Macrophage-Based Microrobots for Anticancer Therapy: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
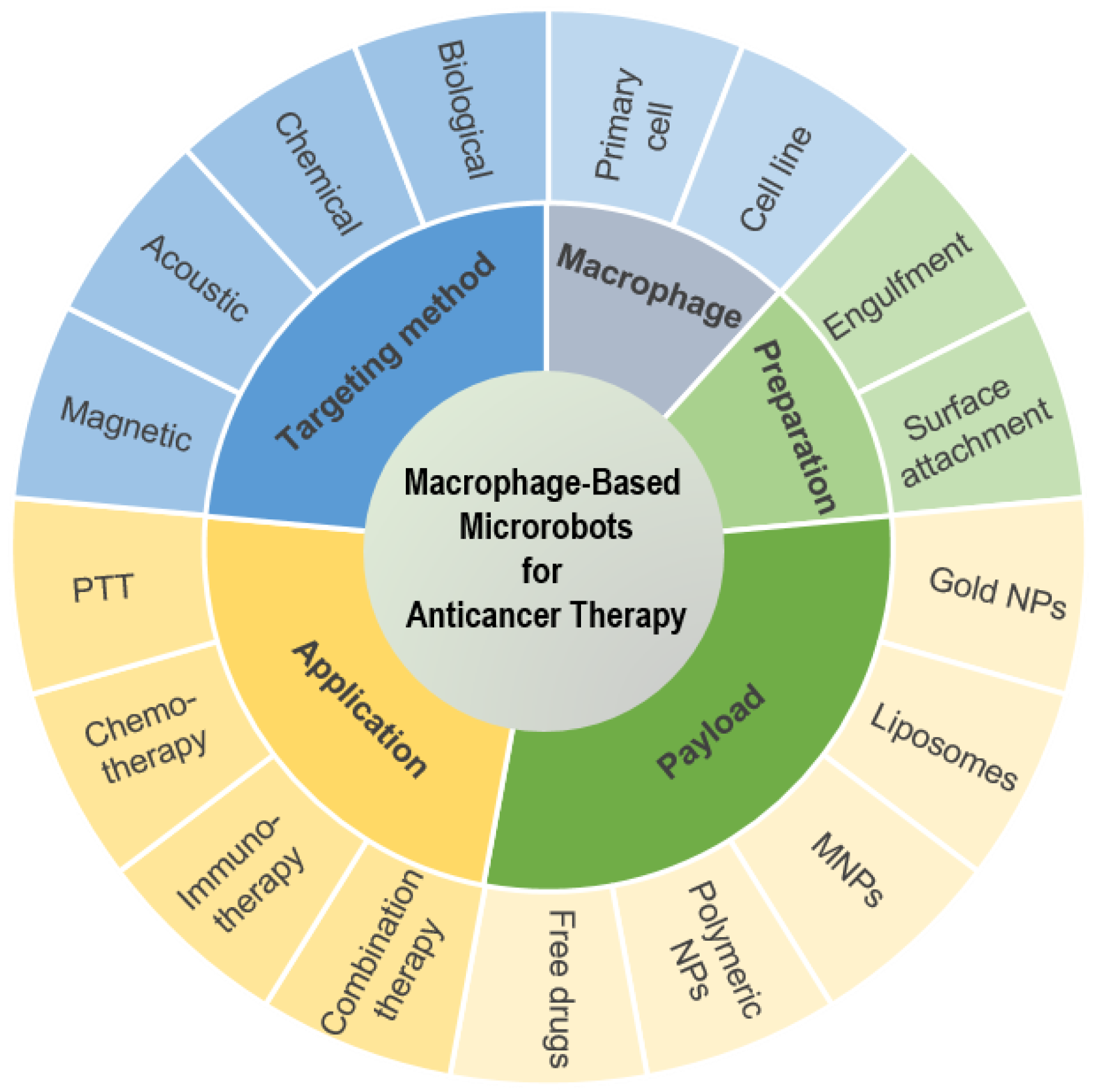
2. Preparation of Macrophage-Based Microrobots
2.1. Macrophage Cells
2.2. Preparation of the Microrobots
2.3. Payloads
2.3.1. Gold-Based Nanoparticles
2.3.2. Liposomes
2.3.3. Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs)
2.3.4. Polymeric Nanoparticles
2.3.5. Free Drugs
3. Targeting of Macrophage-Based Microrobots
3.1. Biological Targeting
3.2. Chemical Targeting
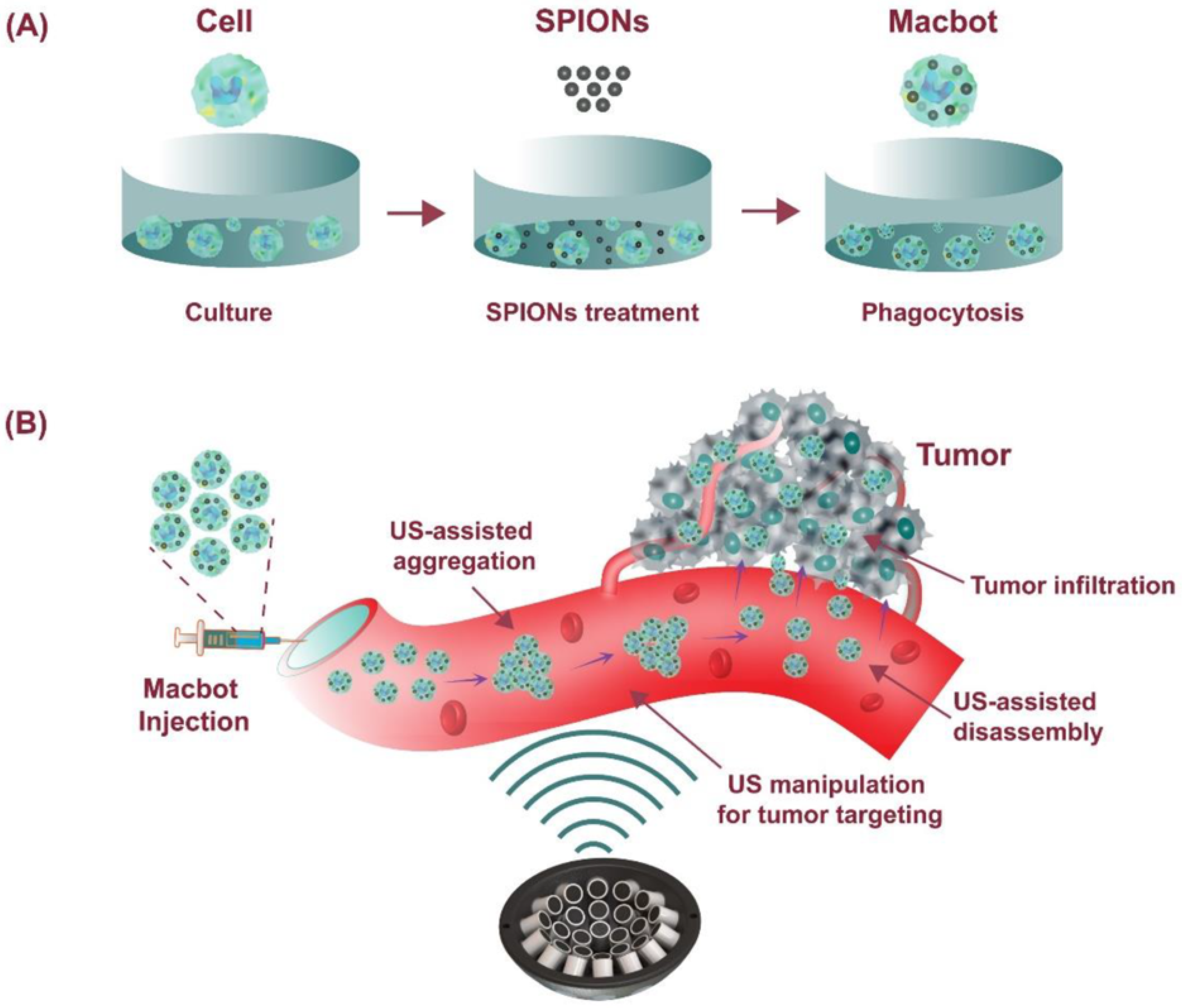
3.3. Acoustic Targeting
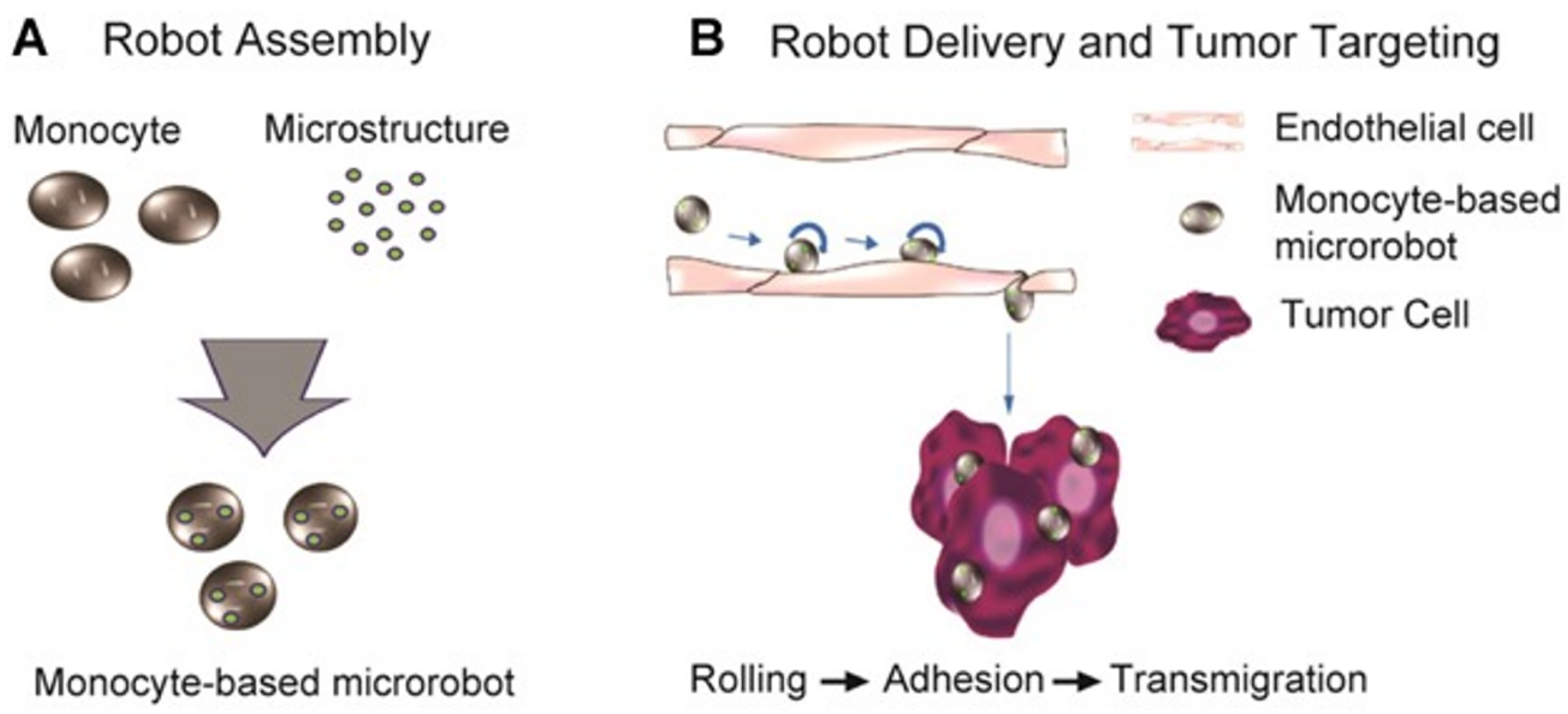
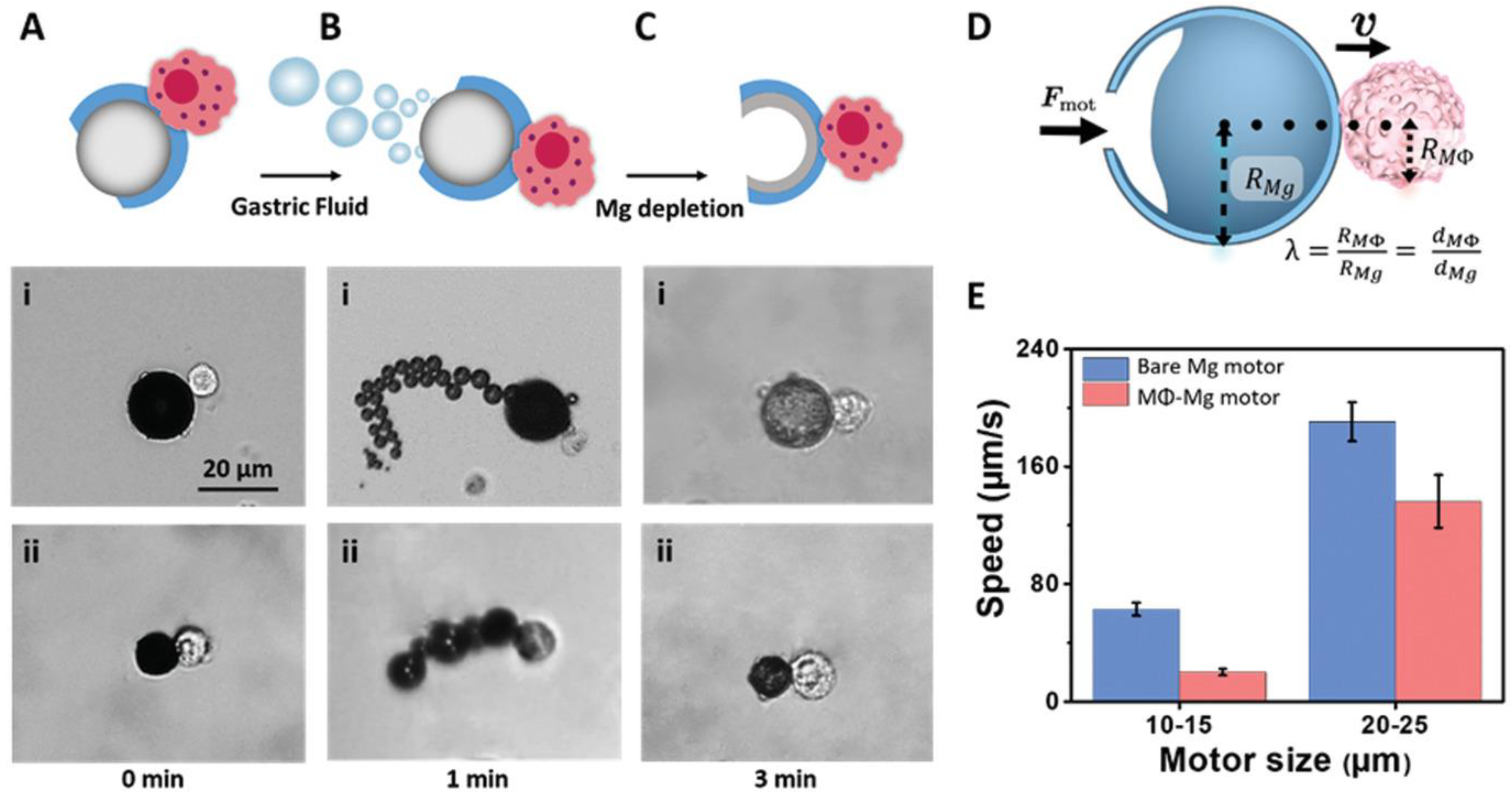
3.4. Magnetic Targeting
4. Applications of Macrophage-Based Microrobots for Anticancer Therapy
4.1. Photothermal Therapy
4.2. Chemotherapy
4.3. Immunotherapy
4.4. Combination Therapy
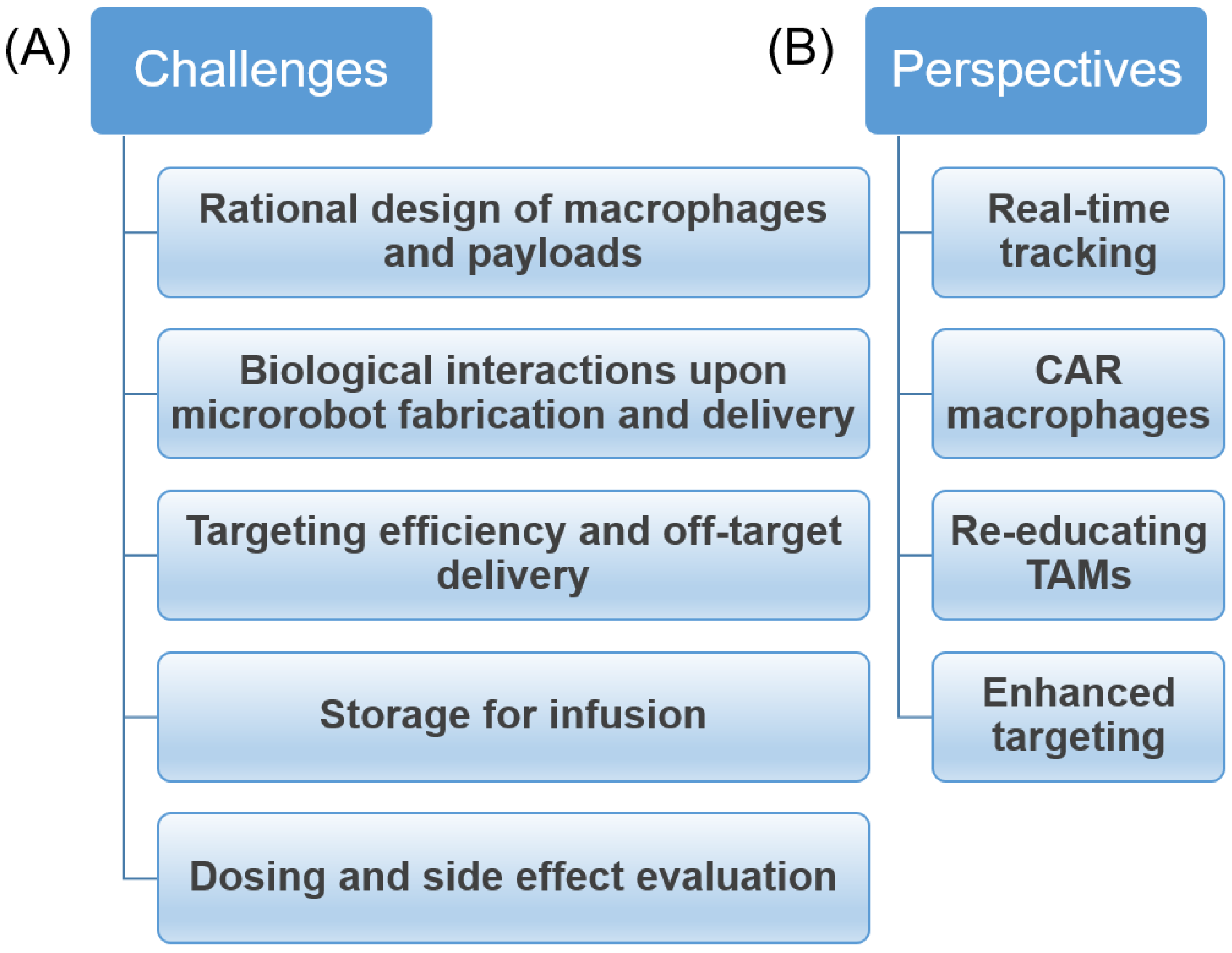
5. Challenges and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Kim, D.-i.; Kwon, S.-h.; Park, S. Magnetically Actuated Drug Delivery Helical Microrobot with Magnetic Nanoparticle Retrieval Ability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19633–19647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, H.; Yasa, I.C.; Yasa, O.; Tabak, A.F.; Giltinan, J.; Sitti, M. 3D-Printed Biodegradable Microswimmer for Theranostic Cargo Delivery and Release. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 3353–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.-Z.; Mushtaq, F.; Deng, S.; Zhu, C.; Torlakcik, H.; Terzopoulou, A.; Qin, X.-H.; Xiao, X.; et al. 3D-Printed Soft Magnetoelectric Microswimmers for Delivery and Differentiation of Neuron-like Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, H.; Dogan, N.O.; Yasa, I.C.; Musaoglu, M.N.; Kulali, Z.U.; Sitti, M. 3D printed personalized magnetic micromachines from patient blood derived biomaterials. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabh0273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.; Benouhiba, A.; Rabenorosoa, K.; Clévy, C.; Cappelleri, D.J. 4D Printing: Enabling Technology for Microrobotics Applications. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wilson, D.A.; Tu, Y.; Peng, F. 3D-Printed Micromotors for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Celi, N.; Zhang, D.; Cai, J. Magnetic Biohybrid Microrobot Multimers Based on Chlorella Cells for Enhanced Targeted Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6320–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Chen, B.; Gao, J.; Li, T.; Ye, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Jiang, J.; et al. Magnetically Actuated Biohybrid Microswimmers for Precise Photothermal Muscle Contraction. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6515–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Cai, J. Micro/Nanofabrication, Assembly, and Actuation Based on Microorganisms: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2200356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhuang, J.; Li, Z.; Gong, H.; de Ávila, B.E.-F.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yin, L.; Karshalev, E.; et al. Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Gu, Z. Bacteria-Driven Hypoxia Targeting for Combined Biotherapy and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5995–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.-W.; Zhuang, J.; Yasa, O.; Sitti, M. Multifunctional Bacteria-Driven Microswimmers for Targeted Active Drug Delivery. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8910–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.-X.; Li, Z.-H.; Liu, X.-H.; Zheng, D.-W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.-Z. Bacteria-Mediated Tumor Therapy Utilizing Photothermally-Controlled TNF-α Expression via Oral Administration. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.-H.; Huang, C.-T.; Su, C.-H.; Yeh, C.-S. Bacteria-Mediated Hypoxia-Specific Delivery of Nanoparticles for Tumors Imaging and Therapy. