Advances in Ghost Imaging of Moving Targets: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
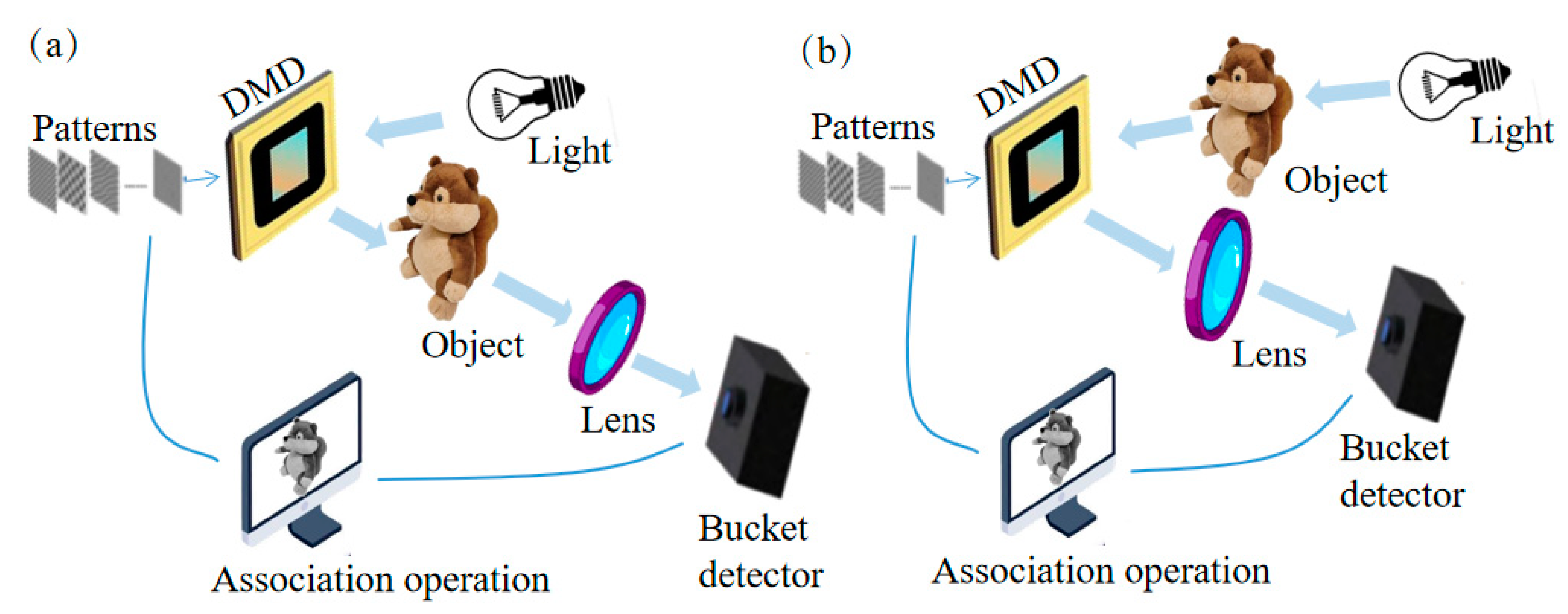
2. Theoretical Basis of GI
3. Research Status of Moving Target GI
4. Improving Image Speed
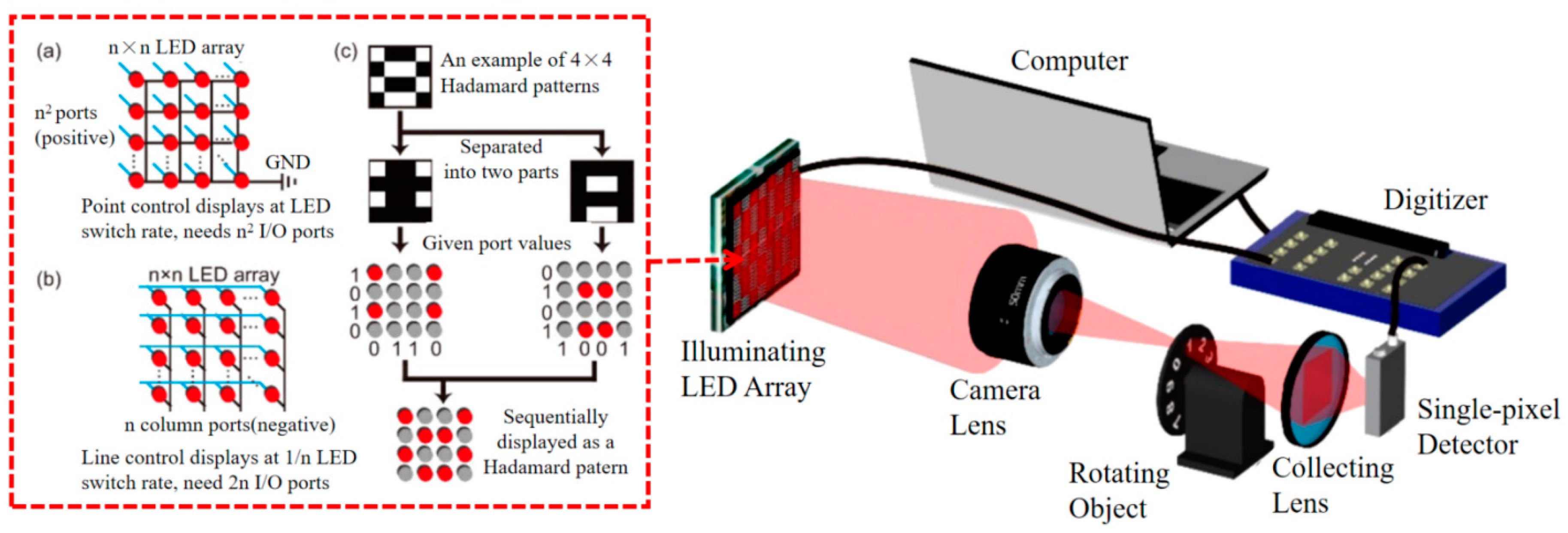
4.1. Improved Light Source Modulation Method
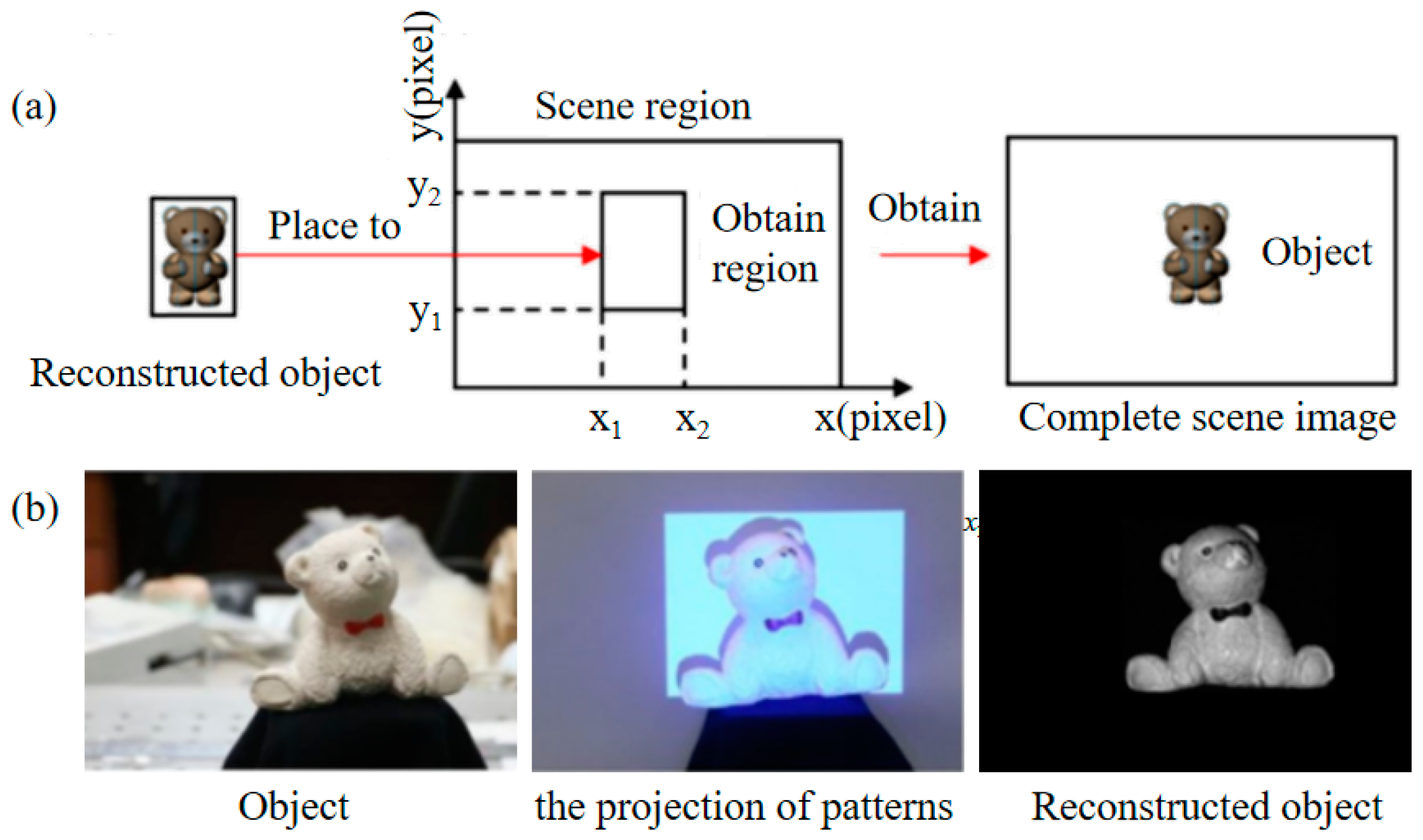
4.2. Selecting the Adaptive Image Region
4.3. Selecting a Suitable Number of Samples
4.4. Estimating Moving Inter-Frame Information
4.5. Developing New Reconstruction Algorithms
4.6. Tracking Target without Image Reconstruction
5. Improving Image Quality
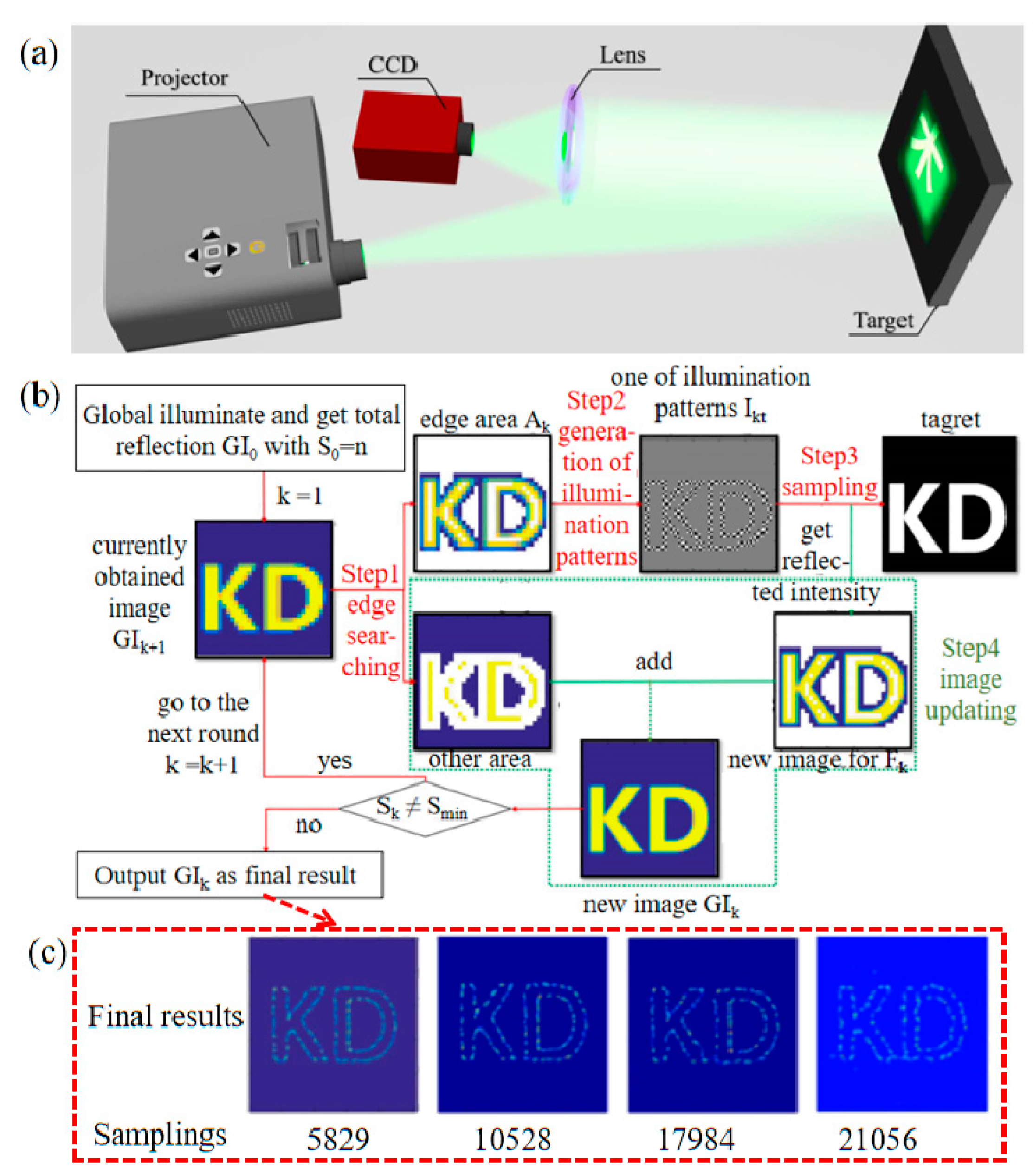
5.1. Designing New Modulation Patterns
5.2. Moving Compensation for Modulation Patterns
6. Challenges and Opportunities
6.1. Stroboscopic Effect Introduced
6.2. Modulation Pattern Combination
6.3. Reconstruction Algorithm Optimization and Innovation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, J.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, F.; Xu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, K. Research progress of APD three-dimensional imaging lidar. Infrared Laser Eng. 2020, 49, 20190549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.-A.; Toninelli, E.; Gregory, T.; Padgett, M.J. Ghost Imaging Using Optical Correlations. Laser Photonics Rev. 2018, 12, 1700143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, Y.; Katz, O.; Silberberg, Y. Ghost imaging with a single detector. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 79, 053840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.F.; Davenport, M.A.; Takhar, D.; Laska, J.N.; Sun, T.; Kelly, K.F.; Baraniuk, R.G. Single-pixel imaging via compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.H. Computational ghost imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 061802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.M.; Johnson, S.D.; Padgett, M.J. Single-pixel imaging 12 years on: A review. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 28190–28208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, M.P.; Gibson, G.M.; Padgett, M.J. Principles and prospects for single-pixel imaging. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkovnik, V.; Astola, J. Computational ghost imaging: Advanced compressive sensing (CS) technique. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2012, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, D.; Pitsch, C.; Paunescu, G.; Lutzmann, P. Detection and jamming resistance of quantum ghost imaging for remote sensing. In Proceedings of the Electro-Optical Remote Sensing XIII, Strasbourg, France, 9–10 September 2019; Volume 1116002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Liang, W.; Cheng, W.; Gong, L. High performance optical encryption based on computational ghost imaging with QR code and compressive sensing technique. Opt. Commun. 2015, 353, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, P.W.W. An introduction to high speed photography and photonics. Imag. Sci. J. 2009, 57, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Hu, C.; Li, E.; Gong, W.; Tong, Z.; Wu, J.; Shen, X.; Han, S. Ghost imaging LiDAR via sparsity constraints using push-broom scanning. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 13219–13228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Gong, W.; Han, S. Pulse-compression ghost imaging lidar via coherent detection. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 25983–25994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Hu, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Han, S. Multi-scale ghost imaging LiDAR via sparsity constraints using push-broom scanning. Opt. Commun. 2019, 448, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Pan, L.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Gong, W.; Han, S. Performance analysis of ghost imaging lidar in background light environment. Photonics Res. 2017, 5, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yu, H.; Shen, X.; Liu, H.; Gong, W.; Liu, Z. A Review of Ghost Imaging via Sparsity Constraints. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, W.-T.; Lin, H.-Z.; Zhang, E.-F.; Liu, J.-Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, P.-X. Multi-scale Adaptive Computational Ghost Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, M.P.; Gibson, G.M.; Bowman, R.W.; Sun, B.; Radwell, N.; Mitchell, K.J.; Welsh, S.S.; Padgett, M.J. Simultaneous real-time visible and infrared video with single-pixel detectors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stantchev, R.I.; Sun, B.; Hornett, S.M.; Hobson, P.A.; Gibson, G.M.; Padgett, M.J.; Hendry, E. Noninvasive, near-field terahertz imaging of hidden objects using a single-pixel detector. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconi, V.; Kumar, V.; Pasquazi, A.; Gongora, J.S.T.; Peccianti, M. Nonlinear field-control of terahertz waves in random media for spatiotemporal focusing. Open Res. Eur. 2022, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, L.; Peters, L.; Cecconi, V.; Cutrona, A.; Rowley, M.; Gongora, J.S.T.; Pasquazi, A.; Peccianti, M. Terahertz Nonlinear Ghost Imaging via Plane Decomposition: Toward Near-Field Micro-Volumetry. ACS Photonics 2023, 10, 1726–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lu, R.; Han, S.; Xie, H.; Du, G.; Xiao, T.; Zhu, D. Fourier-Transform Ghost Imaging with Hard X Rays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceddia, D.; Paganin, D.M. On Random-Matrix Bases, Ghost Imaging and X-ray Phase Contrast Computational Ghost Imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 062119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.X.; He, Y.H.; Wu, L.A.; Chen, L.M.; Wang, B.B. Tabletop x-ray ghost imaging with ultra-low radiation. Optica 2018, 5, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Z. Experimental Study on Anti-Disturbance Ability of Underwater Ghost Imaging. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2021, 58, 0611002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-X.; Cao, J.; Zhou, D.; Cui, H.; Hao, Q. Ghost imaging through scattering medium by utilizing scattered light. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 11243–11253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-X.; Cao, J.; Zhou, D.; Hao, Q. Scattering medium-robust computational ghost imaging with random superimposed-speckle patterns. Opt. Commun. 2023, 529, 129083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.H.; Twiss, R.Q. Twiss Correlation between photons in two coherent beams of light. J. Astrophys. Astron. 1994, 15, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennink, R.S.; Bentley, S.J.; Boyd, R.W. “Two-photon” coincidence imaging with a classical source—Art. no. 113601. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 113601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, T.B.; Shih, Y.H.; Strekalov, D.V.; Sergienko, A.V. Optical imaging by means of two-photon quantum entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 1995, 52, R3429–R3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-H.; Liu, Q.; Luo, K.-H.; Wu, L.-A. Lensless ghost imaging with true thermal light. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wu, H.; Wang, R.; He, Z.; Li, H.; Gan, J.; Zhao, G. Computational ghost imaging with uncertain imaging distance. Opt. Commun. 