Abstract
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to collate the infection rates of Fasciola spp. in intermediate host snails and their distribution in Africa. The overall infectivity prevalences of Galba truncatula, Radix natalensis, and Pseudosuccinea columella are 52%, 8%, and 3%, respectively. The intermediate host snails native to Africa (R. natalensis and G. truncatula) have been examined more than the invasive P. columella. The studies included in the review ranged from 1999 to 2022. North Africa has the highest prevalence of G. truncatula, with an infection rate of 52%. The review reveals that naturally infected intermediate host snails (G. truncatula, R. natalensis, and P. columella) are found in various regions of Africa. G. truncatula accounts for 22% (from three countries) of the studies included in the review and it was only found in the North African region with the highest overall infection rate of 52%. More studies on infection rate and distribution are needed to effectively control and prevent future transmissions.
1. Introduction
Worldwide, fascioliasis is an emerging infection. Climate change effects may result in increased rainfall in some regions and decreased freezing temperatures in others, resulting in the emergence of new habitats for Fasciola and its hosts [1]. New irrigation projects and other man-made environmental changes may result in more appropriate habitats being available [2]. Fascioliasis is one of the most neglected zoonotic diseases in Africa despite being a threat to human and animal health. Good knowledge of the life cycles, host specificity, and geographic distribution of the important medical and veterinary parasites transmitted by intermediate host snails is a crucial requirement in the fight against them. Freshwater snails have been of interest to the research world as they are intermediate hosts for several diseases in animals and humans including fascioliasis. Fascioliasis, a trematode infection, thrives in tropical and subtropical countries. According to Dida et al. [3], before 1992, the total number of reported human cases of fascioliasis was considered to be less than 3000. More recent statistics show that between 2.4 and 17 million people are infected, with an additional 91.1 million people at risk of infection [4]. Trematode infections are still one of Africa’s most common and pervasive tropical diseases, especially in areas near freshwater bodies [5,6]. Fascioliasis is transmitted through two different hosts (intermediate and definitive). In nature, freshwater snails serve as the intermediate hosts for the development of its asexual stage. Humans are accidental hosts, but cattle and other ruminants serve as the final hosts for the sexual stage. The spread of the parasites and their vectors to new areas can be facilitated by migration, globalization, and the import and export of livestock. Together, all of these factors may lead to an expansion of endemic regions and a rise in the prevalence of Fasciola in livestock as well as in humans [6,7,8]. Because herding communities are constantly near the cattle they keep, fascioliasis is a disease that is highly prevalent in these communities [9]. Sripa and Piratae [10] suggested that it is possible to check for local transmission using knowledge about a particular type of snail in a given area. Over a million people in 90 countries are estimated to have been infected by parasitic diseases involving snail intermediate hosts [6]. The transmission dynamics of fascioliasis will be further complicated by climate change as it may change the presence, distribution, abundance, and infection rates of the intermediate host snails. Climate change may also result in the changing of interactions between animals and humans with the fasciola-infested waterbodies and pastures through changes in livelihoods.
Fascioliasis is caused by infection of trematodes belonging to the genus Fasciola spp. These Fasciola spp. are zoonotic pathogens whose common causative agents are Fasciola hepatica (Linnaeus, 1758) and Fasciola gigantica (Cobbold, 1855; Galba Schrank, 1803). The presence and distribution of intermediate host snails determine the geographic range of fascioliasis [11]. According to Moema and Baker [12] in Africa, Radix natalensis (Krauss, 1848) is involved in the transmission of F. gigantica whereas Galba truncatula (Muller, 1774) is involved in the transmission of F. hepatica, with any epidemiological cross-over being regarded to be unusual [13]. Galba truncatula is an intermediate host of the liver fluke F. hepatica, which is mostly accountable for human disease. It is distinguished by its amphibious lifestyle, adaptation to cooler habitats, and capacity to endure drought periods and other adverse climatic circumstances in unstable waterbodies [14]. It has been established that the invasive Pseudosuccinea columella (Say, 1817) serves as an intermediate host for both F. hepatica and F. gigantica in numerous countries [15]. Mage et al. [16] carried out a study in Central France over a period of 10–12 years to analyze the changes in the prevalence of fascioliasis. The infectivity prevalence of snails ranged from 4.7% (1989) to 7.2% (1993) and slowly decreased after that date reaching 3.3% (in 2000). Furthermore, Cucher et al. [17] obtained two samples from Argentina which were analyzed and identified as P. columella and the infection rate was 17.5% and 51.3% by direct examination and PCR, respectively. A study by [18] showed that P. columella can coexist with R. natalensis in some parts of South Africa. Fascioliasis is unfortunately not a recognized and reportable disease in many of the least developed countries, which are ravaged by poverty and infectious diseases. The first vital components in any planned intervention strategy include generating knowledge about this disease and raising awareness within the affected communities [19]. This systematic meta-analysis aimed to determine the infection rate of Fasciola spp. transmitted by intermediate host snails and their distribution in Africa. The results of this study show the role of these intermediate host snail species in fascioliasis transmission and its potential presence in both humans and animals and regional hotspots in different parts of Africa.