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3493–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felfoul, O.; Mohammadi, M.; Taherkhani, S.; de Lanauze, D.; Zhong Xu, Y.; Loghin, D.; Essa, S.; Jancik, S.; Houle, D.; Lafleur, M.; et al. Magneto-aerotactic bacteria deliver drug-containing nanoliposomes to tumour hypoxic regions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.-W.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.-H.; Xu, L.; Li, C.-X.; Li, B.; Fan, J.-X.; Cheng, S.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. Optically-controlled bacterial metabolite for cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Jin, D.; Hu, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Ren, Z.; Wang, D.; Ji, S.; Hu, K.; et al. Environmentally Adaptive Shape-Morphing Microrobots for Localized Cancer Cell Treatment. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18048–18059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Llano, L.E.; Liu, Y.-H.; Henson, T.; Meyer, C.C.; Baghdasaryan, O.; Khan, S.; Lin, C.-L.; Wang, A.; Hu, C.-M.J.; Tan, C. Engineering Cyborg Bacteria Through Intracellular Hydrogelation. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdasaryan, O.; Khan, S.; Lin, J.-C.; Lee-Kin, J.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Hu, C.-M.J.; Tan, C. Synthetic control of living cells by intracellular polymerization. Trends Biotechnol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhao, C.X. Macrophage-mediated cancer drug delivery. Mater. Today Sustain. 2021, 11–12, 100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendeckel, U.; Venz, S.; Wolke, C. Macrophages: Shapes and functions. ChemTexts 2022, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, C. A smart pathogen detector engineered from intracellular hydrogelation of DNA-decorated macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, D.; Chen, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Gu, D.; Gao, C. Intracellular hydrogelation of macrophage conjugated probiotics for hitchhiking delivery and combined treatment of colitis. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Tian, Q.; Xie, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, S. Macrophages-Mediated Delivery of Small Gold Nanorods for Tumor Hypoxia Photoacoustic Imaging and Enhanced Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15251–15261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, N.; Kim, Y.; Kweon, H.-S.; Oh, W.-Y.; Park, J.-H. Macrophage-Mediated Exocytosis of Elongated Nanoparticles Improves Hepatic Excretion and Cancer Phototherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28450–28457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Deng, Q.; Kang, L.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. A Smart Nanoparticle-Laden and Remote-Controlled Self-Destructive Macrophage for Enhanced Chemo/Chemodynamic Synergistic Therapy. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13894–13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.H.; Kim, S.T.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, K.; Wu, J.H.; Jeong, J.; Song, A.Y.; Lee, K.-M.; Kim, Y.K. Labeling of macrophage cell using biocompatible magnetic nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 07B309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Peng, H.; Wei, R.; Wang, C.; Feng, M. Tunneling Nanotubular Expressways for Ultrafast and Accurate M1 Macrophage Delivery of Anticancer Drugs to Metastatic Ovarian Carcinoma. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1078–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
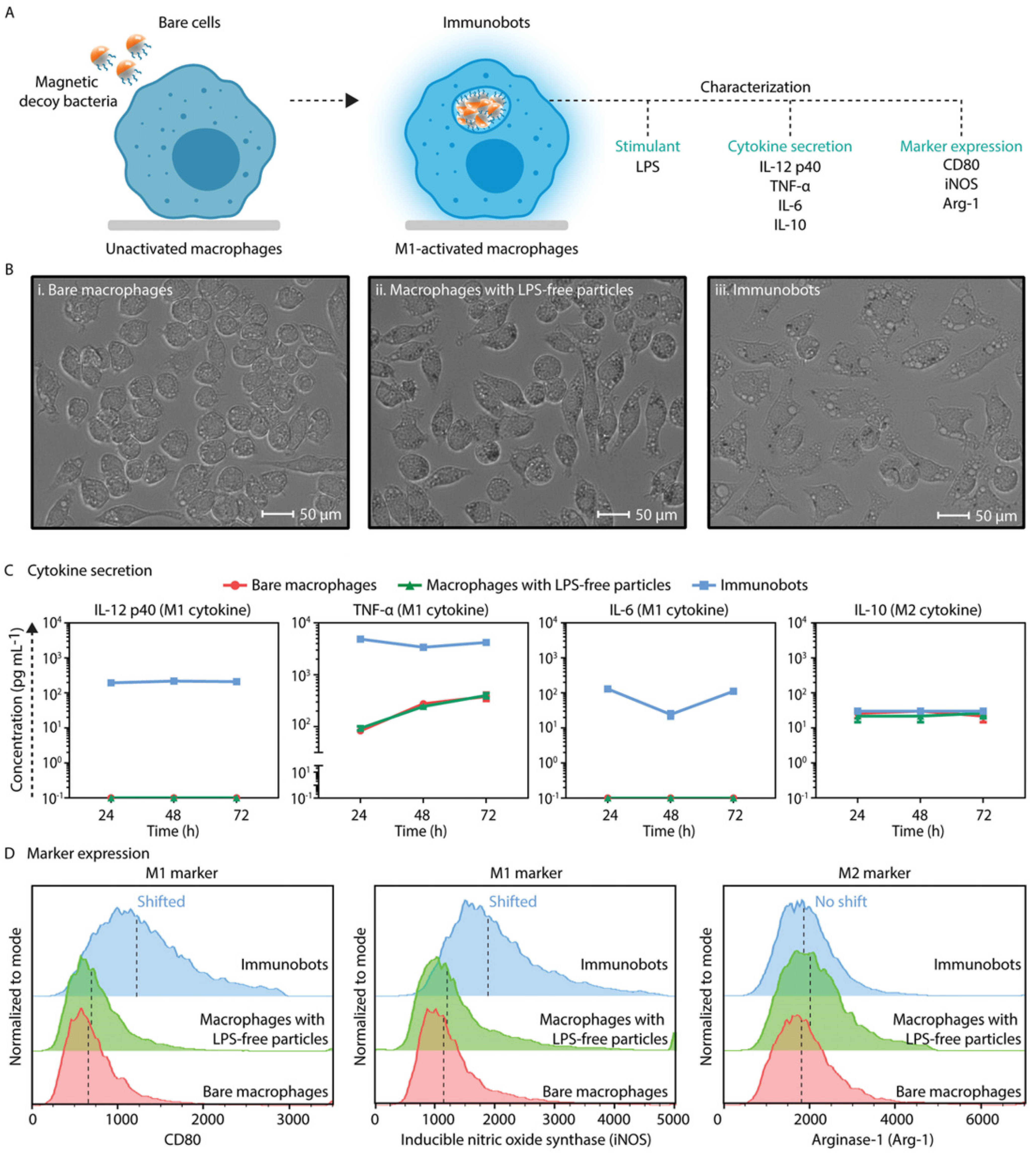
