Application of a Customised Franz-Type Cell Coupled with HPTLC to Monitor the Timed Release of Bioactive Components in Complex Honey Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Honey and Honey-Based Formulations
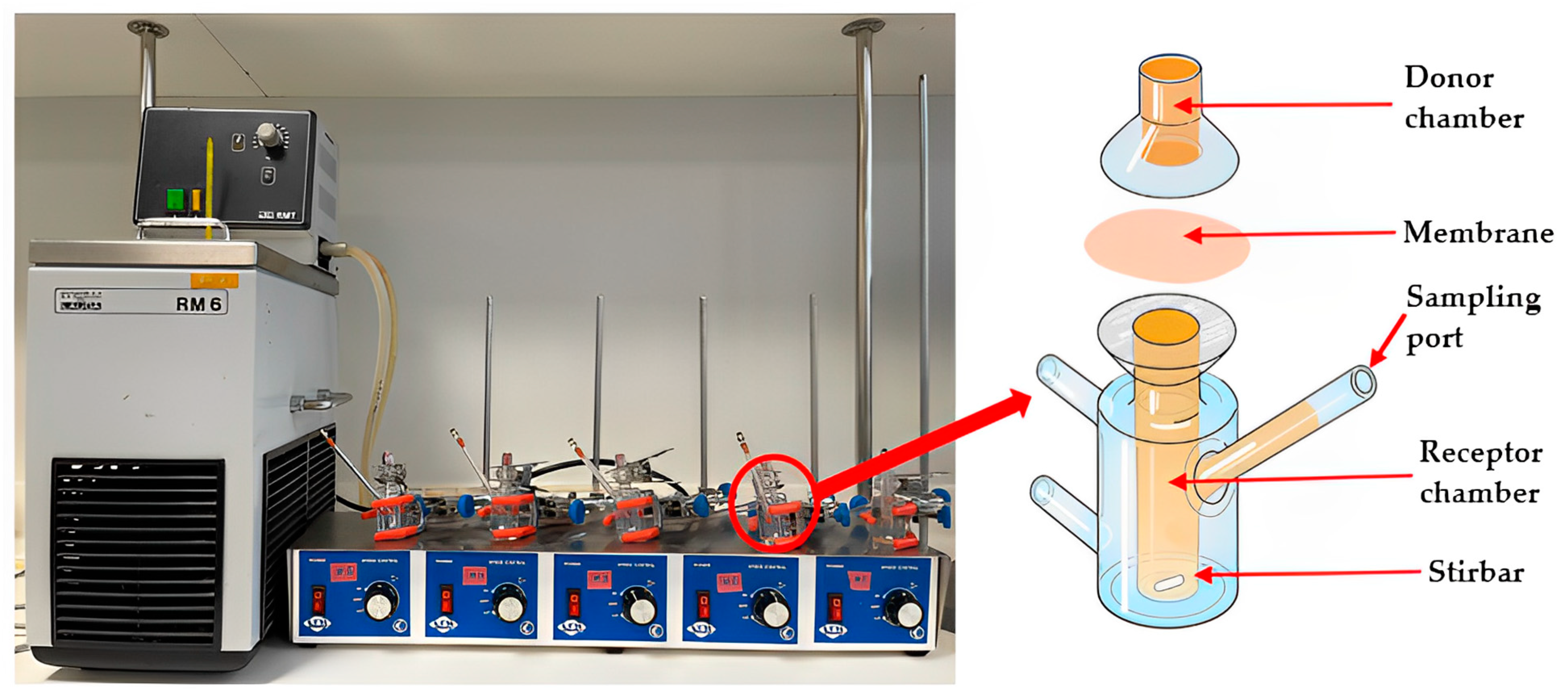
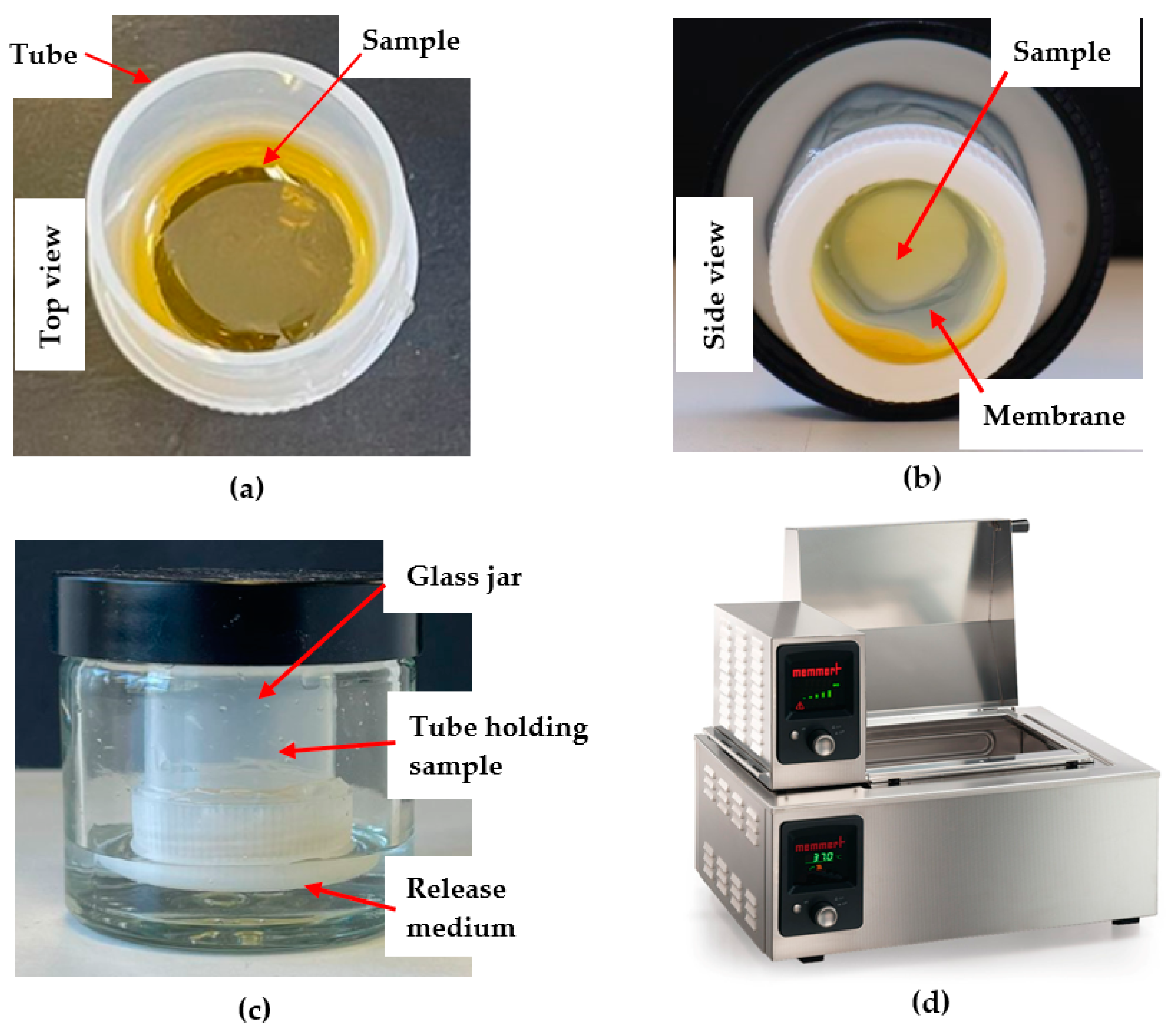
2.3. Commercial Franz Cell Diffusion Apparatus
2.4. Customised Franz-Type Cell Setup on Shaking Water Bath
2.5. Preanalysis Sample Preparation
2.6. HPTLC Analysis of Released Honey Constituents
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
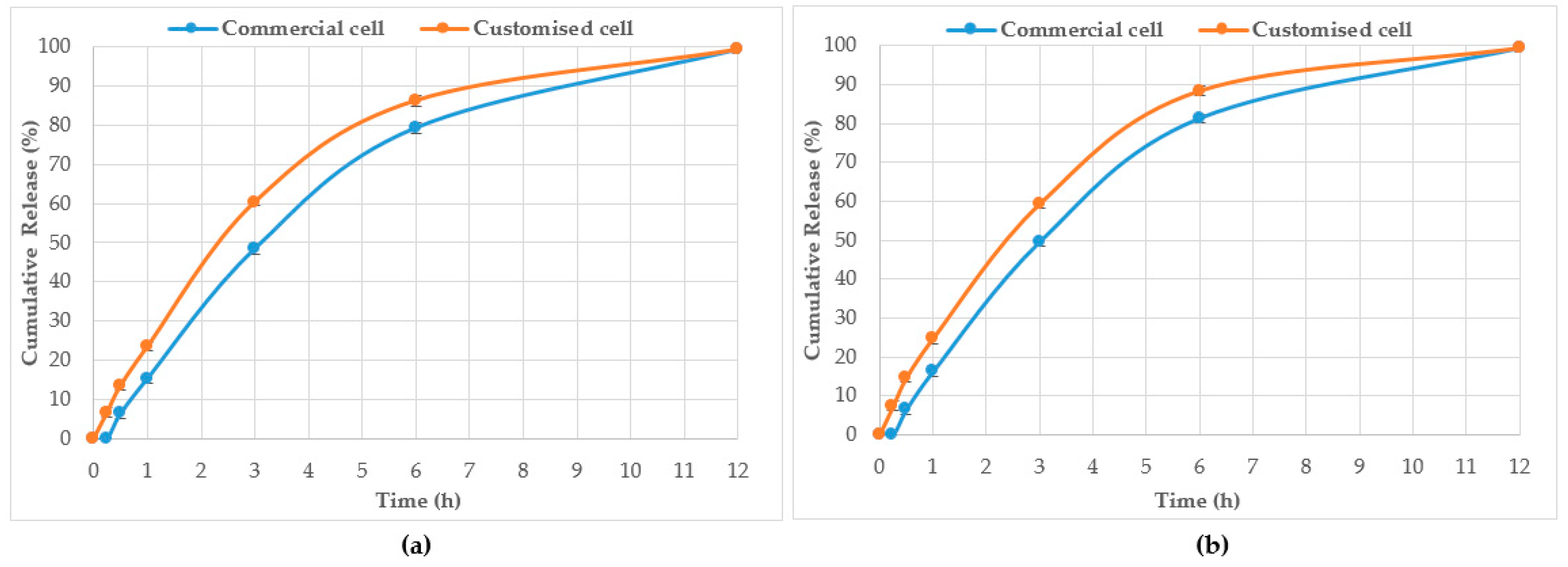
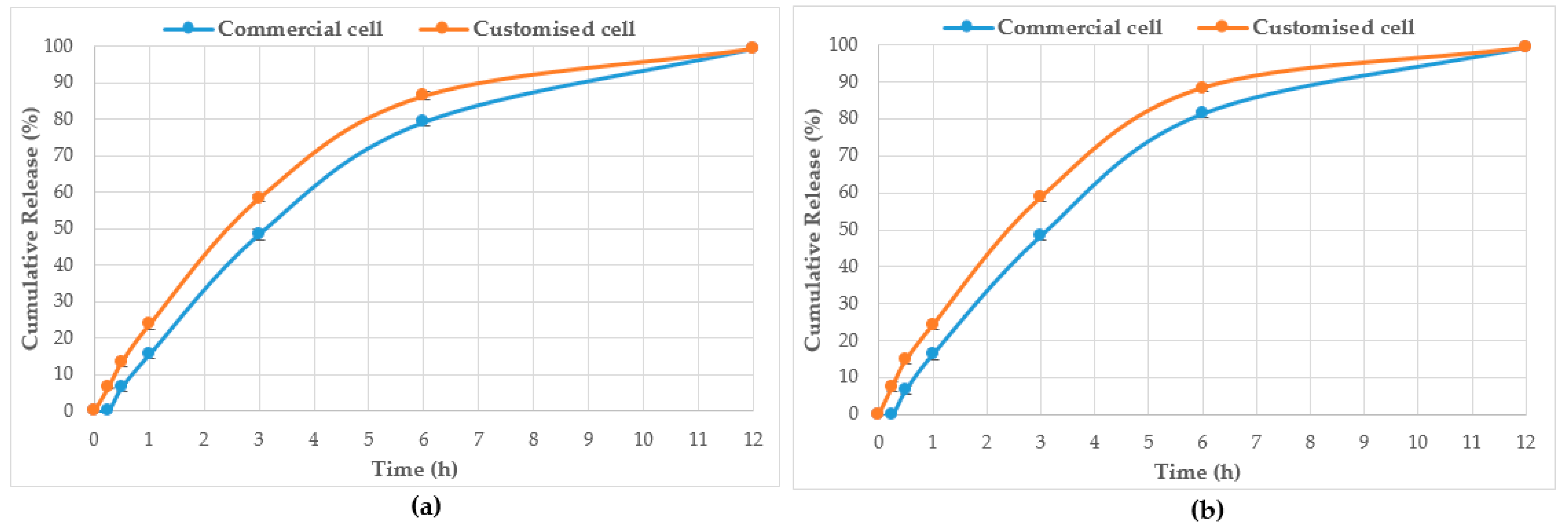
3.1. Pure Honeys
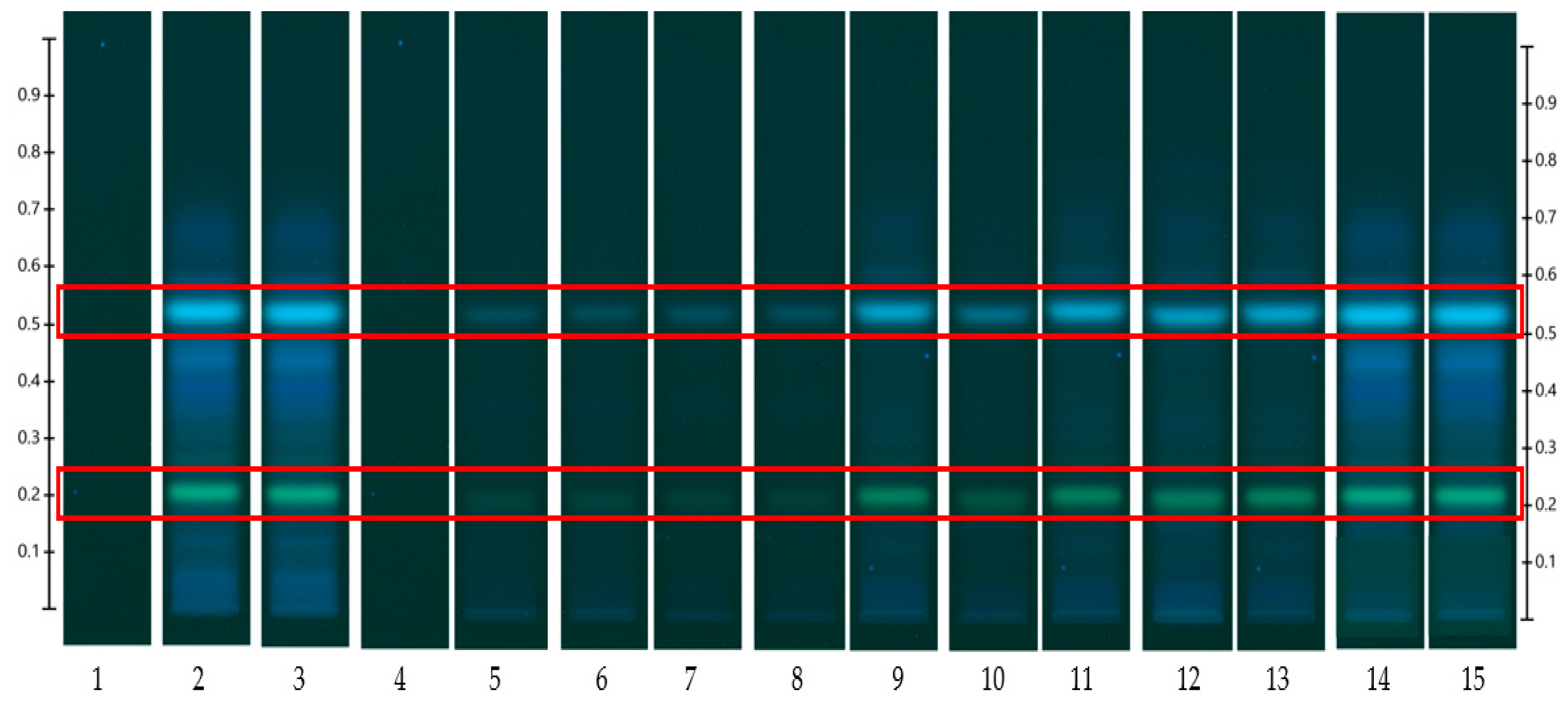
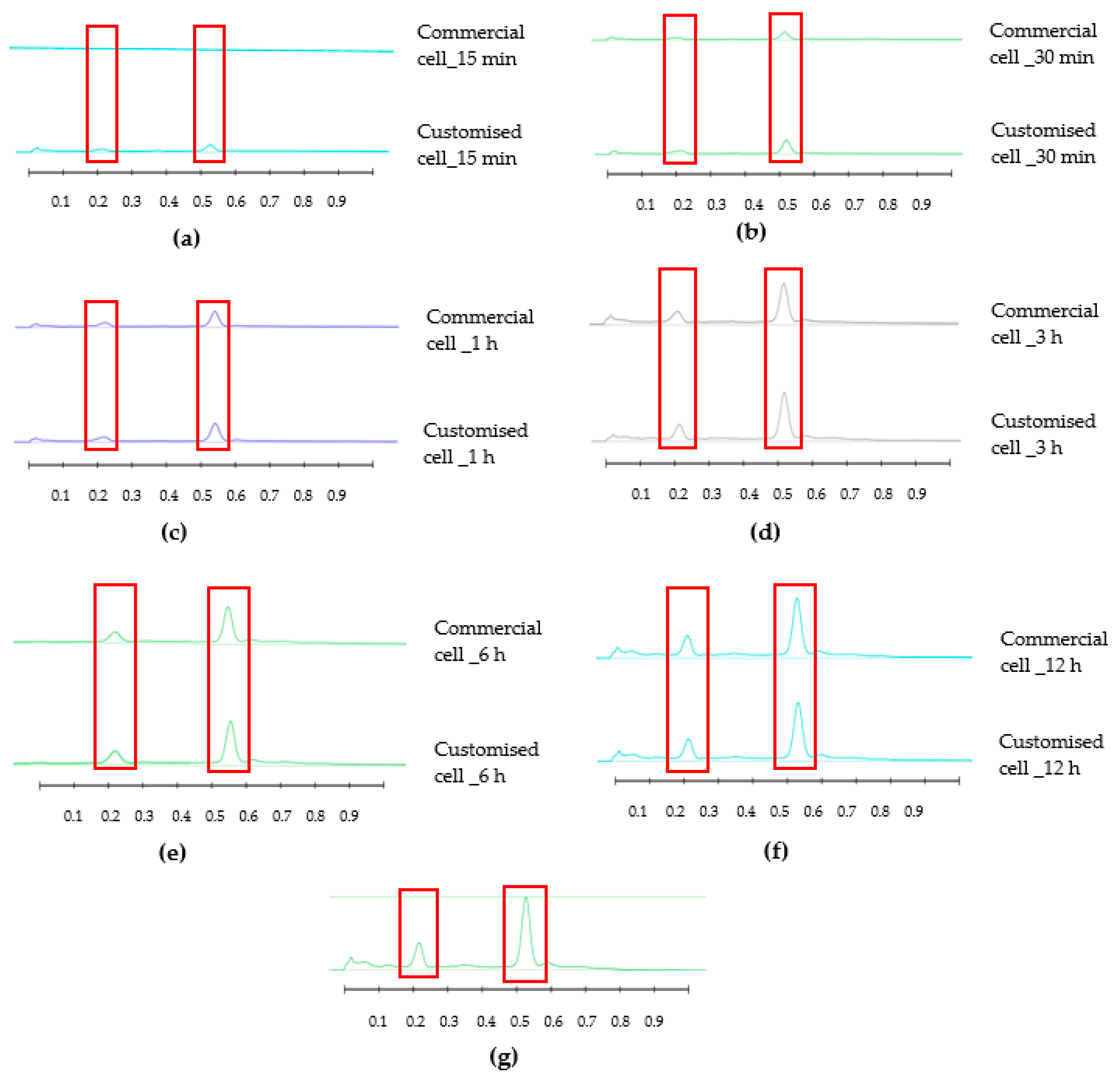
3.2. Honey-Loaded Pregel Formulations

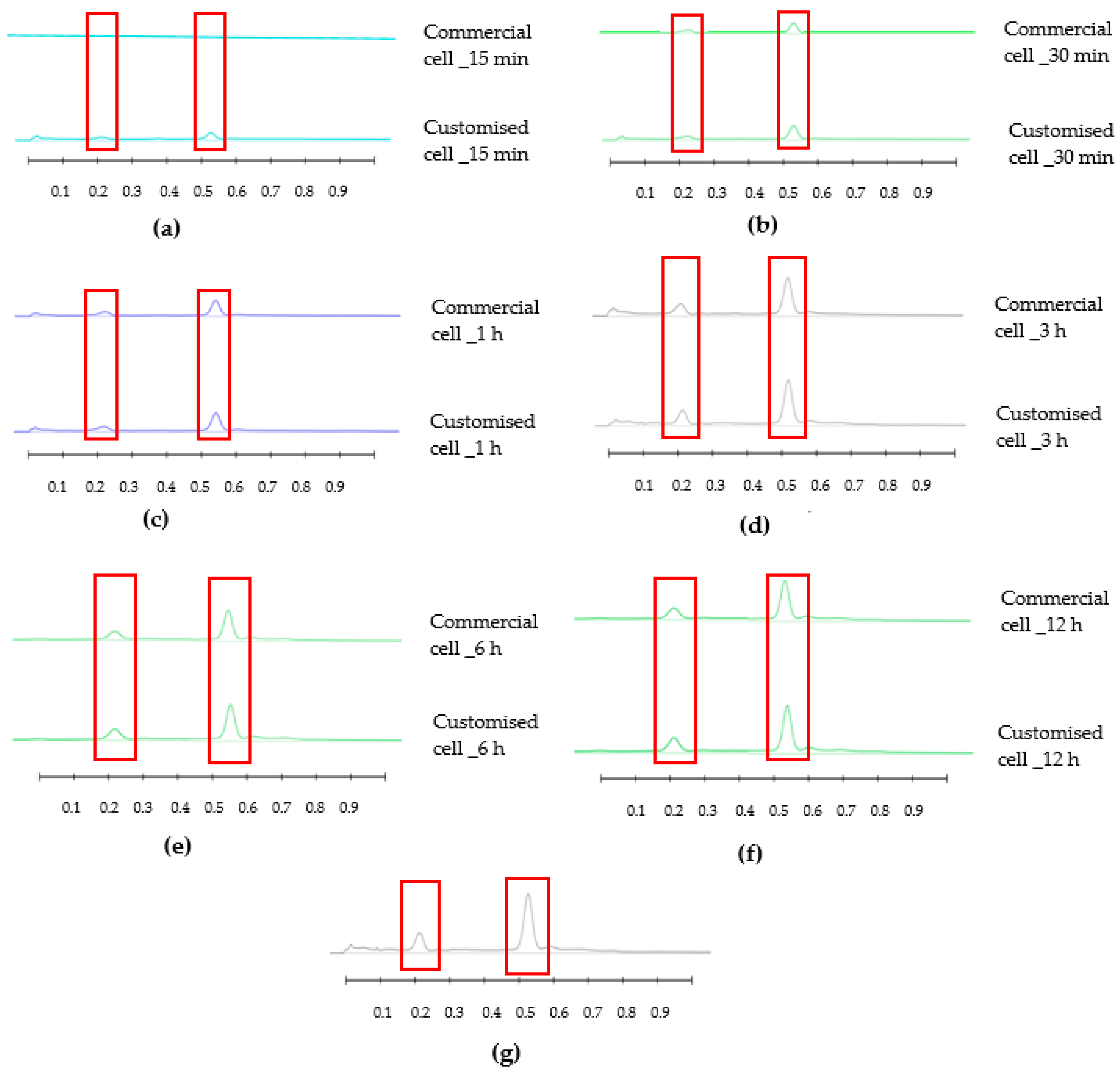
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, C.K.; Friedel, H.D.; Barker, A.R.; Buhse, L.F.; Keitel, S.; Cecil, T.L.; Kraemer, J.; Morris, J.M.; Reppas, C.; Stickelmeyer, M.P.; et al. FIP/AAPS joint workshop report: Dissolution/in vitro release testing of novel/special dosage forms. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 782–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewert, M.; Dressman, J.; Brown, C.; Shah, V.P. FIP/AAPS guidelines for dissolution/in vitro release testing of novel/special dosage forms. Dissolution Technol. 2003, 10, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Chow, S.F. In Vitro Release Study of the Polymeric Drug Nanoparticles: Development and Validation of a Novel Method. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardot, J.; Beyssac, E.; Alric, M. In vitro-in vivo correlation: Importance of dissolution in IVIVC. Dissolution Technol. 2007, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambito, Y.; Pedreschi, E.; Di Colo, G. Is dialysis a reliable method for studying drug release from nanoparticulate systems?—A case study. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 434, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.P.; Elkins, J.S.; Williams, R.L. Evaluation of the test system used for in vitro release of drugs from topical dermatological drug products. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 1999, 4, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.L.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Hettiarachchi, D.; Locher, C. Determination of Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Honey-Loaded Topical Formulations: A focus on Western Australian Honeys. Appl. Sci. 2023, 11, 7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.L.