2019, 445, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wei, Q.; Shen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, J.; Han, S. Lensless Fourier-transform ghost imaging with classical incoherent light. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 75, 021803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.-L.; Cheng, J.; Chen, A.-X.; Liu, Z.-M. Computational ghost imaging with higher-order cosh-Gaussian modulated incoherent sources in atmospheric turbulence. Opt. Commun. 2015, 352, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Edgar, M.P.; Sun, B.; Radwell, N.; Gibson, G.M.; Padgett, M.J. 3D single-pixel video. J. Opt. 2016, 18, 035203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.M.; Sun, B.; Edgar, M.P.; Phillips, D.B.; Hempler, N.; Maker, G.T.; Malcolm, G.P.A.; Padgett, M.J. Real-time imaging of methane gas leaks using a single-pixel camera. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Bo, Z.; Chen, M.; Gong, W.; Han, S. Ghost imaging of a moving target with an unknown constant speed. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 251120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-B.; Lu, T.-A.; Peng, J.-Z.; Zhong, J.-G. Fourier single-pixel imaging techniques and applications. Infrared Laser Eng. 2019, 48, 603002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, C.; Chen, M.; Gong, W.; Han, S. Ghost imaging for an axially moving target with an unknown constant speed. Photonics Res. 2015, 3, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhou, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J. Demonstration of single pixel computational ghost imaging with pseudo-randomly patterned illumination from a liquid crystal display. In Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Optical Engineering Conferences, Changchun, China, 24–28 July 2016; Lv, Y., Bao, W., Zhang, G., Eds.; p. 101411G. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.-H.; Chen, W.; Penuelas, J.; Padgett, M.; Sun, M.-J. 1000 fps computational ghost imaging using LED-based structured illumination. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador-Balaguer, E.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Chabert, C.; Pla, F.; Lancis, J.; Tajahuerce, E. Low-cost single-pixel 3D imaging by using an LED array. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 15623–15631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Ultrahigh-Speed Color Imaging with Single-Pixel Detectors at Low Light Level. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 12, 034049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Usami, R.; Saito, K.; Honda, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Watanabe, E. Optical correlator-based computational ghost imaging towards high-speed computational ghost imaging. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, SKKA02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; Li, X. Adaptive regional single-pixel imaging based on the Fourier slice theorem. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 15118–15130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Lin, H.; Xu, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, W. Tracking and imaging of moving objects with temporal intensity difference correlation. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 27851–27861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Sun, S.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, W. Feedback ghost imaging by gradually distinguishing and concentrating onto the edge area. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2021, 19, 041102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Gu, J.-H.; Lin, H.-Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, W.-T. Gradual ghost imaging of moving objects by tracking based on cross correlation. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 5594–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, S.; Hahamovich, E.; Rosenthal, A. Single-pixel imaging of dynamic objects using multi-frame motion estimation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Yao, M.; Zheng, G.; Zhong, J. Image-free classification of fast-moving objects using “learned” structured illumination and single-pixel detection. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 13269–13278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Yin, K.; Huang, J.; Yuan, K.; Zhu, W.; Xie, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y. Fast tracking of moving objects using single-pixel imaging. Opt. Commun. 2019, 440, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ye, J.; Deng, Q.; Zhong, J. Image-free real-time detection and tracking of fast moving object using a single-pixel detector. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 35394–35401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, J. Image-free real-time 3-D tracking of a fast-moving object using dual-pixel detection. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 4734–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Song, M.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Lei, H.-D.; Yu, Y.-J.; Wu, L.-A. Image-free real-time target tracking by single-pixel detection. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Taguchi, H.; Iwata, T.; Takaya, Y.; Yasui, T. Single-pixel imaging by Hadamard transform and its application for hyperspectral imaging. In Proceedings of the Spie/cos Photonics Asia, Beijing, China, 12–14 October 2016; Volume 10021, p. 100210B 6. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.; O’Sullivan, M.N.; Boyd, R.W. High-order thermal ghost imaging. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 3343–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Cui, H.; Zhou, D.; Han, B.; Hao, Q. Retina-like Computational Ghost Imaging for an Axially Moving Target. Sensors 2022, 22, 4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Shi, D.; Meng, W.; Zha, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W. Fast Localization and Single-Pixel Imaging of the Moving Object Using Time-Division Multiplexing. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.07371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Lei, X.; Shi, Z.; Qiu, L.; Fu, X. Single-pixel imaging of a randomly moving object. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 40389–40400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, X.R.; Zhao, Q. Single-pixel imaging of a translational object. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 5547–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, G.G. Image motion compensation with frame transfer CCDs. In Proceedings of the Machine Vision and Three-Dimensional Imaging Systems for Inspection and Metrology II, Boston, MA, USA, 28–31 October 2002; Volume 4567, pp. 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, S.; Sun, M.; Gao, Y.; Lei, T.; Xie, Z.; Yuan, X. Motion estimation and quality enhancement for a single image in dynamic single-pixel imaging. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 12841–12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Song, Z.; Yu, W.-K.; Wu, L.-A. Tracking Compensation in Computational Ghost Imaging of Moving Objects. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chang, C.; Wu, G.; Luo, B.; Yin, L. Compressive Ghost Imaging of the Moving Object Using the Low-Order Moments. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-K.; Sun, S.; Lin, H.-Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, W.-T. Denoising ghost imaging under a small sampling rate via deep learning for tracking and imaging moving objects. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 37284–37293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tu, Y.; Liu, L.; Perz, M.; Vogels, I.M.; Heynderickx, I.E. Stroboscopic Effect of LED Lighting. SID Int. Symp. Dig. Technol. Pap. 2015, 46, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedhart, P.T.; Khalilzada, M.; Bezemer, R.; Merza, J.; Ince, C. Sidestream Dark Field (SDF) imaging: A novel stroboscopic LED ring-based imaging modality for clinical assessment of the microcirculation. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15101–15114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming-Fei, L.; Xiao-Fan, M.; Lian-Jie, Z.; Juan, H.; Ran, Y.; Kai, L.; An-Ning, Z. Single-pixel remote imaging based on Walsh-Hadamard transform. Acta Phys. Sin. 2016, 65, 064201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, G.; Zhong, J. Hadamard single-pixel imaging versus Fourier single-pixel imaging. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 19619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Accelerating the Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9906, pp. 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

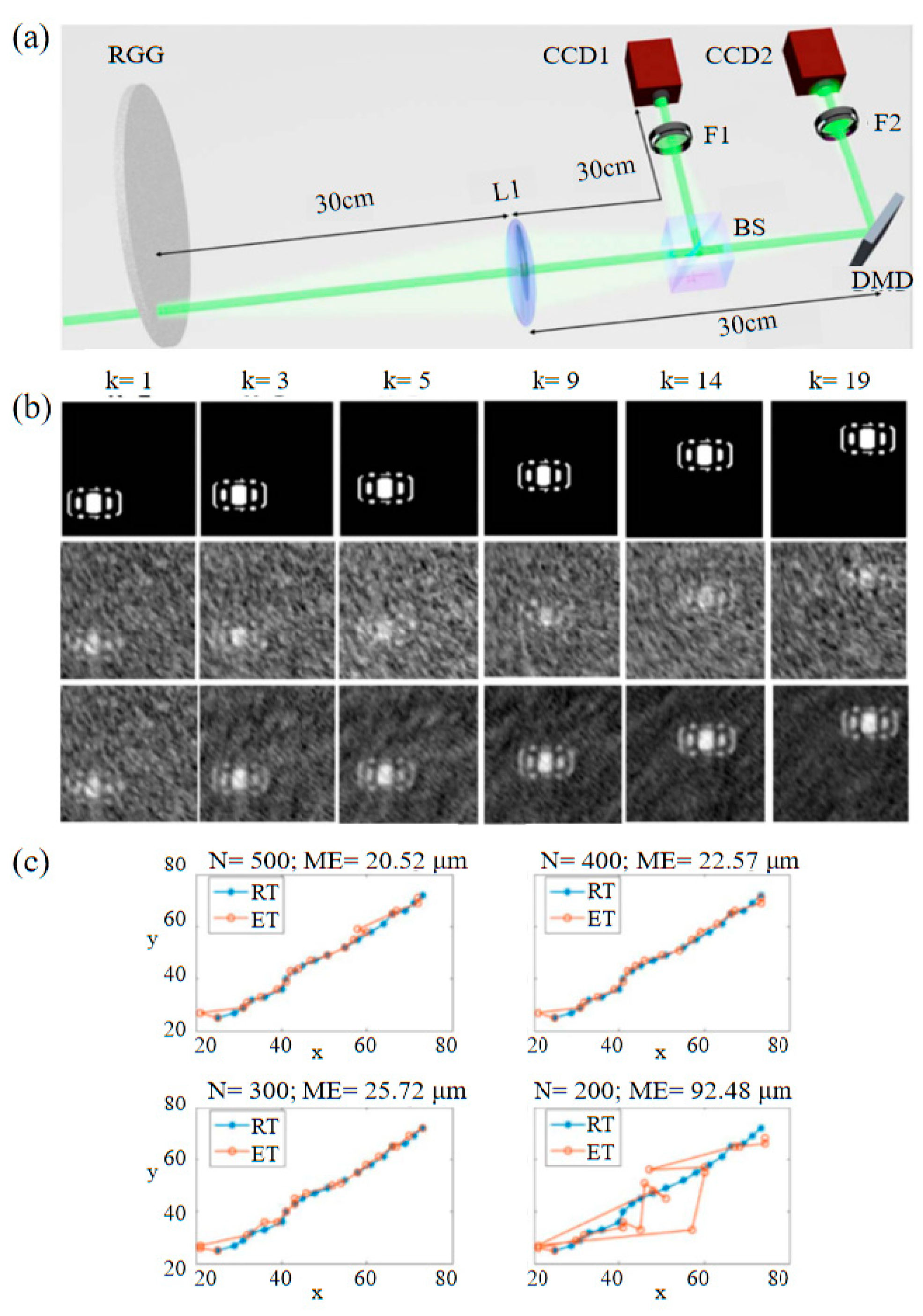


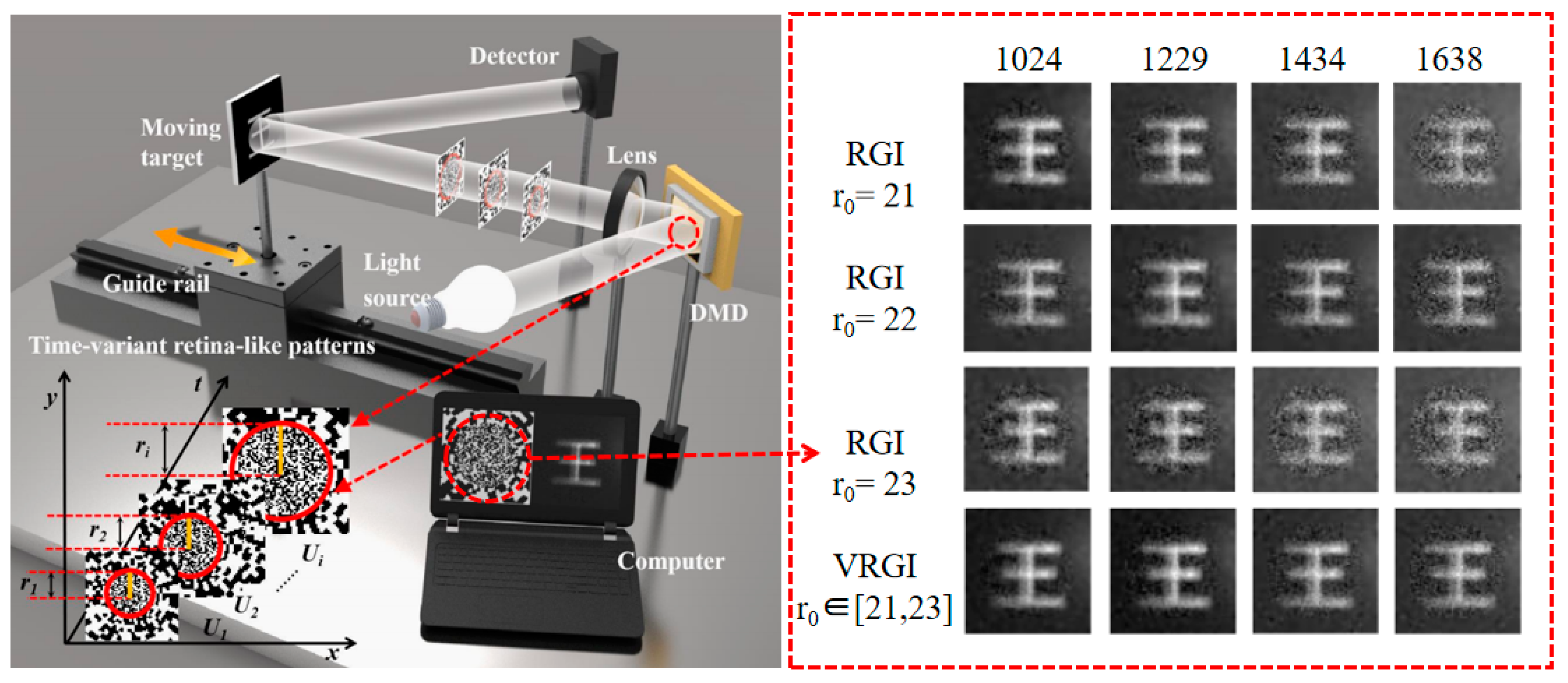
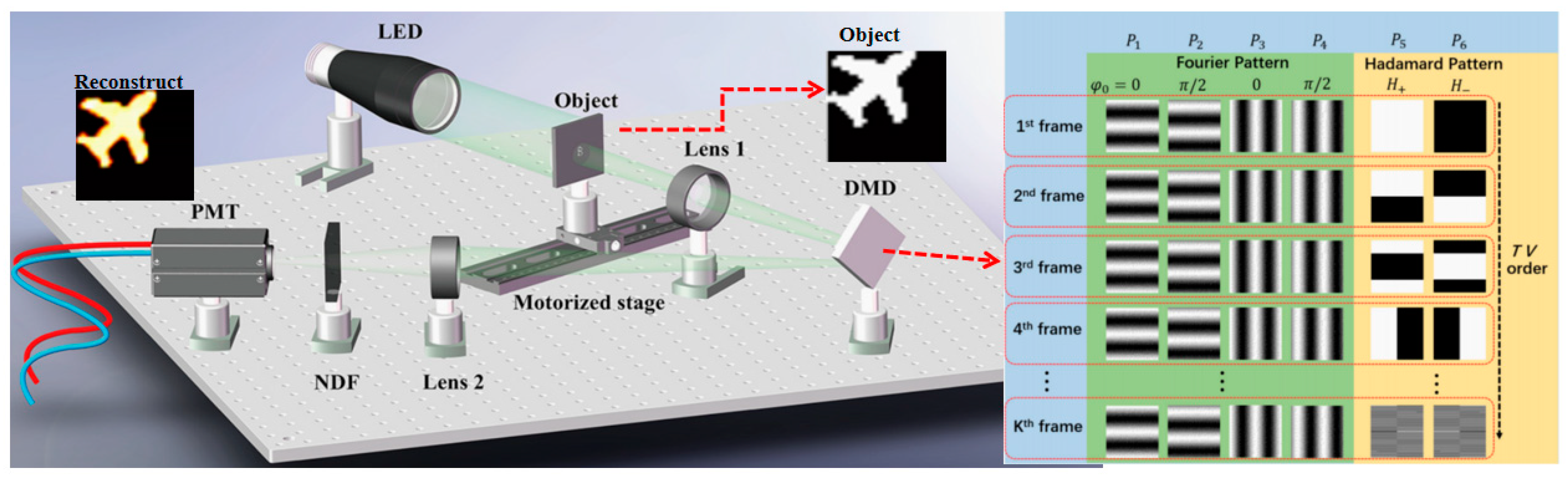
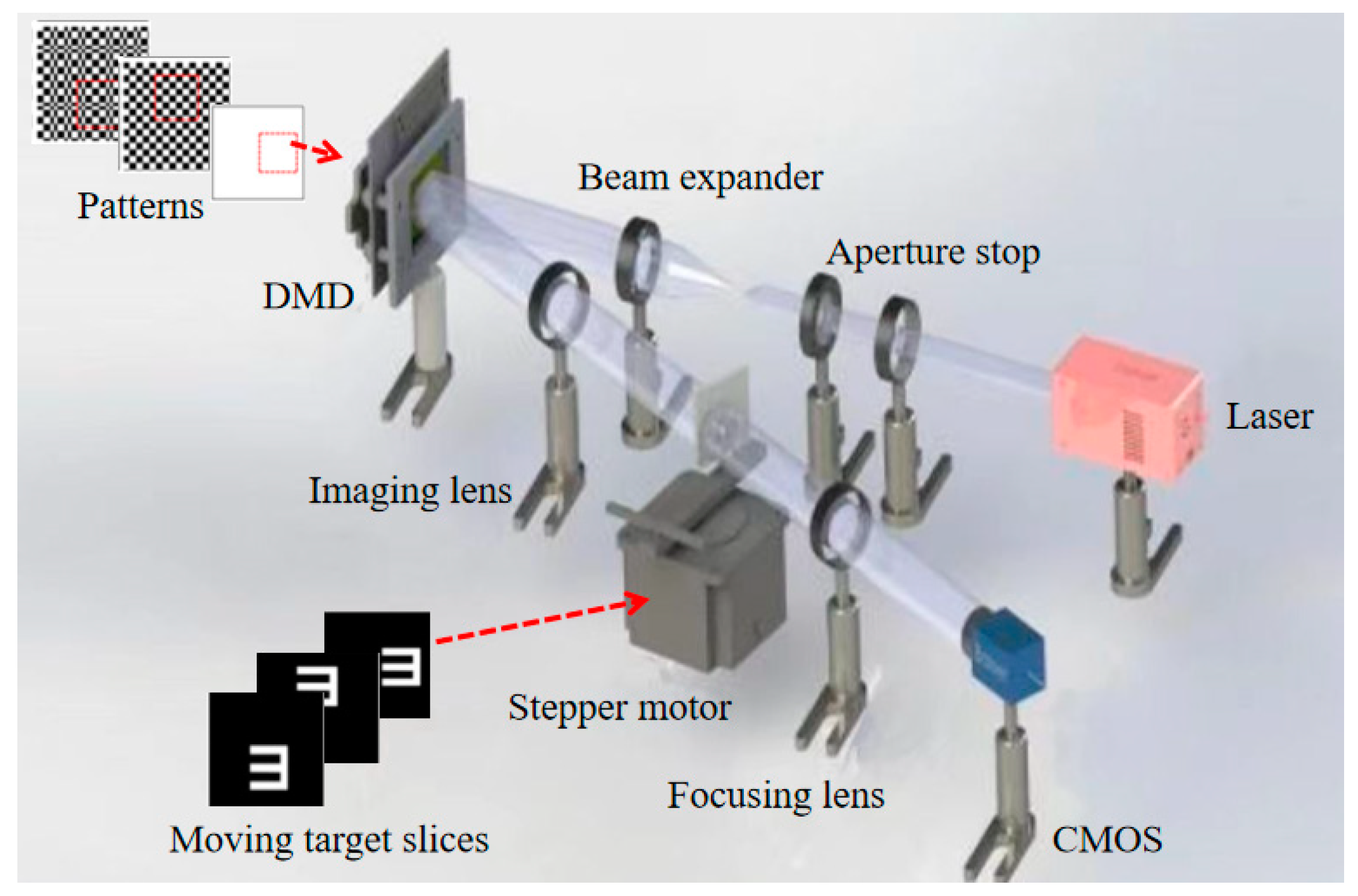
| Classification | Improve Imaging Speed | Improve Image Quality | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core method | Improving light source modulation method | Selecting the adaptive imaging region | Selecting a suitable number of samples | Estimating motion inter-frame information | Developing new reconstruction algorithms | Tracking target without image reconstruction | Designing new modulation patterns | Moving compensation for modulation patterns |
| Principle | Develop a new LED array | Image the part of the area where the target is located, then place it at the location of the object in the scene | Select appropriate sampling number with the spatial sparsity of object | Divide the motion into several frames and estimate the information between them | Introduce another algorithm or neural networks into reconstruction algorithm | Obtain spatial information about the target object | Design the structure of patterns with the movement characteristics | Move patterns to make it remain relatively stationary with the object |