- Dogan, N.O.; Ceylan, H.; Suadiye, E.; Sheehan, D.; Aydin, A.; Yasa, I.C.; Wild, A.-M.; Richter, G.; Sitti, M. Remotely Guided Immunobots Engaged in Anti-Tumorigenic Phenotypes for Targeted Cancer Immunotherapy. Small 2022, 18, 2204016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Nguyen, V.; Le, V.H.; Zheng, S.; Han, J.; Park, J.-O. Preparation of tumor targeting cell-based microrobots carrying NIR light sensitive therapeutics manipulated by electromagnetic actuating system and Chemotaxis. J. Micro-Bio Robot. 2018, 14, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, S.J.; Christie, C.; Hong, S.J.; Trinidad, A.; Peng, Q.; Uzal, F.A.; Hirschberg, H. Nanoparticle-loaded macrophage-mediated photothermal therapy: Potential for glioma treatment. Lasers Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Su, Y.; Kim, G.B.; Selvi, E.; Ma, C.; Aragon-Sanabria, V.; Hsieh, J.-T.; Dong, C.; Yang, J. Immune Cell-Mediated Biodegradable Theranostic Nanoparticles for Melanoma Targeting and Drug Delivery. Small 2017, 13, 1603121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, S.; Jung, H.E.; Zheng, S.; Park, B.J.; Ko, S.Y.; Park, J.O.; Park, S. Monocyte-based microrobot with chemotactic motility for tumor theragnosis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 2132–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Ju, E.J.; Jung, J.; Park, J.; Chung, H.K.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Song, S.Y.; et al. Use of macrophages to deliver therapeutic and imaging contrast agents to tumors. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J. Primary M1 macrophages as multifunctional carrier combined with PLGA nanoparticle delivering anticancer drug for efficient glioma therapy. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Wang, H.; He, X.; Tan, T.; Hu, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Bioengineered Macrophages Can Responsively Transform into Nanovesicles To Target Lung Metastasis. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4762–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Destache, C.J.; Morehead, J.R.; Mosley, R.L.; Boska, M.D.; Kingsley, J.; Gorantla, S.; Poluektova, L.; Nelson, J.A.; Chaubal, M.; et al. Development of a macrophage-based nanoparticle platform for antiretroviral drug delivery. Blood 2006, 108, 2827–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.A.; Huang, P.-J.; Iwamoto, Y.; Ibsen, K.N.; Chan, E.M.; Hitomi, Y.; Ford, P.C.; Mitragotri, S. Macrophage-mediated delivery of light activated nitric oxide prodrugs with spatial, temporal and concentration control. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 3729–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-R.; Stanton-Maxey, K.J.; Stanley, J.K.; Levin, C.S.; Bardhan, R.; Akin, D.; Badve, S.; Sturgis, J.; Robinson, J.P.; Bashir, R.; et al. A Cellular Trojan Horse for Delivery of Therapeutic Nanoparticles into Tumors. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3759–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhu, S.; Qin, K.; Fan, X.; An, L. Macrophages Loaded with Fe Nanoparticles for Enhanced Photothermal Ablation of Tumors. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, N.; Swiston, A.J.; Gilbert, J.B.; Alcaraz, M.L.; Cohen, R.E.; Rubner, M.F.; Mitragotri, S. Cell-Based Drug Delivery Devices Using Phagocytosis-Resistant Backpacks. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H105–H109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Gilbert, J.B.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, V.; Cohen, R.E.; Rubner, M.F.; Mitragotri, S. Monocyte-mediated delivery of polymeric backpacks to inflamed tissues: A generalized strategy to deliver drugs to treat inflammation. J. Control. Release 2015, 199, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Q.; Gong, T.; et al. Live Macrophage-Delivered Doxorubicin-Loaded Liposomes Effectively Treat Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 9799–9809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Yan, N.; Hu, Y.; Fang, H.; Guo, Z.; Sun, P.; Tian, H.; Chen, X. Macrophages loaded CpG and GNR-PEI for combination of tumor photothermal therapy and immunotherapy. Sci. China Mater. 2018, 61, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.-F.; Wang, H.; Li, P.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Small gold nanorods laden macrophages for enhanced tumor coverage in photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 74, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, Y.; Gogatsubo, S.; Ohba, T.; Fujita, T. Enhanced macrophage delivery to the colon using magnetic lipoplexes with a magnetic field. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materón, E.M.