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Hettiarachchi, D.; Locher, C. Honey-Based Medicinal Formulations: A Critical Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Foster, K.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Locher, C. A Review of the phytochemistry and bioactivity of clover honeys (Trifolium spp.). Foods 2022, 11, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.L.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Hettiarachchi, D.; Locher, C. A Review of Commonly Used Methodologies for Assessing the Antibacterial Activity of Honey and Honey Products. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attimarad, M.; Ahmed, K.K.; Aldhubaib, B.E.; Harsha, S. High-performance thin layer chromatography: A powerful analytical technique in pharmaceutical drug discovery. Pharm. Methods 2011, 2, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tscherch, K.; Biller, J.; Lehmann, M.; Trusch, M.; Rohn, S. One- and two-dimensional high-performance thin-layer chromatography as an alternative analytical tool for investigating polyphenol-protein interactions. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.L.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Hettiarachchi, D.; Locher, C. Design, Preparation and Physicochemical Characterisation of Alginate Based Honey-Loaded Topical Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2023, 11, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.L.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Hettiarachchi, D.; Locher, C. Monitoring the Release of Methylglyoxal (MGO) from Honey and Honey-Based Formulations. Molecules 2023, 28, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, L.C.; Gandal, M.J.; Lin, R.; Liang, Y.; Siegel, S.J. In vitro-in vivo correlations of scalable PLGA-Risperidone implants for the treatment of schizophrenia. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, S.S.; DeLuca, P.P. Development of a dialysis in vitro release method for biodegradable microspheres. AAPS PharmSciTech 2005, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, S.; Faraj, J.A.; Dorati, R.; DeLuca, P.P. A short term quality control tool for biodegradable microspheres. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, N.; Burgess, D.J. A novel in vitro release method for submicron-sized dispersed systems. AAPS Pharm. Sci. 1999, 1, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, G.L.; Shah, V.P.; Tenjarla, S.N.; Corbo, M.; DeMagistris, D.; Feldman, T.G.; Franz, T.J.; Miran, D.R.; Pearce, D.M.; Sequeira, J.A.; et al. Assessment of value and applications of in vitro testing of topical dermatological drug products. Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Y.; Huang, J.P.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, Y.S. A Transdermal Measurement Platform Based on Microfluidics. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 9343824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca, C.H.; Barrera-Ocampo, A.; Lasso, J.C.; Camacho, N.; Yarce, C.J. Franz Diffusion Cell Approach for Pre-Formulation Characterisation of Ketoprofen Semi-Solid Dosage Forms. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, F.; Caspers, P.J.; Puppels, G.J.; Lane, M.E. Franz Cell Diffusion Testing and Quantitative Confocal Raman Spectroscopy: In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lane, M.E.; Hadgraft, J.; Heinrich, M.; Chen, T.; Lian, G.; Sinko, B. A comparison of the in vitro permeation of niacinamide in mammalian skin and in the Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeation Assay (PAMPA) model. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 556, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliopoulos, F.; Sil, B.C.; Al Hossain, A.S.M.M.; Moore, D.J.; Lucas, R.A.; Lane, M.E. Topical delivery of niacinamide: Influence of neat solvents. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 579, 119137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pensado, A.; Chiu, W.S.; Cordery, S.F.; Rantou, E.; Bunge, A.L.; Delgado-Charro, M.B.; Guy, R.H. Stratum Corneum Sampling to Assess Bioequivalence between Topical Acyclovir Products. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dosage Form | Method | USP Apparatus Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Oral solid dosage forms | Basket apparatus, paddle apparatus, reciprocating cylinder, or flow-through cell | Dissolution Apparatus 1, Apparatus Type 2, Dissolution Apparatus Type 3, Dissolution Apparatus 4 |
| Oral suspensions | Paddle apparatus | Apparatus Type 2 |
| Oral disintegrating tablets | Paddle apparatus and disintegration method | Apparatus Type 2 |
| Chewable tablets | Basket apparatus, paddle apparatus, or reciprocating cylinder | Dissolution Apparatus 1, Apparatus Type 2, Dissolution Apparatus Type 3 |
| Powders and granules | Flow-through cell (powder/granule sample cell) | Dissolution Apparatus 4 |
| Thin dissolvable films | Basket apparatus and disintegration method | Dissolution Apparatus 1 |
