Epidemiology and Characteristics of Rickettsia australis (Queensland Tick Typhus) Infection in Hospitalized Patients in North Brisbane, Australia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Distribution of Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derne, B.; Weinstein, P.; Musso, D.; Lau, C. Distribution of rickettsioses in Oceania: Past patterns and implications for the future. Acta Trop. 2015, 143, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Rickettsial Reference Laboratory. Disease Description and/or Epidemiology. 2015. Available online: http://www.rickettsialab.org.au/-!about (accessed on 22 July 2015).
- NNDSS. Australia’s Notifiable Disease Status: Annual Report of the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System. Department of Health and Ageing, 2013. Available online: http://www.commcarelink.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/cda-pubs-annlrpt-nndssar.htm (accessed on 22 July 2015).
- Faa, A.G.; Graves, S.R.; Stenos, J. A serological survey of rickettsial infections in the Gazelle Peninsula, East New Britain and a review of the literature. PNG Med. J. 2006, 49, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, S.; Stenos, J. Rickettsioses in Australia. In Rickettsiology and Rickettsial Diseases; Hechemy, K.E., Brouqui, P., Samuel, J.E., Raoult, D.A., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 1166, pp. 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, S. Management of rickettsial diseases and Q Fever. Med. Today 2013, 14, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sexton, D.J.; Banks, J.; Graves, S.; Hughes, K.; Dwyer, B. Prevalence of antibodies to spotted fever group rickettsiae in dogs from south-eastern Australia. Am. J. Trop. Reed. Hyg. 1991, 45, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Sexton, D.J.; Dwyer, B.; Kemp, R.; Graves, S. Spotted fever group rickettsial infections in Australia. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1991, 13, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, S.C.; Walker, A.R. Ticks of Australia. The species that infect domestic animals and humans. Zootaxa 2014, 3816, 1–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrick, E.H. The challenge of north Queensland fevers. Australas. Ann. Med. 1957, 6, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
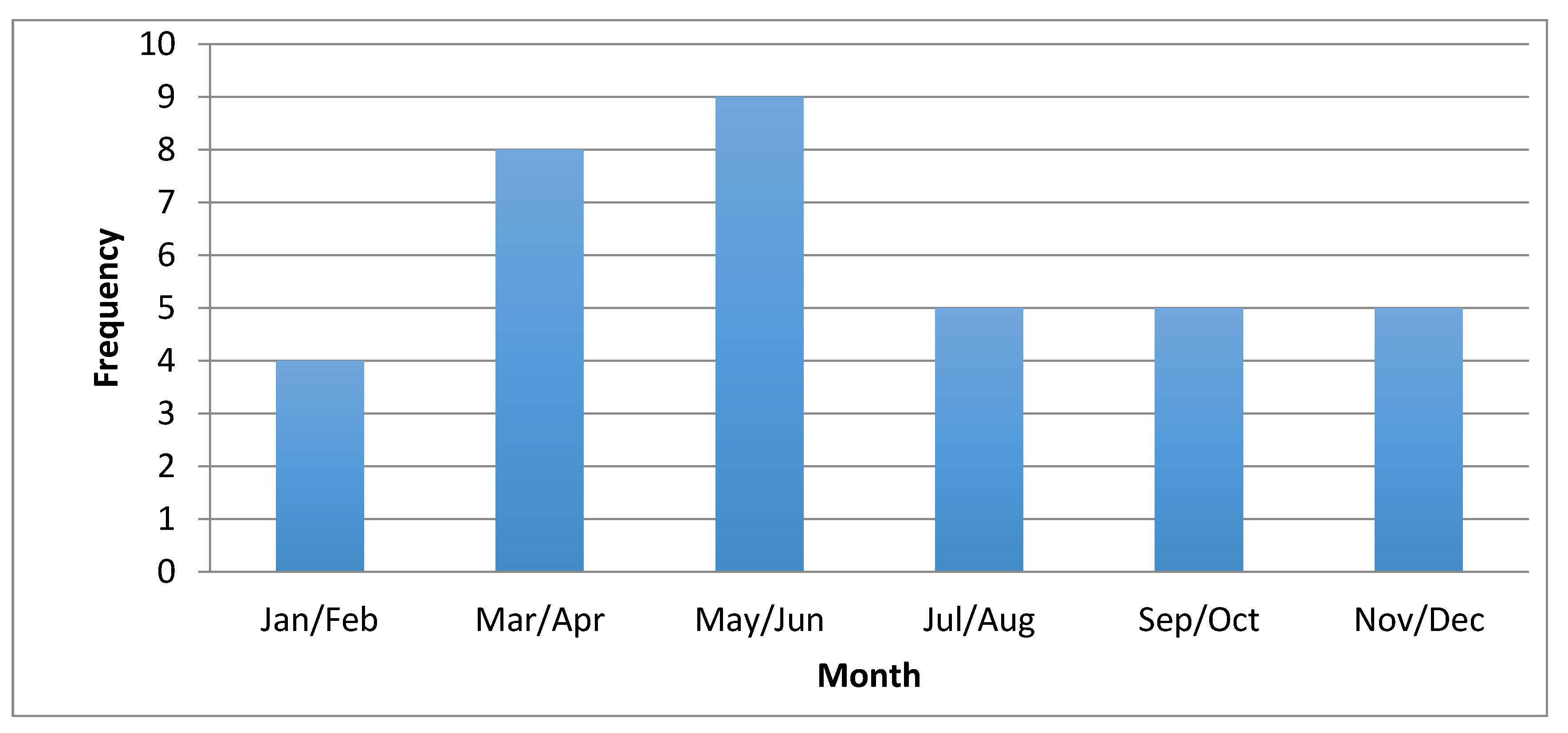

| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Age | 3–72 years (Mean 39.5, Median 36.1) |
| Sex | Male-to-female ratio 1:1.1 |
| 17/36 (47%) |
| 19/36 (53%) |
| Occupation | |
| 3/36 (8%) |
| 3/36 (8%) |
| Hobby/activity | |
| 3/36 (8%) |
| 3/36 (8%) |
| 2/36 (6%) |
| 1/36 (3%) |
| Residence on acreage/property | 4/36 (11%) |
| Recent travel (e.g., holiday) | 11/36 (31%) |
| Tick bite | 17/36 (47%) |
| 14/36 (39%) |
| 3/36 (8%) |
| Frequency of known risk factors | |
| 8/36 (22%) |
| 13/36 (36%) |
| 13/36 (36%) |
| 3/36 (8%) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stewart, A.; Armstrong, M.; Graves, S.; Hajkowicz, K. Epidemiology and Characteristics of Rickettsia australis (Queensland Tick Typhus) Infection in Hospitalized Patients in North Brisbane, Australia. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed2020010
Stewart A, Armstrong M, Graves S, Hajkowicz K. Epidemiology and Characteristics of Rickettsia australis (Queensland Tick Typhus) Infection in Hospitalized Patients in North Brisbane, Australia. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2017; 2(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed2020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleStewart, Adam, Mark Armstrong, Stephen Graves, and Krispin Hajkowicz. 2017. "Epidemiology and Characteristics of Rickettsia australis (Queensland Tick Typhus) Infection in Hospitalized Patients in North Brisbane, Australia" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 2, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed2020010
APA StyleStewart, A., Armstrong, M., Graves, S., & Hajkowicz, K. (2017). Epidemiology and Characteristics of Rickettsia australis (Queensland Tick Typhus) Infection in Hospitalized Patients in North Brisbane, Australia. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 2(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed2020010