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Carr, O.; Joshi, N.; Picciani, P.H.S.; Dalmaschio, C.J.; Davis, F.; Shimizu, F.M. Magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 6, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cong, Z.; Xie, L.; Tang, S.; Ren, C.; Peng, X.; Tang, D.; Wan, F.; Han, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Magnetically Powered Immunogenic Macrophage Microrobots for Targeted Multimodal Cancer Therapy. Small 2023, 19, 2301489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Han, J.; Go, G.; Zhen, J.; Zheng, S.; Le, V.H.; Park, J.-O.; Park, S. Feasibility study of dual-targeting paclitaxel-loaded magnetic liposomes using electromagnetic actuation and macrophages. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Alimu, G.; Du, Z.; Yan, T.; Li, H.; Ma, R.; Lan, Z.; Yu, Z.; Alifu, N.; Sun, K. Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for NIR-Induced Photothermal Therapy of Potential Application in Cervical Cancer. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 21793–21801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Tu, X.; Zhang, Z. Manganese Doped Iron Oxide Theranostic Nanoparticles for Combined T1 Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4650–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Wang, S.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, X.; Fu, D.; Shen, S.; Yang, W. Polydopamine-Coated Magnetic Composite Particles with an Enhanced Photothermal Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15876–15884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Shao, Y.; Peng, J.; Dai, X.; Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Shi, D. Near-infrared laser light mediated cancer therapy by photothermal effect of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4078–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Wang, S.; Zheng, R.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, X.; Fu, D.; Yang, W. Magnetic nanoparticle clusters for photothermal therapy with near-infrared irradiation. Biomaterials 2015, 39, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhen, J.; Nguyen, V.D.; Go, G.; Choi, Y.; Ko, S.Y.; Park, J.-O.; Park, S. Hybrid-Actuating Macrophage-Based Microrobots for Active Cancer Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Hu, W.; Fan, Y.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. Macrophage-mediated tumor homing of hyaluronic acid nanogels loaded with polypyrrole and anticancer drug for targeted combinational photothermo-chemotherapy. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7057–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
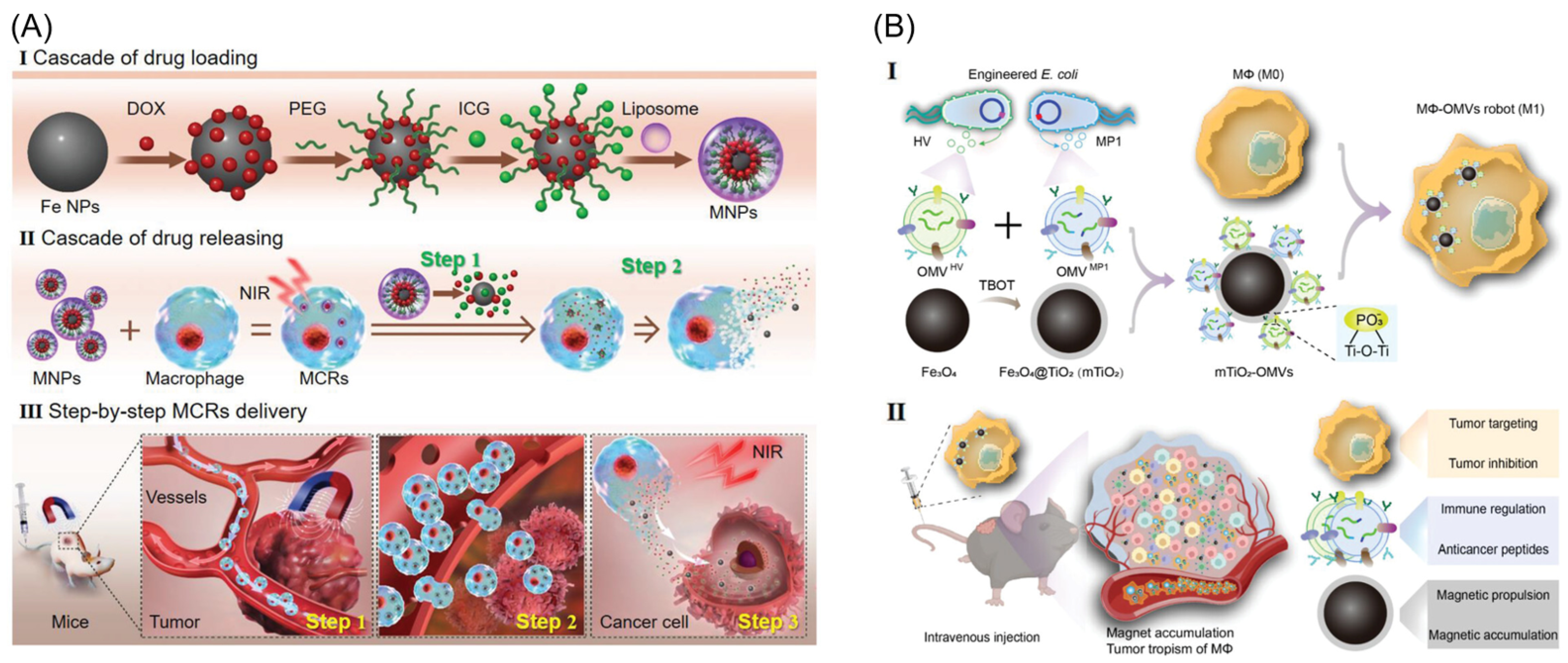
- Zhang, X.; Si, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Tian, H. Polymerization and coordination synergistically constructed photothermal agents for macrophages-mediated tumor targeting diagnosis and therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 264, 120382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wang, D.; Mei, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; He, B.; Dai, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Macrophage mediated biomimetic delivery system for the treatment of lung metastasis of breast cancer. J. Control. Release 2015, 204, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminin, D.; Wang, Y.-M. Macrophages as a “weapon” in anticancer cellular immunotherapy. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, Q.; He, J.; Mei, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Macrophage-mediated multi-mode drug release system for photothermal combined with anti-inflammatory therapy against postoperative recurrence of triple negative breast cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, B.; Zhao, X.; Hao, N. Acoustics-Actuated Microrobots. Micromachines 2022, 13, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, K.; Viktorova, J.; Plutnar, J.; Ruml, T.; Hoang, L.; Pumera, M. Chemical Microrobots as Self-Propelled Microbrushes against Dental Biofilm. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Liu, W.; Esteban-Fernández de Ávila, B.; Angsantikul, P.; Sandraz, E.; Wang, J.; Xu, T.; Soto, F.; Ramez, V.; et al. Enteric Micromotor Can Selectively Position and Spontaneously Propel in the Gastrointestinal Tract. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9536–9542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
