Exploring the Relationship of Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder with Emotional Dysregulation: A Twin Study in Childhood and Adolescence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Behavioral Measures
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.3.1. Preliminary Analyses
2.3.2. Model Fitting Analyses
3. Results
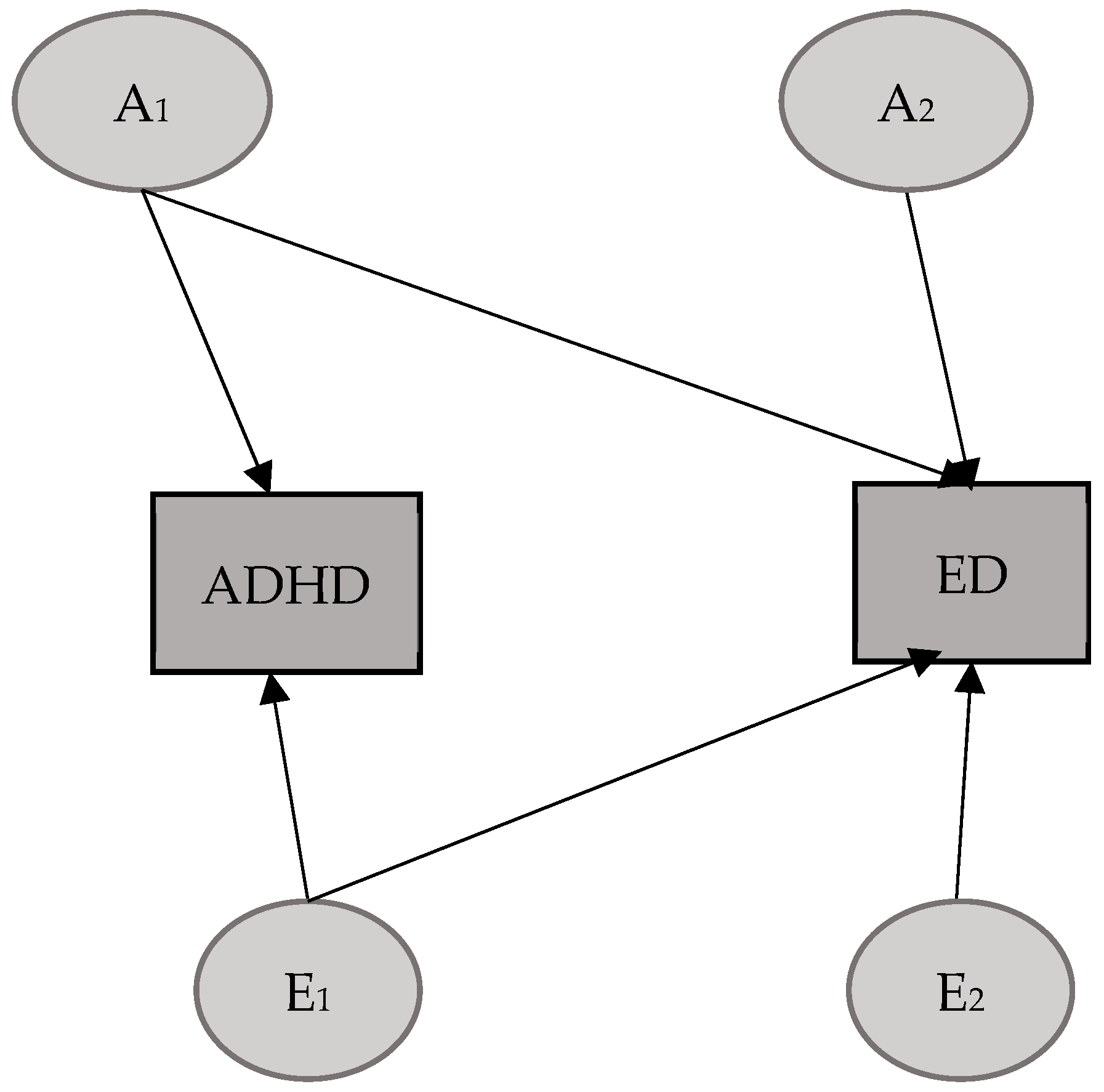
3.1. ADHD–ED Model
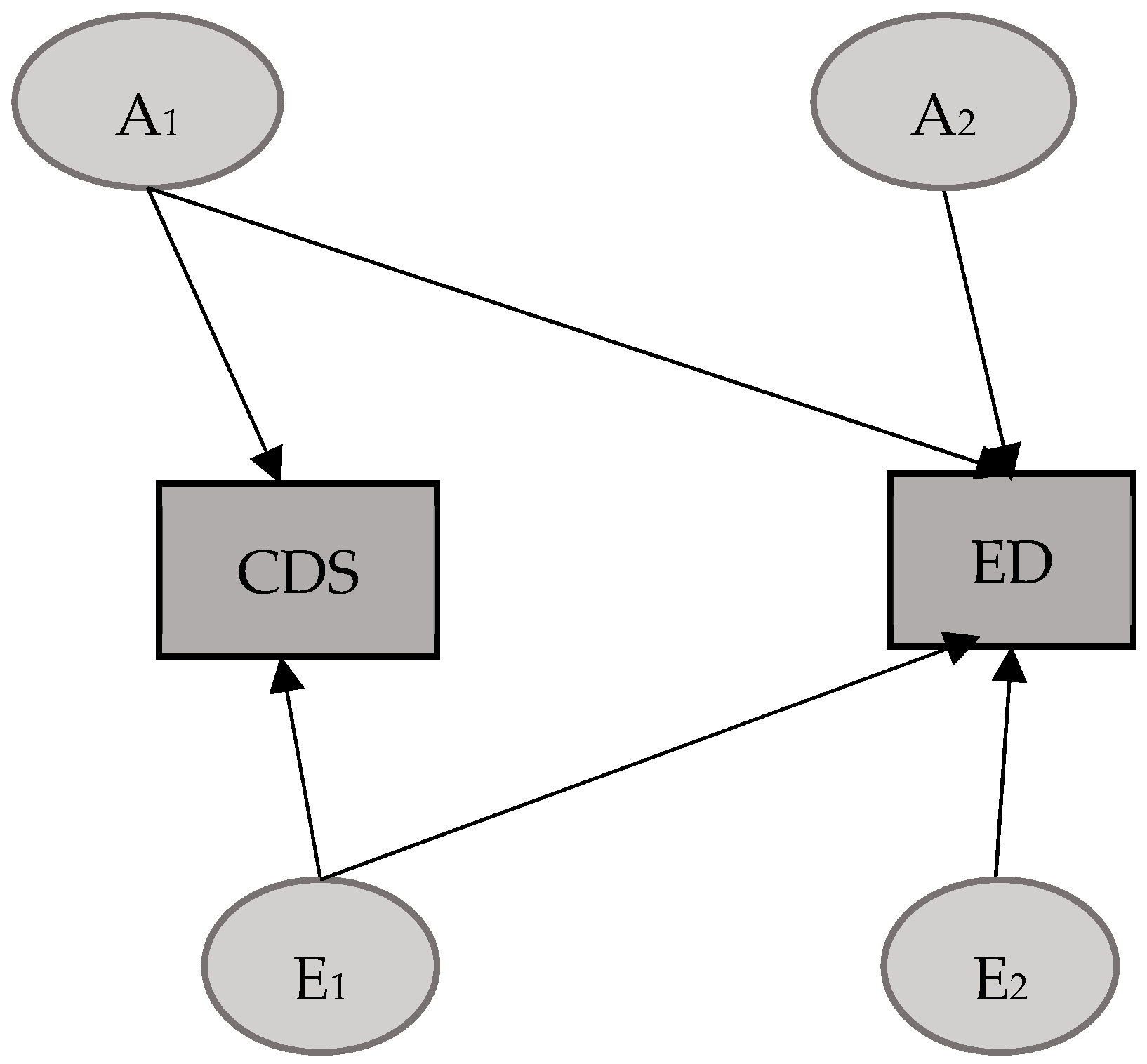
3.2. CDS–ED Model
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Becker, S.P.; Leopold, D.R.; Burns, G.L.; Jarrett, M.A.; Langberg, J.M.; Marshall, S.A.; McBurnett, K.; Waschbusch, D.A.; Willcutt, E.G. The Internal, External, and Diagnostic Validity of Sluggish Cognitive Tempo: A Meta-Analysis and Critical Review. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 55, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.P.; Willcutt, E.G.; Leopold, D.R.; Fredrick, J.W.; Smith, Z.R.; Jacobson, L.A.; Burns, G.L.; Mayes, S.D.; Waschbusch, D.A.; Froehlich, T.E.; et al. Report of a Work Group on Sluggish Cognitive Tempo: Key Research Directions and a Consensus Change in Terminology to Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 62, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.P.; Willcutt, E.G. Advancing the Study of Sluggish Cognitive Tempo via DSM, RDoC, and Hierarchical Models of Psychopathology. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2019, 28, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredrick, J.W.; Becker, S.P. Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome (Sluggish Cognitive Tempo) and Social Withdrawal: Advancing a Conceptual Model to Guide Future Research. J. Atten. Disord. 2023, 27, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.P. Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome: A Construct at the Crossroads. Am. Psychol 2025, 80, 812–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.P.; Burns, G.L.; Smith, Z.R.; Langberg, J.M. Sluggish Cognitive Tempo in Adolescents with and without ADHD: Differentiation from Adolescent-Reported ADHD Inattention and Unique Associations with Internalizing Domains. J. Abnorm. Child. Psychol. 2020, 48, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.P.; Webb, K.L.; Dvorsky, M.R. Initial Examination of the Bidirectional Associations between Sluggish Cognitive Tempo and Internalizing Symptoms in Children. J. Clin. Child. Adolesc. Psychol. 2021, 50, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moruzzi, S.; Rijsdijk, F.; Battaglia, M. A Twin Study of the Relationships among Inattention, Hyperactivity/Impulsivity and Sluggish Cognitive Tempo Problems. J. Abnorm. Child. Psychol. 2014, 42, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.P.; Burns, G.L.; Leopold, D.R.; Olson, R.K.; Willcutt, E.G. Differential Impact of Trait Sluggish Cognitive Tempo and ADHD Inattention in Early Childhood on Adolescent Functioning. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2018, 59, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrick, J.W.; Becker, S.P.; Kofler, M.J.; Jarrett, M.A.; Burns, G.L.; Luebbe, A.M. Disentangling the Effects of Attentional Difficulties on Fears of Social Evaluation and Social Anxiety Symptoms: Unique Interactions with Sluggish Cognitive Tempo. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 131, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giuli, G.; Amico, C.; De Francesco, S.; Giani, L.; Tüzün, G.; Galli, F.; Caputi, M.; Forresi, B.; Scaini, S. Emotional Dysregulation and Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome: Exploring Their Relationship Through the Lens of Twin Studies. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, G.L.; Becker, S.P.; Geiser, C.; Leopold, D.R.; Willcutt, E.G. Are Sluggish Cognitive Tempo, ADHD, and Oppositional Defiant Disorder Trait- or State-Like Constructs from Prekindergarten to Fourth Grade? J. Clin. Child. Adolesc. Psychol. 2020, 49, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.T.; Atkinson, E.A.; Davis, H.A.; Riley, E.N.; Oltmanns, J.R. The General Factor of Psychopathology. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 16, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredrick, J.W.; Becker, S.P. Sluggish Cognitive Tempo (Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome) and Academic Functioning: A Systematic Review and Agenda for Future Research. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2023, 26, 82–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inci Izmir, S.B.; Aktan, Z.D.; Ercan, E.S. The Comparison of Psychological Factors and Executive Functions of Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome to ADHD and ADHD Comorbid with Oppositional Defiant Disorder. J. Atten. Disord. 2024, 28, 1555–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willoughby, E.A.; Polderman, T.J.C.; Boutwell, B.B. Behavioural Genetics Methods. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2023, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, K.S. Twin Studies of Psychiatric Illness: Current Status and Future Directions. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1993, 50, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcutt, E.G. The Etiology of ADHD in Adolescents. In ADHD in Adolescents: Development, Assessment, and Treatment; Becker, S.P., Ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 36–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sáez, B.; Servera, M.; Becker, S.P.; Burns, G.L. Optimal Items for Assessing Sluggish Cognitive Tempo in Children Across Mother, Father, and Teacher Ratings. J. Clin. Child. Adolesc. Psychol. 2019, 48, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaini, S.; Medda, E.; Battaglia, M.; De Giuli, G.; Stazi, M.A.; D’Ippolito, C.; Fagnani, C. A Twin Study of the Relationships between Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome and Anxiety Phenotypes in Childhood and Adolescence. Res. Child. Adolesc. Psychopathol. 2023, 51, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, G.L.; Servera, M.; Bernad, M.D.M.; Carrillo, J.M.; Cardo, E. Distinctions Between Sluggish Cognitive Tempo, ADHD-IN, and Depression Symptom Dimensions in Spanish First-Grade Children. J. Clin. Child. Adolesc. Psychol. 