Non-Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia in Childhood: A Review
Abstract
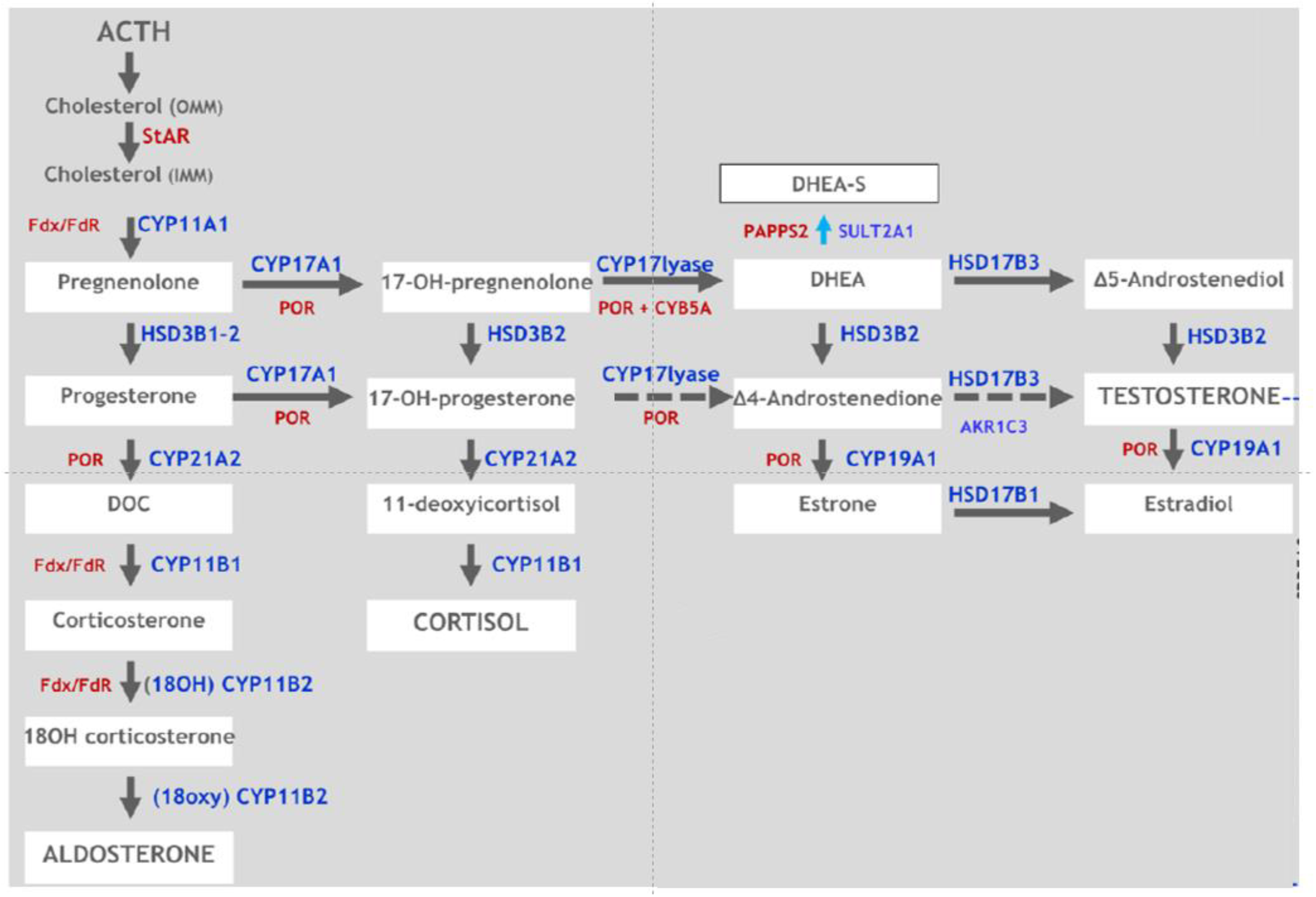
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Findings
| Feature | Females | Males |
|---|---|---|
| Premature pubarche and/or premature onset of axillary hair | + | + |
| Prepubertal tall stature in respect to mid-parental height | + | + |
| Increased growth velocity for chronological age | + | + |
| Advanced bone age | + | + |
| Central precocious puberty * | + | + |
| Severe acne | + | + |
| Hirsutism | + | − |
| Polycystic ovary syndrome (adolescent girls/adult women) | + | − |
| Testicular ectopic adrenal rests | − | rare |
| Irregular cycles | + | − |
| Oily hair in girls/male pattern balding (in late adolescence/adulthood) | + | − |
| Impaired adult height | + | + |
3. Diagnosis
4. Treatment
5. Conclusions
- The awareness of family pediatricians and general practitioners on high prevalence of this disease, to improve early diagnoses.