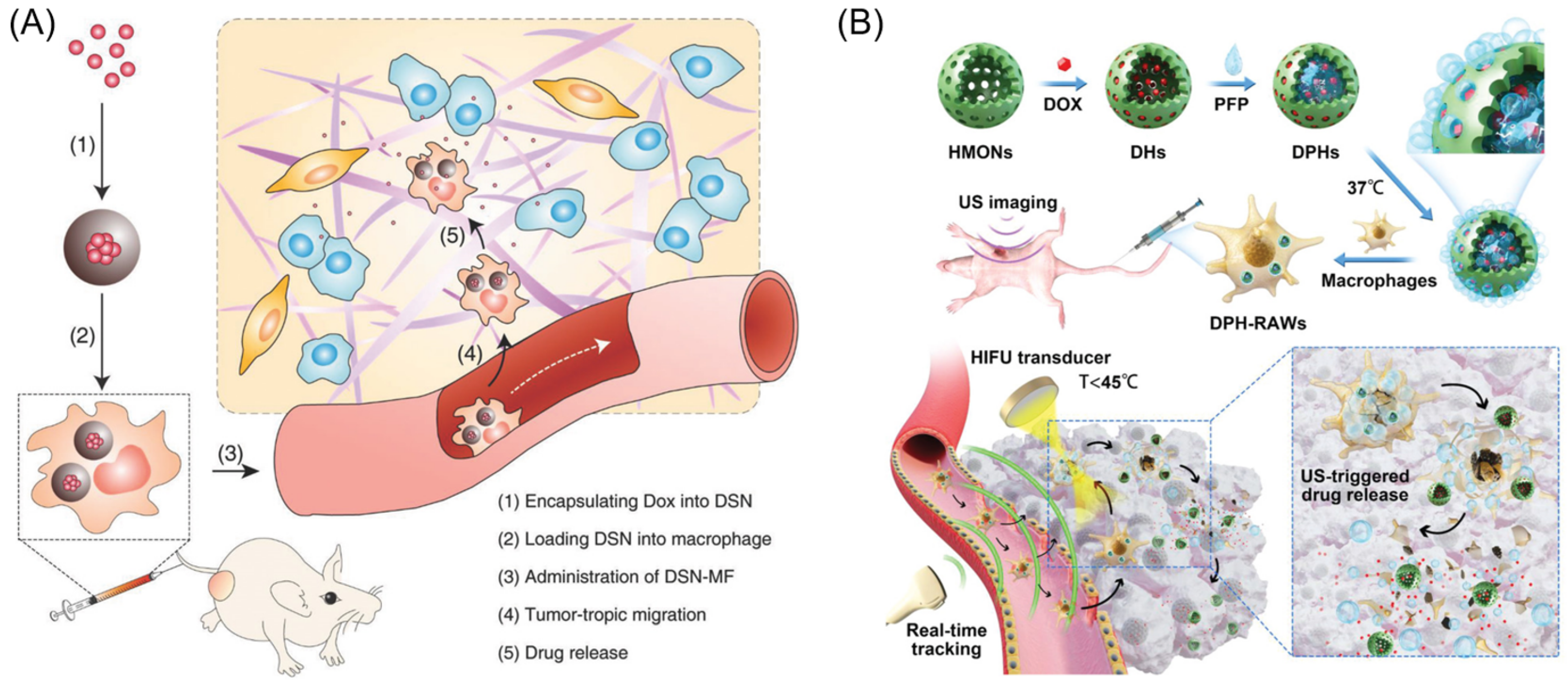
- de Ávila, B.E.-F.; Angsantikul, P.; Li, J.; Angel Lopez-Ramirez, M.; Ramírez-Herrera, D.E.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Chen, C.; Delezuk, J.; Samakapiruk, R.; Ramez, V.; et al. Micromotor-enabled active drug delivery for in vivo treatment of stomach infection. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Angsantikul, P.; Liu, W.; Esteban-Fernández de Ávila, B.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Xu, M.; Sandraz, E.; Wang, X.; Delezuk, J.; Gao, W.; et al. Micromotors Spontaneously Neutralize Gastric Acid for pH-Responsive Payload Release. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2156–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Dong, R.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Li, J.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Artificial Micromotors in the Mouse’s Stomach: A Step toward in Vivo Use of Synthetic Motors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Mundaca-Uribe, R.; Gong, H.; Esteban-Fernández de Ávila, B.; Beltrán-Gastélum, M.; Karshalev, E.; Nourhani, A.; Tong, Y.; Nguyen, B.; Gallot, M.; et al. A Macrophage–Magnesium Hybrid Biomotor: Fabrication and Characterization. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, H.; Chen, Z.; Yin, T.; Zheng, M.; Cai, L. Twin-bioengine self-adaptive micro/nanorobots using enzyme actuation and macrophage relay for gastrointestinal inflammation therapy. Sci Adv 2023, 9, eadc8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Pané, S.; Zhang, L.; Pumera, M. Magnetically Driven Micro and Nanorobots. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 4999–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, S.; Soler, L.; Katuri, J. Chemically Powered Micro- and Nanomotors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1414–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, T.; Yan, F.; et al. In-vivo programmable acoustic manipulation of genetically engineered bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Soto, F.; Ma, P.; Ahmed, R.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Akin, D.; Fu, K.; et al. Acoustic Fabrication of Living Cardiomyocyte-based Hybrid Biorobots. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 10219–10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Gao, W.; Xu, T.; Christianson, C.; Gao, W.; Galarnyk, M.; He, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Turning Erythrocytes into Functional Micromotors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12041–12048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, A.; Rufo, J.; Guo, F.; Gu, Y.; Li, P.; Lata, J.; Huang, T.J. Acoustic tweezers for the life sciences. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, A.; Corkett, T.; Drinkwater, B.W. Ultraino: An Open Phased-Array System for Narrowband Airborne Ultrasound Transmission. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2018, 65, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem, M.A.; Maxwell, A.D.; Wang, Y.-N.; Cunitz, B.W.; Khokhlova, V.A.; Sapozhnikov, O.A.; Bailey, M.R. Noninvasive acoustic manipulation of objects in a living body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16848–16855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, A.; Marzo, A.; Malkin, R.; Drinkwater, B.W. Three-dimensional ultrasonic trapping of micro-particles in water with a simple and compact two-element transducer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 16848–16855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Lu, C.; Liu, C.; Bai, X.; Zhao, L.; Feng, S.; Liu, Y. Ultrasonic tweezer for multifunctional droplet manipulation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, A.; Seah, S.A.; Drinkwater, B.W.; Sahoo, D.R.; Long, B.; Subramanian, S. Holographic acoustic elements for manipulation of levitated objects. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.X.; Nguyen, V.D.; Jung, D.; Choi, E.; Kim, C.-S.; Park, J.-O.; Kang, B. Acoustically Driven Cell-Based Microrobots for Targeted Tumor Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, W.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Feng, L. Acoustic and magnetic hybrid actuated immune cell robot for target and kill cancer cells. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 7936–7941. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, M.; Ren, L. Driving modes and characteristics of biomedical micro-robots. Eng. Regen. 2023, 4, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, T.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. Selective and Independent Control of Microrobots in a Magnetic Field: A Review. Engineering 2023, 24, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Song, Z.; Zhan, G.; Bai, X.; Feng, L. Cell-Based Micro/Nano-Robots for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Small 2023, 2304607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Bai, X.; Jia, L.; Sun, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Precise Control of Customized Macrophage Cell Robot for Targeted Therapy of Solid Tumors with Minimal Invasion. Small 2021, 17, 2103986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
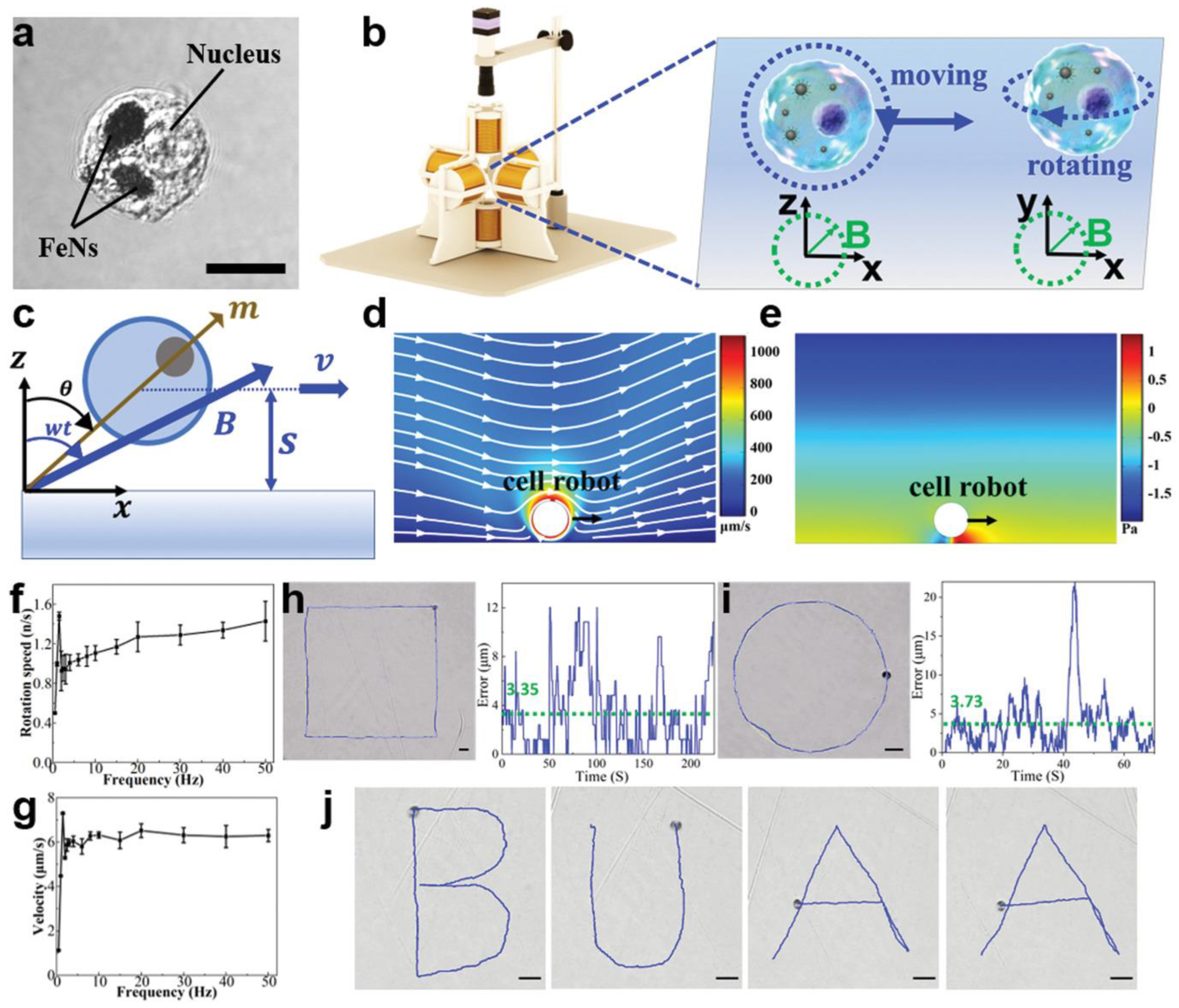
- Dai, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, H.; Ji, Y.; Wang, C.; Song, L.; Liang, S.; Chen, D.; Feng, Y.; et al. Magnetically Actuated Cell-Robot System: Precise Control, Manipulation, and Multimode Conversion. Small 2022, 18, 2105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Min, H.-K.; Kim, H.Y.; Han, J.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, C.-S.; Park, J.-O.; Choi, E. Primary Macrophage-Based Microrobots: An Effective Tumor Therapy In Vivo by Dual-Targeting Function and Near-Infrared-Triggered Drug Release. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 8492–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthana, M.; Kennerley, A.J.; Hughes, R.; Fagnano, E.; Richardson, J.; Paul, M.; Murdoch, C.; Wright, F.; Payne, C.; Lythgoe, M.F.; et al. Directing cell therapy to anatomic target sites in vivo with magnetic resonance targeting. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Guan, X.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J. Recent advances in selective photothermal therapy of tumor. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chechetka, S.A.; Yuba, E.; Kono, K.; Yudasaka, M.; Bianco, A.; Miyako, E. Magnetically and Near-Infrared Light-Powered Supramolecular Nanotransporters for the Remote Control of Enzymatic Reactions. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 6586–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-K.; Makkouk, A.R.; Krasieva, T.; Sun, C.-H.; Madsen, S.J.; Hirschberg, H. Photothermal treatment of glioma; an in vitro study of macrophage-mediated delivery of gold nanoshells. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 104, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, S.J.; Baek, S.K.; Makkouk, A.R.; Krasieva, T.; Hirschberg, H. Macrophages as cell-based delivery systems for nanoshells in photothermal therapy. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Zheng, Y.-R.; Gadde, S.; Pfirschke, C.; Zope, H.; Engblom, C.; Kohler, R.H.; Iwamoto, Y.; Yang, K.S.; Askevold, B.; et al. Tumour-associated macrophages act as a slow-release reservoir of nano-therapeutic Pt(IV) pro-drug. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Tang, W.; Wen, R.; Zhou, S.; Lee, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; Delahunty, I.M.; Zhen, Z.; et al. Nanoparticle-Laden Macrophages for Tumor-Tropic Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1805557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, H.; Tian, H.; Yan, F. Real-Time Imaging Tracking of Engineered Macrophages as Ultrasound-Triggered Cell Bombs for Cancer Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, F.; Curtis, L.T.; Yesantharao, P.; Tanei, T.; Alexander, J.F.; Wu, M.; Lowengrub, J.; Liu, X.; Ferrari, M.; Yokoi, K.; et al. Enhanced performance of macrophage-encapsulated nanoparticle albumin-bound-paclitaxel in hypo-perfused cancer lesions. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12544–12552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Marchesi, F.; Garlanda, C. Macrophages as tools and targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 799–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Chen, J.Y.; Weissman-Tsukamoto, R.; Volkmer, J.-P.; Ho, P.Y.; McKenna, K.M.; Cheshier, S.; Zhang, M.; Guo, N.; Gip, P.; et al. Macrophages eat cancer cells using their own calreticulin as a guide: Roles of TLR and Btk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Rao, L.; Yao, H.; Wang, Z.; Ning, P.; Chen, X. Engineering Macrophages for Cancer Immunotherapy and Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Purohit, M.P.; Pahuja, R.; Patnaik, S.; Shukla, Y.; Kumar, P.; Gupta, K.C. Pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization enhances the anti-cancer efficacy of self-assembled galactomannan nanoparticles entrapped with hydrazinocurcumin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 1159–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, L.; Cai, Z.; Jiang, W.; Liu, J.; Tai, Z.; Li, G.; Gong, C.; Gao, S.; Gao, Y. A novel macrophage-mediated biomimetic delivery system with NIR-triggered release for prostate cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Min, H.-K.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, C.-S.; Han, J.; Park, J.-O.; Choi, E. Macrophage-Mediated Delivery of Multifunctional Nanotherapeutics for Synergistic Chemo–Photothermal Therapy of Solid Tumors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10130–10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.-H.; Zhu, X.-D.; Long, M.; Lai, X.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Shi, J.; Lu, Q.; et al. Metal-Coordinated Adsorption of Nanoparticles to Macrophages for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ma, T.; Zhu, D.; Liu, T.; Lv, F. Tumor targeted combination therapy mediated by functional macrophages under fluorescence imaging guidance. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Guan, Z.; Dai, X.; Shen, Y.; Wei, Q.; Ren, L.; Jiang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. Engineered macrophages as near-infrared light activated drug vectors for chemo-photodynamic therapy of primary and bone metastatic breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Wang, T.; Mu, W.; Yang, R.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, S.; Gao, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N. Nanoparticle-Loaded Polarized-Macrophages for Enhanced Tumor Targeting and Cell-Chemotherapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; He, J.; Sun, X.; Younis, M.H.; Cui, D.; Xiao, H.; Gao, D.; et al. Engineering CpG-ASO-Pt-loaded Macrophages (CAP@M) For Synergistic Chemo-/Gene-/Immuno-Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2201178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Shao, S.; Shen, Y.; Wang, K. Macrophages as Active Nanocarriers for Targeted Early and Adjuvant Cancer Chemotherapy. Small 2016, 12, 5108–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kivimäe, S.; Dolor, A.; Szoka, F.C. Macrophage-based cell therapies: The long and winding road. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Ding, Q.; Wu, S.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Zhou, M. Recent Advances in Macrophage-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lu, L.; Xue, C.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xia, Z.; Dai, L.; Luo, Z.; Mao, Y.; et al. Polarization of tumor-associated macrophage phenotype via porous hollow iron nanoparticles for tumor immunotherapy in vivo. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.-D.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.-K.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.-Z. Artificially Reprogrammed Macrophages as Tumor-Tropic Immunosuppression-Resistant Biologics to Realize Therapeutics Production and Immune Activation. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, N.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhou, H.; Bai, R.; You, M.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophage and Tumor-Cell Dually Transfecting Polyplexes for Efficient Interleukin-12 Cancer Gene Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.; Zhao, S.-K.; Wen, C.; Tian, R.; Lin, L.; Cai, B.; Sun, Y.; Kang, F.; Yang, Z.; He, L.; et al. Activating Macrophage-Mediated Cancer Immunotherapy by Genetically Edited Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Luo, Z.; Shi, Q.; Liu, G.; Wu, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, D. Engineering Endogenous Tumor-Associated Macrophage-Targeted Biomimetic Nano-RBC to Reprogram Tumor Immunosuppressive Microenvironment for Enhanced Chemo-Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, B.; Ou, J.; Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Jiang, J.; Ye, Y.; Wang, S.; Tong, F.; et al. Magnetically powered helical hydrogel motor for macrophage delivery. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 25, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Fu, W.; Cheang, U.K. Immunomodulation and delivery of macrophages using nano-smooth drug-loaded magnetic microrobots for dual targeting cancer therapy. iScience 2022, 25, 104507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No. | Macrophage Type | Payload | Targeting Method | Therapy | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ma P388-D1 | Gold nanoshells | Biological | PTT | [91] |
| 2 | RAW 264.7 | P[Fe-DA]-NPs | Biological | PTT | [57] |
| 3 | RAW 264.7 | PLGA-b-PEG drug–silica nanocomplex (DSN) | Biological | Chemotherapy | [94] |
| 4 | RAW 264.7 | DOX/PFP-loaded HMONs | Biological | Chemotherapy of breast cancer | [95] |
| 5 | J774A.1 and primary bone marrow macrophages | Magnetic decoy bacteria | Magnetic | Immunotherapy | [29] |
| 6 | RAW 264.7 | Liposomes containing: MNPs, DOX, ICG | Magnetic | PTT–chemotherapy combination | [85] |
| 7 | Primary macrophages from a murine spleen | MNPs, DOX-Lip | Biological, Magnetic | PTT–chemotherapy combination | [87] |
| 8 | RAW 264.7 | AuNRs, DOX-Lip | Biological | PTT–chemotherapy combination | [102] |
| 9 | RAW 264.7 | DOX-MPN | Biological | PTT–chemotherapy combination | [103] |
| 10 | RAW 264.7 | IR-RC, DOX-NPs | Biological | PTT–chemotherapy combination | [104] |
| 11 | RAW 264.7 | MDM | Biological | Photodynamic–chemotherapy combination | [26] |
| 12 | Primary macrophages | Oxa(IV)@ZnPc@M | Biological | Photodynamic–chemotherapy combination | [105] |
| 13 | RAW 264.7 | SLNP | Biological | Cell–chemotherapy combination | [106] |
| 14 | RAW 264.7 | CpG-ASO-Pt | Biological | Chemo-gene-immunotherapy | [107] |
| 15 | RAW 264.7 | mTiO2-OMVs | Magnetic, Biological | Multimodal therapy | [48] |
| 16 | RAW 264.7 | PLL@Mg/TiO2 | Chemical | [67] | |
| 17 | RAW 264.7 | SPIONs | Acoustic | [80] | |
| 18 | J774A.1 | PLGA-DTX-Fe3O4 | Magnetic, Biological | Chemotherapy | [55] |
| 19 | RAW 264.7 | AuNRs | Biological | PTT | [45] |
| 20 | RAW 264.7 | Free DOX | Biological | Chemotherapy | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, V.D.; Park, J.-O.; Choi, E. Macrophage-Based Microrobots for Anticancer Therapy: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8070553
Nguyen VD, Park J-O, Choi E. Macrophage-Based Microrobots for Anticancer Therapy: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(7):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8070553
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Van Du, Jong-Oh Park, and Eunpyo Choi. 2023. "Macrophage-Based Microrobots for Anticancer Therapy: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives" Biomimetics 8, no. 7: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8070553
APA StyleNguyen, V. D., Park, J.-O., & Choi, E. (2023). Macrophage-Based Microrobots for Anticancer Therapy: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Biomimetics, 8(7), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8070553