2013, 42, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servera, M.; Bernad, M.D.M.; Carrillo, J.M.; Collado, S.; Burns, G.L. Longitudinal Correlates of Sluggish Cognitive Tempo and ADHD-Inattention Symptom Dimensions with Spanish Children. J. Clin. Child. Adolesc. Psychol 2016, 45, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevincok, D.; Ozbay, H.C.; Ozbek, M.M.; Tunagur, M.T.; Aksu, H. ADHD Symptoms in Relation to Internalizing and Externalizing Symptoms in Children: The Mediating Role of Sluggish Cognitive Tempo. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2020, 74, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, N.B.; Wells, E.L.; Soto, E.F.; Marsh, C.L.; Jaisle, E.M.; Harvey, T.K.; Kofler, M.J. Executive Functioning and Emotion Regulation in Children with and without ADHD. Res. Child. Adolesc. Psychopathol. 2022, 50, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, H.; Hirsch, O.; Albrecht, B.; Chavanon, M.-L. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Emotion Regulation Over the Life Span. Curr. Psychiatry Rep 2019, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodalski, E.A.; Flory, K.; Meinzer, M.C. A Scoping Review of Factors Associated With Emotional Dysregulation in Adults With ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2023, 27, 1540–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo Jiménez, E.A.; Jané Ballabriga, M.C.; Bonillo Martin, A.; Arrufat, F.J.; Serra Giacobo, R. Executive Functioning in Children and Adolescents With Symptoms of Sluggish Cognitive Tempo and ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2015, 19, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, W.L.M.; Lewandowski, L.J.; Lovett, B.J.; Antshel, K.M. Executive Dysfunction and Functional Impairment Associated With Sluggish Cognitive Tempo in Emerging Adulthood. J. Atten. Disord. 2017, 21, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonuga-Barke, E.J.S.; Becker, S.P.; Bölte, S.; Castellanos, F.X.; Franke, B.; Newcorn, J.H.; Nigg, J.T.; Rohde, L.A.; Simonoff, E. Annual Research Review: Perspectives on Progress in ADHD Science – from Characterization to Cause. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2023, 64, 506–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merwood, A.; Chen, W.; Rijsdijk, F.; Skirrow, C.; Larsson, H.; Thapar, A.; Kuntsi, J.; Asherson, P. Genetic Associations Between the Symptoms of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Emotional Lability in Child and Adolescent Twins. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2014, 53, 209–220.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conners, C.K.; Sitarenios, G.; Parker, J.D.A.; Epstein, J.N. The Revised Conners’ Parent Rating Scale (CPRS-R): Factor Structure, Reliability, and Criterion Validity. J. Abnorm. Child. Psychol. 1998, 26, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Francesco, S.; Amico, C.; De Giuli, G.; Giani, L.; Fagnani, C.; Medda, E.; Scaini, S. Exploring the Comorbidity between Internalizing/Externalizing Dimensions and Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome through Twin Studies: A Narrative Review. J. Transl. Genet. Genom. 