| Chewing gum | Special apparatus (Ph. Eur.) | |
| Dermal delivery systems (patches) | Paddle over disk, cylinder, and reciprocating holder | Apparatus 5, Apparatus 6, Apparatus 7 |
| Topical (semisolid dosage forms) | Franz cell diffusion system | |
| Suppositories | Paddle apparatus, modified basket apparatus or dual chamber flow-through cell | Apparatus Type 2, Dissolution Apparatus 1 (modified), Dissolution Apparatus 4 (dual chamber) |
| Micro-particulate formulations | Modified flow-through cell | Dissolution Apparatus 4 (modified) |
| Implants | Modified flow-through cell | Dissolution Apparatus 4 (modified) |
| Aerosols | Cascade impactor |
| Parameters | Franz Cell | Customised Franz-Type Cell Setup |
|---|---|---|
| Release surface area | 0.78 cm2 | 3.80 cm2 |
| Simulation of in vivo motility | Magnetic stirrer | Shaking water bath |
| Temperature | Can be set (e.g., at 37 °C) | Can be set (e.g., at 37 °C) |
| Number of samples per run | 5 | Up to 20 |
| Likelihood of bubble formation upon sample application | High | Very low |
| Volume of receptor compartment | Fixed | Flexible, can be small |
| Capacity to measure release of actives present at low concentration in formulation | Relatively low | Relatively high, depending on size of receptor compartment |
| Option of customization to specific requirements | Not possible | Possible |
| Botanical Origin | Supplier, Year |
|---|---|
| WA Manuka Honey 1 (Leptospermum scoparium) | Hive and Wellness, 2019 |
| WA Manuka Honey 2 (Leptospermum scoparium) | Manuka Life, 2019 |
| WA Coastal Peppermint (Agonis flexuosa) | Margaret River Honey Company, 2019 |
| WA Jarrah Honey (Eucalyptus marginata) | Hive and Wellness, 2019 |
| New Zealand Manuka Honey (Leptospermum scoparium) | Hive and Wellness, 2018 |
| Sample | Components (RF) | % Components of Baseline Released at Different Time Points (h) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.50 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 12 | ||||||||
| Franz | New | Franz | New | Franz | New | Franz | New | Franz | New | Franz | New | ||
| Jarrah pure honey | 0.21 | 0.00 | 6.6 ± 1.2 | 6.3 ± 1.1 | 13.5 ± 1.2 | 15.2 ± 1.2 | 23.4 ± 1.1 | 48.4 ± 1.3 | 60.3 ± 0.9 | 79.2 ± 1.4 | 86.2 ± 1.3 | 99.2 ± 0.8 | 99.3 ± 0.6 |
| 0.53 | 0.00 | 7.3 ± 1.2 | 6.4 ± 1.1 | 14.6 ± 1.1 | 16.2 ± 1.4 | 24.7 ± 1.3 | 49.5 ± 1.0 | 59.2 ± 1.0 | 81.2 ± 1.2 | 88.2 ± 1.2 | 99.3 ± 0.8 | 99.2 ± 0.7 | |
| Jarrah pre-gel | 0.21 | 0.00 | 6.3 ± 1.0 | 6.5 ± 1.2 | 13.4 ± 1.2 | 15.4 ± 1.1 | 23.6 ± 1.4 | 48.4 ± 1.4 | 58.2 ± 0.9 | 79.1 ± 1.0 | 86.3 ± 1.2 | 99.3 ± 0.7 | 99.3 ± 0.6 |
