Advancements in Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To provide a systematic overview of CAD-based methods for CD diagnosis;
- To highlight the strengths and limitations of current methods in order to give guidance for improving the quality of future research;
- To provide a discussion of the existing challenges of commonly applied techniques to identify gaps in the existing research and highlight areas where further investigation is needed.
Review Methodology
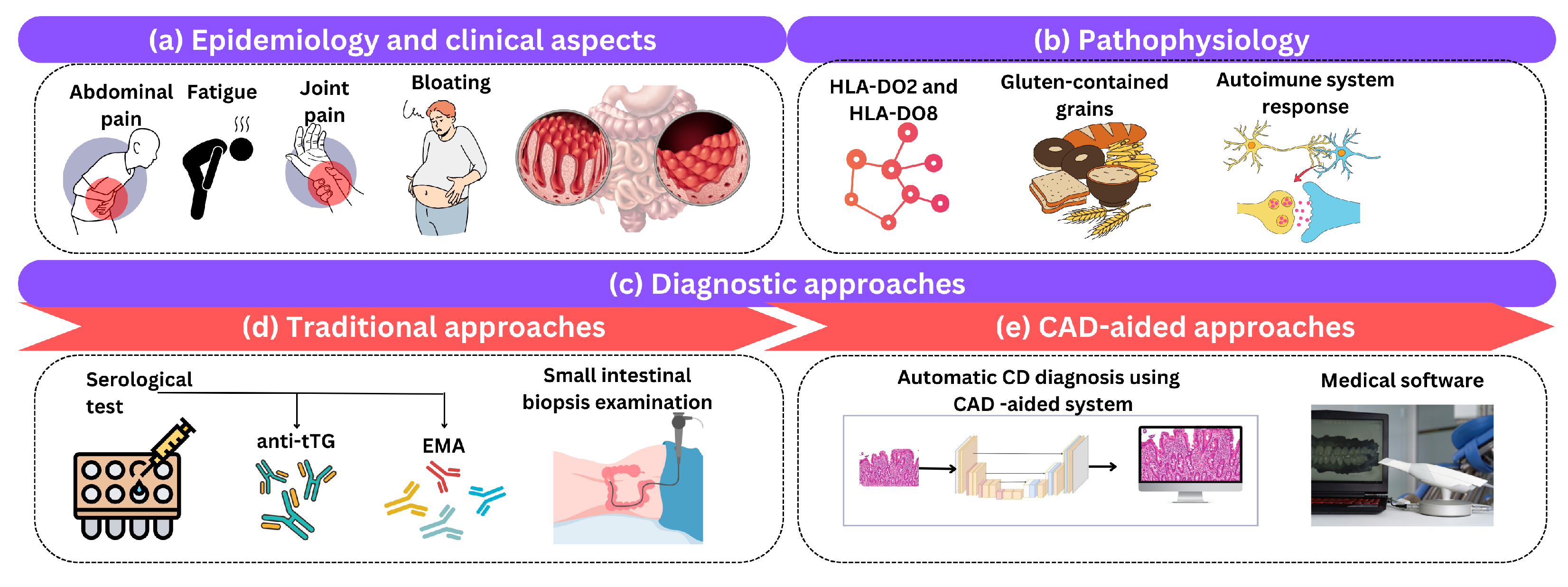
2. Clinical Background
2.1. Celiac Disease Epidemiology and Clinical Aspects
2.2. Celiac Disease Pathophysiology
2.3. Bio-Inspired Intelligent Approaches for CD Diagnosis
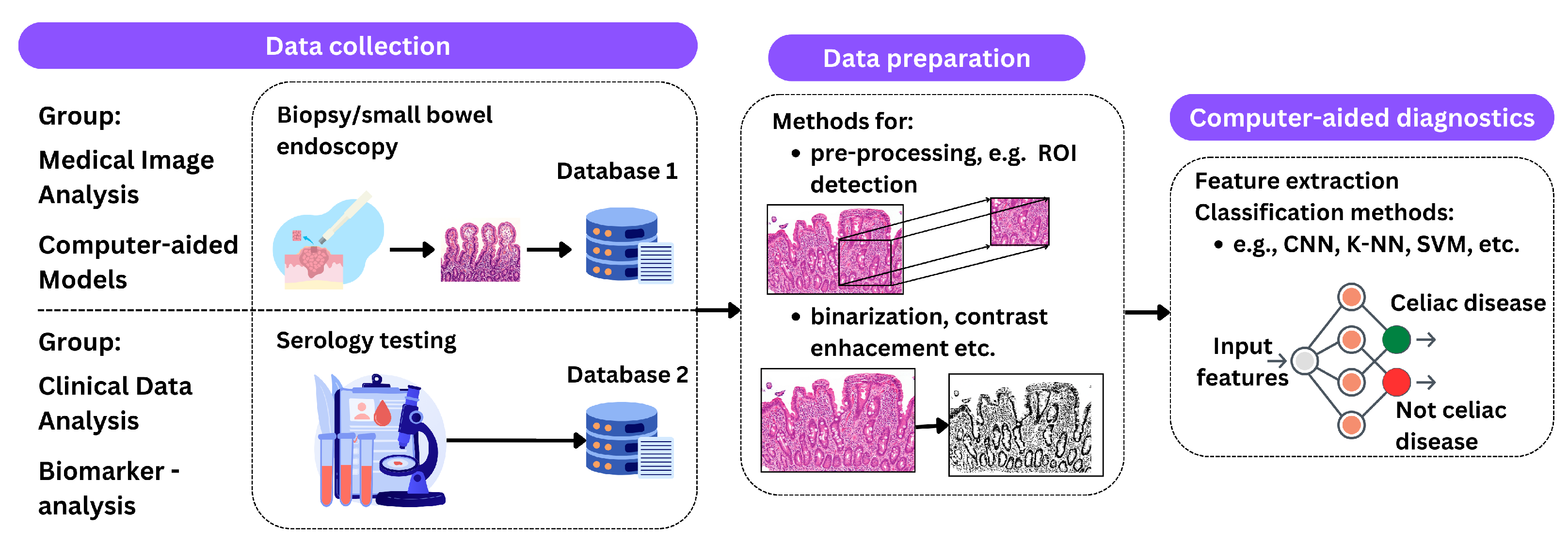
3. Celiac Disease Diagnostic Methods
- Medical image analysis:
- -
- Endoscopy with biopsy: computer techniques can be used to analyze endoscopic images of the small intestinal mucosa to identify changes characteristic of CD.
- -
- Image processing and analysis: image processing algorithms can help identify morphological changes in intestinal tissue associated with CD.
- Biomarker analysis:
- -
- Blood tests: computational methods can be used to analyze laboratory results, including the presence of specific antibodies (such as anti-tTG antibodies) indicative of CD.
- -