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategies and Inclusion Criteria
The search was conducted in three search databases, Google Scholar, Pubmed, Scopus, and other sources (reference list of included articles). The search terms used were as follows: “Fasciola intermediate host”, “intermediate host snails”, “snail intermediate host”, “intermediate host”, “freshwater snails”, “freshwater snail host”, “snail vector”, “malacology survey”, “Lymnaea columella”, “Lymnaea natalensis”, “Lymnaea truncatula”, “Pseudosuccinea columella”, “Radix natalensis”, “Galba truncatula”, “infection”, “infection rate”, “intensity”, “prevalence”, “incidence”, “Fascioliasis”, “liver fluke”, “Fasciola hepatica”, “Fasciola gigantica”, “Fasciola sp.”, “Africa”. These search terms were combined using the Boolean operators (AND; OR) to construct search phrases. The last phrase “Africa” was further categorized into African regions in the following manner: North African countries—Algeria OR Egypt OR Libya OR Morocco OR Sudan OR Tunisia OR and Western Sahara; Central or Middle African countries—Angola OR Cameroon OR Central African Republic OR Chad OR Congo Republic—Brazzaville OR Democratic Republic of Congo OR Equatorial Guinea OR Gabon OR and São Tomé and Principe; Southern African countries—Botswana OR Lesotho OR Namibia OR South Africa OR Swaziland OR Lesotho; OR Madagascar OR Malawi OR Mauritius OR Mozambique OR Zambia OR and Zimbabwe; East African countries—Burundi OR Comoros OR Djibouti OR Ethiopia OR Eritrea OR Kenya OR Réunion OR Rwanda OR Seychelles OR Somalia OR Somaliland OR Tanzania OR Uganda; Western Africa—Benin OR Burkina Faso OR Cape Verde OR Côte D’Ivoire OR Gambia OR Ghana OR Guinea OR Guinea-Bissau OR Liberia OR Mali OR Mauritania OR Niger OR Nigeria OR Senegal OR Sierra Leone OR Togo. See Supplementary Material File S1 for the full literature search terms and combinations that were used on PubMed, Google Scholar, and other databases.
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were used for the paper selection process (Figure 1). The following were requirements for all articles to be included in this study: (a) studies reporting data from any African country, (b) studies reporting data on fascioliasis infection on intermediate host snails from the Family lymnaeidae (P. columella, R. natalensis, and G. truncatula) to species level, (c) studies reporting distribution of the Family lymnaeidae within Africa, (d) studies that mentioned the diagnostic used in detecting infected snails, (e) only studies written in English, and (f) studies that reported infection in snails that had been sampled from the field and not laboratory-infected snails. Studies without full texts, studies that were review articles, and meta-analyses were excluded. The articles that qualified to be included in the review were retrieved and exported from the different database libraries to the Endnote 20 reference manager.
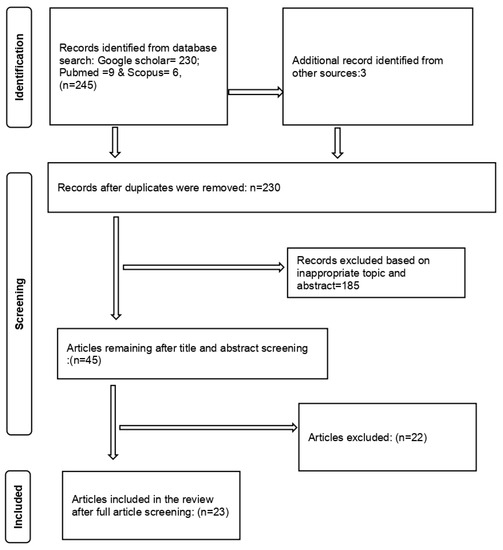
Figure 1.
PRISMA diagram of the articles included in the meta-analysis.
2.2. Data Extraction and Quality Appraisal
The first author’s name, the year of publication, the country of the study, the species of snails used (collection, examination, and infection), the number of snails, as well as the diagnostics used to detect Fasciola infection were all included in the data extraction format from the assessed articles. Using the 10 quality-control criteria outlined by the Joanna Briggs Institute Prevalence Critical Appraisal [16], the quality of all included research was evaluated (Supplementary Material File S2).
2.3. Data Analysis
The pooled prevalence estimates from the eligible studies were obtained using an inverse variance heterogeneity (IVhet) model in MetaXL version 5.3 (a Microsoft Excel add-in tool for meta-analysis). The IVhet model was chosen above the fixed-effect and random-effect models because, in the absence of heterogeneity, the confidence interval coverage stays relatively close to the nominal level [20,21]. To display the estimated prevalence and its 95% confidence interval, forest plots were created. Cochran’s Q statistic was utilized to gauge the degree of study heterogeneity, and Higgin’s inconsistency statistic (i2) was used to measure the degree of study variability. When Higgins’s i2 value is less than 25%, 50%, and 75%, it can be considered that it demonstrates strong homogeneity, medium heterogeneity, and high heterogeneity, respectively [22]. Using the Luis Furuya-Kanamori (LFK) index of the Doi plot, publication bias was evaluated. The size of the LFK index determined the degree of publishing bias. An LFK value within the range of “±1” was considered to be “symmetrical” and classified as the absence of publication bias, while an LFK value outside the range of “±2” was considered to be major asymmetry and high publication bias. Additionally, to explain the observed heterogeneity, subgroup analysis was performed using our data stratified by snail species and the African regions where the studies were conducted [23,24].
