Impaired Lung Function and Quality of Life Outcomes in Patients with Tuberculosis: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Ethics
2.5. Study Tools and Protocol
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
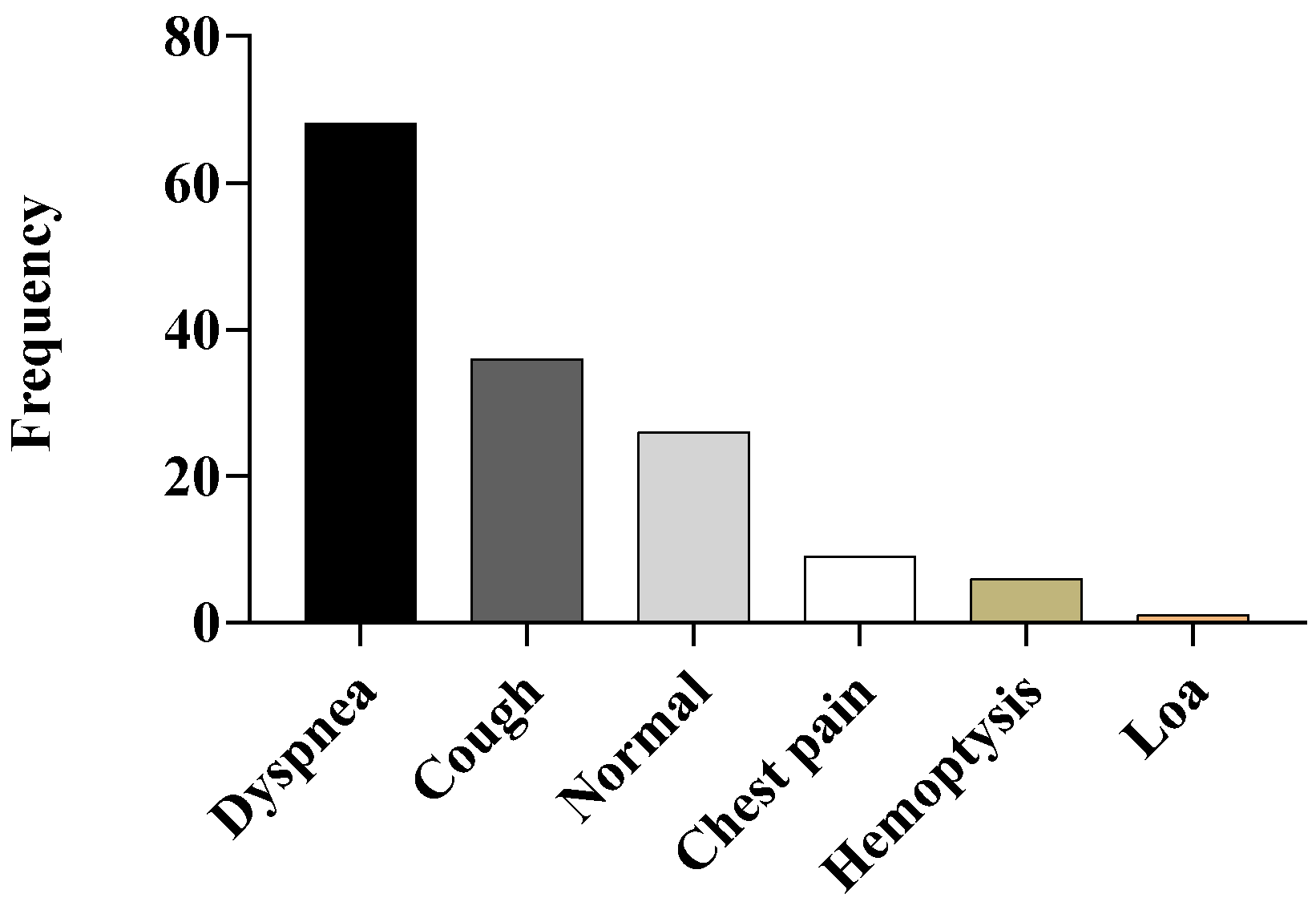
3.1. Demographic Data
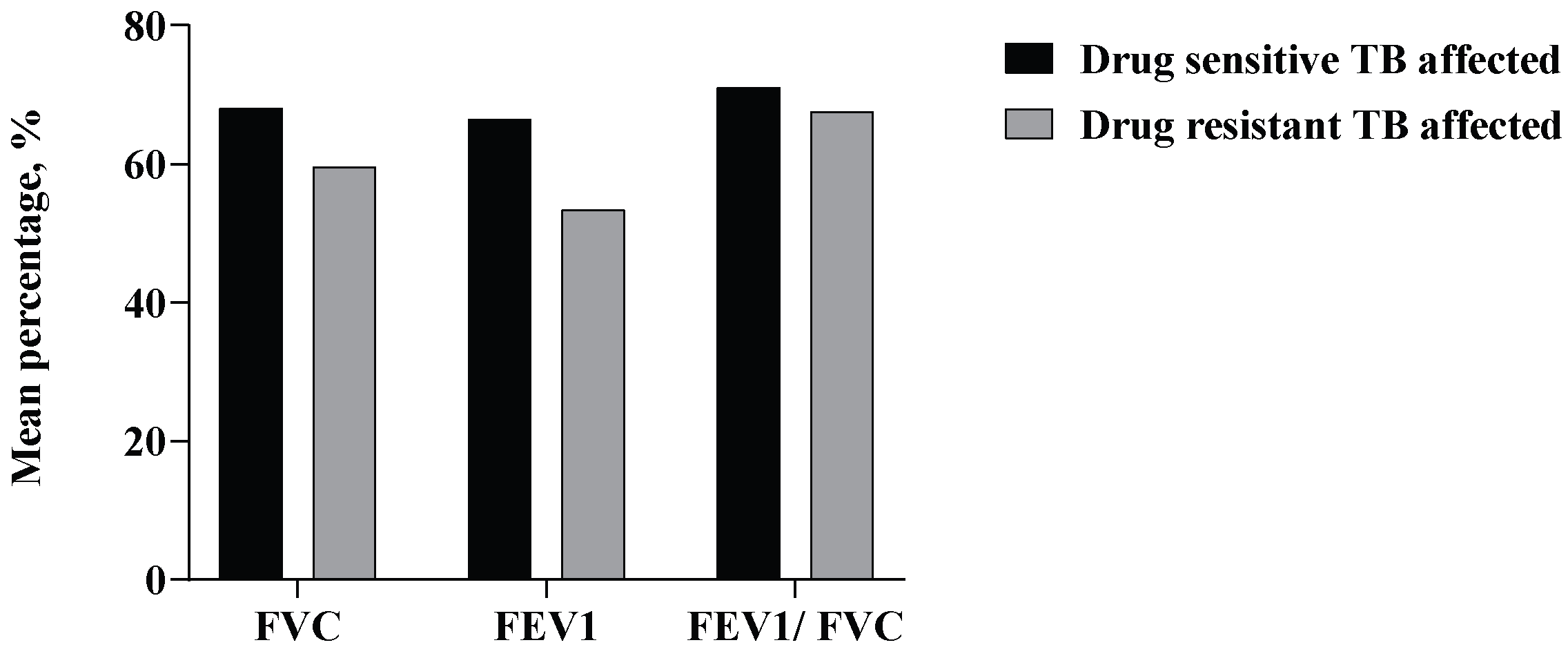
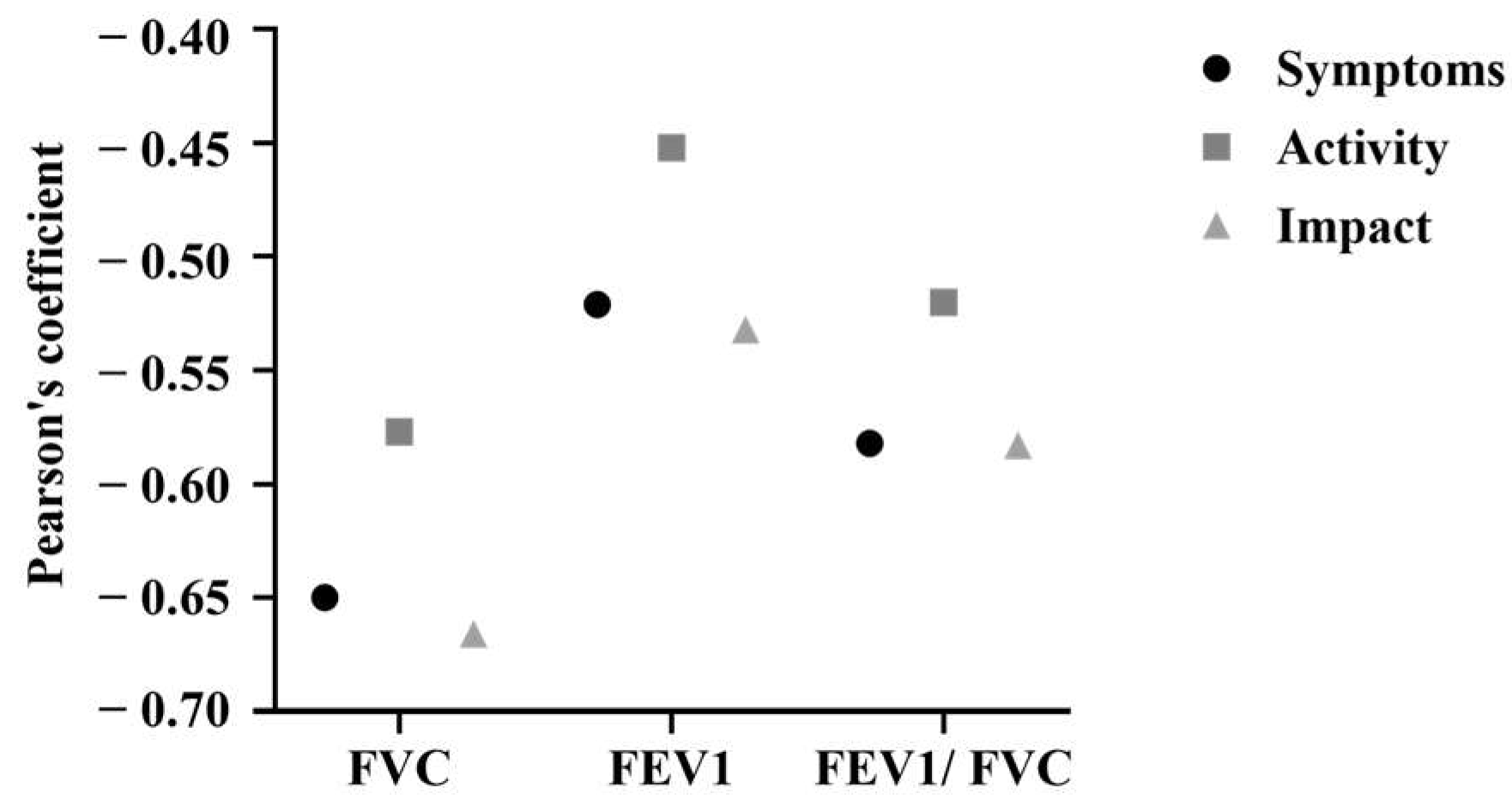
3.2. Pulmonary Function Test (PFT)
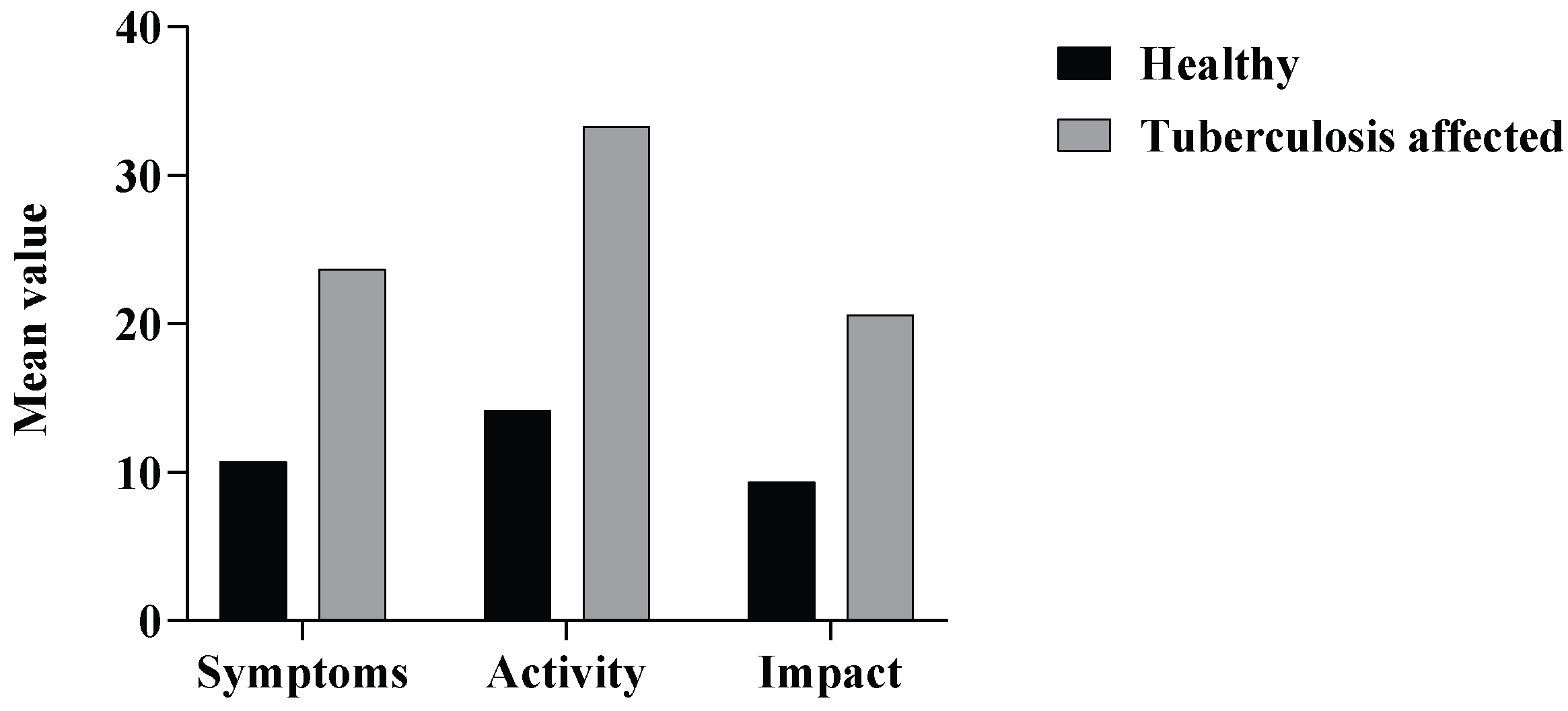
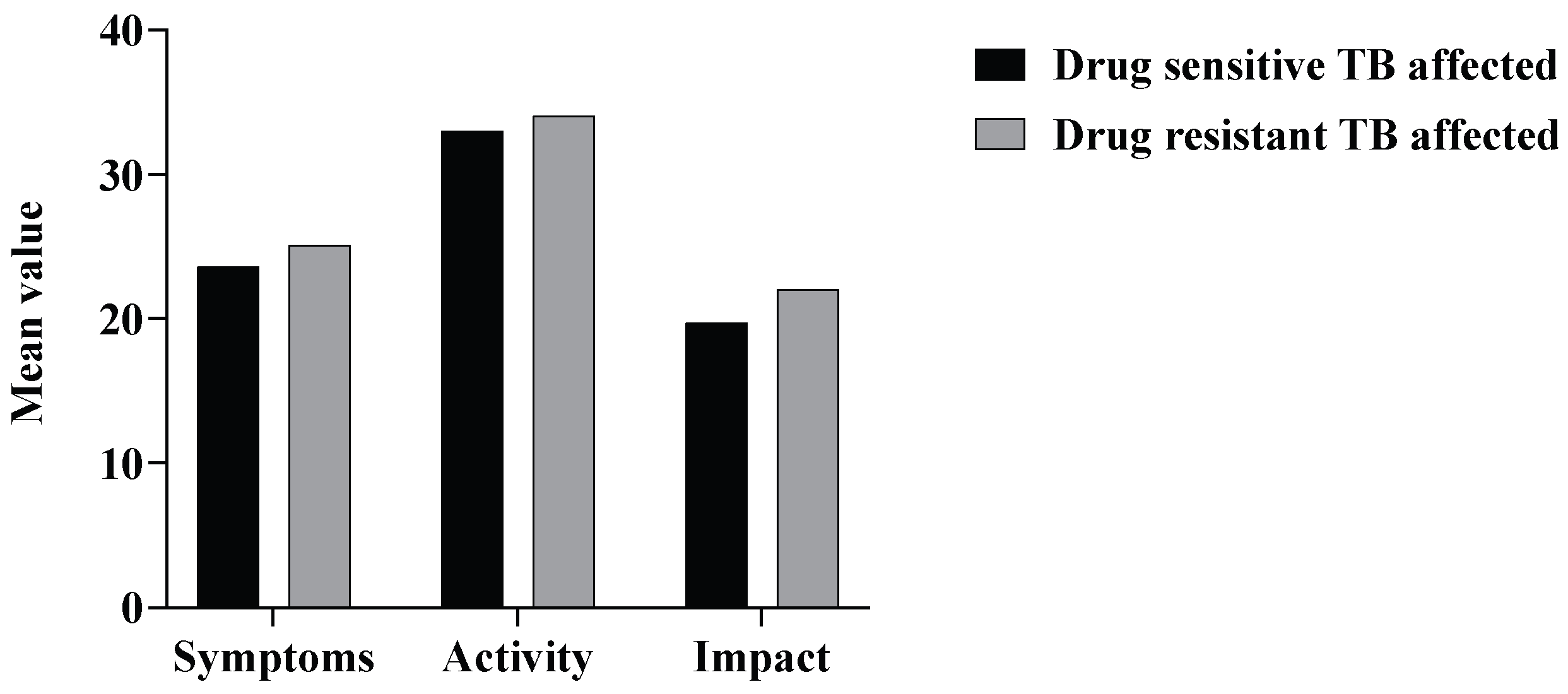
3.3. St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Tuberculosis. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Banerjee, S.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Taraphdar, P.; Dasgupta, A. Effect of DOTS on Quality of Life among Tuberculosis Patients: A Follow-up Study in a Health District of Kolkata. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Ahmed, S.; Benedetti, A.; Greenaway, C.; Lalli, M.; Leavens, A.; Menzies, D.; Vadeboncoeur, C.; Vissandjée, B.; Wynne, A.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life and Tuberculosis: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2015, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The End TB Strategy. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-programme-on-tuberculosis-and-lung-health/the-end-tb-strategy (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- India TB Report 2022—Central Tuberculosis Division. Available online: https://tbcindia.mohfw.gov.in/2023/06/06/india-tb-report-2022/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Rajpal, S.; Arora, V.K. Latent TB (LTBI) Treatment: Challenges in India with an Eye on 2025. Indian J. Tuberc. 2020, 67, S43–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Basu, S.; Chopra, K.K. Achieving TB Elimination in India: The Role of Latent TB Management. Indian J. Tuberc. 2019, 66, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.; Parmar, M.; Dash, G.C.; Solanki, H.; Chauhan, S.; Sharma, J.; Sahoo, K.C.; Mahapatra, P.; Rao, R.; Kumar, R.; et al. The Prevalence of Tuberculosis Infection in India: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2023, 157, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, G.H.; Jereb, J.; Lobue, P.; Iademarco, M.F.; Metchock, B.; Vernon, A.; Division of Tuberculosis Elimination; National Center for HIV, STD, and TB Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Guidelines for Using the QuantiFERON-TB Gold Test for Detecting Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection, United States. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. Recomm. Rep. 2005, 54, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Drug-resistant TB. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-programme-on-tuberculosis-and-lung-health/tb-reports/global-tuberculosis-report-2022/tb-disease-burden/2-3-drug-resistant-tb (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Seung, K.J.; Keshavjee, S.; Rich, M.L. Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis and Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a017863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chushkin, M.I.; Ots, O.N. Impaired Pulmonary Function after Treatment for Tuberculosis: The End of the Disease? J. Bras. Pneumol. 2017, 43, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana Mancuzo, E.; Martins Netto, E.; Sulmonett, N.; de Souza Viana, V.; Croda, J.; Lineu Kritski, A.; Carvalho de Queiroz Mello, F.; de Souza Elias Nihues, S.; Rosas Sodre Azevedo, K.; Spíndola de Miranda, S. Spirometry Results after Treatment for Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Comparison between Patients with and without Previous Lung Disease: A Multicenter Study. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2020, 46, e20180198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufemi, A.O.; Chikaodinaka, A.A.; Abimbola, P.; Oluwatoyin, A.T.; Oluwafunmilola, A.; Fasanmi, K.T.; Efosa, E.G. Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) Scores Vary with Treatment and May Identify Potential Defaulters during Treatment of Tuberculosis. Malawi Med. J. 2018, 30, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasobant, S.; Nazli Khatib, M.; Syed, Z.Q.; Gaidhane, A.M.; Shah, H.; Narkhede, K.; Bhavsar, P.; Patel, J.; Sinha, A.; Puwar, T.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) of Patients with Tuberculosis: A Review. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, M.; Usman, A.; Ma, J.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J.; Zaman, M.; Dragoman, A.; Jiatong Chen, S.; Farooqi, M.; Raina, P. Associations between Lung Function and Physical and Cognitive Health in the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA): A Cross-Sectional Study from a Multicenter National Cohort. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, e1003909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, N.; Lowers, J.; Magee, M.J.; Auld, S.C.; Hunt, W.R.; Fitzpatrick, A.; Lama, V.; Kavalieratos, D. Pulmonary Function and Quality of Life in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis. Lung 2023, 201, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Moço, V.J.; Lopes, A.J.; dos Santos Vigário, P.; de Almeida, V.P.; de Menezes, S.L.S.; Guimarães, F.S. Pulmonary Function, Functional Capacity and Quality of Life in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis. Rev. Port. Pneumol. 2015, 21, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanaparthy, R.; Mota, P.; Khan, R.; Ehsan, M.; Qureshi, A.; ZuWallack, R.; Leidy, N. A Longitudinal Assessment of Sleep Variables during Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2015, 12, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghai-Ravary, R.; Quint, J.K.; Goldring, J.J.P.; Hurst, J.R.; Donaldson, G.C.; Wedzicha, J.A. Determinants and Impact of Fatigue in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sánchez, I.; Cabrera-Martos, I.; Díaz-Pelegrina, A.; Valenza-Demet, G.; Moreno-Ramírez, M.P.; Valenza, M.C. Physical and Functional Impairment During and After Hospitalization in Subjects with Severe COPD Exacerbation. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.C.; Lee, A.L.; McGinley, J.; Anderson, G.P.; Clark, R.A.; Thompson, M.; Clarke, S.; Baker, T.; Irving, L.B.; Denehy, L. Balance and Falls in Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Prospective Study. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 14, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, A.; Krenke, R.; Kuziemski, K.; Czajkowska-Malinowska, M.; Celejewska-Wójcik, N.; Kuznar-Kaminska, B.; Farnik, M.; Bokiej, J.; Miszczuk, M.; Damps-Konstanska, I.; et al. Distribution and Characteristics of COPD Phenotypes & ndash; Results from the Polish Sub-Cohort of the POPE Study. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, P.J.Z.; Porto, L.; Kristensen, C.H.; Santos, A.H.; Menna-Barreto, S.S.; Prado-Lima, P.A.S. Do Post-Traumatic Stress Symptoms and Exacerbations in COPD Patients. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2015, 12, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansel, N.N.; Wu, A.W.; Chang, B.; Diette, G.B. Quality of Life in Tuberculosis: Patient and Provider Perspectives. