Legionella pneumophila Presence in Dental Unit Waterlines: A Cultural and Molecular Investigation in the West Bank, Palestine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites, Water and Biofilm Sampling
2.2. Measurement of Physical and Chemical Background Parameters
2.3. Cultivation Dependent Analysis (CDA) of Water and Biofilm
2.4. Cultivation Independent Analysis (CIA) of Water and Biofilm (16S rDNA PCR)
2.5. Serogrouping of Legionella Isolates
2.6. L. pneumophila 16S rRNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Physico-Chemical Properties and Legionella Count in Tap Water and Drinking Unit Water Line
3.2. Comparing Cultivation-Dependent Analysis (CDA) with Cultivation-Independent Analysis (CIA)
3.3. Distribution of L. pneumophila According to Serogroups in Dental Sites
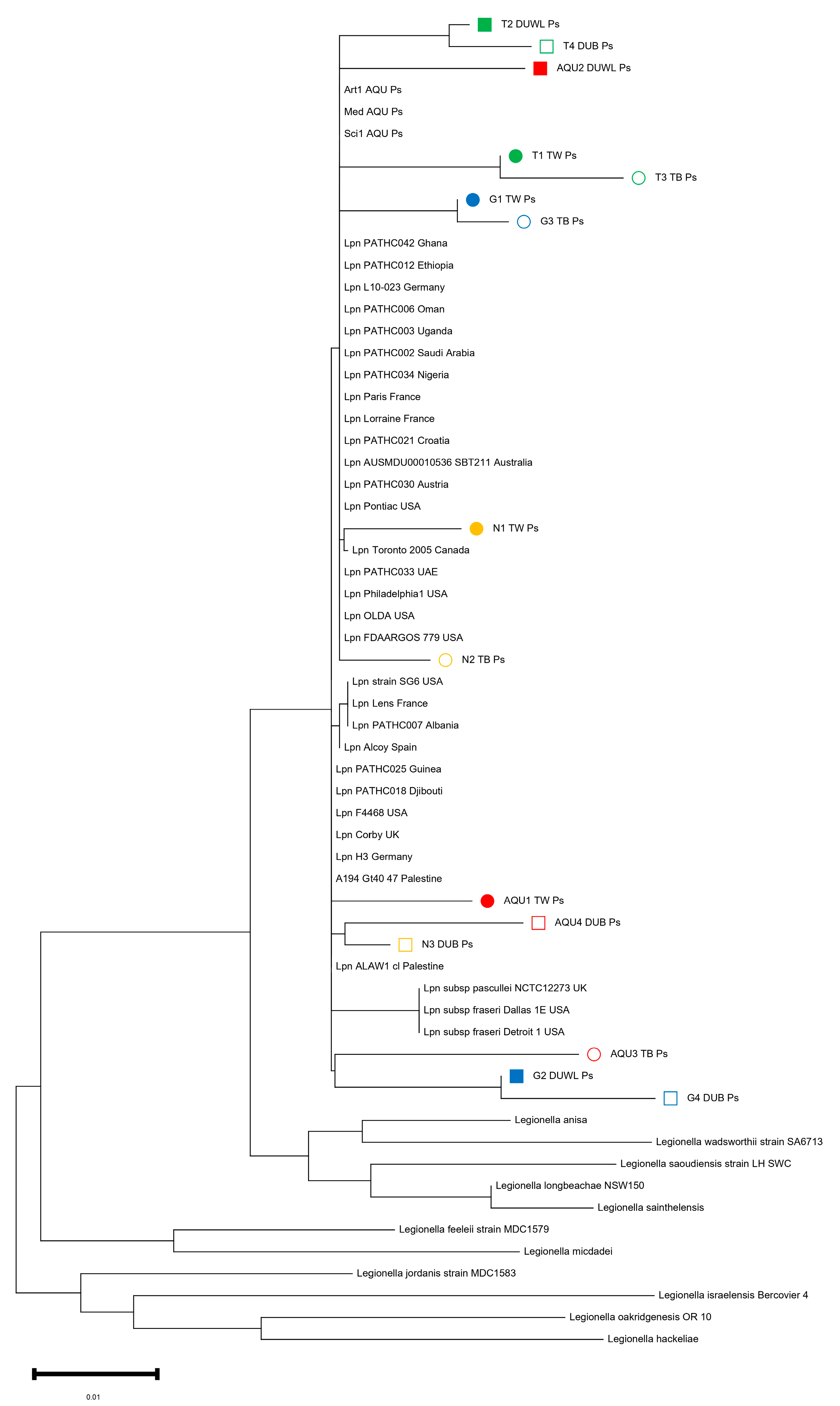
3.4. 16S RNA Sequencing of L. pneumophila Isolates
4. Discussion
4.1. Legionella Abundance in Dental Water and Biofilm Samples from the West Bank
4.2. Importance of the Study Findings in Dental Water Management Strategy and Health Impact on Chronic Diseases
4.3. Comparing L. pneumophila 16S rRNA Sequences from the West Bank to the International Database
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- David, S.; Afshar, B.; Mentasti, M.; Ginevra, C.; Podglajen, I.; Harris, S.R.; Chalker, V.J.; Jarraud, S.; Harrison, T.G.; Parkhill, J. Seeding and Establishment of Legionella pneumophila in Hospitals: Implications for Genomic Investigations of Nosocomial Legionnaires’ Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, H.; Peretz, A.; Lesnik, R.; Aizenberg-Gershtein, Y.; Rodriguez-Martinez, S.; Sharaby, Y.; Pastukh, N.; Brettar, I.; Hofle, M.G.; Halpern, M. Comparison of sputum microbiome of legionellosis-associated patients and other pneumonia patients: Indications for polybacterial infections. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercante, J.W.; Winchell, J.M. Current and emerging Legionella diagnostics for laboratory and outbreak investigations. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 95–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleres, G.; Couto, N.; Lokate, M.; van der Sluis, L.W.M.; Ginevra, C.; Jarraud, S.; Deurenberg, R.H.; Rossen, J.W.; Garcia-Cobos, S.; Friedrich, A.W. Detection of Legionella anisa in Water from Hospital Dental Chair Units and Molecular Characterization by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuvo, B.; Totaro, M.; Cristina, M.L.; Spagnolo, A.M.; Di Cave, D.; Profeti, S.; Baggiani, A.; Privitera, G.; Casini, B. Prevention and Control of Legionella and Pseudomonas spp. Colonization in Dental Units. Pathogens 2020, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, K.M.; Boczek, L.A.; Chae, S.; Ryu, H. Legionellosis and Recent Advances in Technologies for Legionella Control in Premise Plumbing Systems: A Review. Water 2020, 12, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajezadeh, M.; Mohseni, F.; Khaledi, A.; Firoozeh, A. Contamination of dental unit water lines (DUWL) with Legionella pneumophila and Pseudomonas aeruginosa; A Middle East systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 12, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, B.; Ghazvini, K.; Movahhed, T.; Ariaee, N.; Shakeri, M.; Makarem, S. Contamination of a dental unit water line system by Legionella pneumophila in the mashhad school of dentistry in 2009. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2012, 14, 376–378. [Google Scholar]
