–0.0211) | 2.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khourcha, S.; Hilal, I.; Elbejjaj, I.; Karkouri, M.; Safi, A.; Hmyene, A.; Oukkache, N. Insight into the Toxicological and Pathophysiological Effects of Moroccan Vipers’ Venom: Assessing the Efficacy of Commercial Antivenom for Neutralization. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8060302
Khourcha S, Hilal I, Elbejjaj I, Karkouri M, Safi A, Hmyene A, Oukkache N. Insight into the Toxicological and Pathophysiological Effects of Moroccan Vipers’ Venom: Assessing the Efficacy of Commercial Antivenom for Neutralization. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(6):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8060302
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhourcha, Soukaina, Ines Hilal, Iatimad Elbejjaj, Mehdi Karkouri, Amal Safi, Abdelaziz Hmyene, and Naoual Oukkache. 2023. "Insight into the Toxicological and Pathophysiological Effects of Moroccan Vipers’ Venom: Assessing the Efficacy of Commercial Antivenom for Neutralization" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 6: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8060302
APA StyleKhourcha, S., Hilal, I., Elbejjaj, I., Karkouri, M., Safi, A., Hmyene, A., & Oukkache, N. (2023). Insight into the Toxicological and Pathophysiological Effects of Moroccan Vipers’ Venom: Assessing the Efficacy of Commercial Antivenom for Neutralization. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(6), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8060302