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 13, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P. Isolation and Stigma: The Experience of Patients with Active Tuberculosis. J. Community Health Nurs. 1999, 16, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.N. Quality of Life with Tuberculosis. J. Clin. Tuberc. Other Mycobact. Dis. 2019, 17, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremers, A.L.; de Laat, M.M.; Kapata, N.; Gerrets, R.; Klipstein-Grobusch, K.; Grobusch, M.P. Assessing the Consequences of Stigma for Tuberculosis Patients in Urban Zambia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, G.M.; Daftary, A.; Engel, N.; O’Driscoll, S.; Ioannaki, A. Tuberculosis Stigma as a Social Determinant of Health: A Systematic Mapping Review of Research in Low Incidence Countries. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 56, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan Aydin, I.; Uluşahin, A. Depression, Anxiety Comorbidity, and Disability in Tuberculosis and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients: Applicability of GHQ-12. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2001, 23, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Leavens, A.; Schwartzman, K.A. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Tuberculosis on Health-Related Quality of Life. Qual. Life Res. 2013, 22, 2213–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswari, R.; Muniyandi, M.; Balasubramanian, R.; Narayanan, P.R. Perceptions of Tuberculosis Patients about Their Physical, Mental and Social Well-Being: A Field Report from South India. Soc. Sci. Med. 2005, 60, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, S.A.; Shah, N.N.; Wani, Z.A.; Nazir, D. A Prospective Study on Quality of Life in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Kashmir, Northern India. Indian J. Tuberc. 2019, 66, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisaka, S.M.B.; Rutebemberwa, E.; Kasasa, S.; Ocen, F.; Nankya-Mutyoba, J. Does Health-Related Quality of Life among Adults with Pulmonary Tuberculosis Improve across the Treatment Period? A Hospital-Based Cross Sectional Study in Mbale Region, Eastern Uganda. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meghji, J.; Auld, S.C.; Bisson, G.P.; Khosa, C.; Masekela, R.; Navuluri, N.; Rachow, A. Post-Tuberculosis Lung Disease: Towards Prevention, Diagnosis, and Care. Lancet Respir. Med. 2025, 13, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.; Villasante, C.; Alonso, J.; Sobradillo, V.; Gabriel, R.; Vilagut, G.; Masa, J.F.; Viejo, J.L.; Jiménez-Ruiz, C.A.; Miravitlles, M. Interpretation of Quality of Life Scores from the St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 19, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.W. St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire: MCID. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2005, 2, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, K.J.; Irusen, E.; Pharaoh, H.; Hanekom, S. Post-Tuberculosis Health-Related Quality of Life, Lung Function and Exercise Capacity in a Cured Pulmonary Tuberculosis Population in the Breede Valley District, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Physiother. 2019, 75, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddireddy, V. Quality of Life, Psychological Interventions and Treatment Outcome in Tuberculosis Patients: The Indian Scenario. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roila, F.; Cortesi, E. Quality of Life as a Primary End Point in Oncology. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, S3–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreto-Binaghi, L.E.; Sartillo-Mendoza, L.G.; Muñoz-Torrico, M.; Guzmán-Beltrán, S.; Carranza, C.; Torres, M.; González, Y.; Juárez, E. Serum Pro-Inflammatory Biomarkers Associated with Improvement in Quality of Life in Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1241121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasipanodya, J.G.; Miller, T.L.; Vecino, M.; Munguia, G.; Bae, S.; Drewyer, G.; Weis, S.E. Using the St. George Respiratory Questionnaire to Ascertain Health Quality in Persons with Treated Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Chest 2007, 132, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.W.; Bosh, T.K. Quality of Life Changes in COPD Patients Treated with Salmeterol. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastien-Hilka, T.; Rosenkranz, B.; Sinanovic, E.; Bennett, B.; Schwenkglenks, M. Health-Related Quality of Life in South African Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, G.P.; Anstey, N.M.; Ardian, M.; Waramori, G.; Tjitra, E.; Kenangalem, E.; Handojo, T.; Kelly, P.M. Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Impaired Lung Function, Disability and Quality of Life in a High-Burden Setting. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2009, 13, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vashakidze, S.A.; Kempker, J.A.; Jakobia, N.A.; Gogishvili, S.G.; Nikolaishvili, K.A.; Goginashvili, L.M.; Magee, M.J.; Kempker, R.R. Pulmonary Function and Respiratory Health after Successful Treatment of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 82, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meguro, M.; Barley, E.A.; Spencer, S.; Jones, P.W. Development and Validation of an Improved, COPD-Specific Version of the St. George Respiratory Questionnaire. Chest 2007, 132, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.; Viegi, G.; Brusasco, V.; Crapo, R.O.