- Marino, F.; Mazzotta, M.; Pascale, M.R.; Derelitto, C.; Girolamini, L.; Cristino, S. First water safety plan approach applied to a Dental Clinic complex: Identification of new risk factors associated with Legionella and P. aeruginosa contamination, using a novel sampling, maintenance and management program. J. Oral. Microbiol. 2023, 15, 2223477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapko, J.; Frauenheim, E.; Juzbasic, M.; Tomas, M.; Matic, S.; Jukic, M.; Samardzic, M.; Skrlec, I. Legionella pneumophila-Virulence Factors and the Possibility of Infection in Dental Practice. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.L.; Strom, O.R.; Pruden, A.; Edwards, M.A. Interactive Effects of Copper Pipe, Stagnation, Corrosion Control, and Disinfectant Residual Influenced Reduction of Legionella pneumophila during Simulations of the Flint Water Crisis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsh, M.B.; Baron, J.L.; Mietzner, S.M.; Rihs, J.D.; Yassin, M.H.; Stout, J.E. Evaluation of Recommended Water Sample Collection Methods and the Impact of Holding Time on Legionella Recovery and Variability from Healthcare Building Water Systems. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaby, Y.; Rodriguez-Martinez, S.; Oks, O.; Pecellin, M.; Mizrahi, H.; Peretz, A.; Brettar, I.; Hofle, M.G.; Halpern, M. Temperature-Dependent Growth Modeling of Environmental and Clinical Legionella pneumophila Multilocus Variable-Number Tandem-Repeat Analysis (MLVA) Genotypes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e03295-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayani, M.; Raisolvaezin, K.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Mirhoseini, S.H. Bacterial biofilm prevalence in dental unit waterlines: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral. Health 2023, 23, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campese, C.; Bitar, D.; Jarraud, S.; Maine, C.; Forey, F.; Etienne, J.; Desenclos, J.C.; Saura, C.; Che, D. Progress in the surveillance and control of Legionella infection in France, 1998–2008. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e30–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ditommaso, S.; Giacomuzzi, M.; Ricciardi, E.; Zotti, C.M. Efficacy of a Low Dose of Hydrogen Peroxide (Peroxy Ag+) for Continuous Treatment of Dental Unit Water Lines: Challenge Test with Legionella pneumophila Serogroup 1 in a Simulated Dental Unit Waterline. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burghal, M.Z.H. Cultural and Molecular Evidence of Legionella pneumophila in Dental Unit Waterlines in the West Bank, Palestine; Al-Quds University: East Jerusalem, Palestine, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yakunin, E.; Kostyal, E.; Agmon, V.; Grotto, I.; Valinsky, L.; Moran-Gilad, J. A Snapshot of the Prevalence and Molecular Diversity of Legionella pneumophila in the Water Systems of Israeli Hotels. Pathogens 2020, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC. Procedures for the Recovery of Legionella from the Environment; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2005; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zayed, A.R.; Pecellin, M.; Salah, A.; Alalam, H.; Butmeh, S.; Steinert, M.; Lesnik, R.; Brettar, I.; Hofle, M.G.; Bitar, D.M. Characterization of Legionella pneumophila Populations by Multilocus Variable Number of Tandem Repeats (MLVA) Genotyping from Drinking Water and Biofilm in Hospitals from Different Regions of the West Bank. Pathogens 2020, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlisch, L.; Henne, K.; Groebe, L.; Draheim, J.; Hofle, M.G.; Brettar, I. Molecular analysis of the bacterial drinking water community with respect to live/dead status. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senderovich, Y.; Gershtein, Y.; Halewa, E.; Halpern, M. Vibrio cholerae and Aeromonas: Do they share a mutual host? ISME J. 2008, 2, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Matawah, Q.A.; Al-Zenki, S.F.; Qasem, J.A.; Al-Waalan, T.E.; Ben Heji, A.H. Detection and Quantification of Legionella pneumophila from Water Systems in Kuwait Residential Facilities. J. Pathog. 2012, 2012, 138389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaei, M.; Hemati, Z.; Moezzi, M.O.; Azimzadeh, N. Isolation and identification of Legionella spp. from different aquatic sources in south-west of Iran by molecular & culture methods. Mol. Biol. Res. Commun. 2016, 5, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zayed, A.R.; Butmeh, S.; Pecellin, M.; Salah, A.; Alalam, H.; Steinert, M.; Hofle, M.G.; Bitar, D.M.; Brettar, I. Biogeography and Environmental Drivers of Legionella pneumophila Abundance and Genotype Composition across the West Bank: Relevance of a Genotype-Based Ecology for Understanding Legionella Occurrence. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiaflaka, A.; Pournaras, S.; Kristo, I.; Mouchtouri, V.A.; Kyritsi, M.; Velonakis, E.; Vatopoulos, A.C.; Hadjichristodoulou, C. Epidemiological Investigation of Legionella pneumophila Serogroup 2 to 14 Isolates from Water Samples by Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism and Sequence-Based Typing and Detection of Virulence Traits. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6102–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mavridou, A.; Smeti, E.; Mandilara, G.; Pappa, O.; Plakadonaki, S.; Grispou, E.; Polemis, M. Prevalence study of Legionella spp. contamination in Greek hospitals. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2008, 18, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghrairi, T.; Chaftar, N.; Jarraud, S.; Berjeaud, J.M.; Hani, K.; Frere, J. Diversity of legionellae strains from Tunisian hot spring water. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma’ayeh, S.Y.; Al-Hiyasat, A.S.; Hindiyeh, M.Y.; Khader, Y.S. Legionella pneumophila contamination of a dental unit water line system in a dental teaching centre. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2008, 6, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Martinez, S.; Sharaby, Y.; Pecellin, M.; Brettar, I.; Hofle, M.; Halpern, M. Spatial distribution of Legionella pneumophila MLVA-genotypes in a drinking water system. Water Res. 2015, 77, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challacombe, S.J.; Fernandes, L.L. Detecting Legionella pneumophila in water systems: A comparison of various dental units. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1995, 126, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M.; Williams, J.F.; Huntington, M.K. Legionella contamination of dental-unit waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.F.; Johnston, A.M.; Johnson, B.; Huntington, M.K.; Mackenzie, C.D. Microbial contamination of dental unit waterlines: Prevalence, intensity and microbiological characteristics. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1993, 124, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, E.; Dallolio, L.; Stagni, F.; Sanna, T.; D’Alessandro, G.; Piana, G. Impact of a risk management plan on Legionella contamination of dental unit water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 2344–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaber, L.; Amro, M.; Tair, H.A.; Bahader, S.A.; Alalam, H.; Butmeh, S.; Hilal, D.A.; Brettar, I.; Hofle, M.G.; Bitar, D.M. Comparison of in situ sequence type analysis of Legionella pneumophila in respiratory tract secretions and environmental samples of a hospital in East Jerusalem. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 2116–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, A.R.; Bunk, B.; Jaber, L.; Abu-Teer, H.; Ali, M.; Steinert, M.; Hofle, M.G.; Brettar, I.; Bitar, D.M. Whole-genome sequencing of the clinical isolate of Legionella pneumophila ALAW1 from the West Bank allows high-resolution typing and determination of pathogenicity mechanisms. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2023, 10, 2168346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, A.R.; Pecellin, M.; Jaber, L.; Butmeh, S.; Bahader, S.A.; Steinert, M.; Hofle, M.G.; Brettar, I.; Bitar, D.M. Cytotoxicity, Intracellular Replication, and Contact-Dependent Pore Formation of Genotyped Environmental Legionella pneumophila Isolates from Hospital Water Systems in the West Bank, Palestine. Pathogens 2021, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, G.; Bornstein, N.; Rayet, I.; Pozzetto, B.; Lenormand, P.H. Nosocomial infection with Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 and 8 in a neonate. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 22, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.K.; Shim, J.I.; Kim, H.E.; Yu, J.Y.; Kang, Y.H. Distribution of Legionella species from environmental water sources of public facilities and genetic diversity of L. pneumophila serogroup 1 in South Korea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6547–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, I.; Zuckerman, T.; Avivi, I.; Finkelstein, R.; Yigla, M.; Rowe, J.M. Nosocomial outbreak of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 3 pneumonia in a new bone marrow transplant unit: Evaluation, treatment and control. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002, 30, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blanky, M.; Rodriguez-Martinez, S.; Halpern, M.; Friedler, E. Legionella pneumophila: From potable water to treated greywater; quantification and removal during treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesauro, M.; Petrelli, F.; Lizioli, A.; Pregliasco, F.; Masia, C.; Cossellu, G.; Farronato, G.; Consonni, M.; Sisto, F. Presence of Legionella spp. in human dental plaque. Ann. Ig. 2018, 30, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehfeld, A.S.; Reber, F.; Lewandowsky, M.M.; Jahn, H.J.; Luck, C.; Petzold, M.; Schaefer, B.; Germelmann, A.R.; Lorenz, K.; Buchholz, U. Could oral hygiene prevent cases of at-home-acquired Legionnaires’ disease?—Results of a comprehensive case-control study on infection sources, risk, and protective behaviors. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1199572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.P.A.; Peplies, J.; Hofle, M.G.; Brettar, I. Bacterial community dynamics in a cooling tower with emphasis on pathogenic bacteria and Legionella species using universal and genus-specific deep sequencing. Water Res. 2017, 122, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Matawah, Q.; Al-Zenki, S.; Al-Azmi, A.; Al-Waalan, T.; Al-Salameen, F.; Hejji, A.B. Legionella detection and subgrouping in water air-conditioning cooling tower systems in Kuwait. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 10235–10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, D.; Baron, J.L.; Ma, X.; Sidari, F.P., 3rd; Wagener, M.M.; Stout, J.E. Water Quality as a Predictor of Legionella Positivity of Building Water Systems. Pathogens 2019, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.R.; Bitar, D.M.; Steinert, M.; Lück, C.; Spröer, C.; Brettar, I.; Höfle, M.G.; Bunk, B. Comparative Genomics of Legionella pneumophila Isolates from the West Bank and Germany Support Molecular Epidemiology of Legionnaires’ Disease. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, D.; Amaro, F.; Zusman, T.; Lifshitz, Z.; Cohen, O.; Gilbert, J.A.; Pupko, T.; Shuman, H.A.; Segal, G. Genomic analysis of 38 Legionella species identifies large and diverse effector repertoires. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlicic, E.; Jaen-Luchoro, D.; Klobucar, R.S.; Jers, C.; Kazazic, S.; Franjevic, D.; Klobucar, G.; Shelton, B.G.; Mijakovic, I. Genomic characterization and assessment of pathogenic potential of Legionella spp. isolates from environmental monitoring. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1091964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaby, Y.; Rodriguez-Martinez, S.; Hofle, M.G.; Brettar, I.; Halpern, M. Quantitative microbial risk assessment of Legionella pneumophila in a drinking water supply system in Israel. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sampling Site (North to South) | Coordinates | Water Type | Leg. Count (CFU/L) ± SD | Temperature °C ± SD | pH ± SD | Conductivity µS/cm ± SD | Chlorine mg/L ± SD | Hardness mg/L ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jenin (Dental Faculty) | 32°23′ N, 35°19′ E | Tap Water | 57 ± 12 | 18 ± 0.7 | 7.8 ± 0.2 | 856 ± 51 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 278 ± 45 |
| DUWL | 53 ± 6 | 19 ± 0.5 | 7.8 ± 0.2 | 862 ± 54 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 264 ± 32 | ||
| Tulkarem (Dental clinics) | 32°31′ N, 32°18′ E | Tap Water | 115 ± 11 | 24 ± 0.7 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 819 ± 28 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 234 ± 31 |
| DUWL | 42 ± 5 | 24 ± 0.8 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 828 ± 41 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 244 ± 38 | ||
| Nablus (Dental clinics) | 32°22′ N, 32°13′ E | Tap Water | 27 ± 9 | 21 ± 0.4 | 7.4 ± 0.2 | 721 ± 51 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 284 ± 19 |
| DUWL | BD | 20 ± 0.4 | 7.3 ± 0.2 | 728 ± 48 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 291 ± 12 | ||
| Abu Deis/East Jerusalem (Dental Faculty) | 31°75′ N, 35°25′ E | Tap Water | 47 ± 5 | 18 ± 0.5 | 7.8 ± 0.2 | 724 ± 49 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 241 ± 11 |