- The improvement of hormonal screening by establishing more accurate basal and stimulated 17-OHP cut-off values for pediatric age not derived from adult studies. At this regard, the more expanded use of new techniques (as LC-MS/MS) in clinical laboratories and the setup of new biomarkers of adrenal androgen excess (as 11-oxyandrogens or 21-deoxycortisol) will offer better guidance to select individuals for genetic testing and to monitor management.
- The criteria to start early hydrocortisone treatment in children will be improved to achieve sound data on benefits and risks. Alternative therapeutic approaches should be explored, too.
- Comparative long-term trials will be developed, comparing “old” and “new” hydrocortisone formulations to obtain better cost/benefit profiles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, P.C.; Speiser, P.W. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 245–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, M.I. Extensive clinical experience: Nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4205–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krone, N.; Braun, A.; Roscher, A.A.; Knorr, D.; Schwarz, H.P. Predicting phenotype in steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency? Comprehensive genotyping in 155 unrelated, well defined patients from southern Germany. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsamo, A.; Baldazzi, L.; Menabò, S.; Cicognani, A. Impact of molecular genetics on congenital adrenal hyperplasia management. Sex Dev. 2010, 4, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Seth, A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: Issues in diagnosis and treatment in children. Indian J. Pediatr. 2014, 81, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenström, A.; Falhammar, H. Diagnosis and management of the patient with non-classic CAH due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, R127–R145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah-Shmouni, F.; Morissette, R.; Sinaii, N.; Elman, M.; Prezant, T.R.; Chen, W.; Pulver, A.; Merke, D.P. Revisiting the prevalence of nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia in US Ashkenazi Jews and Caucasians. Genet Med. 2017, 19, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyal, O.; Tenenbaum-Rakover, Y.; Shalitin, S.; Israel, S.; Weintrob, N. Adult height of subjects with nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livadas, S.; Dracopoulou, M.; Dastamani, A.; Sertedaki, A.; Maniati-Christidi, M.; Magiakou, A.M.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; Chrousos, G.P.; Dacou-Voutetakis, C. The spectrum of clinical, hormonal and molecular findings in 280 individuals with nonclassical congenital adrenal hyperplasia caused by mutations of the CYP21A2 gene. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 82, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaş-Erdeve, S.; Çetinkaya, S.; Yavaş Abalı, Z.; Şükran Poyrazoğlu, S.; Baş, F.; Berberoğlu, M.; Sıklar, Z.; Korkmaz, Z.; Buluş, D.; Demet Akbaş, E.; et al. Clinical, biochemical and genetic features with nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency and final height. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 30, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, H.G.; Schulze, N.; Bettendorf, M.; Binder, G.; Bonfig, W.; Denzer, C.; Dunstheimer, D.; Salzgeber, K.; Schmidt, H.; Schwab, K.O.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in children and adolescents with nonclassical congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Mol. Cell. Pediatr. 2020, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasniewska, M.G.; Morabito, L.A.; Baronio, F.; Einaudi, S.; Salerno, M.; Bizzarri, C.; Russo, G.; Chiarito, M.; Grandone, A.; Guazzarotti, L.; et al. Growth trajectory and adult height in children with nonclassical congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2020, 93, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, L.; Lebenthal, Y.; Phillip, M.; Shalitin, S.; Tenenbaum, A.; Bello, R. Obesity and cardiometabolic risk factors in children and young adults with non-classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falhammar, H.; Nordenström, A. Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: Clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. Endocrine 2015, 50, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.I.; Abraham, M.; Gonzalez, B.; Dumic, M.; Razzaghy-Azar, M.; Chitayat, D.; Sun, L.; Zaidi, M.; Wilson, R.C.; Yuen, T. Genotype-phenotype correlation in 1,507 families with congenital adrenal hyperplasia owing to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2611–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, C.M.; Oberfield, S.E. Recommendations for treatment of non classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia (NCCAH): An update. Steroids 2012, 77, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, N.; Yordam, N. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia in Turkey: A review of 273 patients. Acta Paediatr. 