Quantitative, High-Throughput Assays for Proteolytic Degradation of Amylin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Amylin Degradation Assays
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Numerical Analyses
3. Results
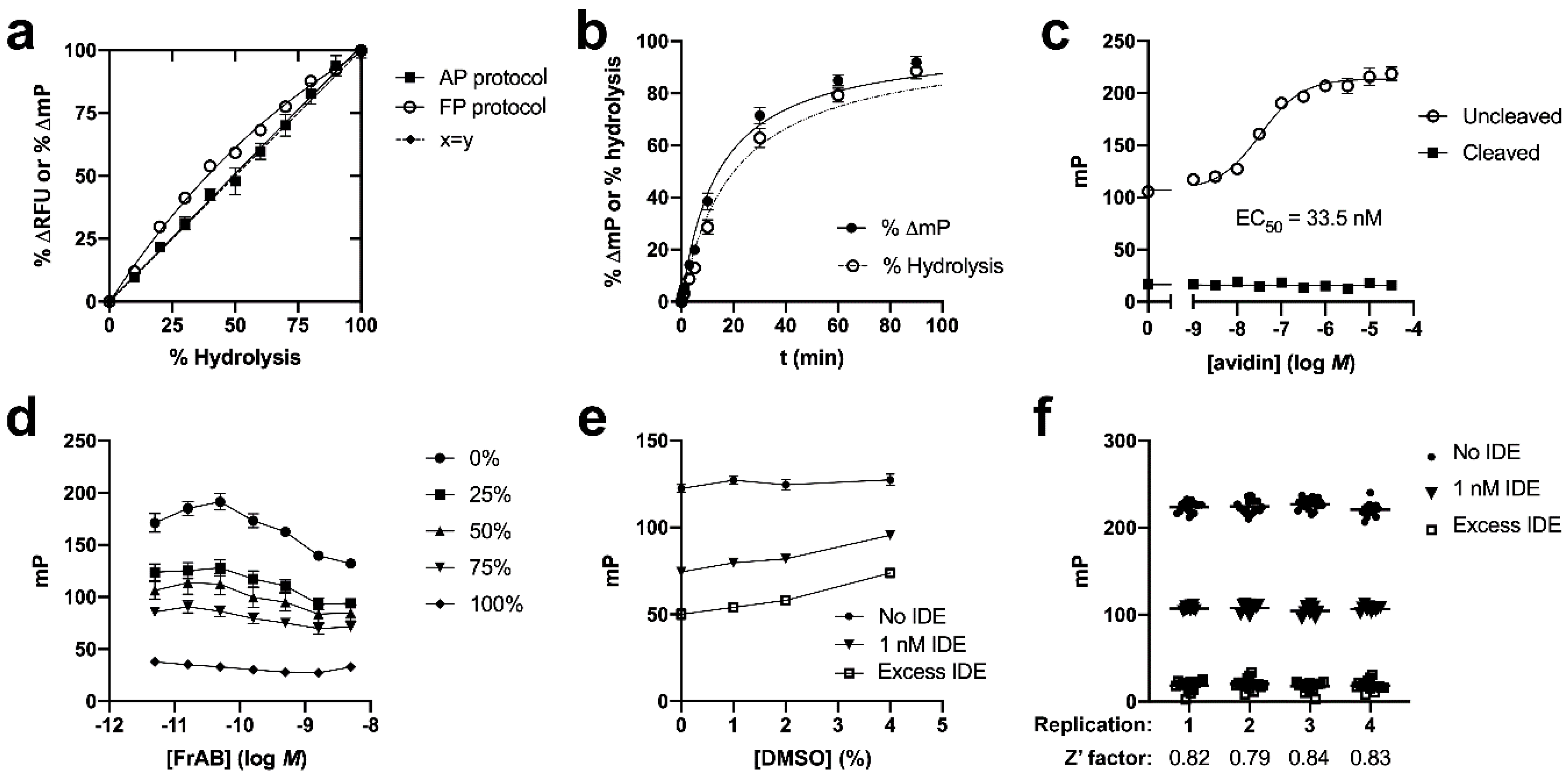
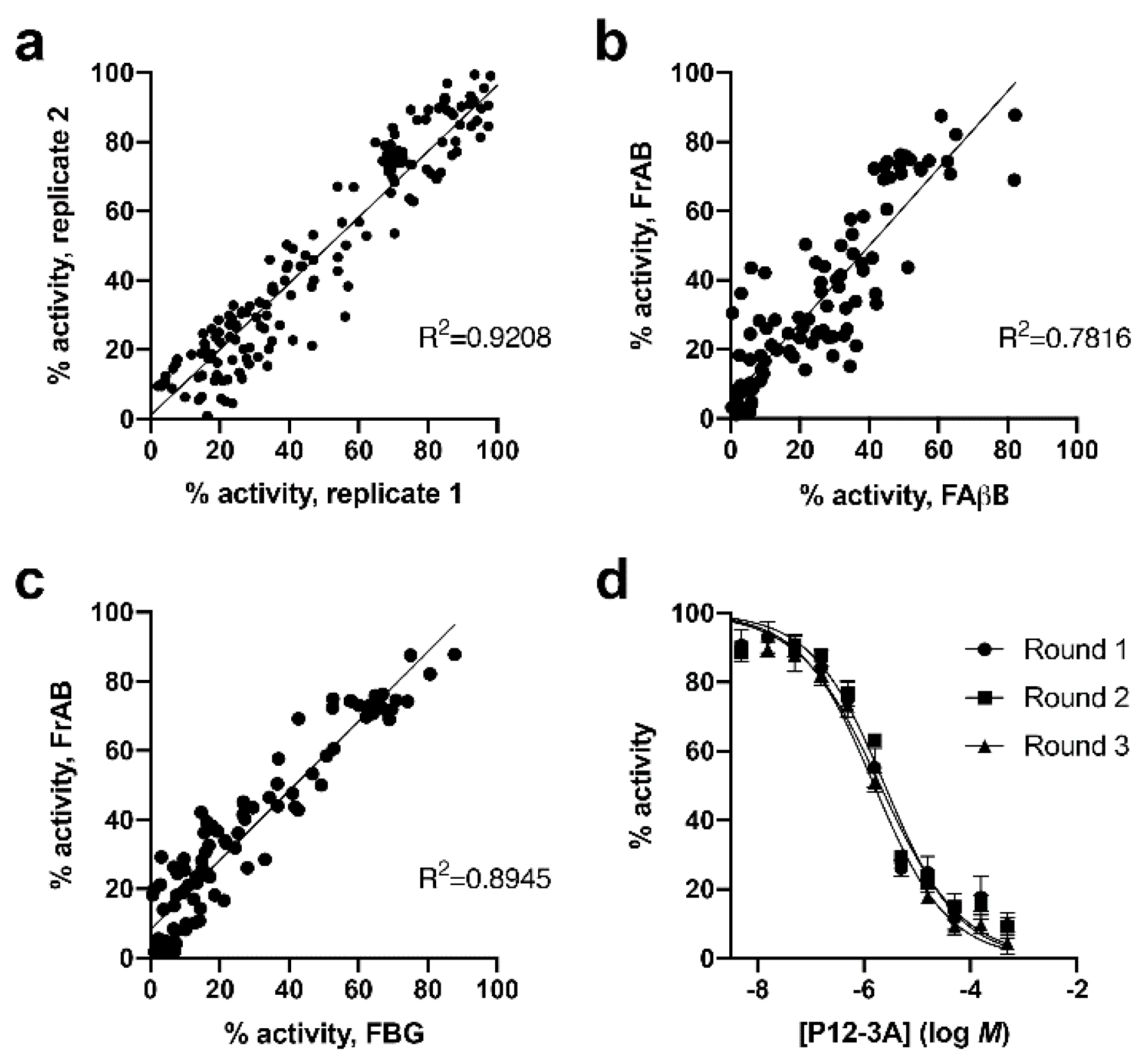
3.1. Development and Characterization of AP and FP-Based Assays for Amylin Degradation
3.2. Development and Characterization of a Fluorescence-Dequenching Amylin Degradation Assay
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hay, D.L.; Chen, S.; Lutz, T.A.; Parkes, D.G.; Roth, J.D. Amylin: Pharmacology, physiology, and clinical potential. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 564–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, S.C.; Lutz, T.A.; Geary, N.; Langhans, W. Pancreatic signals controlling food intake; insulin, glucagon and amylin. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1219–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishoyi, A.K.; Roham, P.H.; Rachineni, K.; Save, S.; Hazari, M.A.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A. Human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP)—A curse in type II diabetes mellitus: Insights from structure and toxicity studies. Biol. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimundo, A.F.; Ferreira, S.; Martins, I.C.; Menezes, R. Islet Amyloid Polypeptide: A Partner in crime with Abeta in the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, M.A. Unraveling Alzheimer’s: Making sense of the relationship between diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 51, 961–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, R.; Cao, P.; Noor, H.; Ridgway, Z.; Tu, L.H.; Wang, H.; Wong, A.G.; Zhang, X.; Abedini, A.; Schmidt, A.M.; et al. Islet amyloid polypeptide: Structure, function, and pathophysiology. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2798269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maianti, J.P.; McFedries, A.; Foda, Z.H.; Kleiner, R.E.; Du, X.Q.; Leissring, M.A.; Tang, W.J.; Charron, M.J.; Seeliger, M.A.; Saghatelian, A.; et al. Anti-diabetic activity of insulin-degrading enzyme inhibitors mediated by multiple hormones. Nature 2014, 511, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Joachimiak, A.; Rosner, M.R.; Tang, W.J. Structures of human insulin-degrading enzyme reveal a new substrate recognition mechanism. Nature 2006, 443, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.G.; Hamel, F.G.; Duckworth, W.C. An insulin-degrading enzyme inhibitor decreases amylin degradation, increases amylin-induced cytotoxicity, and increases amyloid formation in insulinoma cell cultures. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2315–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.G.; Duckworth, W.C.; Hamel, F.G. Degradation of amylin by insulin-degrading enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36621–36625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, M.F.; Meier, D.T.; Zraika, S.; Templin, A.T.; Mellati, M.; Hull, R.L.; Leissring, M.A.; Kahn, S.E. Inhibition of insulin-degrading enzyme does not increase islet amyloid deposition in vitro. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3462–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulifson, I.C.; Cao, P.; Miao, L.; Kopecky, D.; Huang, L.; White, R.D.; Samayoa, K.; Gardner, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, K.; et al. Identification of human islet amyloid polypeptide as a BACE2 substrate. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leissring, M.A. Abeta-degrading proteases: Therapeutic potential in Alzheimer disease. CNS Drugs 2016, 30, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sladek, R.; Rocheleau, G.; Rung, J.; Dina, C.; Shen, L.; Serre, D.; Boutin, P.; Vincent, D.; Belisle, A.; Hadjadj, S.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 2007, 445, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.F.; Efendic, S.; Nordman, S.; Ostenson, C.G.; Brismar, K.; Brookes, A.J.; Prince, J.A. Quantitative trait loci near the insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) gene contribute to variation in plasma insulin levels. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2137–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maianti, J.P.; Tan, G.A.; Vetere, A.; Welsh, A.J.; Wagner, B.K.; Seeliger, M.A.; Liu, D.R. Substrate-selective inhibitors that reprogram the activity of insulin-degrading enzyme. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, W.; Leissring, M.A.; Hemming, M.L.; Chang, A.Y.; Selkoe, D.J. Alternative splicing of human insulin-degrading enzyme yields a novel isoform with a decreased ability to degrade insulin and amyloid beta-protein. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 6513–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leissring, M.A.; Lu, A.; Condron, M.M.; Teplow, D.B.; Stein, R.L.; Farris, W.; Selkoe, D.J. Kinetics of amyloid beta-protein degradation determined by novel fluorescence- and fluorescence polarization-based assays. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 37314–37320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chung, T.D.; Oldenburg, K.R. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suire, C.N.; Lane, S.; Leissring, M.A. Development and characterization of quantitative, high-throughput-compatible assays for proteolytic degradation of glucagon. SLAS Discov. 