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
The search yielded 245 articles from the different databases, and 15 were identified as duplicates and therefore removed. The 230 remaining articles were screened by title and abstract resulting in the exclusion of 185 articles. Forty-five articles remained after the title and abstract screening. After the full article screening, 22 articles were excluded and 23 articles were considered eligible for inclusion in the systematic review and meta-analysis (Figure 1). The studies included in this review ranged from 1999 to 2022.
The review focused on African countries, but the 23 included articles were from 10 countries (Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3). The method of diagnosis used to detect the Fasciola infection was cercarial shedding for 14 articles, 5 articles used both cercarial shedding and crushing, 3 articles used PCR, and 1 article used dissecting.
3.2. Infection Rates of Fasciola Intermediate Host Snail Species and Their Distribution in Africa
The highest infection rate was 43.5% (n = 10) in Egypt and 17.4% (n = 4) in Nigeria. Following was Algeria with 8.7% (n = 2), while Zambia, Tanzania, Sudan, Ethiopia, Tunisia, and South Africa all consisted of 4% (n = 1). Of the 23 articles, 53.3% (n = 14) reported on R. natalensis (Table 1); 20% (n = 5) reported on G. truncatula; and 17% (n = 4) of the articles reported on P. columella.


Table 1.
Infection rates of Radix natalensis with Fasciola spp. in African regions.
Table 1.
Infection rates of Radix natalensis with Fasciola spp. in African regions.
| African Region | Country | Sample Size | Positive | Infection Rate (%) | Method | Sampling Period | Quality Score | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Africa | Egypt | 1500 | 1110 | 74 | Cercariae shedding and crushing | April 2016–September 2017 | 10 | [25] |
| Egypt | 918 | 197 | 21.5 | Crushing and Cercariae shedding | January 2004–December 2006 | 10 | [26] | |
| Egypt | 917 | 51 | 5.5 | Cercariae shedding and crushing | Not specified | 9 | [27] | |
| Egypt | 4939 | 27 | 0.6 | Crushing technique | March 1997–February 1999 | 10 | [28] | |
| Sudan | 1710 | 412 | 23.7 | Cercarial shedding | Not specified | 9 | [29] | |
| Egypt | 2237 | 91 | 41 | Cercariae shedding | December –August 2005 | 10 | [30] | |
| West Africa | Nigeria | 211 | 18 | 8.5 | Cercarial shedding | January–May 2019 | 10 | [31] |
| Nigeria | 372 | 4 | 1.1 | Cercariae shedding | June–December 2014 | 10 | [32] | |
| Nigeria | 2180 | 12 | 1.7 | Cercariae shedding | August–September 2011 | 10 | [33] | |
| Nigeria | 630 | 69 | 10.95 | Cercariae shedding | January 2013–December 2013 | 10 | [34] | |
| East Africa | Ethiopia | 747 | 11 | 1.5 | Cercariae shedding | March–May 2016 | 10 | [35] |
| Tanzania | 832 | 86 | 10.3 | Cercariae shedding | July 1996–June 1997 | 10 | [36] | |
| Ethiopia | 412 | 11 | 2.7 | Cercarial shedding | February–May 2016 | 10 | [37] | |
| Southern Africa | Zambia | 984 | 135 | 13.7 | Cercariae shedding | August–October 2003 | 10 | [38] |
The information in Table 1 is for R. natalensis; it includes the citation of the study the information was extracted from, the country, African region, duration of sampling, sample size, positive snails, infection rate, and the method of diagnosis.
The pooled prevalence estimate of infectivity for R. natalensis (Figure 2) was 8% (95% CI: 0.00–0.20) with a significantly low degree of heterogeneity (I2 = 100%, p = 0.00). The Southern Africa region had the highest prevalence estimate infectivity at 14% (95% CI: 0.12–0.16), followed by North Africa 8% (95% CI: 0.00–0.41), West Africa 7% (95% CI: 0.00–0.24), and East Africa had the least, which was 5% (95% CI: 0.00–0.11).
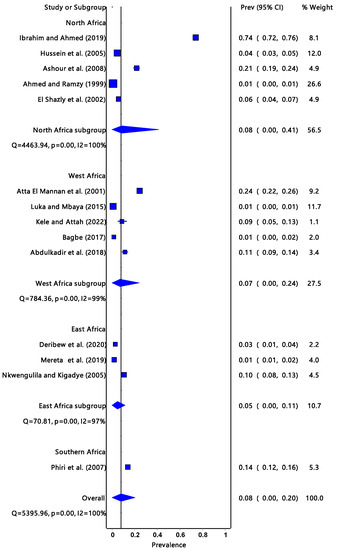
Figure 2.