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; van der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; Hankinson, J.; et al. Interpretative Strategies for Lung Function Tests. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 948–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.R.; Patrick, D.L. The Assessment of Health Status among Patients with COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 36s–45s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.A.; Lewin, S.A.; Smith, H.J.; Engel, M.E.; Fretheim, A.; Volmink, J. Patient Adherence to Tuberculosis Treatment: A Systematic Review of Qualitative Research. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Overview of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Disease. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/hcp/clinical-overview/drug-resistant-tuberculosis-disease.html (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Dookie, N.; Ngema, S.L.; Perumal, R.; Naicker, N.; Padayatchi, N.; Naidoo, K. The Changing Paradigm of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Treatment: Successes, Pitfalls, and Future Perspectives. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e0018019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustini, A. Risk Factors for Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis in Europe: A Systematic Review. Thorax 2006, 61, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, L.; Crossa, A.; Gilman, R.H.; Herrera, C.; Bonilla, C.; Jave, O.; Cabrera, J.L.; Martin, L.; Escombe, A.R.; Moore, D.A.J. Tuberculosis in Household Contacts of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2011, 15, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung-Delgado, K.; Guillen-Bravo, S.; Revilla-Montag, A.; Bernabe-Ortiz, A. Mortality among MDR-TB Cases: Comparison with Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis and Associated Factors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, C.A.; Crossa, A.; Jave, H.O.; Mitnick, C.D.; Jamanca, R.B.; Herrera, C.; Asencios, L.; Mendoza, A.; Bayona, J.; Zignol, M.; et al. Management of Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Peru: Cure Is Possible. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Santha, T.; Garg, R.; Frieden, T.R.