| Advantages | Improve the modulation speed of the light source | Reduce the number of patterns and have high numerical efficiency algorithm | Reduce sampling time, track and image multiple moving objects | Image moving objects in inaccessible environments | Have algorithms that require little computation | Have high speed detection and high efficiency calculation | Image objects in unknown motion states | Have a simple structure and does not require hardware compensation |
| Disadvantages | The power is unstable for a long time | It is only applicable to single target in the background of uniform gray distribution | Peripheral areas are not imaged properly | Objects moving too fast cannot be imaged | Algorithms related to deep learning require a lot of training | Unable to get an image of the target object | The imaging effect on rotating objects is not ideal | The specific motion of the object must be known |
| Development direction | Living microscopy, 3D imaging, light detection and ranging | Local imaging | Target tracking, living tissue imaging, medical imaging | Translational or rotating object imaging | Rapid classification of flowing cells, assembly-line inspection, aircraft classification in defense applications | Remote sensing imaging, biomedical imaging, Real-time tracking imaging | Remote sensing imaging, unmanned driving | Target tracking, remote sensing imaging, medical diagnosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, M.; Cao, J.; Cui, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, T. Advances in Ghost Imaging of Moving Targets: A Review. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8050435
Shi M, Cao J, Cui H, Zhou C, Zhao T. Advances in Ghost Imaging of Moving Targets: A Review. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(5):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8050435
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Moudan, Jie Cao, Huan Cui, Chang Zhou, and Tianhua Zhao. 2023. "Advances in Ghost Imaging of Moving Targets: A Review" Biomimetics 8, no. 5: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8050435
APA StyleShi, M., Cao, J., Cui, H., Zhou, C., & Zhao, T. (2023). Advances in Ghost Imaging of Moving Targets: A Review. Biomimetics, 8(5), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8050435