The forest plot represents the prevalence estimate of Fasciola intermediate host snail Radix natalensis extracted from studies included in the review [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38].
3.2.1. Infection Rates of Galba Truncatula in African Regions
A total of 5 articles from the eligible (23) focus on G. truncatula sp (Table 2). Interestingly, from the articles obtained, its distribution is restricted to the North African region (Algeria (n = 2); Egypt (n = 2); and Tunisia (n= 1)). The infection rate of the intermediate host ranged between 3.1% and 19.2%; the lowest (3.1%) was recorded in Egypt [27] and the highest (19.2%) was recorded in Tunisia [39].


Table 2.
Infection rates of Galba truncatula with Fasciola spp. in African regions.
Table 2.
Infection rates of Galba truncatula with Fasciola spp. in African regions.
| African Region | Country | Sample Size | Positive Snails | Infection Rate (%) | Method | Sampling Period | Quality Score | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Africa | Algeria | 722 | 75 | 10.7 | Multiplex PCR | Not specified | 9 | [40] |
| Tunisia | 1346 | 1218 | 19.2 | Cercariae shedding | July 2004–May 2005 | 10 | [39] | |
| Egypt | 731 | 71 | 9.7 | Crushing technique | March–May 2014 | 10 | [41] | |
| Egypt | 215 | 7 | 3.1 | Cercariae shedding and crushing | Not specified | 9 | [27] | |
| Algeria | 1303 | 888 | 4.0 | Crushing technique | November 2002–May 2003 | 10 | [42] |
The pooled prevalence estimated infectivity for G. truncatula (Figure 3) was 52% (95% CI: 0.05–0.97) with a significantly low degree of heterogeneity (I2 = 100%, p = 0.00) and it was only found in the North African region.
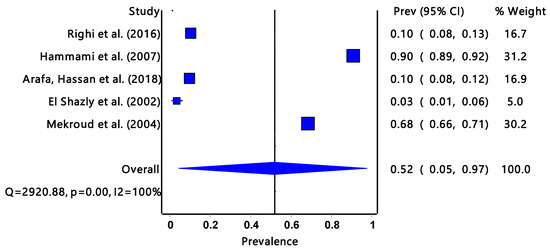
Figure 3.
The forest plot represents the pooled prevalence estimate of Fasciola intermediate host snail Galba truncatula extracted from studies included in the review [27,39,40,41,42].
3.2.2. Infection Rates of Pseudosuccinea Columella in African Regions
Table 3 shows 4 articles from the 23 eligible. These articles focus on the P. columella sp. From the articles obtained, its distribution is limited to the North African region (Egypt (n = 3)) and the South African region (South Africa (n = 1)). The infection rate of the intermediate host ranged between 0% and 100%; the lowest was recorded in Egypt [27] and the highest (100%) was recorded in South Africa [15].


Table 3.
Infection rates of Pseudosuccinea columella with Fasciola spp. in African regions.
Table 3.
Infection rates of Pseudosuccinea columella with Fasciola spp. in African regions.
| African Region | Country | Sample Size | Positive | Infection Rate (%) | Method | Sampling Period | Quality Score | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southern Africa | South Africa | 100 | 100 | 100 | PCR | November 2017–July 2018 | 10 | [15] |
| North Africa | Egypt | 4087 | 81 | 2.0 | Crushing technique | March 1997–February 1999 | 10 | [28] |
| Egypt | 296 | 38 | 12.84 | PCR | Not specified | 9 | [43] | |
| Egypt | 45 | 0 | 0 | Cercariae shedding and crushing | Not specified | 9 | [27] |
The invasive P. columella (Figure 4) pooled prevalence estimate of infectivity was 3% (95% CI: 0.00–1.00) and it had a moderate-to-high degree of heterogeneity (I2 = 100%, p = 0.00). Interestingly the infectivity data were obtained from two regions, Southern Africa at 100% (95%CI: 0.98–1.00) and North Africa at 2% (95% CI: 0.00–0.15).
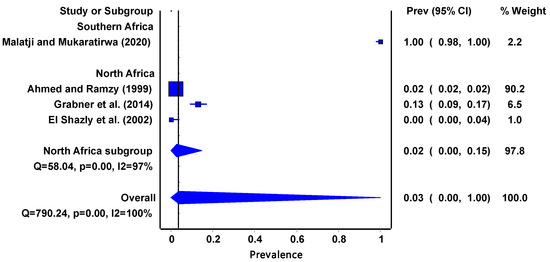
Figure 4.
The forest plot represents the pooled prevalence estimate of Fasciola intermediate host snail P. columella extracted from studies included in the review [15,27,28,43].
The Fasciola spp. (Figure 5) pooled prevalence estimate of infectivity was 10% (95% CI: 0.00–0.24) and it had a moderate to a high degree of heterogeneity (I2= 100%, p = 0.00). The infectivity of F. gigantica was 7% (95% CI: 0.00–0.17) and F. hepatica infectivity was 22% (95% CI: 0.00–0.79).