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Subramani, R.; Gopi, P.G.; Selvakumar, N.; Ganapathy, S.; Charles, N.; Rajamma, J.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with Default, Failure and Death among Tuberculosis Patients Treated in a DOTS Programme in Tiruvallur District, South India, 2000. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2002, 6, 780–788. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez, P.G.; Floyd, K.; Portocarrero, J.; Alarcón, E.; Rapiti, E.; Ramos, G.; Bonilla, C.; Sabogal, I.; Aranda, I.; Dye, C.; et al. Feasibility and Cost-Effectiveness of Standardised Second-Line Drug Treatment for Chronic Tuberculosis Patients: A National Cohort Study in Peru. Lancet 2002, 359, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Yadav, R.; Sharma, M.; Saini, V.; Koushal, V. Quality of Life of Multi Drug Resistant Tuberculosis Patients: A Study of North India. Acta Med. Iran. 2014, 52, 448–453. [Google Scholar]
- Jaber, A.A.S.; Ibrahim, B. Health-Related Quality of Life of Patients with Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Yemen: Prospective Study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2019, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, U.; Sharma, A.; Srivastava, D.K.; Durga, R. Health-Related Quality of Life of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients: A Study of Eastern Uttar Pradesh, India. Indian J. Tuberc. 2022, 69, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gare, K.P.; Sebakeng, M.; Molefi, M. The Health-Related Quality of Life of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients Receiving Treatment in Botswana. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dheda, K.; Gumbo, T.; Maartens, G.; Dooley, K.E.; McNerney, R.; Murray, M.; Furin, J.; Nardell, E.A.; London, L.; Lessem, E.; et al. The Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Management of Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant, and Incurable Tuberculosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 291–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vallière, S.; Barker, R.D. Residual Lung Damage after Completion of Treatment for Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2004, 8, 767–771. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, A.L.; Marais, B.J.; Mitnick, C.D.; Garden, F.L.; Lecca, L.; Contreras, C.; Yauri, Y.; Garcia, F.; Marks, G.B. Chronic Airflow Obstruction after Successful Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis. ERJ Open Res. 2017, 3, 00026-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbatova, E.V.; Taylor, A.; Gammino, V.M.; Bayona, J.; Becerra, M.; Danilovitz, M.; Falzon, D.; Gelmanova, I.; Keshavjee, S.; Leimane, V.; et al. Predictors of Poor Outcomes among Patients Treated for Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis at DOTS-plus Projects. Tuberculosis 2012, 92, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
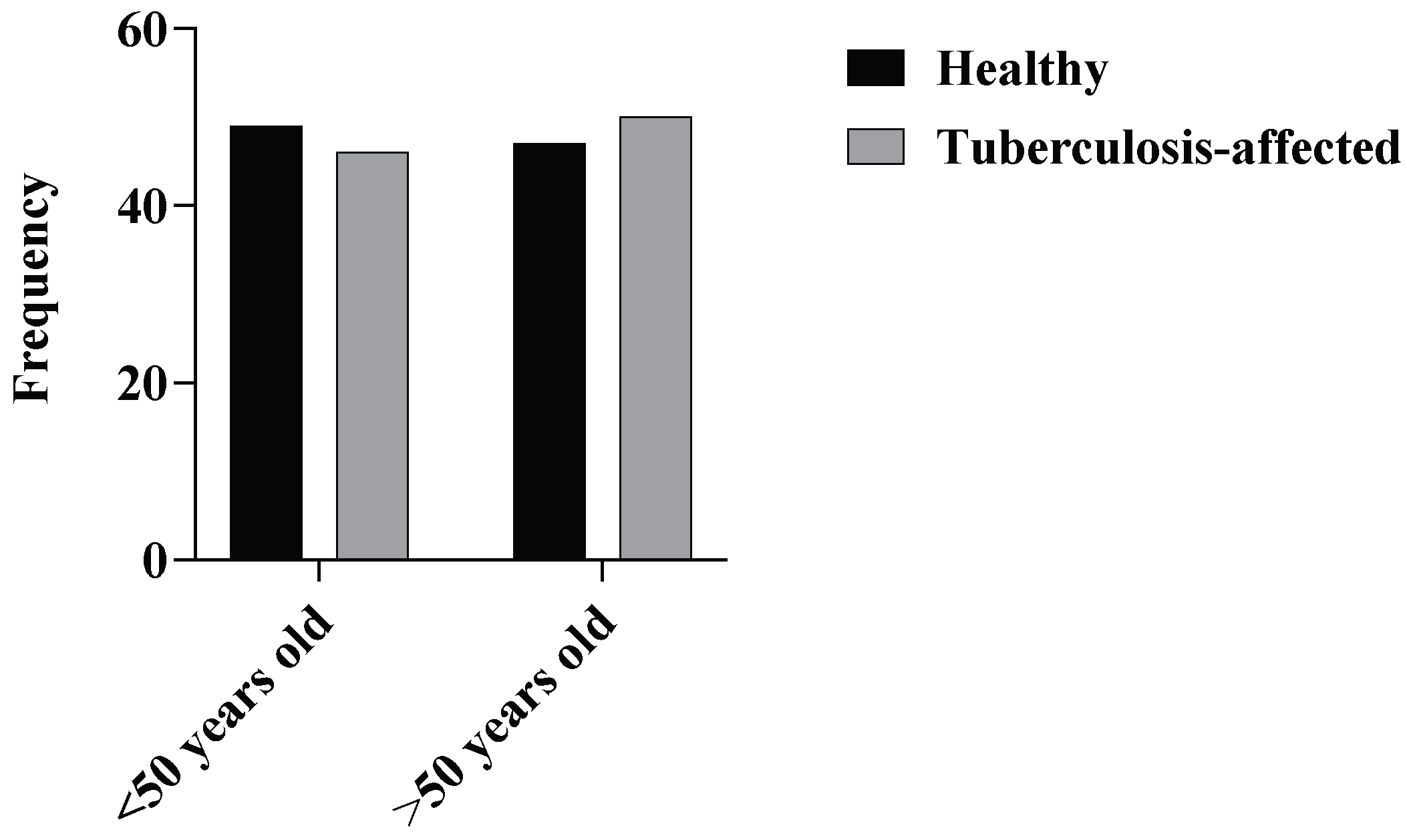
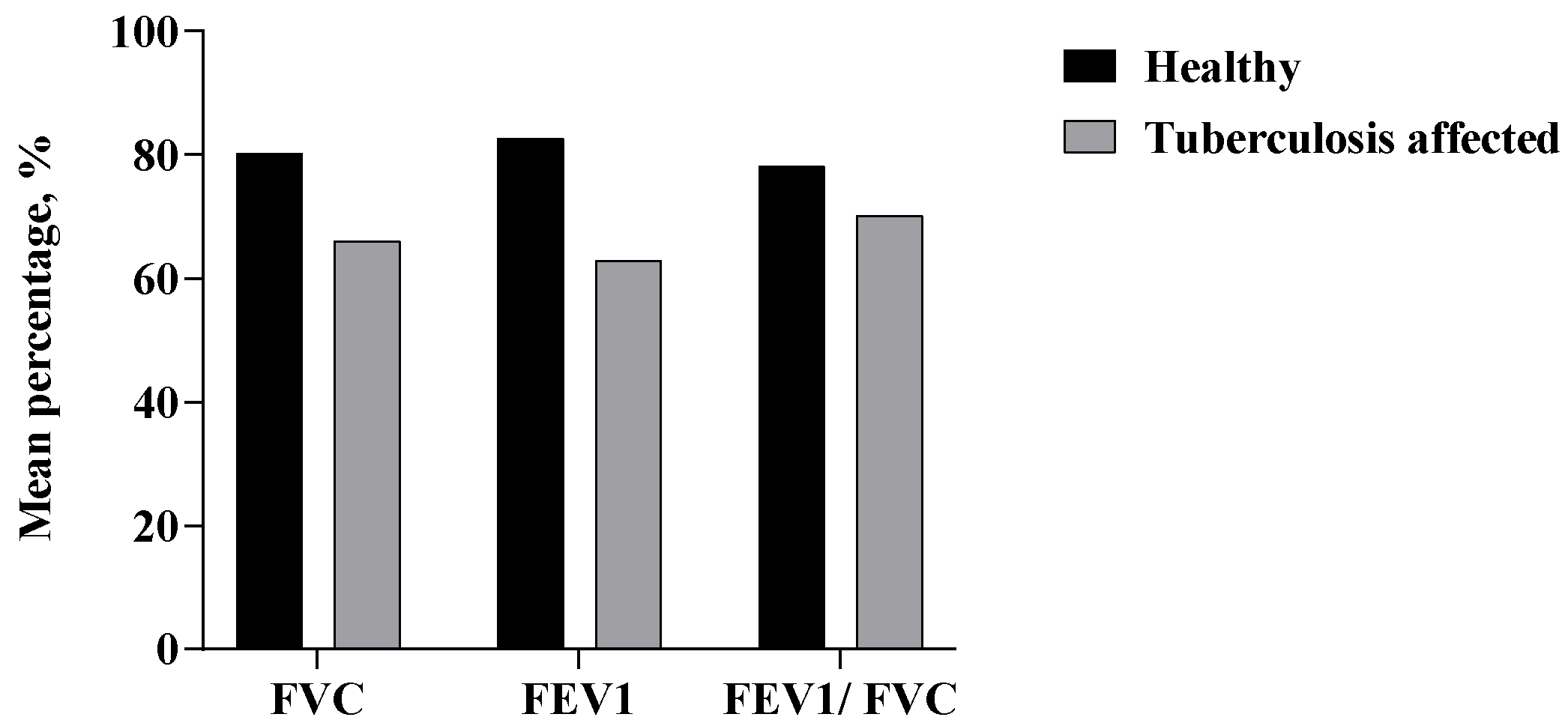
| Parameters | Number of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| I. 35–45 years | 9 (9.37%) |
| II. 45–55 years | 46 (47.92%) |
| III. 55–65 years | 22 (22.92%) |
| IV. 65–75 years | 19 (19.79%) |
| Total Male respondents | 65 (67.71%) |
| Total Female respondents | 31 (32.29%) |
| Smoking habit | 71 (73.95%) |
| I. Males | 48 (67.60%) |
| II. Females | 23 (32.40%) |
| Alcohol consumption | 65 (67.71%) |
| I. Males | 43 (66.15%) |
| II. Females | 22 (33.85%) |
| Recurrent TB cases | 22 (22.91%) |
| Incidence of DR-TB | 27 (28.12%) |
| (within 27 DR-TB-affected respondents) | |
| I. Isoniazid resistance | 16/27 (59.26%) |
| II. Rifampicin resistance | 3/27 (11.11%) |
| III. XDR-TB | 8/27 (29.63%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jagadeesh, V.; Chikkahonnaiah, P.; Dubey, M.; Byrappa, S.H.; Sridhar, H.B.; Amachawadi, R.G.; Veeranna, R.P. Impaired Lung Function and Quality of Life Outcomes in Patients with Tuberculosis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090247
Jagadeesh V, Chikkahonnaiah P, Dubey M, Byrappa SH, Sridhar HB, Amachawadi RG, Veeranna RP. Impaired Lung Function and Quality of Life Outcomes in Patients with Tuberculosis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(9):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090247
Chicago/Turabian StyleJagadeesh, Varshini, Prashanth Chikkahonnaiah, Muskan Dubey, Shashidhar H. Byrappa, Hari Balaji Sridhar, Raghavendra G. Amachawadi, and Ravindra P. Veeranna. 2025. "Impaired Lung Function and Quality of Life Outcomes in Patients with Tuberculosis: A Cross-Sectional Study" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 9: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090247
APA StyleJagadeesh, V., Chikkahonnaiah, P., Dubey, M., Byrappa, S. H., Sridhar, H. B., Amachawadi, R. G., & Veeranna, R. P. (2025). Impaired Lung Function and Quality of Life Outcomes in Patients with Tuberculosis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(9), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090247