- Analysis of genetic data: computer methods can be used to analyze genetic markers associated with CD to determine genetic predisposition.
- Computer-aided models:
- -
- ML: enables the development of models that can be trained on datasets to identify characteristic patterns of CD based on medical images or clinical data.
- -
- DL: is a branch of ML that uses deep neural networks to process complex data. It can be applied to the analysis of medical images or genetic data to diagnose CD.
- Clinical data analysis:
- -
- Symptom data: computational methods can analyze patient’s symptoms and clinical data to identify patterns suggestive of CD.
3.1. Medical Image Analysis
3.2. Biomarker Analysis
3.3. Computer-Aided Models
3.4. Clinical Data Analysis
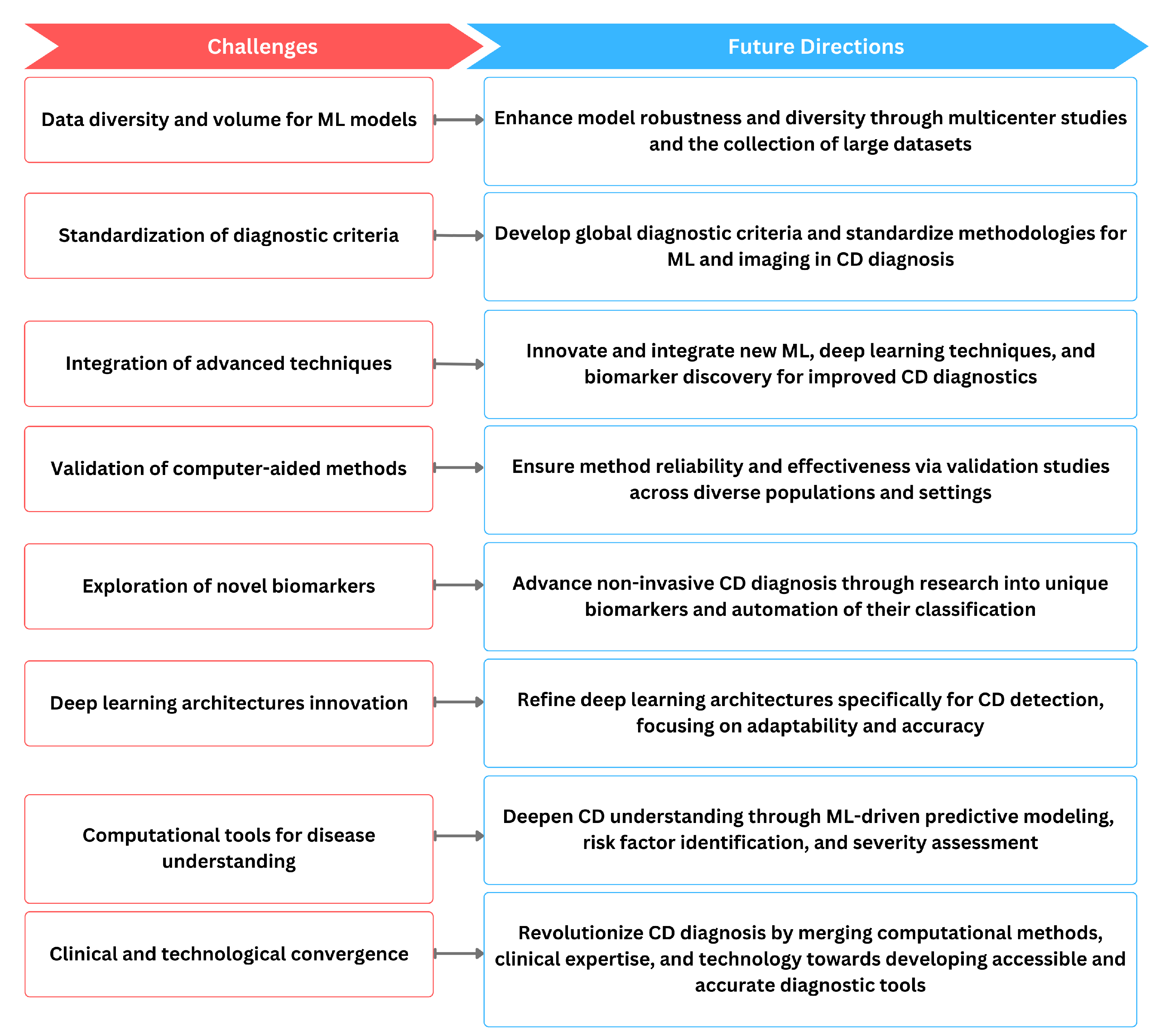
4. Challenges in the Standardization and Clinical Adaptation
- Variability in Imaging Techniques. Advanced imaging methods have shown promise in identifying morphological changes associated with CD. Nonetheless, the lack of standardized imaging protocols across different healthcare facilities poses a significant challenge. The interpretation of imaging results can vary considerably due to differences in equipment, operator expertise, and diagnostic criteria. Establishing uniform imaging standards and training protocols is essential to ensure consistent and reliable diagnosis of CD across various clinical settings [46].
- Biomarker Analysis Specificity and Sensitivity. While biomarker analysis offers a non-invasive avenue for CD detection, the specificity and sensitivity of these markers can be variable. The heterogeneity of CD manifestations means that no single biomarker can provide a definitive diagnosis in all cases. The challenge lies in identifying a panel of biomarkers that, when used in conjunction, offer high diagnostic accuracy. Additionally, the variability in laboratory methods and the interpretation of results can further complicate the standardization of biomarker analysis [47].
- Integration of Computer-Aided Diagnostics. CAD tools harness the power of AI to analyze complex datasets and improve the diagnostic process. However, integrating these systems into clinical practice requires overcoming several hurdles. These include the need for extensive validation studies to prove their efficacy, addressing concerns related to data privacy and security, and ensuring the compatibility of these tools with existing healthcare IT infrastructure. Furthermore, the acceptance of such technologies by healthcare professionals necessitates comprehensive training and evidence of their utility in improving patients’ outcomes [1].