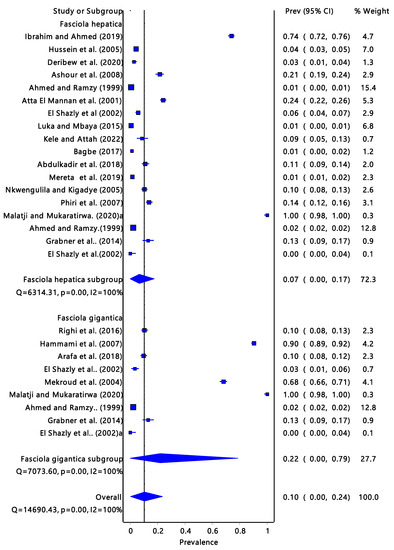
Figure 5.
Forest plot represents the pooled prevalence estimate of Fasciola gigantica and Fasciola hepatica extracted from the studies included in the review [15,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44].
The Doi plot showed a significant publication bias, as indicated by the LFK index of 2.78, which indicates a significant asymmetry (Figure 6).
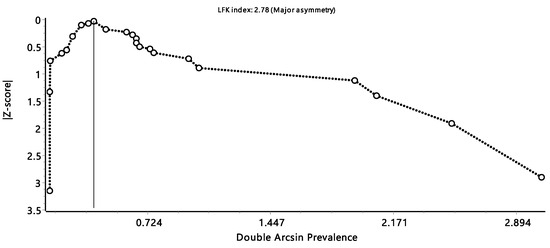
Figure 6.
Luis Furuya-Kanamori (LFK) index of the Doi plot presents the publication bias.
4. Discussion
The systematic review and meta-analysis were carried out to determine the infection rate of Fasciola intermediate host snails (P. columella, R. natalensis, and G. truncatula) and their distribution in African regions. The distribution of the intermediate host snails and the rate of their infections are indicators of disease hotspots and are hence important to know from a disease control perspective. The findings of this review suggest that naturally infected intermediate host snails (P. columella, R. natalensis, and G. truncatula) are found in various regions of Africa; however, no studies on the infection rates of Fasciola intermediate host snails were identified from the Central African region. This may be attributed to conflict in Central African countries which limits research activities; hence, it is not easy to determine infection rates of Fasciola intermediate host snails in that region [45].
The native intermediate host snails’ (R. natalensis and G. truncatula) infectivity prevalence has been studied more than that of invasive P. columella. Radix natalensis accounts for 60.9% of the studies included in the review which were from various African regions. The Southern Africa region had the highest Fasciola infection prevalence but consisted of one study [38], followed by the North Africa region which consisted of studies mainly from Egypt [25,26,27,28,30]. The results of this review showed that Egypt had the highest Fasciola infection prevalence in Africa. These findings are in agreement with Nyindo and Lukambagire [19], who stated that, to date, fascioliasis has been identified in many countries and Egypt has the highest prevalence. Radix natalensis had a low overall Fasciola infection rate of 8%. There was a wide distribution of R. natalensis (North Africa, East Africa, West Africa, and Southern Africa) compared to the other intermediate host snails in this study. Most countries in these regions practice livestock farming and the migration of livestock contributes to the distribution of Fasciola spp. The wide distribution of R. natalensis was also noted by Malatjli et al. [44], where lymnaeide snail species appeared in 10 of the 12 countries in the East and Southern Africa regions. The results of this review aligned with Moema and Barker [12] who suggested that the primary snail host for F. hepatica or F. gigantica, common in Africa, is the R. natalensis snail. The study by Wamae et al. [46] further stated that the most prevalent liver fluke in sub-Saharan Africa is F. gigantica, which thrives in warmer climates probably as a result of the vast distribution of its intermediate host R. natalensis.
Galba truncatula accounts for 22% (from three countries) of the studies included in the review and it was only found in the North African region with the highest overall infection rate of 52%. Countries in the North African region usually have hot climatic conditions with little rainfall. The study from Tunisia had a significantly high Fasciola prevalence rate compared to studies from Algeria and Egypt [11,27,39,40,42]. Galba truncatula is an amphibious organism and can survive long dry periods, hence the high percentage of Fasciola infection [47]. Temperature is one of the environmental conditions that can affect the host–parasite interaction by compromising immunological processes, thereby lowering host resistance to infections [48].
The results of this review show that there is an overlap of distribution between R. natalensis and G. truncatula in Africa. According to Malatji et al. [45], overlaps can be local, as in the Nile Delta in Egypt, where the climate is favorable for the coexistence of Galba and Radix species throughout the year, or zonal, as in highland areas where the cold-mild weather favors F. hepatica and G. truncatula and the lowlands provide the warm-hot climate for Radix spp. and the F. gigantica system. This latter type of overlap has been described [47].