2024, 8, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stazi, M.A.; Cotichini, R.; Patriarca, V.; Brescianini, S.; Fagnani, C.; D’Ippolito, C.; Cannoni, S.; Ristori, G.; Salvetti, M. The Italian Twin Project: From the Personal Identification Number to a National Twin Registry. Twin Res. 2002, 5, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medda, E.; Toccaceli, V.; Fagnani, C.; Nisticò, L.; Brescianini, S.; Salemi, M.; Ferri, M.; D’Ippolito, C.; Alviti, S.; Arnofi, A.; et al. The Italian Twin Registry: An Update at 18 Years From Its Inception. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2019, 22, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesenti-Gritti, P.; Spatola, C.A.M.; Fagnani, C.; Ogliari, A.; Patriarca, V.; Stazi, M.A.; Battaglia, M. The Co-Occurrence between Internalizing and Externalizing Behaviors: A General Population Twin Study. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2008, 17, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, H.H. A Zygosity Questionnaire for Young Twins: A Research Note. Behav. Genet. 1991, 21, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, T.M.; Rescorla, L.A. Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms & Profiles: Child Behavior Checklist for Ages 6–18, Teacher’s Report Form, Youth Self-Report: An Integrated System of Multi-Informant Assessment; University of Vermont, Research Center for Children Youth & Families: Burlington, VT, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Spatola, C.A.M.; Fagnani, C.; Pesenti-gritti, P.; Ogliari, A.; Stazi, M.-A.; Battaglia, M. A General Population Twin Study of the CBCL/6-18 DSM-Oriented Scales. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2007, 46, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, T.M.; Becker, A.; Döpfner, M.; Heiervang, E.; Roessner, V.; Steinhausen, H.-C.; Rothenberger, A. Multicultural Assessment of Child and Adolescent Psychopathology with ASEBA and SDQ Instruments: Research Findings, Applications, and Future Directions. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, M.; Battaglia, M.; Marino, C.; Mahendran, N.; Andrade, B.F. Clinical Utility of the CBCL Dysregulation Profile in Children with Disruptive Behavior. J. Affect. Disord 2019, 253, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, J.; Petty, C.; Monuteaux, M.C.; Evans, M.; Parcell, T.; Faraone, S.V.; Wozniak, J. The CBCL-Pediatric Bipolar Disorder Profile Predicts a Subsequent Diagnosis of Bipolar Disorder and Associated Impairments in ADHD Youth Growing Up: A Longitudinal Analysis. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 70, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoff, R.R.; Ayer, L.A.; Rettew, D.C.; Hudziak, J.J. Assessment of Dysregulated Children Using the Child Behavior Checklist: A Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve Analysis. Psychol. Assess. 