| DUWL | 54 ± 12 | 18 ± 0.4 | 7.7 ± 0.2 | 728 ± 21 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 235 ± 18 | ||
| Hebron (Dental clinics) | 31°52′ N, 31°31′ E | Tap Water | BD | 17 ± 0.2 | 7.9 ± 0.3 | 762 ± 12 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 261 ± 62 |
| DUWL | BD | 18 ± 0.2 | 7.9 ± 0.2 | 757 ± 33 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 266 ± 27 |
| CDA 1 | CIA 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Site | L. pneumophila Isolates/Total Number 3 | % of Isolates | Leg. Counts (Mean of Tap Water) (CFU/L) ± SD | Leg. Counts (Mean of DUWL) (CFU/L) ± SD | Legionella spp. (Lgsp) Positive Samples/Total Number | % of Positive Samples | L. pneumophila (Lpn) Positive Samples/Total Number | % of Positive Samples |
| Jenin | 11/56 | 19.6 | 57 ± 12 | 53 ± 6 | 43/56 | 76.8 | 43/56 | 76.8 |
| Tulkarem | 7/31 | 22.6 | 115 ± 11 | 42 ± 5 | 29/31 | 93.5 | 26/31 | 83.9 |
| Nablus | 4/46 | 8.7 | 27 ± 9 | BD | 37/46 | 80.4 | 36/46 | 78.3 |
| Abu Deis/East Jerusalem | 6/44 | 13.6 | 47 ± 5 | 54 ± 12 | 34/44 | 77.3 | 34/44 | 77.3 |
| Hebron | 0/8 | 0.0 | BD | BD | 4/8 | 50.0 | 3/8 | 37.5 |
| Total | 28/185 | 15.1 | NA | NA | 147/185 | 79.5 | 142/185 | 76.8 |
| Sample Type | ||||||||
| Tap water | 7/39 | 17.9 | NA | NA | 35/39 | 89.7 * | 32/39 | 82.1 |
| DU water | 6/50 | 12 | NA | NA | 27/50 | 54 * | 27/50 | 54 |
| Total water | 13/89 | 14.6 | NA | NA | 62/89 | 69.7 | 59/89 | 66.3 |
| Tap biofilm | 9/45 | 20 | NA | NA | 41/45 | 91.1 | 41/45 | 91.1 |
| DU biofilm | 6/51 | 11.8 | NA | NA | 44/51 | 86.3 | 42/51 | 82.4 |
| Total biofilm | 15/96 | 15.6 | NA | NA | 85/96 | 88.5 | 83/96 | 86.5 |
| Sampling Site | No. of Isolates | No. Sg 1 (%) | No. Sg 2–14 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jenin | 11 | 9 (81.8%) | 2 (18.2%) |
| Tulkarem | 7 | 6 (85.7%) | 1 (14.3%) |
| Nablus | 4 | 3 (75%) | 1 (25%) |
| Abu Deis/East Jerusalem | 6 | 3 (50%) | 3 (50%) |
| Hebron | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 28 | 21 (75%) | 7 (25%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zayed, A.R.; Burghal, M.; Butmeh, S.; Samba-Louaka, A.; Steinert, M.; Bitar, D.M. Legionella pneumophila Presence in Dental Unit Waterlines: A Cultural and Molecular Investigation in the West Bank, Palestine. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8110490
Zayed AR, Burghal M, Butmeh S, Samba-Louaka A, Steinert M, Bitar DM. Legionella pneumophila Presence in Dental Unit Waterlines: A Cultural and Molecular Investigation in the West Bank, Palestine. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(11):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8110490
Chicago/Turabian StyleZayed, Ashraf R., Mutasem Burghal, Suha Butmeh, Ascel Samba-Louaka, Michael Steinert, and Dina M. Bitar. 2023. "Legionella pneumophila Presence in Dental Unit Waterlines: A Cultural and Molecular Investigation in the West Bank, Palestine" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 11: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8110490
APA StyleZayed, A. R., Burghal, M., Butmeh, S., Samba-Louaka, A., Steinert, M., & Bitar, D. M. (2023). Legionella pneumophila Presence in Dental Unit Waterlines: A Cultural and Molecular Investigation in the West Bank, Palestine. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(11), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8110490