| 0.53 | 0.00 | 7.5 ± 1.2 | 6.5 ± 1.1 | 14.7 ± 1.1 | 16.2 ± 1.4 | 24.2 ± 1.3 | 48.2 ± 1.2 | 58.7 ± 1.2 | 81.3 ± 0.9 | 88.3 ± 1.0 | 99.3 ± 0.8 | 99.3 ± 0.7 | |
| WA Manuka 1 pure honey | 0.38 | 0.00 | 6.4 ± 1.1 | 6.5 ± 1.1 | 13.4 ± 1.1 | 15.5 ± 1.1 | 23.7 ± 1.2 | 48.4 ± 1.2 | 58.3 ± 0.9 | 79.2 ± 1.1 | 86.3 ± 1.1 | 99.4 ± 0.8 | 99.5 ± 0.7 |
| WA Manuka 1 pre-gel | 0.38 | 0.00 | 6.3 ± 10. | 6.6 ± 1.1 | 13.5 ± 1.3 | 15.4 ± 1.1 | 23.7 ± 1.2 | 48.4 ± 1.2 | 58.8 ± 1.0 | 79.2 ± 1.0 | 86.5 ± 1.2 | 99.4 ± 0.7 | 99.4 ± 0.7 |
| WA Manuka 2 pure honey | 0.38 | 0.00 | 7.6 ± 1.1 | 6.6 ± 1.1 | 14.8 ± 1.1 | 16.3 ± 1.2 | 24.3 ± 1.3 | 48.3 ± 1.2 | 58.7 ± 1.1 | 81.4 ± 1.0 | 88.4 ± 1.1 | 99.4 ± 1.1 | 99.4 ± 0.9 |
| WA Manuka 2 pre-gel | 0.38 | 0.00 | 7.5 ± 1.0 | 6.4 ± 1.1 | 14.6 ± 1.2 | 16.4 ± 1.1 | 24.4 ± 1.1 | 48.6 ± 1.3 | 58.7 ± 1.2 | 81.6 ± 0.9 | 88.5 ± 1.1 | 99.4 ± 0.9 | 99.4 ± 1.0 |
| CP pure honey | 0.20 | 0.00 | 7.3 ± 1.0 | 7.5 ± 1.0 | 14.4 ± 1.1 | 15.5 ± 1.1 | 24.6 ± 1.0 | 49.4 ± 1.2 | 59.1 ± 0.9 | 79.8 ± 1.0 | 87.3 ± 1.0 | 99.2 ± 0.9 | 99.2 ± 0.8 |
| 0.53 | 0.00 | 7.8 ± 1.1 | 7.6 ± 1.1 | 15.2 ± 1.1 | 17.3 ± 1.2 | 25.2 ± 1.3 | 48.9 ± 1.2 | 59.0 ± 1.1 | 82.1 ± 1.0 | 89.2 ± 1.1 | 99.3 ± 0.7 | 99.4 ± 0.7 | |
| CP pre-gel | 0.20 | 0.00 | 6.3 ± 1.0 | 6.6 ± 1.1 | 13.5 ± 1.3 | 15.4 ± 1.1 | 23.7 ± 1.2 | 48.4 ± 1.2 | 58.8 ± 1.0 | 79.2 ± 1.0 | 86.5 ± 1.2 | 99.4 ± 0.7 | 99.4 ± 0.8 |
| 0.53 | 0.00 | 7.8 ± 1.1 | 7.3 ± 1.2 | 16.1 ± 1.2 | 17.2 ± 1.1 | 25.3 ± 1.1 | 49.1 ± 1.2 | 59.2 ± 1.1 | 82.4 ± 0.9 | 89.4 ± 1.1 | 99.5 ± 0.9 | 99.5 ± 0.7 | |
| NZ Manuka pure honey | 0.32 | 0.00 | 7.4 ± 1.0 | 7.5 ± 1.0 | 14.4 ± 1.1 | 15.4 ± 1.1 | 24.6 ± 1.0 | 49.3 ± 1.2 | 59.1 ± 0.9 | 79.8 ± 1.0 | 87.4 ± 1.0 | 99.3 ± 0.9 | 99.3 ± 0.8 |
| 0.39 | 0.00 | 7.7 ± 1.1 | 7.5 ± 1.1 | 15.4 ± 1.1 | 17.3 ± 1.2 | 25.3 ± 1.3 | 49.0 ± 1.2 | 58.9 ± 1.1 | 82.5 ± 1.0 | 89.4 ± 1.1 | 99.4 ± 0.7 | 99.4 ± 0.7 | |
| NZ Manuka pre-gel | 0.32 | 0.00 | 6.3 ± 1.1 | 6.3 ± 1.1 | 13.4 ± 1.0 | 15.7 ± 1.1 | 23.8 ± 1.0 | 48.5 ± 1.2 | 58.7 ± 1.0 | 79.3 ± 1.1 | 86.6 ± 1.2 | 99.6 ± 0.7 | 99.5 ± 0.8 |
| 0.39 | 0.00 | 7.8 ± 1.1 | 7.3 ± 1.0 | 16.2 ± 1.2 | 17.2 ± 1.0 | 25.3 ± 1.1 | 49.2 ± 1.2 | 59.2 ± 1.0 | 82.4 ± 0.9 | 89.4 ± 1.0 | 99.6 ± 0.8 | 99.7 ± 0.8 | |
| Sample | Components (RF) | % Released per Unit Area of the Dialysis Membrane | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.50 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 12 | ||||||||
| Franz | New | Franz | New | Franz | New | Franz | New | Franz | New | Franz | New | ||