2010, 22, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, M.C.; Hunter, M.D.; Pritikin, J.N.; Zahery, M.; Brick, T.R.; Kirkpatrick, R.M.; Estabrook, R.; Bates, T.C.; Maes, H.H.; Boker, S.M. OpenMx 2.0: Extended Structural Equation and Statistical Modeling. Psychometrika 2016, 81, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, S.; Scaini, S.; Alessandri, G.; Medda, E.; Camoni, L.; Stazi, M.A.; Fagnani, C. Age-Related Variations of Genetic and Environmental Contributions to the Covariation of Fear, Distress and Externalizing Symptoms: A Twin Study in Childhood and Adolescence. Child. Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2023, 55, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markon, K.E.; Krueger, R.F. An Empirical Comparison of Information-Theoretic Selection Criteria for Multivariate Behavior Genetic Models. Behav. Genet. 2004, 34, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.A.; Jacobson, K.C.; Raine, A.; Lozano, D.I.; Bezdjian, S. Genetic and Environmental Bases of Childhood Antisocial Behavior: A Multi-Informant Twin Study. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2007, 116, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendler, K.S.; Myers, J.M.; Maes, H.H.; Keyes, C.L.M. The Relationship Between the Genetic and Environmental Influences on Common Internalizing Psychiatric Disorders and Mental Well-Being. Behav. Genet. 2011, 41, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrett, M.A.; Rapport, H.F.; Rondon, A.T.; Becker, S.P. ADHD Dimensions and Sluggish Cognitive Tempo Symptoms in Relation to Self-Report and Laboratory Measures of Neuropsychological Functioning in College Students. J. Atten. Disord. 2017, 21, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pliszka, S. Practice Parameter for the Assessment and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2007, 46, 894–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, N.; Hajri, M.; Abbes, Z.; Halayem, S.; Bouden, A. Emotion-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Externalizing Disorders in Children and Adolescents: An Attempt to Resolve Emotion Regulation Difficulties. Eur. Psychiatry 2022, 65, S442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiello-Robbins, C.; Sauer-Zavala, S.; Brody, L.R.; Barlow, D.H. Exploring the Effects of the Mindfulness and Countering Emotional Behaviors Modules From the Unified Protocol on Dysregulated Anger in the Context of Emotional Disorders. Behav. Ther. 2020, 51, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derella, O.J.; Johnston, O.G.; Loeber, R.; Burke, J.D. CBT-Enhanced Emotion Regulation as a Mechanism of Improvement for Childhood Irritability. J. Clin. Child. Adolesc. Psychol. 2019, 48, S146–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Merrin, G.J.; Slavich, G.M. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and Emotion Dysregulation Phenotypes: An Intersectional Analysis of Race/Ethnicity and Gender in a Nationally Representative U.S. Sample. Child. Abuse Negl. 2024, 158, 107129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.D.; Shevlin, M.; Karatzias, T.; Charak, R.; Spinazzola, J. Can Developmental Trauma Disorder Be Distinguished from Posttraumatic Stress Disorder? A Confirmatory Factor Analytic Test of Four Structural Models. Res. Child. Adolesc. Psychopathol. 