2018, 23, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.D.; Yasgar, A.; Peryea, T.; Braisted, J.C.; Jadhav, A.; Simeonov, A.; Coussens, N.P. Fluorescence polarization assays in high-throughput screening and drug discovery: A review. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2016, 4, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, W.; Mansourian, S.; Leissring, M.A.; Eckman, E.A.; Bertram, L.; Eckman, C.B.; Tanzi, R.E.; Selkoe, D.J. Partial loss-of-function mutations in insulin-degrading enzyme that induce diabetes also impair degradation of amyloid beta-protein. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Hay, S.O.; Lane, A.L.; Caulfield, T.R.; Claussin, C.; Bertrand, J.; Masson, A.; Choudhry, S.; Fauq, A.H.; Maharvi, G.M.; Leissring, M.A. Optimization of peptide hydroxamate inhibitors of insulin-degrading enzyme reveals marked substrate-selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2246–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suire, C.N.; Nainar, S.; Fazio, M.; Kreutzer, A.G.; Paymozd-Yazdi, T.; Topper, C.L.; Thompson, C.R.; Leissring, M.A. Peptidic inhibitors of insulin-degrading enzyme with potential for dermatological applications discovered via phage display. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Manolopoulou, M.; Bian, Y.; Schilling, A.B.; Tang, W.J. Molecular basis for the recognition and cleavages of IGF-II, TGF-alpha, and amylin by human insulin-degrading enzyme. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajava, A.V.; Aebi, U.; Steven, A.C. The parallel superpleated beta-structure as a model for amyloid fibrils of human amylin. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leissring, M.A.; Malito, E.; Hedouin, S.; Reinstatler, L.; Sahara, T.; Abdul-Hay, S.O.; Choudhry, S.; Maharvi, G.M.; Fauq, A.H.; Huzarska, M.; et al. Designed inhibitors of insulin-degrading enzyme regulate the catabolism and activity of insulin. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