| Jarrah pure honey | 0.21 | 0 | 1.7 ±0.5 | 8.1 ± 0.5 | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 19.5 ± 0.4 | 6.2 ± 0.5 | 62.0 ± 0.7 | 15.9 ± 0.6 | 101.6 ± 0.6 | 22.7 ± 0.6 | 127.2 ± 0.4 | 26.1 ± 0.6 |
| 0.53 | 0 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 8.2 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 20.8 ± 0.5 | 6.5 ± 0.5 | 63.5 ± 0.4 | 15.6 ± 0.4 | 104.1 ± 0.5 | 23.2 ± 0.5 | 127.3 ± 0.5 | 26.1 ± 0.5 | |
| Jarrah pre-gel | 0.21 | 0 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 8.3 ± 0.4 | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 19.8 ± 0.6 | 6.2 ± 0.6 | 62.0 ± 0.5 | 15.3 ± 0.5 | 101.5 ± 0.5 | 22.7 ± 0.4 | 127.3 ± 0.6 | 26.1 ± 0.5 |
| 0.53 | 0 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 8.4 ± 0.5 | 3.9 ± 0.5 | 20.8 ± 0.5 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 61.8 ± 0.5 | 15.5 ± 0.6 | 104.2 ± 0.6 | 23.2 ± 0.6 | 127.3 ± 0.5 | 26.1 ± 0.4 | |
| WA Manuka 1 pure honey | 0.38 | 0 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 8.4 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.4 | 19.8 ± 0.4 | 6.2 ± 0.4 | 62.0 ± 0.6 | 15.3 ± 0.7 | 101.5 ± 0.4 | 22.7 ± 0.5 | 127.5 ± 0.4 | 26.2 ± 0.6 |
| WA Manuka 1 pre-gel | 0.38 | 0 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 8.5 ± 0.5 | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 17.2 ± 0.6 | 6.2 ± 0.5 | 62.1 ± 0.5 | 15.5 ± 0.7 | 101.6 ± 0.6 | 22.8 ± 0.5 | 127.4 ± 0.5 | 26.1 ± 0.6 |
| WA Manuka 2 pure honey | 0.38 | 0 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 8.4 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 0.5 | 20.9 ± 0.5 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 62.0 ± 0.6 | 15.5 ± 0.4 | 104.4 ± 0.5 | 23.3 ± 0.5 | 127.5 ± 0.5 | 26.2 ± 0.6 |
| WA Manuka 2 pre-gel | 0.38 | 0 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 8.2 ± 0.6 | 3.9 ± 0.5 | 21.0 ± 0.4 | 6.4 ± 0.6 | 62.3 ± 0.5 | 15.4 ± 0.6 | 104.6 ± 0.5 | 23.3 ± 0.5 | 127.4 ± 0.6 | 26.1 ± 0.4 |
| CP pure honey | 0.20 | 0 | 1.9 ± 0.4 | 9.7 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 19.8 ± 0.4 | 6.5 ± 0.4 | 63.3 ± 0.5 | 15.6 ± 0.6 | 102.3 ± 0.5 | 23.0 ± 0.6 | 127.2 ± 0.5 | 26.1 ± 0.5 |
| 0.53 | 0 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 9.7 ± 0.5 | 4.0 ± 0.6 | 22.2 ± 0.6 | 6.6 ± 0.4 | 62.7 ± 0.4 | 15.5 ± 0.5 | 105.3 ± 0.5 | 23.5 ± 0.4 | 127.4 ± 0.4 | 26.2 ± 0.6 | |
| CP pre-gel | 0.20 | 0 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 8.5 ± 0.4 | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 19.7 ± 0.5 | 6.2 ± ±0.7 | 62.1 ± 0.5 | 15.5 ± 0.4 | 101.6 ± 0.6 | 22.8 ± 0.6 | 127.4 ± 0.5 | 26.1 ± 0.5 |