- Regulatory and Ethical Considerations The adoption of advanced diagnostics for CD also involves navigating regulatory approvals and ethical considerations. Ensuring the safety, efficacy, and ethical use of these technologies requires rigorous clinical trials and regulatory scrutiny. Moreover, the ethical implications of widespread screening and the potential for overdiagnosis must be carefully considered, ensuring that the benefits of early detection outweigh the risks associated with unnecessary interventions.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| anti-tTG | Anti-Tissue Transglutaminase |
| anti-EMA | Anti-Endomysial Antibodies |
| ACC | Accuracy |
| AUROC | Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| BCR | B-cell Receptor |
| BCSE | Block-wise Channel Squeeze-and-Excitation |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Diagnosis |
| CD | Celiac Disease |
| CDSS | Clinical Decision Support System |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DCNN | Deep Convolutional Neural Network |
| DEGPR | Deep Guided Posterior Regularization |
| DGP | Deamidated Gliadin Peptide |
| DT-CWT | Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform |
| DWT | Discrete Wavelet Transform |
| EE | Environmental Enteropathy |
| EED | Environmental Enteric Dysfunction |
| grad-CAMs | gradient-weighted Class Activation Maps |
| HLA | Human Leukocyte Antigen |
| HMIC | Hierarchical Medical Image classification |
| KD | Knowledge Distillation |
| LOOCV | Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation |
| LTP | Local Ternary Pattern |
| LTPs | Local Ternary Patterns |
| MIL | Multiple Instance Learning |
| NBI | Narrow-band Imaging |
| NCD | Non-Celiac Disease |
| OCR | Overall Classification Rate |
| PER | Prediction Error Rate |
| POCT | Point-of-Care Testing |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| RGB | Red Green Blue |
| SBCE | Small Bowel Capsule Endoscopy |
| SE | Squeeze and Excitation |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms |
| SNVA | Small Bowel Villous Atrophy |
| SPT | Steerable Pyramid Transform |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| VA | Villous Atrophy |
| VCE | Video Capsule Endoscopy |
| WLI | White-light Imaging |
| WMDR | Weighted Multi-factor Dimensionality Reduction |
| WSI | Whole Slide Images |
References
- Molder, A.; Balaban, D.V.; Jinga, M.; Molder, C. Current Evidence on Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Celiac Disease: Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffar, H.M.; Ahsan, W.; Koser, H.N. Celiac Disease: An Autoimmune Disorder. Pak. J. Health Sci. 2022, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.F.; Mjeed, M.S. Challenges in Celiac Disease Diagnosis. SAR J. Med. 2023, 4, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoleru, C.A.; Dulf, E.H.; Ciobanu, L. Automated detection of celiac disease using Machine Learning Algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Leffler, D.A.; Bai, J.C.; Biagi, F.; Fasano, A.; Green, P.H.R.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Kelly, C.P.; Leonard, J.N.; et al. The Oslo definitions for coeliac disease and related terms. Gut 2012, 62, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilipenko, A.P.; Mazurov, V.I.; Gaydukova, I.Z. Frequency of musculoskeletal and other extra-intestinal symptoms in patients with celiac disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollid, L.M.; Lie, B.A. Celiac disease genetics: Current concepts and practical applications. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2005, 3, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirru, E.; Jores, R.D.; Rossino, R.; Corpino, M.; Cucca, F.; Congia, M. Low-Risk Human Leukocyte Antigen Genes and Mild Villous Atrophy Typify Celiac Disease with Immunoglobulin A Deficiency. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahin, Y.; Mermer, S. Frequency of celiac disease and distribution of HLA-DQ2/DQ8 haplotypes among siblings of children with celiac disease. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2022, 11, 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.J.; Jabri, B.; Dermody, T.S. A viral trigger for celiac disease. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bañares, F.; Beltrán, B.; Salas, A.; Comino, I.; Ballester-Clau, R.; Ferrer, C.; Molina-Infante, J.; Rosinach, M.; Modolell, I.; Rodríguez-Moranta, F.; et al. Persistent Villous Atrophy in De Novo Adult Patients with Celiac Disease and Strict Control of Gluten-Free Diet Adherence: A Multicenter Prospective Study (CADER Study). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Shimoni, O.; Wallach, M.G. Celiac disease: From etiological factors to evolving diagnostic approaches. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, S.M.; Majid, M.; Qayyum, A.; Awais, M.; Alnowami, M.; Khan, M.K. Medical image analysis using convolutional neural networks: A review. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.P.; Samala, R.K.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Zhou, C. Deep learning in medical image analysis. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis: Challenges and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Saken, M.; Yagci, M.B.; Yumusak, N. Impact of image segmentation techniques on celiac disease classification using scale invariant texture descriptors for standard flexible endoscopic systems. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2021, 29, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegenbart, S.; Uhl, A.; Vécsei, A.; Wimmer, G. Scale invariant texture descriptors for classifying celiac disease. Med. Image Anal. 2013, 17, 458–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowsari, K.; Sali, R.; Ehsan, L.; Adorno, W.; Ali, A.; Moore, S.; Amadi, B.; Kelly, P.; Syed, S.; Brown, D. Hmic: Hierarchical medical image classification, a deep learning approach. Information 2020, 11, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, S.; Ehsan, L.; Shrivastava, A.; Sengupta, S.; Khan, M.; Kowsari, K.; Guleria, S.; Sali, R.; Kant, K.; Kang, S.J.; et al. Artificial intelligence-based analytics for diagnosis of small bowel enteropathies and black box feature detection. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.; Al-Boni, M.; Khan, M.N.; Sadiq, K.; Iqbal, N.T.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Kelly, P.; Amadi, B.; Ali, S.A.; Moore, S.R.; et al. Assessment of machine learning detection of environmental enteropathy and celiac disease in children. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e195822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, O.; De Michele, S.; Koh, J.E.; Jahmunah, V.; Lih, O.S.; Kamath, A.P.; Barua, P.D.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Lewis, S.K.; Green, P.H.; et al. Automated analysis of small intestinal lamina propria to distinguish normal, Celiac Disease, and Non-Celiac Duodenitis biopsy images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 230, 107320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sali, R.; Ehsan, L.; Kowsari, K.; Khan, M.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Syed, S.; Brown, D.E. Celiacnet: Celiac disease severity diagnosis on duodenal histopathological images using deep residual networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 November 2019; pp. 962–967. [Google Scholar]