The invasive P. columella accounts for 17% of the studies included in the review which yielded an overall infection rate of 3%. The prevalence of Fasciola infectivity in P. columella may be affected by biological factors such as predators and competitors because it is still adapting in the African regions. Predators prey on freshwater snails and consume trematode larvae, miracidia. Consequently, the prevalence of freshwater snail infection with trematodes may be reduced. The distribution and infectivity of these Fasciola intermediate host snails may be further complicated by climate change. Hence, there is need for more studies on the impact of climate change on their presence, abundance, co-habitation, and infectivity.
In Africa, the infection rate of Fasciola spp. in the definitive hosts is significantly much more studied than in the intermediate host snails. It is important to note that the infection rate of ruminants can be significantly higher than that of intermediate hosts. One of the reasons is that it is easier to deal with livestock than to deal with snails whose abundance and distribution are not easy to estimate. Livestock are of more economic importance than intermediate hosts. There were reports about fascioliasis in ruminants from Chad, Egypt, Ethiopia, Kenya, Nigeria, Sudan, Tanzania, Tunisia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. The highest number of reports were recorded in Kenya and Ethiopia. According to Jones et al. [49], the majority of infections are caused by bovine fascioliasis, which is widely distributed throughout the world and accounts for 29% of zoonoses. The infection rate of Fasciola spp. in the intermediate host snails may give an indication of the presence and burden of the disease in the community, i.e., livestock and humans. El Shazly et al. [27] examined all three intermediate host snails which were co-existing in Egypt. Radix natalensis, G. truncatula, and P. columella had infection rates of 5.5%, 3.1%, and 0%, respectively. The results from this review (Figure 5) suggested that F. hepatica has the highest infection prevalence at 22% compared to F. gigantica at 7%; however, the overall pooled prevalence was low. These findings were in line with the results (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4) obtained from the Fasciola infection prevalence of intermediate host snails of these Fasciola spp. In this study. Generally, the prevalence was fairly low. According to Bowden [50], a hospital in Egypt received patients with fever of unknown origin, and 4% of them tested positive for F. hepatica. Previously endemic in isolated foci along the Nile River in Egypt, the F. hepatica-caused disease is now widespread throughout the Nile valley. According to an earlier study by Esteban et al. [51] that looked at parasite causes of pediatric hepatomegaly, about 8.7% of the patients under investigation had fascioliasis in the villages in the Nile Delta of Egypt. This is an indication of the consequences of the transmission of Fasciola.
The main limitation of this review is that the cercarial shedding method was used in 70% (16/23) of the studies included in the review to determine Fasciola infections. Due to its accessibility and affordability, this is a frequent diagnostic technique for identifying infections, and the cercarial shedding technique is time- and labor-intensive; it is known to significantly underestimate the true prevalence of infection in the intermediate host snail. The low pooled prevalence in this meta-analysis may therefore be partially attributable to the infection detection method [52]. A significant number of reviews in Africa focus on the infection rate of Fasciola in definitive hosts [53,54,55,56], and according to our knowledge, there has not been a review focusing on the infection rate of intermediate host snails in all the regions of Africa; hence, the need of this review is significant.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this review has revealed that naturally infected Lymnaeide intermediate host snails are distributed in the various African regions and the Fasciola infection prevalence varies in the different regions depending on the IH and Fasciola spp. Overall, the low number of studies retrieved shows that the role of intermediate host snails in the transmission of Fasciola spp. is still neglected in Africa. This calls for more studies on the comparative analysis of the environmental and climatic factors related to the presence, abundance, co-habitation, and infection rates of these Fasciola intermediate host snails and to elucidate the potential impacts of climate change on the transmission dynamics of this disease in Africa. Our findings also emphasize the need for more malacology surveys using enhanced infectivity diagnostic methods throughout the various African regions to improve the diagnosis of infection and integrated snail control strategies to prevent the spread of fascioliasis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/tropicalmed8100467/s1, File S1: Search strategy; File S2: Quality assessment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.I.H., T.M. (Tawanda Manyangadze) and M.J.C.; methodology, M.I.H., and T.M. (Tawanda Manyangadze); data curation, M.I.H., and T.M. (Tafadzwe Mindu); formal analysis, M.I.H.; writing—original draft preparation, M.I.H.; writing—review and editing, M.I.H., T.M. (Tawanda Manyangadze), C.K. and M.J.C.; supervision, M.J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No. 101000365.

Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Moses Chimbari, Chester Kalinda, Tawanda Manyangadze, and Tafadzwa Mindu for their advice and assistance that made this article a success. The administrative and technical assistance provided by Nokwanda Majola and Sambulo Gombela is gratefully acknowledged by the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Beesley, N.; Caminade, C.; Charlier, J.; Flynn, R.; Hodgkinson, J.; Martinez-Moreno, A.; Martinez-Valladares, M.; Perez, J.; Rinaldi, L.; Williams, D. Fasciola and fasciolosis in ruminants in Europe: Identifying research needs. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydock, L.; Pomroy, W.; Stevenson, M.; Lawrence, K. A growing degree-day model for determination of Fasciola hepatica infection risk in New Zealand with future predictions using climate change models. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 228, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dida, G.O.; Gelder, F.B.; Anyona, D.N.; Matano, A.-S.; Abuom, P.O.; Adoka, S.O.; Ouma, C.; Kanangire, C.K.; Owuor, P.O.; Ofulla, A.V. Distribution and abundance of schistosomiasis and fascioliasis host snails along the Mara River in Kenya and Tanzania. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2014, 4, 24281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Abdurahman, M.; Zewdu, M. Growing significance of fascioliasis as an emerging zoonosis. Ethiop. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2014, 1, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Black, C.L.; Mwinzi, P.N.; Muok, E.M.; Abudho, B.; Fitzsimmons, C.M.; Dunne, D.W.; Karanja, D.M.; Secor, W.E.; Colley, D.G. Influence of exposure history on the immunology and development of resistance to human Schistosomiasis mansoni. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourin, E.; Alda, P.; Vázquez, A.; Hurtrez-Boussès, S.; Vittecoq, M. Impact of human activities on fasciolosis transmission. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, J.; Ghebretinsae, A.H.; Levecke, B.; Ducheyne, E.; Claerebout, E.; Vercruysse, J. Climate-driven longitudinal trends in pasture-borne helminth infections of dairy cattle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozio, E. How globalization and climate change could affect foodborne parasites. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 208, 107807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Fascioliasis. In Digenetic Trematodes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 77–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sripa, J.; Kiatsopit, N.; Piratae, S. Prevalence of trematode larvae in intermediate hosts: Snails and fish in Ko Ae sub-district of Khueang Nai, Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2016, 47, 399–409. [Google Scholar]
- Arafa, W.M. Detection of Fasciola hepatica infection in cattle and Lymnaea truncatula snails in Dakhla Oasis, Egypt. Egypt. Vet. Med. Soc. Parasitol. J. 2015, 11, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moema, E.; King, P.; Baker, C. Cercariae developing in Lymnaea natalensis Krauss, 1848 collected in the vicinity of Pretoria, Gauteng Province, South Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2008, 75, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kock, K.; Wolmarans, C.; Bornman, M. Distribution and habitats of the snail Lymnaea truncatula, intermediate host of the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica, in South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2003, 74, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, R.T. The Ecology of Freshwater Molluscs; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Malatji, M.; Mukaratirwa, S. Molecular detection of natural infection of Lymnaea (Pseudosuccinea) columella (Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae) with Fasciola gigantica (Digenea: Fasciolidae) from two provinces of South Africa. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mage, C.; Bourgne, H.; Toullieu, J.-M.; Rondelaud, D.; Dreyfuss, G. Fasciola hepatica and Paramphistomum daubneyi: Changes in prevalences of natural infections in cattle and in Lymnaea truncatula from central France over the past 12 years. Vet. Res. 2002, 33, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucher, M.; Carnevale, S.; Prepelitchi, L.; Labbé, J.; Wisnivesky-Colli, C. PCR diagnosis of Fasciola hepatica in field-collected Lymnaea columella and Lymnaea viatrix snails. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatji, M.; Lamb, J.; Mukaratirwa, S. Molecular characterization of liver fluke intermediate host lymnaeids (Gastropoda: Pulmonata) snails from selected regions of Okavango Delta of Botswana, KwaZulu-Natal and Mpumalanga provinces of South Africa. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2019, 17, 100318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyindo, M.; Lukambagire, A.-H. Fascioliasis: An ongoing zoonotic trematode infection. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 786195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, S.A.; Barendregt, J.J.; Khan, S.; Thalib, L.; Williams, G.M. Advances in the meta-analysis of heterogeneous clinical trials I: The inverse variance heterogeneity model. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, S.A.; Furuya-Kanamori, L. Selecting the best meta-analytic estimator for evidence-based practice: A simulation study. JBI Evid. Implement. 2020, 18, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, E.; Kang, H. Introduction to systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2018, 71, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, J.P. Interpretation of tests of heterogeneity and bias in meta-analysis. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2008, 14, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; Ahmed, A.K. Trematode cercarial fauna obtained from the field-collected freshwater snails Lymnaea natalensis in Egypt. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, A.; Mostafa, B.; Taha, H.; Azzam, A. Distribution of Natural Populations of Lymnaea Snails in Some Egyptian Governorates and Their Natural Infection with Fasciola. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 16, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- El Shazly, A.M.; Helmy, M.M.; Haridy, F.M.; El Sharkawy, E.M.; Morsy, T.A. Fasciola immature stages sought in Lymnaea species and Biomphalaria species in the water bodies of Dakahlia Governorate. J.-Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Ramzy, R.M. Infection of two lymnaeid snails with Fasciola gigantica in Giza, a field study. J.-Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 687–696. [Google Scholar]