| 0.53 | 0 | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 9.4 ± 0.5 | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 22.1 ± 0.5 | 6.7 ± 0.4 | 63.0 ± 0.4 | 15.6 ± 0.5 | 105.7 ± 0.4 | 23.5 ± 0.6 | 127.6 ± 0.5 | 26.2 ± 0.5 | |
| NZ Manuka pure honey | 0.32 | 0 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 9.6 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 19.8 ± 0.5 | 6.5 ± 0.6 | 63.2 ± 0.5 | 15.6 ± 0.6 | 102.3 ± 0.5 | 23.0 ± 0.4 | 127.3 ± 0.4 | 26.1 ± 0.4 |
| 0.39 | 0 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 9.6 ± 0.5 | 4.1 ± 0.5 | 22.2 ± 0.4 | 6.6 ± 0.7 | 62.8 ± 0.4 | 15.5 ± 0.5 | 105.8 ± 0.6 | 23.5 ± 0.4 | 127.5 ± 0.5 | 26.2 ± 0.6 | |
| NZ Manuka pre-gel | 0.32 | 0 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 8.1 ± 0.5 | 3.5 ± 0.6 | 20.1 ± 0.4 | 6.3 ± 0.7 | 62.1 ± 0.5 | 15.5 ± 0.4 | 101.6 ± 0.6 | 22.8 ± 0.5 | 127.6 ± 0.5 | 26.2 ± 0.5 |
| 0.39 | 0 | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 9.4 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 22.1 ± 0.5 | 6.7 ± 0.3 | 63.0 ± 0.4 | 15.6 ± 0.6 | 105.7 ± 0.4 | 23.5 ± 0.5 | 127.8 ± 0.6 | 26.2 ± 0.5 | |
| Sample | Component of Interest (Presented by RF Values) | Time (h) Required to Release 25, 50, and 75% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T25% | T50% | T75% | |||||
| Franz | New | Franz | New | Franz | New | ||
| Pure JAR honey extract | 0.21 | 1.6 ± 1.1 | 1.1 ± 1.2 | 3.1 ± 1.3 | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 5.7 ± 1.0 | 5.2 ± 1.2 |
| 0.53 | 1.5 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 1.1 | 3.0 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 5.1 ± 1.1 | |
| JAR pre-gel extract | 0.21 | 1.6 ± 1.0 | 1.1 ± 1.2 | 3.1 ± 1.0 | 2.6 ± 1.1 | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 5.2 ± 1.3 |
| 0.53 | 1.5 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 1.1 | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 5.1 ± 1.0 | |
| WA Manuka 1 pure honey | 0.38 | 1.6 ± 1.2 | 1.1 ± 1.1 | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 2.6 ± 1.1 | 5.7 ± 1.1 | 5.2 ± 1.0 |
| WA Manuka 1 pre-gel | 0.38 | 1.6 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 1.1 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 5.7 ± 1.1 | 5.2 ± 1.1 |
| WA Manuka 2 pure honey | 0.38 | 1.5 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 5.1 ± 1.1 |
| WA Manuka 2 pre-gel | 0.38 | 1.5 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 2.6 ± 1.2 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 5.1 ± 1.1 |