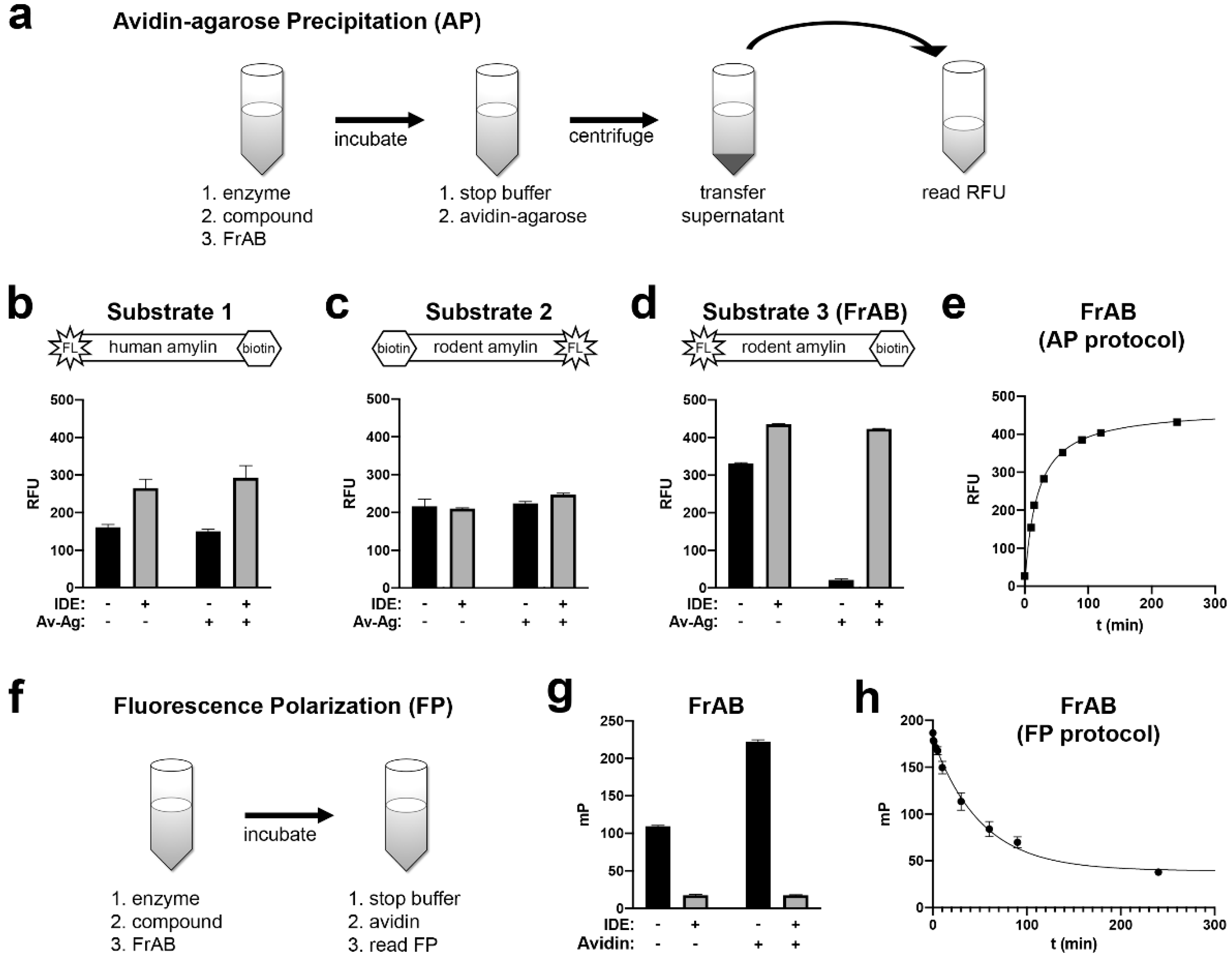


| Name | Sequence 1 | Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate 1 | 5-FAM-KCNTATCATQRLANFLVHSSNNFGAILSSTNVGSNTY- [Lys(Ahx-biotin)]-amide | biotin does not bind to avidin |
| Substrate 2 | [Lys(Ahx-biotin)]- CNTATCATQRLANFLVRSSNNLGPVLPPTNVGSNT- [Lys(FITC)]-amide | biotin does not bind to avidin |
| Substrate 3 (FrAB) | 5-FAM-KCNTATCATQRLANFLVRSSNNLGPVLPPTNVGSNTY-[Lys(Ahx-biotin)]-amide | -- |
| Substrate 4 (FRAM) | KCNTATCATQR[Lys(DABCYL)]ANFLVR[Glu(EDANS)]-SNNLGPVLPPTNVGSNTY | utility may be limited to IDE |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suire, C.N.; Brizuela, M.K.; Leissring, M.A. Quantitative, High-Throughput Assays for Proteolytic Degradation of Amylin. Methods Protoc. 2020, 3, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps3040081
Suire CN, Brizuela MK, Leissring MA. Quantitative, High-Throughput Assays for Proteolytic Degradation of Amylin. Methods and Protocols. 2020; 3(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps3040081
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuire, Caitlin N., Monica K. Brizuela, and Malcolm A. Leissring. 2020. "Quantitative, High-Throughput Assays for Proteolytic Degradation of Amylin" Methods and Protocols 3, no. 4: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps3040081
APA StyleSuire, C. N., Brizuela, M. K., & Leissring, M. A. (2020). Quantitative, High-Throughput Assays for Proteolytic Degradation of Amylin. Methods and Protocols, 3(4), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps3040081