2022, 50, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliem, J.A.; Gliem, R.R. Calculating, Interpreting, and Reporting Cronbach’s Alpha Reliability Coefficient for Likert-Type Scales. In Proceedings of the Midwest Research-to-Practice Conference in Adult, Continuing, and Community Education, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 8–10 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nikstat, A.; Riemann, R. On the Etiology of Internalizing and Externalizing Problem Behavior: A Twin-Family Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietveld, M.J.H.; Posthuma, D.; Dolan, C.V.; Boomsma, D.I. ADHD: Sibling Interaction or Dominance: An Evaluation of Statistical Power. Behav. Genet. 2003, 33, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Voces, M.; Díaz-Vázquez, B.; López-Romero, L.; Villar, P.; Romero, E. Gender Differences in Co-Developmental Trajectories of Internalizing and Externalizing Problems: A 7-Year Longitudinal Study from Ages 3 to 12. Child. Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2024, 55, 1073–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdaway, A.S.; Becker, S.P. Sluggish Cognitive Tempo and Student-Teacher Relationship Quality: Short-Term Longitudinal and Concurrent Associations. Sch. Psychol. Q. 2018, 33, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, S.E.; Gardner, C.O.; Kendler, K.S. Age-Related Changes in Heritability of Behavioral Phenotypes over Adolescence and Young Adulthood: A Meta-Analysis. Twin. Res. Hum. Genet. 2007, 10, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeuw, J.; Klein, M.; Mota, N.; Brouwer, R.; Van ‘T Ent, D.; Al-Hassaan, Z.; Franke, B.; Boomsma, D.; Hulshoff Pol, H. Multivariate Genetic Structure of Externalizing Behavior and Structural Brain Development in a Longitudinal Adolescent Twin Sample. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-Bahmani, D.; Eisenhut, L.; Mikoteit, T.; Helfenstein, N.; Brühl, A.B.; Dürsteler, K.M.; Bizimana, J.-M.; Becker, S.P.; Brand, S. Cross-Sectional and Quasi-Longitudinal Examination of Childhood and Adult Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome, Depression, Anxiety, Stress, and Insomnia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ADHD Min–Max: 0–13 | CDS Min–Max: 0–8 | ED Min–Max: 0–58 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | |
| Total sample (N = 800) | 2.9 (2.7) * | 0.8 (1.1) ** | 11.7 (8.7) *** |
| Males (N = 376) | 3.5 (3.9) | 0.8 (1.1) | 12.7 (9.2) |
| Females (N = 424) | 2.3 (2.4) | 0.8 (1.1) | 10.8 (8.1) |
| p < 0.01 | p = 0.94 | p = 0.04 | |
| MZ (N = 288) | 2.8 (2.6) | 0.8 (1.0) | 11.7 (8.5) |
| DZ (N = 512) | 3.0 (2.7) | 0.8 (1.1) | 11.7 (8.7) |
| p = 0.32 | p = 0.57 | p = 0.89 |
| ADHD–ED | CDS–ED | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within-Twin/Cross-Trait Correlations | |||||
| ADHD | ED | CDS | ED | ||
| ADHD | 1 | - | CDS | 1 | - |
| ED | 0.62 * | 1 | ED | 0.48 * | |