| CP pure honey | 0.20 | 1.6 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 5.6 ± 1.0 | 5.1 ± 1.2 |
| 0.53 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 1.1 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 5.0 ± 1.1 | |
| CP pre-gel | 0.20 | 1.6 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 5.2 ± 1.1 |
| 0.53 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 1.1 | 3.0 ± 1.2 | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 5.0 ± 1.1 | |
| NZ Manuka pure honey | 0.32 | 1.6 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 1.2 | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 5.6 ± 1.1 | 5.1 ± 1.2 |
| 0.39 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 1.1 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 5.4 ± 1.1 | 5.0 ± 1.1 | |
| NZ Manuka pre-gel | 0.32 | 1.6 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 5.2 ± 1.2 |
| 0.39 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 3.0 ± 1.2 | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 5.0 ± 1.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hossain, M.L.; Nguyen, M.; Benington, L.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Hettiarachchi, D.; Locher, C. Application of a Customised Franz-Type Cell Coupled with HPTLC to Monitor the Timed Release of Bioactive Components in Complex Honey Matrices. Methods Protoc. 2023, 6, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps6040070
Hossain ML, Nguyen M, Benington L, Lim LY, Hammer K, Hettiarachchi D, Locher C. Application of a Customised Franz-Type Cell Coupled with HPTLC to Monitor the Timed Release of Bioactive Components in Complex Honey Matrices. Methods and Protocols. 2023; 6(4):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps6040070
Chicago/Turabian StyleHossain, Md Lokman, Minh Nguyen, Leah Benington, Lee Yong Lim, Katherine Hammer, Dhanushka Hettiarachchi, and Cornelia Locher. 2023. "Application of a Customised Franz-Type Cell Coupled with HPTLC to Monitor the Timed Release of Bioactive Components in Complex Honey Matrices" Methods and Protocols 6, no. 4: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps6040070
APA StyleHossain, M. L., Nguyen, M., Benington, L., Lim, L. Y., Hammer, K., Hettiarachchi, D., & Locher, C. (2023). Application of a Customised Franz-Type Cell Coupled with HPTLC to Monitor the Timed Release of Bioactive Components in Complex Honey Matrices. Methods and Protocols, 6(4), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps6040070