1997, 86, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneux, C.; Tardy, V.; Dib, A.; Mornet, E.; Billaud, L.; Charron, D.; Morel, Y.; Kuttenn, F. Phenotype-genotype correlation in 56 women with nonclassical congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, C.; Azziz, R.; Carmina, E.; Dewailly, D.; Fruzzetti, F.; Ibañez, L.; Knochenhauer, E.S.; Marcondes, J.A.; Mendonca, B.B.; Pignatelli, D.; et al. 21-Hydroxylase-deficient nonclassic adrenal hyperplasia is a progressive disorder: A multicenter study. Am. J. Obstetr. Gynecol. 2000, 183, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, E.D.; Brown, J.J.; Ghareebian, H.; Mariash, C. Dual heterozygous mutations in CYP21A2 and CYP11B1 in a case of nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 8, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasniewska, M.; Raiola, G.; Galati, M.C.; Salzano, G.; Rulli, I.; Zirilli, G.; De Luca, F. Non-classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency in boys with prepubertal or pubertal gynecomastia. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2008, 167, 1083–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtoğlu, S.; Hatipoğlu, N. Non-classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia in childhood. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, V.L.; Russo, G.; Bertelloni, S.; Gargantini, L.; Balducci, R.; Chiesa, L.; Livieri, C.; De Sanctis, C.; Einaudi, S.; Virdis, R.; et al. Final height in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: The Italian experience. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 16, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- New, M.I.; Gertner, J.M.; Speiser, P.W.; del Balzo, P. Growth and final height in classical and nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1989, 12, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Tamhane, S.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, R.; Iqbal, A.M.; Prokop, L.J.; Bancos, I.; Speiser, P.W.; Murad, M.H. Cardiovascular and metabolic outcomes in congenital adrenal hyperplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 4097–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delai, A.; Gomes, P.M.; Foss-Freitas, M.C.; Elias, J.; Antonini, S.R.; Castro, M.; Moreira, A.C.; Mermejo, L.M. Hyperinsulinemic-Euglycemic Clamp Strengthens the Insulin Resistance in Nonclassical Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Simon, A.; Brener, A.; Segev-Becker, A.; Yackobovitch-Gavan, M.; Uretzky, A.; Schachter Davidov, A.; Alaev, A.; Oren, A.; Eyal, O.; Weintrob, N.; et al. Body composition in children and adolescents with non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia and the risk for components of metabolic syndrome: An observational study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1022752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witchel, S.F.; Azziz, R. Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2010, 2010, 625105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcioni, B.; Renzulli, M.; Marasco, G.; Baronio, F.; Gambineri, A.; Ricciardi, D.; Ortolano, R.; Farina, D.; Gaudiano, C.; Cassio, A.; et al. Prevalence and ultrasound patterns of testicular adrenal rest tumors in adults with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aycan, Z.; Keskin, M.; Lafcı, N.G.; Savaş-Erdeve, Ş.; Baş, F.; Poyrazoğlu, Ş.; Öztürk, P.; Parlak, M.; Ercan, O.; Güran, T.; et al. Genotype of congenital adrenal hyperplasia patients with testicular adrenal rest tumor. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 65, 104654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, P.W.; Azziz, R.; Baskin, L.S.; Ghizzoni, L.; Hensle, T.W.; Merke, D.P.; Meyer-Bahlburg, H.F.; Miller, W.L.; Montori, V.M.; Oberfield, S.E.; et al. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4133–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baronio, F.; Marzatico, A.; De Iasio, R.; Ortolano, R.; Fanolla, A.; Radetti, G.; Balsamo, A.; Pession, A.; Cassio, A. Premature Pubarche: Time to Revise the Diagnostic Approach? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Kashimada, K.; Amano, N.; Takasawa, K.; Nakamura-Utsunomiya, A.; Yatsuga, S.; Mukai, T.; Ida, S.; Isobe, M.; Fukushi, M.; et al. Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of 21-hydroxylase deficiency (2021 revision). Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2022, 31, 116–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livadas, S.; Bothou, C. Management of the female with non-classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia (NCCAH): A patient-oriented approach. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, S.; Turcu, A.F. Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia: What do endocrinologists need to know? Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2021, 50, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcu, A.F.; El-Maouche, D.; Zhao, L.; Nanba, A.T.; Gaynor, A.; Veeraraghavan, P.; Auchus, R.J.; Merke, D.P. Androgen excess and diagnostic steroid biomarkers for nonclassic 21-hydroxylase deficiency without cosyntropin stimulation. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.L.; Lim, E.M.; Zhang, R.; Beilby, J.P.; Watts, G.F.; Brown, S.J.; Stuckey, B.G.A. Serum 21-deoxycortisol for diagnosis of non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia in women with androgen excess. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.; Withe, M.; Ross, R.J. Immediate-release granule formulation of hydrocortisone, Alkindi®, for treatment of paediatric adrenal insufficiency (Infacort development programme). Exp. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 13, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, U.; Whitaker, M.J.; Wiegand, S.; Krude, H.; Porter, J.; Davies, M.; Digweed, D.; Voet, B.; Ross, R.J.; Blankenstein, O. Absorption and tolerability of taste-masked hydrocortisone granules in neonates, infants and children under 6 years of age with adrenal insufficiency. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 88, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, U.; Braune, K.; Whitaker, M.J.; Wiegand, S.; Krude, H.; Porter, J.; Digweed, D.; Voet, B.; Ross, R.; Blankenstein, O. A prospective study of children aged 0-8 years with CAH and adrenal insufficiency treated with hydrocortisone granules. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e1433–e1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merke, D.P.; Mallappa, A.; Arlt, W.; Brac de la Perriere, A.; Lindén Hirschberg, A.; Juul, A.; Newell-Price, J.; Perry, C.G.; Prete, A.; Rees, D.A.; et al. Modified-release hydrocortisone in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e2063–e2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Suresh, M.; Jaber, M.; Mercado Munoz, Y.; Sarafoglou, K. Case Report: Anastrozole as a monotherapy for pre-pubertal children with non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güven, A.; Nurcan Cebeci, A.; Hancili, S. Gonadotropin releasing hormone analog treatment in children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia complicated by central precocious puberty. Hormones 2015, 14, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CAH Phenotype | Genetic Status of CYP21A2 Gene Variants | 21-OH Residual Activity, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homozygous | Heterozygous | ||
| Salt wasting | Null/Null | A/Null or A/A | 0–1 |
| Simple virilizing | B/B | B/A or B/Null | 1–5 |
| Non-classic | C/C | C/B or C/A or C/Null | 15–60 |
| Carriers | Null or A or B or C | >60 * | |
| Authors | Total Series, n | Age at Diagnosis, Years | Females, n (%) | Males, n (%) | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyal et al. [8] | 122 | 11.3 ± 7.7 | 99 (81%) | 23 (19) | 4.3/1.0 |
| Livadas et al. [9] | 107 | F 0.6–6.8 * M 2.0–8.9 * | 94 (88) | 13 (12) | 7.2/1.0 |
| Savas-Erdeve et al. [10] | 258 | 9.8 ± 4.3 | 229 (89) | 29 (11) | 7.9/1.0 |
| Dörr et al. [11] | 134 | 7.1 ± 4.4 | 105 (78) | 29 (22) | 3.6/1.0 |
| Wasniewska et al. [12] | 192 | 7.4 ± 3.7 | 140 (73) | 52 (27) | 2.6/1.0 |
| De Vries et al. [13] | 114 | 7.9 ± 4.2 | 92 (81) | 22 (19) | 4.2/1.0 |
| Hydrocortisone Treated | Untreated | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Authors | n | AH, SDS | AH-MPH, SDS | p | n | AH, SDS | AH-MPH, SDS | p |
| Eyal et al. [8] | 66 | −0.9 ± 0.8 | −0.4 ± 0.7 | 0.03 | 49 | −0.3 ± 1.1 | −0.05 ± 0.8 | NS |
| Wasniewska et al. [12] | 171 | −0.4 ± 1.0 | −0.3 ± 0.9 | − | 21 | −0.3 ± 1.4 | 0.6 ± 1.1 | − |
| Authors | 17OHP, ng/mL * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Baseline Values | ≤2.0 ng/mL, % | ACTH Stimulated Peak | ≤10.0 ng/mL, % | |
| Livadas et al. [9] | 9.4 (4.9–22.9) ° | 2.1 | 32.5 (25.0–52.5) ° | none |
| Savas-Erdeve et al. [10] | 11.6 (0.2–78.1) ^ | NR | 21.0 (5.3–168.6) ^ | 7.0 |
| Dörr et al. [11] | 14.5 (0.3–112) ^ | 3.8 ^^ | 61.1 ± 79.9 § | none |
| Baronio et al. [32] | 43.9 (1.1–56.1) | 16.6 | 44.0 (33.7–74.1) | none |
| Personal experience (unpublished) | 10.0 (0.9–16.5) ^ | 22.0 | 45.2 (3.5–91.7) | 12.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertolucci, G.; Tyutyusheva, N.; Sepich, M.; Baldinotti, F.; Caligo, M.A.; Sessa, M.R.; Peroni, D.G.; Bertelloni, S. Non-Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia in Childhood: A Review. Sexes 2023, 4, 462-472. https://doi.org/10.3390/sexes4040030
Bertolucci G, Tyutyusheva N, Sepich M, Baldinotti F, Caligo MA, Sessa MR, Peroni DG, Bertelloni S. Non-Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia in Childhood: A Review. Sexes. 2023; 4(4):462-472. https://doi.org/10.3390/sexes4040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertolucci, Giulia, Nina Tyutyusheva, Margherita Sepich, Fulvia Baldinotti, Maria Adelaide Caligo, Maria Rita Sessa, Diego Giampiero Peroni, and Silvano Bertelloni. 2023. "Non-Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia in Childhood: A Review" Sexes 4, no. 4: 462-472. https://doi.org/10.3390/sexes4040030
APA StyleBertolucci, G., Tyutyusheva, N., Sepich, M., Baldinotti, F., Caligo, M. A., Sessa, M. R., Peroni, D. G., & Bertelloni, S. (2023). Non-Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia in Childhood: A Review. Sexes, 4(4), 462-472. https://doi.org/10.3390/sexes4040030