| Cross-Twin/Within-Trait correlations | |||||
| ADHD | ED | CDS | ED | ||
| MZ | 0.51 * | 0.74 * | MZ | 0.37 * | 0.75 * |
| DZ | 0.15 * | 0.55 * | DZ | 0.10 * | 0.54 * |
| Cross-Twin/Cross-Trait correlations | |||||
| MZ | ADHD | ED | MZ | CDS | ED |
| ADHD | 1 | - | CDS | 1 | - |
| ED | 0.51 * | - | ED | 0.37 * | 1 |
| DZ | ADHD | ED | DZ | CDS | ED |
| ADHD | 1 | - | CDS | 1 | - |
| ED | 0.37 * | 1 | ED | 0.29 * | 1 |
| Model | ctm | ep | −2LL | df | AIC | BIC | diffLL | Δdf | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 14 | −342.594 | 1484 | −314.594 | −258.714 | - | - | - |
| 1 | 13 | −341.168 | 1485 | −315.168 | −263.279 | 1.42645 | 1 | 0.23 |
| 2 | 12 | −339.030 | 1486 | −315.030 | −267.133 | 2.13736 | 1 | 0.14 |
| Standardized Components | ||
|---|---|---|
| A | E | |
| Vp (ADHD) | 0.43 (0.30–0.53) | 0.57 (0.47–0.70) |
| Vp (ED) | 0.76 (0.70–0.81) | 0.24 (0.19–0.30) |
| Cov (ADHD-ED) | 0.86 (0.75–0.95) | 0.14 (0.05–0.25) |
| Genetic and environmental correlations | ||
| ADHD-ED | ra = 0.92 (0.82–1) | re = 0.23 (0.19–0.30) |
| Model | ctm | ep | −2LL | df | AIC | BIC | diffLL | Δdf | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 14 | −853.738 | 1477 | −825.738 | −769.858 | - | - | - |
| 1 | 13 | −852.481 | 1478 | −826.481 | −774.592 | 1.25685 | 1 | 0.26 |
| 2 | 12 | −849.167 | 1479 | −825.1675 | −777.269 | 3.31440 | 1 | 0.07 |
| Standardized Components | ||
|---|---|---|
| A | E | |
| Vp (CDS) | 0.29 (0.16–0.41) | 0.71 (0.59–0.84) |
| Vp (ED) | 0.77 (0.70–0.81) | 0.23 (0.19–0.30) |
| Cov (CDS-ED) | 0.81 (0.66–0.95) | 0.19 (0.05–0.34) |
| Genetic and environmental correlations | ||
| CDS-ED | ra = 0.81 (0.64–1) | re = 0.22 (0.06–0.36) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scaini, S.; De Francesco, S.; Giani, L.; Battaglia, M.; Medda, E.; Fagnani, C. Exploring the Relationship of Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder with Emotional Dysregulation: A Twin Study in Childhood and Adolescence. Methods Protoc. 2025, 8, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8040094
Scaini S, De Francesco S, Giani L, Battaglia M, Medda E, Fagnani C. Exploring the Relationship of Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder with Emotional Dysregulation: A Twin Study in Childhood and Adolescence. Methods and Protocols. 2025; 8(4):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8040094
Chicago/Turabian StyleScaini, Simona, Stefano De Francesco, Ludovica Giani, Marco Battaglia, Emanuela Medda, and Corrado Fagnani. 2025. "Exploring the Relationship of Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder with Emotional Dysregulation: A Twin Study in Childhood and Adolescence" Methods and Protocols 8, no. 4: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8040094
APA StyleScaini, S., De Francesco, S., Giani, L., Battaglia, M., Medda, E., & Fagnani, C. (2025). Exploring the Relationship of Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder with Emotional Dysregulation: A Twin Study in Childhood and Adolescence. Methods and Protocols, 8(4), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8040094