- DiPalma, J.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Tafe, L.J.; Torresani, L.; Hassanpour, S. Resolution-based distillation for efficient histology image classification. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 119, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbaz, A.; Lafraxo, S.; Charfi, S.; El Ansari, M.; Koutti, L. Bleeding classification in wireless capsule endoscopy images based on inception-resnet-v2 and cnns. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 15–17 August 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Elmes, S.; Chakraborti, T.; Fan, M.; Uhlig, H.; Rittscher, J. Automated Annotator: Capturing Expert Knowledge for Free. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), virtual, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 2664–2667. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, A.K.; Mohapatra, C.; Das, P.; Makharia, G.; Mehra, L.; Prathosh, A.P. DeGPR: Deep Guided Posterior Regularization for Multi-Class Cell Detection and Counting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 23913–23923. [Google Scholar]
- Caetano dos Santos, F.L.; Michalek, I.M.; Laurila, K.; Kaukinen, K.; Hyttinen, J.; Lindfors, K. Automatic classification of IgA endomysial antibody test for celiac disease: A new method deploying machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magazzù, G.; Aquilina, S.; Barbara, C.; Bondin, R.; Brusca, I.; Bugeja, J.; Camilleri, M.; Cascio, D.; Costa, S.; Cuzzupè, C.; et al. Recognizing the emergent and submerged iceberg of the celiac disease: ITAMA project—Global strategy protocol. Pediatr. Rep. 2022, 14, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemesh, O.; Polak, P.; Lundin, K.E.; Sollid, L.M.; Yaari, G. Machine learning analysis of naïve B-cell receptor repertoires stratifies celiac disease patients and controls. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Qian, H.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Lewis, S.K.; Bhagat, G.; Green, P.H.; Xu, S.; Huang, L.; Gao, R.; Liu, Y. Celiac disease diagnosis from videocapsule endoscopy images with residual learning and deep feature extraction. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 187, 105236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Jamil, Z.; Ehsan, L.; Zulqarnain, F.; Srivastava, S.; Siddiqui, S.; Fernandes, P.; Raghib, M.; Sengupta, S.; Mujahid, Z.; et al. Quantitative Morphometry and Machine Learning Model to Explore Duodenal and Rectal Mucosal Tissue of Children with Environmental Enteric Dysfunction. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2023, 108, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.E.W.; Hagiwara, Y.; Oh, S.L.; Tan, J.H.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Green, P.H.; Lewis, S.K.; Acharya, U.R. Automated diagnosis of celiac disease using DWT and nonlinear features with video capsule endoscopy images. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 90, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molder, A.; Balaban, D.V.; Molder, C.C.; Jinga, M.; Robin, A. Computer-Based Diagnosis of Celiac Disease by Quantitative Processing of Duodenal Endoscopy Images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicnesh, J.; Wei, J.K.E.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Oh, S.L.; Bhagat, G.; Lewis, S.K.; Green, P.H.; Acharya, U.R. Automated diagnosis of celiac disease by video capsule endoscopy using DAISY Descriptors. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammit, S.C.; McAlindon, M.E.; Greenblatt, E.E.; Maker, M.; Siegelman, J.; Leffler, D.A.; Yardibi, O.; Raunig, D.L.; Brown, T.; Sidhu, R. Quantification of Celiac Disease Severity Using Video Capsule Endoscopy: A Comparison of Human Experts and Machine Learning Algorithms. Curr. Med. Imaging 2023, 19, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, J.E.W.; De Michele, S.; Sudarshan, V.K.; Jahmunah, V.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Ooi, C.P.; Gururajan, R.; Gururajan, R.; Oh, S.L.; Lewis, S.K.; et al. Automated interpretation of biopsy images for the detection of celiac disease using a machine learning approach. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 203, 106010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheppach, M.W.; Rauber, D.; Stallhofer, J.; Muzalyova, A.; Otten, V.; Manzeneder, C.; Schwamberger, T.; Wanzl, J.; Schlottmann, J.; Tadic, V.; et al. Detection of duodenal villous atrophy on endoscopic images using a deep learning algorithm. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmer, G.; Gadermayr, M.; Vécsei, A.; Uhl, A. Improving Endoscopic Decision Support Systems by Translating between Imaging Modalities. In Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging: 5th International Workshop, SASHIMI 2020, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2020, Lima, Peru, October 4, 2020, Proceedings 5; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, F.; Cote, K.; Najafian, K.; Ovens, K.; Miao, Y.; Zakarian, R.; Reinhold, C.; Forghani, R.; Savadjiev, P.; Gao, Z.H. A deep learning-based pipeline for celiac disease diagnosis using histopathological images. In Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns: 19th International Conference, CAIP 2021, Virtual Event, September 28–30, 2021, Proceedings, Part I 19; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Tomer, R.; Patiyal, S.; Dhall, A.; Raghava, G.P. Prediction of celiac disease associated epitopes and motifs in a protein. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1056101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammit, S.C.; Bull, L.A.; Sanders, D.S.; Galvin, J.; Dervilis, N.; Sidhu, R.; Worden, K. Towards the Probabilistic Analysis of Small Bowel Capsule Endoscopy Features to Predict Severity of Duodenal Histology in Patients with Villous Atrophy. J. Med. Syst. 2020, 44, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Yu, G.; Ren, W.; Guo, M.; Wang, J. DualWMDR: Detecting epistatic interaction with dual screening and multifactor dimensionality reduction. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccialli, F.; Calabrò, F.; Crisci, D.; Cuomo, S.; Prezioso, E.; Mandile, R.; Troncone, R.; Greco, L.; Auricchio, R. Precision medicine and machine learning towards the prediction of the outcome of potential celiac disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostamkolaei, S.K.; Ju, J.M.; Marietta, E.V.; Van Dyke, C.T.; Rajasekaran, J.; Jayaraman, V.; Wang, T.; Bei, K.; Rajasekaran, K.E.; Krishna, K.; et al. Synthetic neoepitopes of the transglutaminase–deamidated gliadin complex as biomarkers for diagnosing and monitoring celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 582–591. [Google Scholar]
- Gruver, A.M.; Lu, H.; Zhao, X.; Fulford, A.D.; Soper, M.D.; Ballard, D.; Hanson, J.C.; Schade, A.E.; Hsi, E.D.; Gottlieb, K.; et al. Pathologist-trained machine learning classifiers developed to quantitate celiac disease features differentiate endoscopic biopsies according to modified marsh score and dietary intervention response. Diagn. Pathol. 2023, 18, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, H. AI-based computer-aided diagnosis (AI-CAD): The latest review to read first. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2020, 13, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galić, I.; Habijan, M.; Leventić, H.; Romić, K. Machine learning empowering personalized medicine: A comprehensive review of medical image analysis methods. Electronics 2023, 12, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Sánchez, A.D.; Tan, I.L.; Gonera-de Jong, B.; Visschedijk, M.C.; Jonkers, I.; Withoff, S. Molecular biomarkers for celiac disease: Past, present and future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
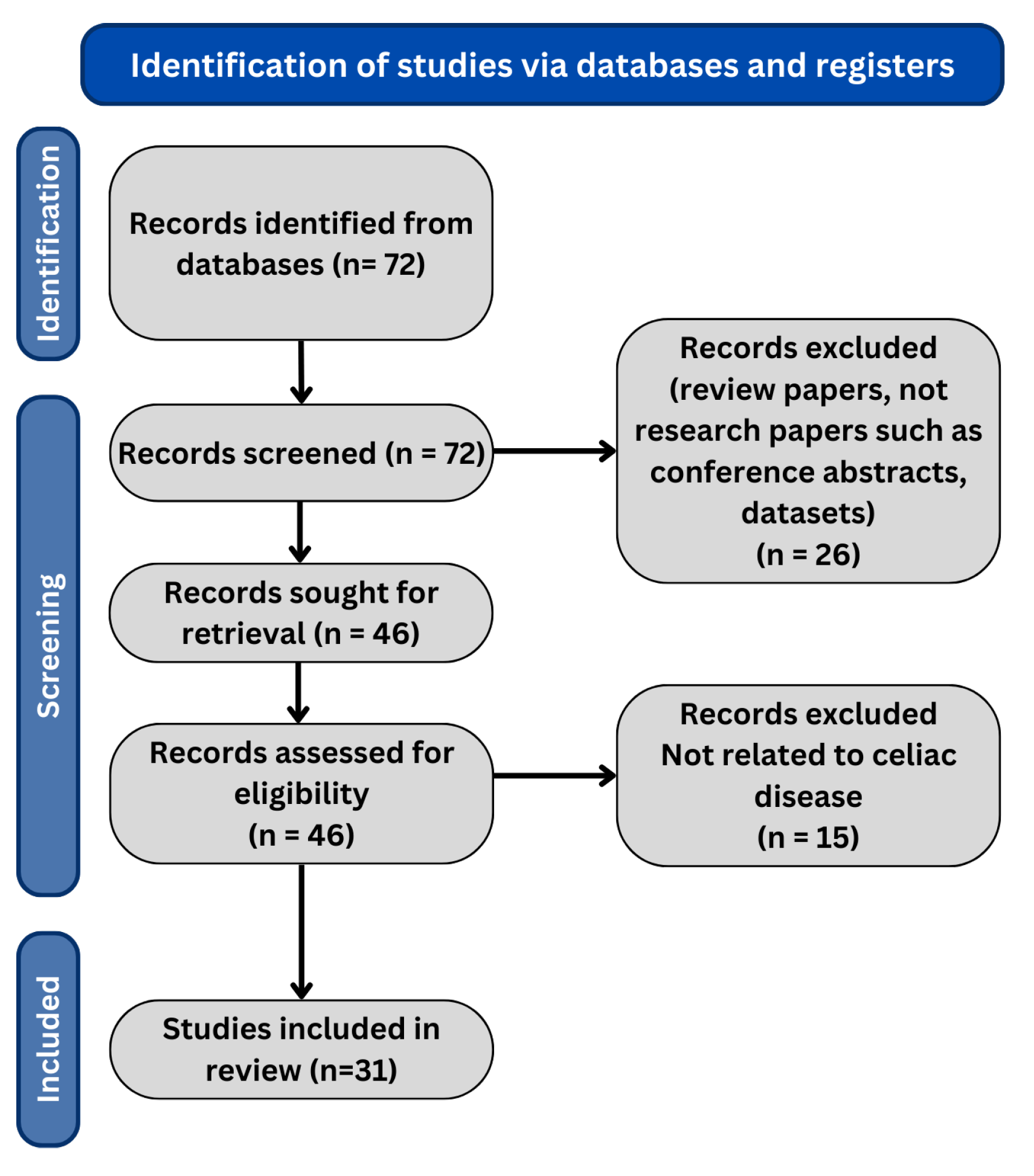

| Database | Search Terms |
|---|---|