- Atta El Mannan, A.; Bushara, H.; Majid, A. Some aspects of the epidemiology of bovine fasciolosis in northern Gazira and Khartoum State. Sudan J. Vet. Res. 2001, 17, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, A.; Califa, R.; Mas-Coma, S. Trematode larval stages infecting Radix natalensis (Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae) in Qena Governorate, Egypt, with special reference to fasciolid cercariae. Res. Rev. Parasitol. 2005, 66, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kele, M.; Attah, D.D. Cercarial shedding and trematodes infestation in freshwater snail species from selected freshwater bodies in Zuru Emirate, Kebbi State, Nigeria. Int. J. Biomed. Health Sci. 2022, 17, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bagbe, A.S. Malacological study of snail intermediate hosts of trematode parasites in Okitipupa Local Government Area, Ondo State, Nigeria. Acad. J. 2017, 9, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Luka, J.; Mbaya, A.W. Cercarial shedding of trematodes and their associated snail intermediate hosts in Borno State, Nigeria. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2015, 5, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadir, F.M.; Maikaje, D.; Umar, Y. Cercarial Diversity in Freshwater Snails from Selected Freshwater Bodies and Its Implication for Veterinary and Public Health in Kaduna State, Nigeria. Int. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2018, 12, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Mereta, S.T.; Bedewi, J.; Yewhalaw, D.; Mandefro, B.; Abdie, Y.; Tegegne, D.; Birke, W.; Mulat, W.L.; Kloos, H. Environmental determinants of distribution of freshwater snails and trematode infection in the Omo Gibe River Basin, southwest Ethiopia. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkwengulila, G.; Kigadye, E. Occurrence of digenean larvae in freshwater snails in the Ruvu Basin, Tanzania. Tanzan. J. Sci. 2005, 31, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deribew, K.; Jaleta, E.; Mandefro, B.; Mekonnen, Z.; Yewhalaw, D.; Abdie, Y.; Mereta, S.T. Effects of land use on intermediate snail host fauna, abundance, distribution and cercariae infection rate in Omo-Gibe river basin, Ethiopia. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, A.; Phiri, I.; Chota, A.; Monrad, J. Trematode infections in freshwater snails and cattle from the Kafue wetlands of Zambia during a period of highest cattle–water contact. J. Helminthol. 2007, 81, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, H.; Hamed, N.; Ayadi, A. Epidemiological studies on Fasciola hepatica in Gafsa Oases (south west of Tunisia). Parasite 2007, 14, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, S.; Benakhla, A.; Mekroud, A.; Ouchene, N.; Sedraoui, S. Prevalence of Fasciola hepatica in Galba truncatula detected by multiplex PCR in the province of El Tarf (Algeria). Trop. Biomed. 2016, 33, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Arafa, W.; Hassan, A.; Snousi, S.; El-Dakhly, K.M.; Holman, P.; Craig, T.; Aboelhadid, S. Fasciola hepatica infections in cattle and the freshwater snail Galba truncatula from Dakhla Oasis, Egypt. J. Helminthol. 2018, 92, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekroud, A.; Benakhla, A.; Vignoles, P.; Rondelaud, D.; Dreyfuss, G. Preliminary studies on the prevalences of natural fasciolosis in cattle, sheep, and the host snail (Galba truncatula) in north-eastern Algeria. Parasitol. Res. 2004, 92, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, D.; Mohamed, F.; Nachev, M.; Méabed, E.; Sabry, A. Invasion Biology Meets Parasitology: A Case Study of Parasite Spill-Back. PloS ONE 2014, 9, e88537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatji, M.; Pfukenyi, D.; Mukaratirwa, S. Fasciola species and their vertebrate and snail intermediate hosts in East and Southern Africa: A review. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukeri, S.; Malatji, M.P.; Sengupta, M.E.; Vennervald, B.J.; Stensgaard, A.-S.; Chaisi, M.; Mukaratirwa, S. Potential Hybridization of Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica in Africa—A Scoping Review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamae, L.; Hammond, J.; Harrison, L.; Onyango-Abuje, J. Comparison of production losses caused by chronic Fasciola gigantica infection in yearling Friesian and Boran cattle. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1998, 30, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Climate change effects on trematodiases, with emphasis on zoonotic fascioliasis and schistosomiasis. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.; Merino, S. Host-parasite interactions under extreme climatic conditions. Current Zoology 2011, 57, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, L. Fascioliasis and fasciolopsiasis: Similar names, similar diseases. J. Spec. Oper. Med. 2008, 8, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, J.-G.; Gonzalez, C.; Curtale, F.; Muñoz-Antoli, C.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D.; El Sayed, M.; El Wakeel, A.A.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.; Montresor, A. Hyperendemic fascioliasis associated with schistosomiasis in villages in the Nile Delta of Egypt. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 69, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, Y.; Rondelaud, D.; Losson, B. The detection and quantification of a digenean infection in the snail host with special emphasis on Fasciola sp. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elelu, N.; Eisler, M. A review of bovine fasciolosis and other trematode infections in Nigeria. J. Helminthol. 2018, 92, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Zhang, H.; Sabir, A.J.; Abbas, R.Z.; Ijaz, M.; Durrani, A.Z.; Saleem, M.H.; Rehman, M.U.; Iqbal, M.K.; Wang, Y. A review on epidemiology, global prevalence and economical losses of fasciolosis in ruminants. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, B. Bovine Fasciolosis in Ethiopia—A review. J. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 2, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Tsega, M. A review on ruminant fasciolosis. Open Access Libr. J. 2015, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).