| Science Citation Index Expanded | computer aided, cad, deep learning, machine learning, artificial intelligence, celiac disease, celiac sprue, segmentation, detection, classification, identification, evaluation, diagnosis |
| Emerging Sources Citation Index | |
| MEDLINE | |
| Data Citation Index | |
| Conference Proceedings Citation Index | |
| KCI-Korean Journal Database | |
| BIOSIS Citation Index | |
| Derwent Innovations Index | |
| SciELO Citation Index | |
| Russian Science Citation Index |
| Authors | Method | Dataset | Modality | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syed et al. [19] | CNN | 3118 images | Biopsy | ACC: 93.4% |
| Tyagi et al. [25] | DeGPR | 55 images | Biopsy | ACC: 87.7% |
| Faust et al. [20] | SVM | 91 images | Biopsy | ACC: 98.53% |
| Syed et al. [18] | CNN | 461 images | Endoscopic | ACC: 98% |
| Garbaz et al. [23] | CNN | 50000 images | Endoscopic | ACC: 98.5% |
| Hegenbart et al. [16] | DT-CWT | 612 images | Endoscopic | OCR: 84.7% |
| Saken et al. [15] | DWT-LBP-cubic SVM | 330 images | Endoscopic | ACC: 94.79% |
| Sali et al. [21] | CNN | 120 images | Histological | ACC: |
| MarshIIIc: | ||||
| 90.61% | ||||
| Elmes et al. [24] | CNN | 30 images | Histological | ACC: 76.6% |
| Kowsari et al. [17] | DCNN, HMIC | 461 images | Histological | ACC: |
| (DCNN) 82.95% | ||||
| (HMIC) 88.01% | ||||
| DiPalma et al. [22] | KD | 1364 patients | Histological | ACC: 85.74% |
| Authors | Method | Dataset | Modality | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caetano dos Santos et al. [26] | SVM | 2597 images | IgA-class EmA | ACC: 96.8% |
| Magazzù et al. [27] | fuzzy CNN | 20,519 images | IgA-class EmA | ACC: 99% |
| Shemesh et al. [28] | MIL | 100 patients | Immune repertoire | F1 score: 85% |
| Authors | Method | Dataset | Modality | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khan et al. [30] | CNN | 290 images | Biopsy | ACC: 49% |
| Koh et al. [35] | Feature engineering | 91 images | Biopsy | ACC: 88.89% |
| and ML | ||||
| Molder et al. [32] | CNN | 82 images | Endoscopy | ACC: 98.24% |
| Stoleru et al. [4] | Linear SVM | 109 films | Endoscopy | ACC: 94.1% |
| Maleki et al. [38] | CNN | 426 images | Histological | ACC: 89.3% |
| Wimmer et al. [37] | CNN | 1045 images | WLI | ACC: 85.6% |
| 616 images | NBI | ACC: 88.3% | ||
| Wang et al. [29] | BCSE | 2140 images | VCE | ACC: 95.94% |
| Koh et al. [31] | SVM RBF | 13 patients | VCE | ACC: 86.47% |
| Vicnesh et al. [33] | SVM RBF | 37 patients | VCE | ACC: 89.82% |
| Zammit et al. [34] | MLA | 63 videos | VCE | 1 > 0.8 |
| Authors | Method | Dataset | Modality | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomer et al. [39] | ML | 1310 peptides | - | ACC: 98% |
| Zammit et al. [40] | ML | 72 patients | SBCE | ACC: 75.3% |
| Cao et al. [41] | DualWMDR | 435,604 SNP | Genome-wide | PER < 0.5 |
| Piccialli et al. [42] | ML | 340 patients | Serology, biopsy | ACC: >75% |
| Rostamkolaei et al. [43] | ML | 169 patients | Serology | ACC: 99% |
| Gruver et al. [44] | ML | 116 patients | Histological | Correlation: >90% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hartmann Tolić, I.; Habijan, M.; Galić, I.; Nyarko, E.K. Advancements in Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080493
Hartmann Tolić I, Habijan M, Galić I, Nyarko EK. Advancements in Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(8):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080493
Chicago/Turabian StyleHartmann Tolić, Ivana, Marija Habijan, Irena Galić, and Emmanuel Karlo Nyarko. 2024. "Advancements in Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review" Biomimetics 9, no. 8: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080493
APA StyleHartmann Tolić, I., Habijan, M., Galić, I., & Nyarko, E. K. (2024). Advancements in Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review. Biomimetics, 9(8), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080493









